French aviation elegance. Part 3
After the end of World War II, the French had to practically restore the fleet and the sea from scratch. Aviation. France has leased four aircraft carriers of military construction from the USA and Great Britain. Ships, mostly obsolete, handed over to France by the Allies and received as a result of reparations from the defeated Germany and Italy. The airplanes based on them were also far from the most modern.
In the early post-war years, the American fighter aircraft of the Second World War Grumman F6F Hellcat, Wout F4U Corsair, and the British Supermarine Sifire were in service with the carrier-based aviation of France.
The first in 1945 was an English escort aircraft carrier “Biter” (in turn, received by the British in the United States by Lend-Lease), renamed “Dixmyd”. The second, in 1946, was hired in the UK for a period of five years by the aircraft carrier Arroomansh (formerly Colossus). In 1951 and 1953, France leased two Independence aircraft carriers in the USA: Lafayette (formerly Langley) and Bois Bello (formerly Bello Wood). Aircraft carrier "Biter" was used as an air transport during the colonial wars in Vietnam and Algeria, withdrawn from fleet in 1960, Lafayette was withdrawn from service in 1960, and Bois Bello in 1963, both aircraft carriers returned to the United States. Arromansch served the longest (the ship was purchased from Britain after the lease expired), his career ended in 1974. In 1957-58, the Arromansh underwent modernization and was reclassified to anti-submarine, and since 1964 the ship was used as a training ship. Arromances-based aircraft, along with the carrier-based aircraft of the British aircraft carriers, took part in the 1956 Egyptian war.
In 1952, a program was adopted to build two aircraft carriers. Unlike the Americans and the British, the French decided that they were better suited for light aircraft carriers. The first aircraft carrier, the Clemenceau, was launched in December 1957. One type with him "Foch" was launched in July 1960 of the year.
Attempts to create their own carrier-based fighter failed, and in 1954, the license issue of the English fighter "Xi Venom" was established, which received the name Aquilon in France.

Production of the new machine was carried out at the plant near Marseille. The Aquilon 203 model was equipped with a 48 Host engine 2336 kg., Manufactured by Fiat and the APQ-65 French radar, as well as the Nord 5103 guided missiles.
The fighter accelerated at an altitude of 1030 km / h., The range with outboard tanks 1730 km.
This aircraft had an airtight cabin with an air regeneration system, a Martin-Baker ejection seat and four Ispano X-guns. A total of 20 machines were built.
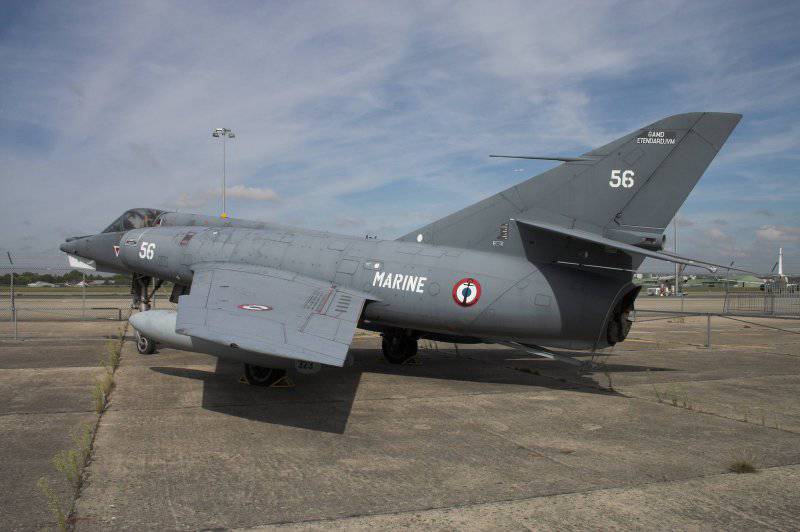
The first deck jet fighter of the French design was the Dassault plane “Etandar” IV M. The initial version of the “Etandar” II (made its first flight in 1956), which conducts its “pedigree” from “Mister”, was developed in accordance with the requirements of NATO to the light fighter . At the same time, the French Navy needed a fighter to base on the Clemenceau and Foch aircraft carriers.
