French aviation elegance. Part 2
Despite attempts to simplify and reduce the cost of the Mirage 5 strike, it remained too expensive, complex, and vulnerable to use as a massive low-altitude strike aircraft designed to render aviation support of ground forces.
In 1964, the headquarters of the French Air Force formulated tactical and technical requirements for a cheap and simple in design supersonic aircraft designed to perform tactical support missions.
Taking into account the economic feasibility of the government of France and the UK signed an agreement 17 May 1965, the joint construction of the aircraft, which would meet the requirements of both countries.
The development of the airframe design was entrusted to Breguet Aviation and British Aircraft, and the creation of the engine to Rolls-Royce and Tyurbomek. Due to operational requirements and safety considerations, a twin-engine scheme was adopted using engines of the joint Anglo-French production of the Adur type.
During the construction of the aircraft, the cooperating firms formed the association SEPECAT. After 18 months from the date of signing the agreement, construction began on the first prototype.
French Air Force needed more double "Jaguars" than single. It is for this reason that the first E-series French Jaguar was the Sparka E, which first flew into the air on November 2 1971 of the year, while the first A-series fighter-bomber performed the first flight of only 20 on April 1972 of the year.
The plane with a normal take-off weight of 11000 kg, accelerated from the ground to 1350 km / h, at an altitude of: 1593 km / h. Combat radius on the profile “big-small-big” height with PTB: 1315 km, without PTB: 815 km.
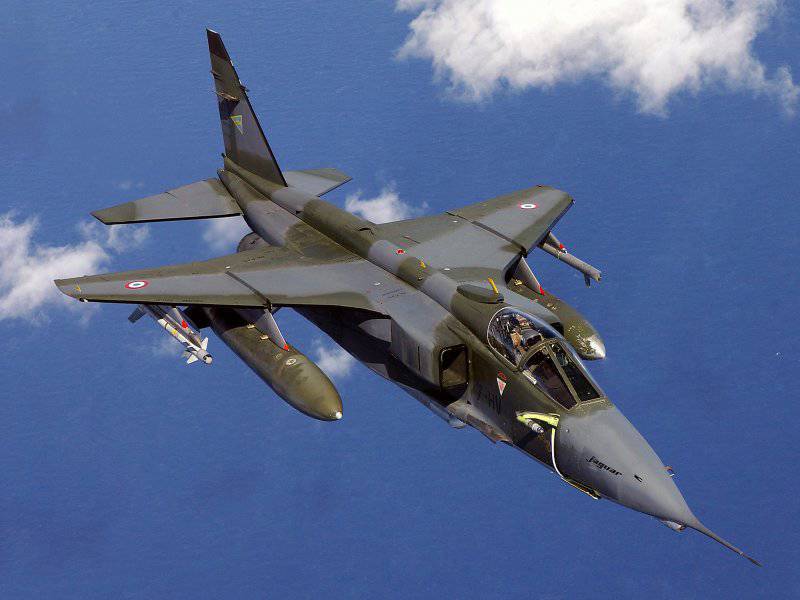
The Jaguar A is a French single-seat modification of a fighter-bomber. Starting with the 18 built aircraft, it is equipped with refueling rods, which allow refueling at altitudes up to 12 000 m with a fuel transfer rate of 700-1000 l / min. Duration of refueling 3-5 min. Compared with the British "Jaguar" is more simple equipment and DEFA 553 guns with 150 ammunition shells.
"Jaguar" E-double modification for the French Air Force. Starting with the 27-series serial in the forward part of the fuselage, instead of the LDPE, a refueling bar was installed, which later appeared on some earlier “Sparki” squadrons of the ES11 for flights to “overseas” territories. Total French Air Force received 40 two-seater "Jaguar E".