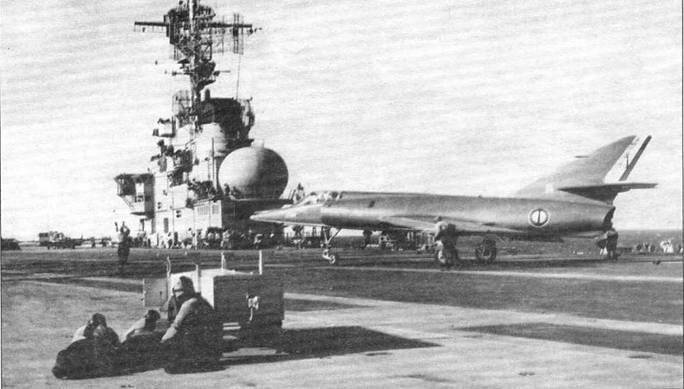
The serial "Etandar" IV M accelerated at an altitude of 1093 km / h. Maximum take-off weight: 10800 kg. Fighting radius, in the version of the fighter: 700 km., In the shock version: 300 km.
The armament consisted of two 30-mm DEFA cannons, each with 100 ammunition, 4 wing pylons designed for a total 1361 kg load — aviation weapons, including AS-X air rockets or Land-air air missiles. , Bombs and NAR.
The aircraft was equipped with a Tomcoh-CSF / EMD Agav radar, an integrated SAGEM ENTA impact navigation system with the SKN-2602 inertial platform, a CGT / CSF laser range finder, a radio altimeter, and an autopilot. The upgraded aircraft were equipped with the Anemone radar.
Having failed to materialize as the “standard European fighter”, the Etandard IV M took its place on the deck of the French aircraft carriers.
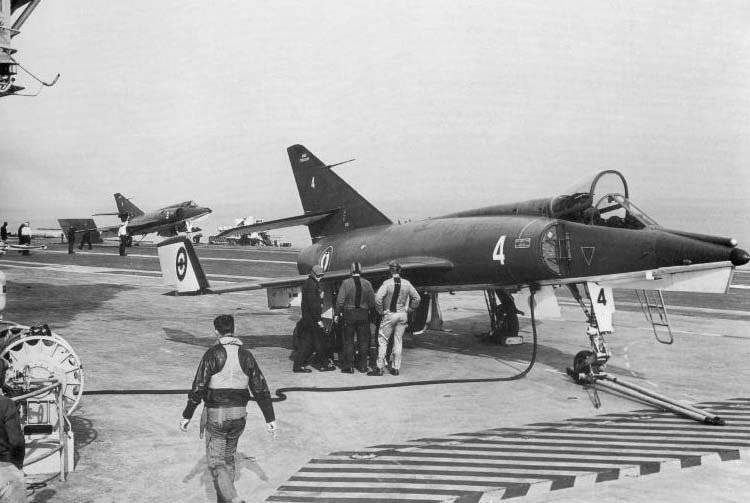

Fully equipped for use in the Ethandard fleet, the IVM made its first flight in 1958. In the 1961-1965, the French Navy delivered the 69 Etmandar IVM aircraft designed to attack naval and land targets and to provide air defense of an aircraft carrier.
The photo reconnaissance aircraft "Ettandar" IVP made the first flight in November 1960, the aircraft was equipped with five cameras, three of which were installed in the forward fuselage, and two - instead of 30-mm guns. The 1962-1965 produced the 21 photo-scanner Etandar IVP.
The baptism of the aircraft was the operation "Sapphire-1". The crisis that erupted in the Horn of Africa in 1974 has pushed France to take decisive steps. A squadron headed by the aircraft carrier "Clemenceau" was assembled. However, the “baptism” turned out to be a purely formality, the planes took off for demonstration flights and photo reconnaissance.

In 1982, in Lebanon, French pilots had to face real danger from Syria’s air defenses. Ensuring the landing of French troops in reconnaissance flights from the "Foch" left "Etandary" IVP. Their task was the reconnaissance of the terrain and the detection of foci of possible danger. The pilots photographed the positions of the Druze “militia” detachments, Syrian troops and several anti-aircraft batteries.
Since then, the life of the Quartet has developed relatively serenely, and on July 1 of the year Istra, a solemn farewell ceremony for the off-ground attack aircraft, the Etmandar IVM, took place on “well-deserved rest”. On this day, the last flight of the machine of this type. "Etandary" reconnaissance modification "IVP" continued to fly.

In 1991, the civil war in Yugoslavia began, NATO forces were drawn into an ever-expanding conflict, and two years later the French fleet launched Operation Balbyusar. For the seemingly hopelessly outdated "Etandarov" scouts, there was a job.
Intelligence in the zone of action of all the warring parties became common in combat, but the focus was on finding the positions, command posts, communications and supplies of the Bosnian Serb army. These same targets were later subjected to the most fierce strikes of NATO aviation. The role of the outdated "Etandarov" was considerable. First, the French units tried to use their data. Secondly, intelligence information was constantly lacking. They barely had time to decrypt the pictures and immediately transferred them to infantrymen and attack pilots.
Flying over Bosnia was neither easy nor safe; aircraft were repeatedly fired upon with anti-aircraft artillery and MANPADS. In April and December, the 1994 of the Etandara received serious damage from air defense weapons. Both incidents ended with forced landings. In spite of this, flights continued, for the entire period from 1993 to July 1995, the pilots of the “Etandarov” IVPM made 554 combat sorties over Bosnia.
At the beginning of the 90-x it was assumed that the scouts "Etandar" IVPM will soon replace the "Rafali" equipped with reconnaissance special containers. But the matter was delayed, and the scouts were exploited until the 2000 year.
At the beginning of the 70-ies, the characteristics of the Etmandar IVM aircraft ceased to meet the increased requirements. Initially, a ship modification of the Jaguar M strike aircraft was intended to replace them; Wout A-7 and McDonnell-Douglas A-4 Skyhawk aircraft were also proposed. "Jaguar" even passed tests on the aircraft carrier. However, for political and economic reasons, it was decided to develop a purely French (“Jaguar” was an Anglo-French car) fighter-bomber based on the Etandard IV aircraft.
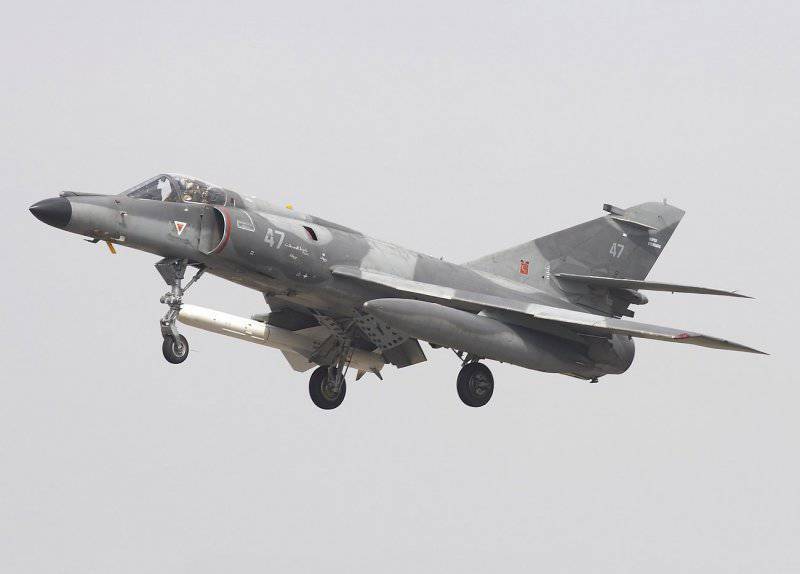
The main objective of the aircraft called the "Super Etandar" was to be the fight against enemy warships and the destruction of important coastal targets. Based on this, the armament complex was being formed, which was assembled around the airborne radar. The new mono-pulse station AGAVE - found a destroyer-class ship at a distance of 111 km, a missile boat - at 40-45 km, and an aircraft - at 28 km. She could search, capture and auto-follow sea and air targets, as well as mapping.
The main weapons The aircraft has become the newest anti-ship guided missile AM 39 "Exochet". She weighed over 650 kg and was equipped with a penetrating high-explosive warhead weighing 160 kg. The combined guidance system ensured the defeat of large sea targets at 50-70 km ranges from a height from 100 meters to 10 km.