Soon on the Jaguar E were tested new warning devices and EW, as well as laser rangefinders, target indicators Marconi Avionics LRMTS. First, the characteristic flat EW container appeared on the keel, then under the shortened LDPE - a wedge-shaped LRMTS window. In this form, the plane went into the series. By 1980, the Adour Mk.102 engines were replaced by the Mk.104, run-in on export aircraft. The Jaguar A fighters-bomber in the French Air Force delivered 160 units, the latter delivered 14 December 1981 of the year.

All modifications, with the exception of the Jaguar B, have stationary weapons in the form of two guns (caliber 30 mm) with a supply of 150 projectiles. on each. French planes are equipped with DEFA cannons, British - with Aiden cannons (modification B is equipped with one cannon). The plane has five locks for external hangers (two under the wing consoles and one under the fuselage) with a total capacity of 4500 kg. Bombs, NURS SNEB containers or Mazhik air-to-air missiles made by Matra can be suspended on under-wing locks (carrying capacity of 1000 kg and 500 kg). The ventral lock (1000 kg) is adapted for hanging bombs and air-to-ground guided missiles (tactical nuclear weapons).
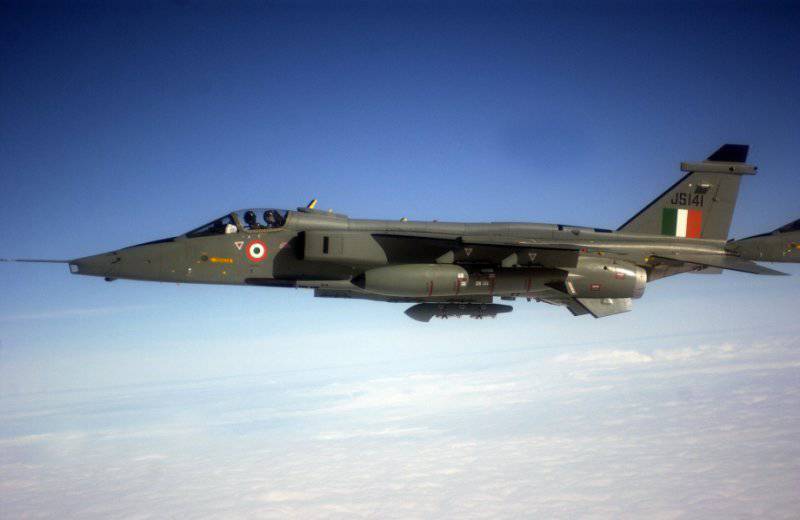
Export deliveries of the Jaguars were carried out in Ecuador, Oman and Nigeria. In India, licensed production was organized, mass production proceeded slowly and continued until the 1992 year (built under a license of more than 100 aircraft). A distinctive feature of the Indian Jaguars has become the adaptability to work with Durendal concrete bombs.
For the first time, the French Jaguars were used in hostilities at the end of 1977 - the beginning of 1978 of the year, during Operation Manatee, directed against the fighters of the Liberation Front of the North-West Africa “Polissario” settled in Senegal. Several combat missions "Jaguars" performed on objects located in the territory of Mauritania, in the former Spanish Sahara. The rebels were well armed. Three "Jaguars" were shot down by air defense.
In the same year, 1978 was used in Chad. Paris assisted its recent colony. During Operation Takyu, in which Jaguars arrived in Chad, four of them were lost. Operation Takyu was not successful; by 1980, the Prolivian forces controlled most of Chad’s territory. Paris had to withdraw its troops from Chad, although the limited military presence of the French in this African country remained.
Jaguars reappeared over Chad in 1983. For almost a year, the planes flew unhindered patrol flights until, in January 1984, one Jaguar was hit by a successful line-up fired from an 23-mm anti-aircraft gun during the attack of a column of rebel equipment.
In Chad, the French used AS-37 Martel anti-radar missiles with the Jaguars to suppress Libyan radar. So 7 January 1987 of the year during the next raid on Quadi Dum was launched ten AS-37 "Martel" missiles. The raid on Quadi Doum was the latest combat use of the Jaguars in Africa.