It was assumed full suspension of one anti-ship missile under the wing. At the same time the place on the opposite pylon was occupied by the fuel tank. For self-defense, it was possible to use a pair of air-to-air heat missiles of the new generation Matra R 550 Mazic or old Sidewinders on unified launch devices.
The rest of the weapons remained without any changes.
24 November 1976 raised the first production aircraft, and 28 June 1978 held official celebrations in Bordeaux to mark the adoption of the Super-Etandard aircraft by French naval aviation. The aircraft was in production from 1976 to 1983 year, built 85 machines.
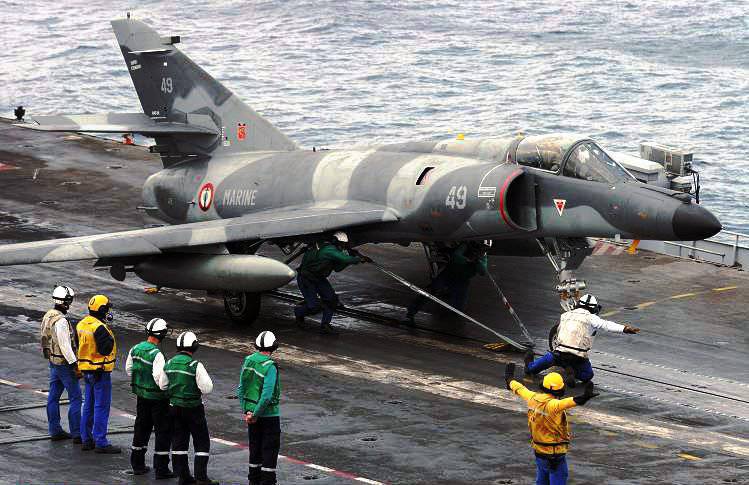

“Super-Etandar” did not shine with outstanding data, but due to the fact that it had a lot in common with the previous model, it was quickly mastered by technical and flight personnel.
Flight characteristics:
Maximum speed at height of 11 000 m: 1380 km / h
Maximum speed at the ground: 1180 km / h
Combat Range: 850 km
Practical ceiling: more than 13 700 m
In January, 1981, the first "Super-Etandar" was finalized for the use of special munition AN-52 equivalent power 15 CT. One such bomb could be suspended on the ventral or right inner underwing pylon. Gradually, all the combat aircraft underwent the same modernization.
In 1983, the Super-Etandars took part in the Olyphant operation in Lebanon.
September 22 under the guise of "Crusaders" flew four "Super-Etandarov." At the end of the day, an official message appeared that in the specified area French aircraft destroyed the enemy’s artillery batteries with 4.
Although the first sortie was successful, during the fighting in Lebanon, two Super Etandar aircraft of the French Navy were shot down by Syrian air defense missile systems.
According to the results of the fighting, the aircraft equipment was improved. A suspension was provided on the right outer pylon of the containers for ejection of false thermal targets and dipole reflectors, while the station of active radio interference was usually suspended on the left outer suspension assembly.
The set of additional tanks included two underwing, with a capacity of 1100 liters and one under vent body 600-liter PTB, and the aircraft suspended arms were expanded. The version with the AS 30 rocket was introduced - one UR under the right wing and a range finder - target designator on the central pylon.
In the early 90s, Super Ethandars participated in hostilities in the territory of the former Yugoslavia. Acting with the aircraft carrier, the Super Ethandars were to provide fire support to the international armed forces in Bosnia. Their task was to block the military activities of all the warring parties, and in practice they attacked the positions of the Bosnian Serb army, waging a real war in the very center of Europe together with aircraft from other NATO countries. Every day, Super Etandars made up to 12 sorties, hunting for tanks and convoys, or assaulting the positions of troops. In July 1995, the aircraft carrier Foch returned to Toulon, and the participation of the French Navy in the Balkan conflict was suspended.
But these aircraft received wide acclaim by participating in another conflict.
At the end of 70, Argentina ordered the 14 "Super-Etandar", the 28 of the AM 39 "Exochet" anti-ship missiles.

By the beginning of the fighting with the British squadron was delivered five aircraft and five missiles.

In 1982, the Argentine Navy’s Super Etandar aircraft were actively used against the ships of the British fleet in the Falkland Islands. The 4 of May 1982, with the AMO.39 “Exochet” missiles launched from aircraft of this type, was sunk by the destroyer of the Sheffield URO. TV screens all over the world have spread around sensational shots - “Exochet” is flying over the water itself and striking the latest British destroyer. Aluminum superstructures caught fire on the ship, the crew could not cope with the fire and was forced to leave the ship. Ironically, on Sheffield there was a command center of the air defense of the entire operational unit, its death turned out to be a ringing slap in the face to the British Admiralty. In addition, at least one nuclear warhead went to the bottom of the Atlantic.
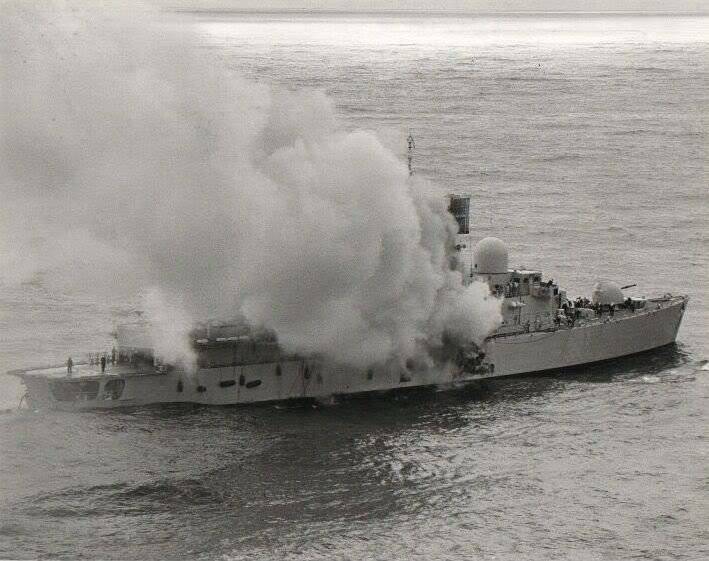

The next victim was the container ship “Atlantic Conveyor” used as an air transport. This time, the pilots of the Argentine "Super Etandarov" aimed their "Exosets" on the aircraft carrier "Hermes". However, the British managed to hide behind a cloud of false targets. The disoriented dipole reflectors and heat traps launched from the ships of the British squadron of the missile "were confused," their heads lost their target, and they went to the tack. And here a number, in some 5-6 km, turned out to be a new victim - the Atlantic Conveyor ro-ro container ship. The huge ship went down, taking with it the 6 medium and 3 heavy transport helicopters, as well as several hundred tons of food, equipment and ammunition intended for expeditionary forces.
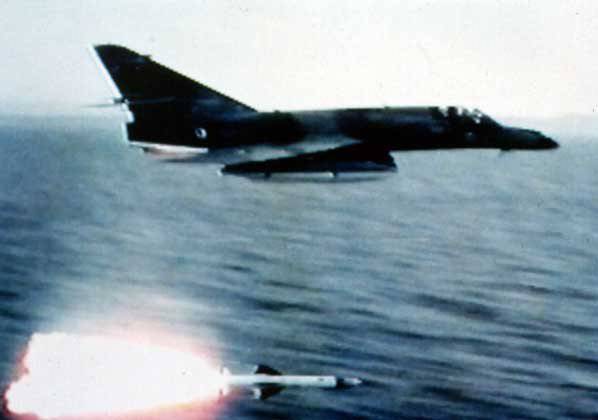

After these events, "Super Etandar" and PKR "Exochet" became interested in Iraq. The Arabs did not hide the fact that they need new weapons to block the waters of the Persian Gulf. They wanted to block the influx of currency into Iran, with which they fought a fierce war for several years. An agreement was signed with Iraq to transfer the five Super-Etandar planes and the first batch of 20 AM 39 missiles. Subsequently, rocket attacks on tankers in the Persian Gulf, which significantly reduced the export of Iranian oil.
During the “Iraq campaign”, one “Super-Etandar” was lost and another one was damaged under unclear circumstances, and the Iranian side stated that both vehicles had fallen victim to their fighters. At the same time, in 1985, it was announced that the lease of the aircraft had expired and all five vehicles were supposedly returned to France. Iraq fully paid for their use, and no questions about compensation for losses were raised.