The Jaguars reached their peak of glory in 1991, taking part in the Desert Shield and Desert Storm operations. "Jaguars" were used only during the day, mainly in simple weather conditions. The first combat sortie of the French Jaguars took place on 17 on January 1991, on the first day of the war. Twelve aircraft struck the positions of SCAD missiles at the Ahmed Al-Jaber airbase. The planes dropped Beluga containers from 30 meters and fired several AS-30L missiles. Above the target, the planes encountered heavy anti-aircraft artillery fire, with the result that four aircraft were damaged. On one, an anti-aircraft projectile hit the right engine, another plane got a Strela missile from the left engine. The engine caught fire, however, the pilot managed to keep control of the aircraft and made an emergency landing. Another “Jaguar” anti-aircraft shell pierced through the cockpit lantern along with the pilot's helmet inside the lantern. The head of the pilot, surprisingly, did not suffer.
However, with the massive suppression of control, radar and anti-aircraft missile systems of Iraq’s defense, almost no special means were used to prevent active actions of the barreled anti-aircraft artillery, as a result of which the Soviet-made paired and quadruple installations caused serious damage to the aviation of the multinational forces.
Under these conditions, light Jaguars successfully performed anti-aircraft maneuvers and suffered smaller losses. The very same aircraft when receiving combat damage was very tenacious.
Subsequently, to prevent losses, it was decided to abandon low-altitude flights and proceed to strikes using guided bombs.
"Jaguar" has earned the glory of a simple and reliable, unpretentious to the conditions of operation of the aircraft with excellent combat survivability. At the Red Flag joint exercises with the United States, which were very close to the combat situation, the fighters of the “defending” side considered the Jaguar to be the most “difficult to attack” strike aircraft. In France, it was discontinued in 2005.
Later on this issue in the French press expressed regret. According to some experts, "Jaguar" was removed from the weapons too quickly. This aircraft lacked the French contingent in Afghanistan. Instead, it used a more expensive and vulnerable Mirage 2000.
At the beginning of the 1960-x began work on determining the appearance of the aircraft, which was supposed to replace the "Mirage" III.
After a series of experiments with a variable geometry wing, lift-marching and dual-engine engines, the Dassault firm opted for the classic layout of the fighter. The decisive advantage of this scheme over the tailless was the opportunity to develop much higher lift coefficients with a balanced aircraft, which is very important for improving maneuverability and takeoff and landing qualities.
The Mirage F1-01 prototype, equipped with the SNECMA Atar 09KD, 7000 kgf, flew for the first time into the 23 December 1966 g. and run. Duty time in the air has tripled. The combat radius doubled when attacking ground targets.
The first and most mass modification of the F1 Mirage for the French Air Force was an all-weather air defense fighter built in two versions. The first of these, the Mirage, F1C, supplied the customer from March 1973 to April 1977. In production, he was replaced by the "Mirage" F1C-200, the deliveries of which ended in December 1983. The main difference with the later version was the availability of equipment for in-flight refueling.
The basis of the fire control system was monopulse radar "Cyrano" IV with a range of target detection of the type "fighter" to 60 km, and tracking - to 45 km.
The aircraft’s armament consisted of the two French 30-mm Defa cannons that were traditional for French fighters. On the external nodes were placed air-to-air missiles of medium range R.530 with semi-active radar or infrared seeker and melee R.550 "Majik" With IR-seeker. A typical combat load option included two R.530 missiles on the wing nodes and two R.550 on the wingtips. Subsequently, the composition of weapons expanded with new modifications of missiles - "Super" R.530F / D and "Magik" 2. The possibilities of attacking ground targets were initially limited to the use of only unguided means of destruction - the NAR and free-fall bombs. Later, the AS.1 “Martel”, the “Exochet” anti-ship missiles and adjustable bombs entered the F37 Mirage arsenal.
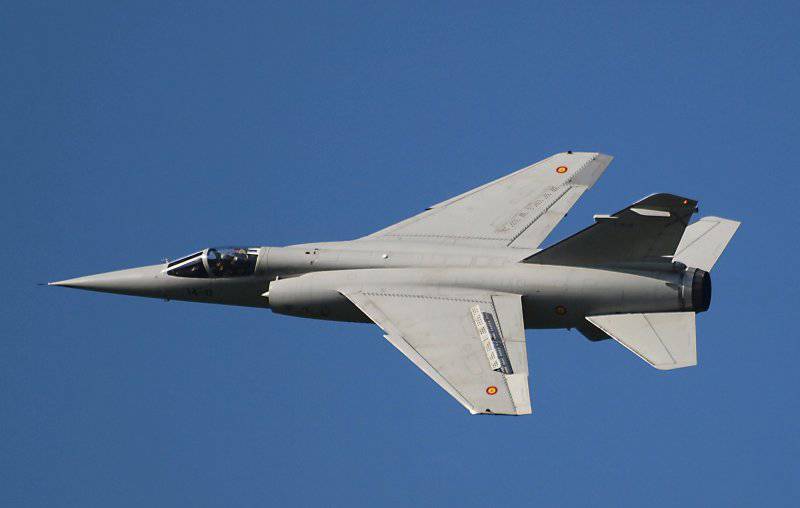
The first foreign buyer of fighters "Mirage" F1 became the Republic of South Africa. After South Africa, Mirages F1 was ordered by Spain, which became the largest European operator of such aircraft after France. Later they were shipped to Greece, Libya, Morocco, Jordan, Iraq, Kuwait and Ecuador.
With export orders, the number of F1 Mirage units built exceeded 350 units. Repeat the success of "bestseller" "Mirage" III failed. By that time, the 4 generation fighters, which had the best performance, had already appeared.
The planes participated in the war in Western Sahara, the war in Angola, the Ecuadorian-Peruvian conflict, the Chadian-Libyan conflict, the Iran-Iraq war, the Persian Gulf war, the Turkish-Greek conflict, and the civil war in Libya.
The French 4 generation aircraft was the Mirage 2000, which first flew in March 10 1978. It was assumed that the aircraft would combine the speed and acceleration characteristics of the F.1 Mirage interceptor fighter with the ability of the Mirage III aircraft to conduct short, maneuverable air combat. During the development of the fighter, the Dassault company again returned to the well-developed “tailless” scheme, which had proven itself well on the Mirage III fighters. From their predecessors, the Mirage 2000 inherited a large wing area and a glider with significant internal volumes for fuel and airborne equipment. It has been applied electrical control system, the aircraft became unstable along the pitch channel. In addition, the combined use of automatic slats and ailerons gave the wing a variable curvature, which further improved flight performance and controllability at low speeds. The fighter was designed to be as light as possible, in order to ensure that, in using a single SNECMA M53-5 turbofan engine, the thrust-to-weight ratio is equal to 1.
The aircraft is equipped with an ejector seat Martin-Baker F10Q, produced under license by the company Hispano-Suiza and ensuring the rescue of the pilot at zero speed and altitude.
The basis of the onboard electronic equipment of the aircraft is a multifunctional pulse-Doppler radar RD-I, which provides a search for air targets against the background of the underlying surface and in free space.
On the double Mirage 2000D and N versions, instead of it, the 5 Antelope radar is installed, which provides an overview of the earth's surface in the forward hemisphere and the flight of the aircraft in the rounding mode of the terrain. The aircraft is also equipped with TAKAN radionavigation system equipment, radar identification systems, warning of the exposure of the enemy's radar, and electronic countermeasures.