The “Super-Etandars” were in March 2011 of the year on board the Charles de Gaulle nuclear aircraft carrier during Operation Harmatan, during which Libya carried out air strikes.
To date, "Super-Etandary" remain in service with the aircraft wing of the French aircraft carrier "Charles de Gaulle". Some of them are stored. In the middle of 2000-x it was assumed that by now all of them will be replaced by the deck modification of the Rafale. But thanks to the shortage of funds and the financial crisis, these well-deserved planes continue to rise into the air.
Since the subsonic "Etandara" it could not be effectively used to intercept high-speed air targets. For use as a deck interceptor in the 1964 year, the 42 Fighter X-Cruiser F-8E was purchased in the USA.
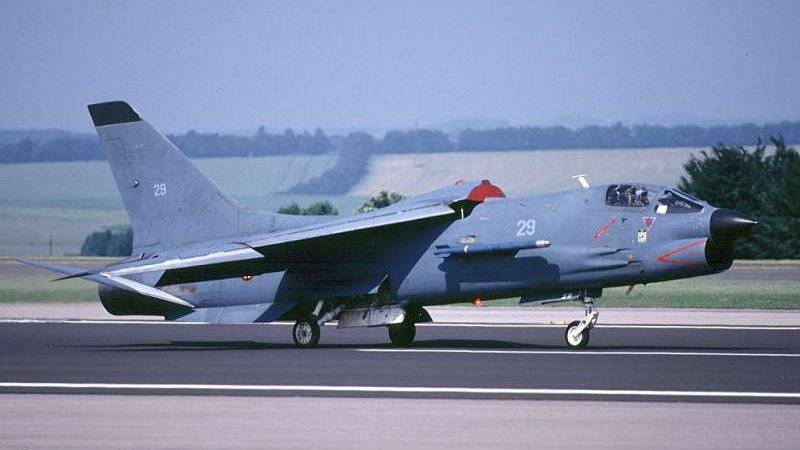

It was a perfect plane for its time. But, given the pace of development of jet aircraft, it is quickly outdated, in the United States, the Cruzadery was withdrawn from service in the middle of the 70's. In addition, the "Kruseyder" could only use melee missiles with TGS, which greatly limited its ability as an interceptor.