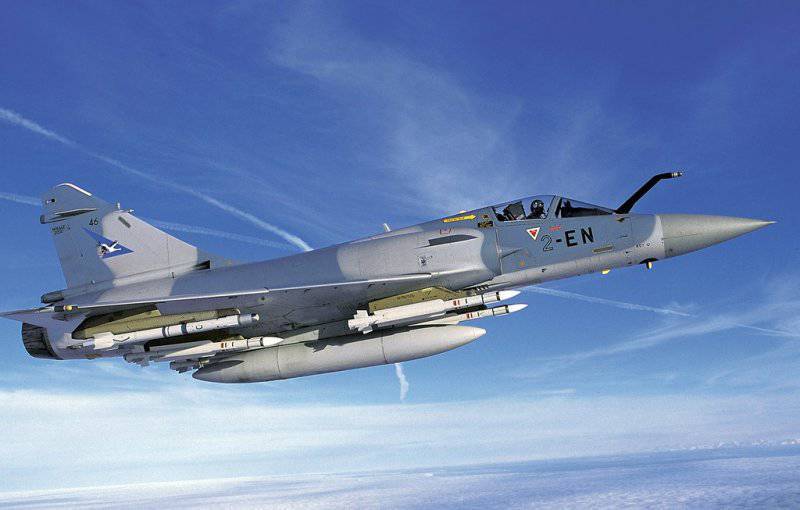
The stationary armament of the aircraft consists of two DEFA 30 caliber mm cannons located in the lower part of the fuselage between the air intakes. On nine locks of external hangers, the aircraft can carry bombs and missiles and a total weight of 5000 kg. A typical 2000C interception load includes two UR Matra "Super" 530D or 530F on internal underwing nodes and two UR Matra 550 "Majik" or "Majik" 2 on external underwing nodes. In a strike configuration, an aircraft can carry up to 18 bombs with a caliber 250 kg or concrete bombs BAR 100; to 16 concrete bombs "Durendal"; one or two BGL bombs caliber 1000 kg with a laser guidance system; five or six Beluga cluster bombs; two laser-guided AS30L UR, anti-radar Matr ARMAT or anti-ship AM39 "Exocet"; four containers with NAR (18x68 mm). The Mirage 2000N is armed with an ASMP rocket with a nuclear warhead of 150 kt.
The first serial fighter-interceptor "Mirage" 2000С made the first flight in November 1982 year, and the first squadron of the French Air Force, equipped with new aircraft, began combat duty in the summer 1984 year. The French Air Force was delivered 121 aircraft "Mirage" 2000С. The total amount of the purchased and ordered Mirage aircraft 2000 (together with two-seater shock modifications) - 547 units.
The further development of the single-seat fighter was the aircraft with the more powerful MNNXX-R53 TRDDF, intended for export deliveries. On the fighters, the RDM radar was installed with a radar-lighting system for air-to-air class-to-medium-range air Super 2D. Aircraft of this type were supplied by the UAE (530 "Mirage" 22EAD), Egypt (2000 "Mirage" 16), India (2000 "Mirage" 42Н) and Peru (2000 "Mirage" 10Р).
In October, the 1990 began flight tests of the multi-purpose Mirage 2000-5 fighter equipped with the new avionics and armament, as well as the more powerful M88-Р20 engine. In 1994, work began on the conversion to the Mirage version of the 2000-5 part of the Mirage 2000C interceptor fighter of the latest release.
The Mirage 2000 of various modifications repeatedly participated in international exercises, where they conducted training aerial battles with fighters produced outside of France.
According to the results of these battles, the US military came to the conclusion that without exception, all modifications of the Mirage 2000 did not have superiority over the Navy and US Air Force fighters.
At the same time, it was noted that in a number of cases the Mirage pilots had previously been able to detect a conventional enemy fighter using an onboard radar. When conducting close maneuvering combat at low speeds, American fighters could not always perform aerobatics available to the Mirage with a delta wing, built according to the “tailless” scheme.
At the same time, the pilots of the Mirage expressed a desire to have a missile similar in their characteristics to the latest AIM-120 AMRAAM.
As part of the French Air Force participated in the fighting against Iraq in 1991 year. Used in hostilities in Bosnia and aggression against Serbia. The French Mirage 2000 members of the international forces in Afghanistan were based at Kabul airport.