Nevertheless, these aircraft for a long time remained in service as part of the French carrier-based aircraft. It was not until December 1999 of the year that the last French Cruiseers were decommissioned, which was the end of forty years of operation of this type of aircraft.
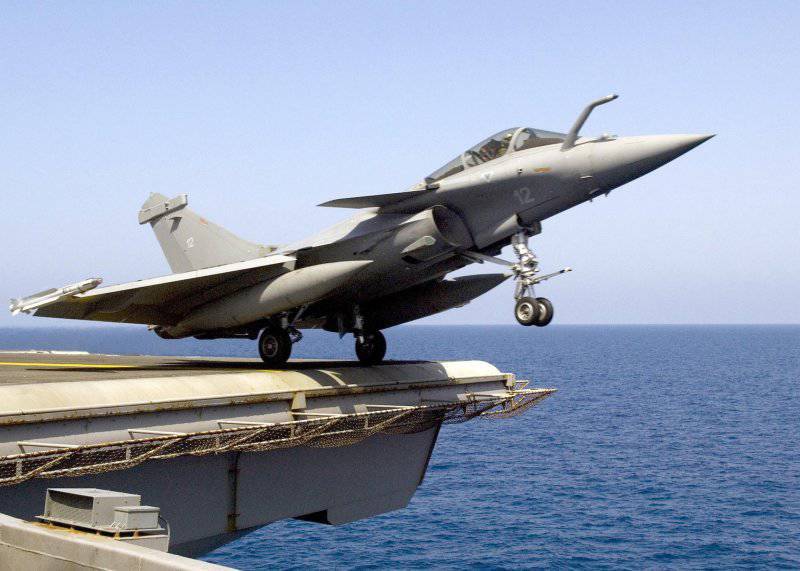
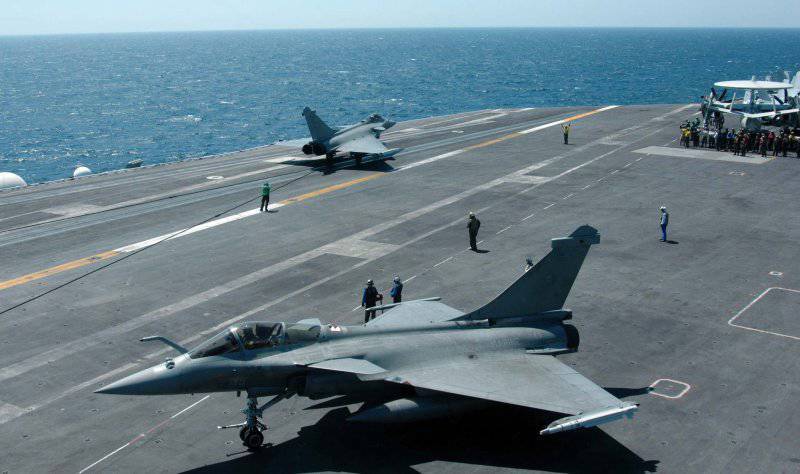
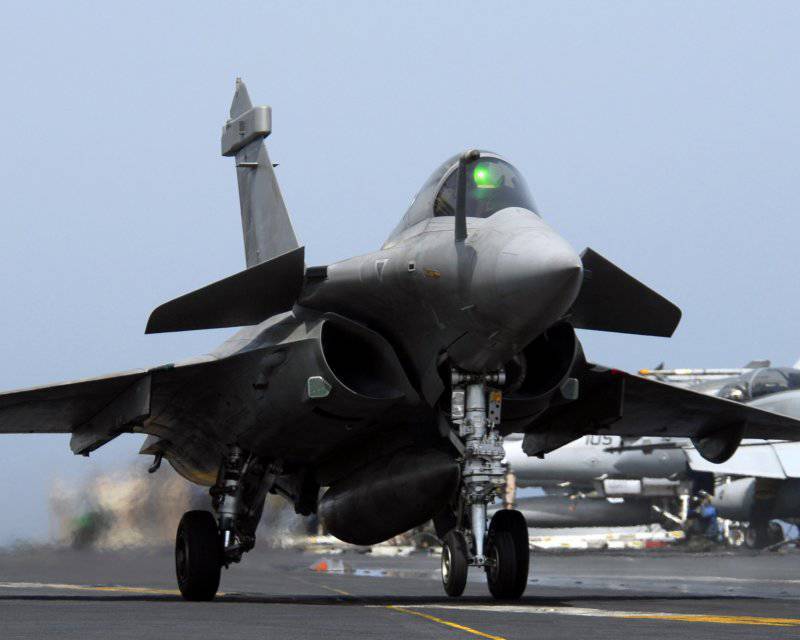
In April, the 1993 of the year on the aircraft carrier made the first landing of the deck version of the Rafale fighter. In July, the French Navy 1999 received the first mass-produced carrier, the Rafale M.
In December, the Rafale M fighters of the F2000 standard, designed to provide air defense of the aircraft carrier group, began to be supplied to the French Navy 1. In June, 2004, the first squadron (naval base in Landiviso) reached full operational readiness.
In the middle of 2006, the French Navy received the first Rafale fighter of the M standard, F2. To date, the Navy should have been armed with about three dozen fighter aircraft of the F2 standard. They should gradually replace the fighter standard. The aircraft are based on the Charles de Gaulle nuclear aircraft carrier.
In the middle of the 2006 of the year, ground and flight tests of the Rafale B fighter began in Istra. In order to test the systems and equipment to be used on aircraft of the F3 standard.