The fighter is in service with the Air Forces of France, Egypt, India, Peru, the United Arab Emirates, Greece, Jordan and Taiwan.
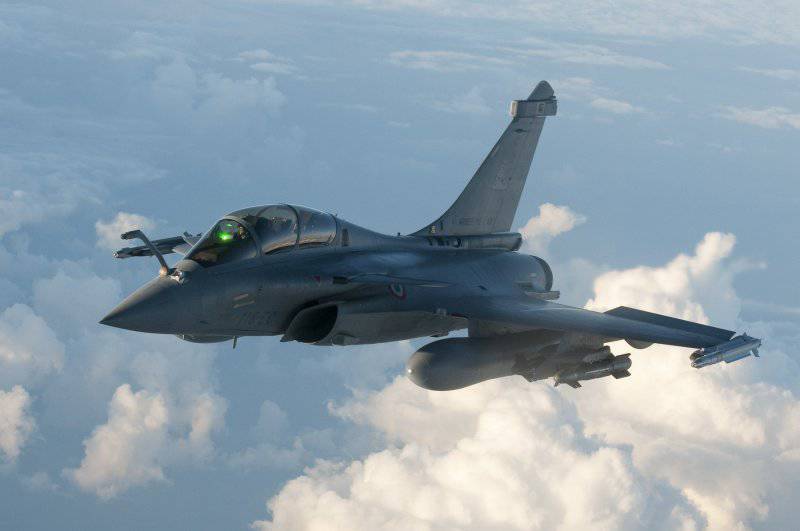
4 July 1986, for the first time, a new fourth-generation multi-purpose fighter, the Rafale (French Flurry), developed by the French company Dassault Aviation, took to the air for the first time.
It was created as part of a rather ambitious project. “One aircraft for all missions” - that was the motto of the Dassault designers when creating “Rafal”, intended to replace six specialized types at once: “Cruzader” and “Super Entandar” - with navy, “Mirage F1”, “Jaguar” and two versions of “Mirage 2000” - in the Air Force. The multifunctionality of the new fighter, the French, first of all, see a means of long-term reduction of defense spending. According to many experts, Rafal will be the last combat aircraft in Europe (after the Swedish Gripen), created entirely in one country.
The Rafal aerodynamic layout is based on Dassault's 40 years of experience in improving the Mirage family of fighters. It is based on the traditional delta wing of a large area, and as a new element, a small front horizontal tail was used. Most likely, the installation of CSP aims to overcome the shortcomings of the Mirage, which are associated with the inability to develop large lift coefficients on the wing due to the lack of feathering that could balance them. MCP, combined with the traditionally low wing load and statically unstable longitudinal layout, is designed to significantly increase the maneuverability of the fighter, although there is no talk of super-maneuverability. In addition, a large wing allows you to lift an unprecedentedly large combat load into the air - 9 t., With an empty aircraft mass around 10 t. The designers of Dassault Aviation succeeded in creating a relatively simple fighter with unregulated air inlets and without air brake flaps, thus simplifying maintenance.
“Rafal” is controlled by a digital electroplating system (EDS), which provides balancing and controllability of a statically unstable aircraft.
On the "Rafale" installed radar RBE2, created jointly by Thomson-CSF and Dassault Electronique. This is the first mass-produced Western fighter radar with a phased array. As stated in the advertising information on the aircraft, in air combat, RBE2 can accompany up to 40 targets, assign priorities to eight of them, and simultaneously attack four.
The MNNXX-88 TRDDF installed on the Rafale production versions is distinguished by its low mass (about 2 kg), compactness (diameter 900 m) and high fuel efficiency. It has a take-off thrust of 0,69 kgf, which increases with boost afterburning to 5100 kgf. It uses a digital control system with which the engine can go from “small gas” mode to maximum afterburner during 7650 s.
The aircraft is installed 30-mm gun Nexter DEFA 791B, ammunition - 125 cartridges.
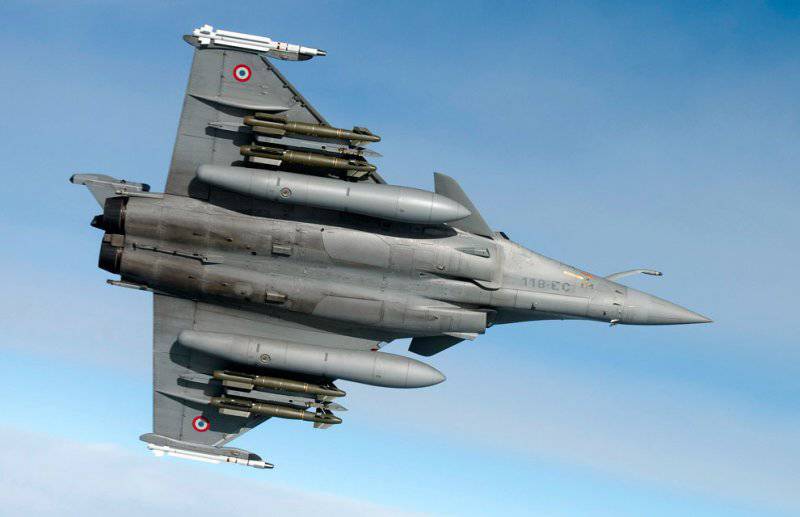
To accommodate the armament there 14 suspension nodes. The main weapon of the air-to-air class on the Rafale is the Mika rocket. It can hit targets in melee and outside visual range. There are two versions of the rocket: the Mika EM with an active radar guidance system and the Mika IR with a thermal imaging homing vessel. Perhaps the use of promising long-range missiles MBDA Meteor, designed for fighter Eurofighter "Typhoon". In addition to air-to-air weapons, a wide range of guided and unguided munitions to destroy ground and surface targets is included in weapons.
To date, there are the following serial options "Rafal":
Rafale B - Double, ground-based.
Rafale D - Single, ground-based.
Rafale M - Single, carrier-based.
Rafale BM - Double, carrier-based.
As of September 2013, the Rafale 121 was produced. In January, 2012 of the year, Rafale won the MRCA tender for the supply of 126 multi-role fighters for the Indian Air Force, which secured a large export order and saved the aircraft from being discontinued. The aircraft participated in the hostilities in Afghanistan and Libya.
The global trends of globalization of the world economy have not spared the French aviation industry. Since the beginning of the 70-ies, a significant part of the program to create new types of aircraft was carried out in the framework of international consortia.
Although all of these consortia worked on the same programs, often there were financial and technical disagreements between the countries from which the contractors participated in these programs.
To prevent this and better co-ordinate in the fight for sales markets, the pan-European aviation and space concern EADS was established in 2000. It includes almost all European aviation consortium as joint-stock companies. Since then, the French aviation industry has largely lost its national framework. Almost all of the leading firms in France are involved
to one degree or another in the pan-European aviation engineering programs.
Despite this, state control over this industry is very large. The French government tightly controls and prevents foreigners from gaining access to the assets and technologies of the national aviation industry.
The basis of the modern aviation industry in France are state-owned or state-controlled firms. The aviation industry has a significant research and experimental base corresponding to modern standards. France is one of the few countries capable of building complex weapons systems, a major exporter of fighters, missiles and helicopters.
Created in France, combat aircraft fully complied with the requirements of their time, possessing good flight data, they bear the imprint of unique French design and elegance.
Based on:
http://uppecheness.do.am/news/geografija_aviacionnoj_promyshlennosti_mira/2013-07-10-38
http://www.be-and-co.com/ako_pdf/ako0309814.pdf
http://machinepedia.org/index.php/Авиационная_промышленность_Франции














Information