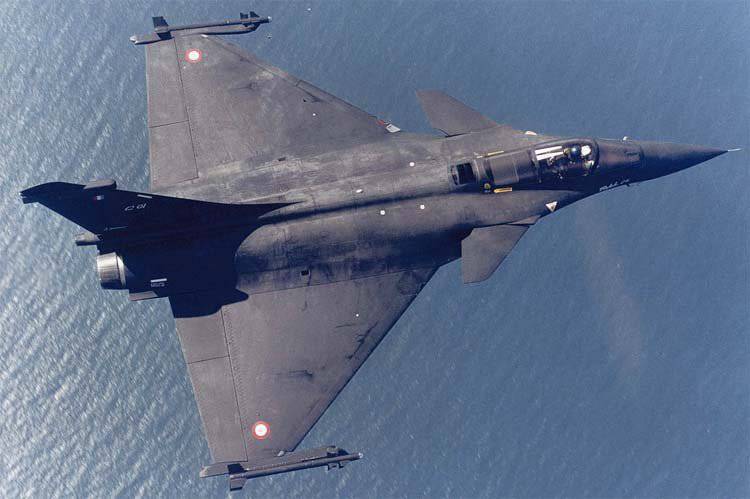

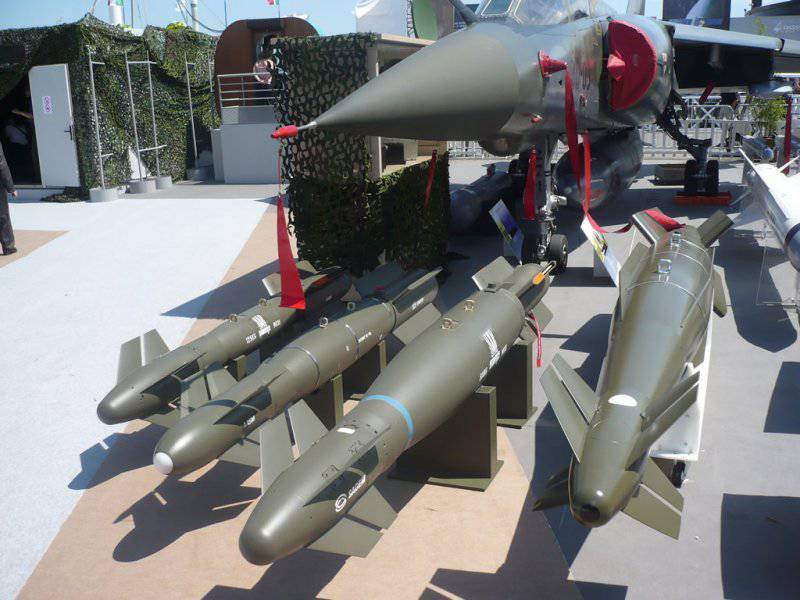
At the end of 2008, a new avionics complex began to be installed on the aircraft, which made it possible to bring fighters up to the F3 standard, i.e. Rafale turned into a fully multi-purpose fighter. Now he is able to carry the RECO-NG reconnaissance equipment container of the new generation and the Exocset AM-39 anti-ship missiles under the fuselage.
Deck "Rafali" have already managed to take part in hostilities. 28 March 2007 of the Rafale M aircraft from the Charles de Gaulle aircraft carrier located off the coast of Pakistan for the first time launched a bombing attack on Taliban fighters at the request of the command of the Dutch troops.
In March 2011, the deck of the Rafali struck at Libyan airfields and air defenses. During the operation "Harmatan", for the first time in real combat operations, 250 caliber aerial bombs were used, equipped with AASM modular sets of high-precision guidance.
Experts consider the use of these bombs from Rafale fighters in combat as the final stage of testing the AASM variant with a laser seeker before adopting the French Air Force. The combat bomb with the AASM module has two targeting modes - pre-programmed to perform the task of hitting a stationary target such as a building or an ammunition depot or programmed by the crew of the aircraft in targeting mode under time-limited conditions.
In 2011, the French Air Force deployed over 1600 APS, including aerial bombs and guided missiles, in Libya during Operation Harmatan. Among them are 225 modular TSA AASM dropped from Rafale aircraft.
The French air force was the first to strike ground targets in Libya on 19 March 2011, when AASM bombs were used to destroy armored vehicles in the Benghazi region in the eastern part of the country. AASM bombs were also used to destroy Soviet-made C-125 anti-aircraft missile systems. They were dropped from an aircraft outside the zone of its effective operation, as well as 24 in March to destroy the Yugoslav-made Galeb jet training aircraft, which was detected by AWACS early warning and control aircraft and destroyed immediately after landing.
Despite the financial crisis, France still demonstrates the ability to independently develop and produce modern competitive aviation equipment and means of destruction. Keeping high technical and technological level of its aviation industry.
Based on:
http://uppecheness.do.am/news/geografija_aviacionnoj_promyshlennosti_mira/2013-07-10-38
http://www.be-and-co.com/ako_pdf/ako0309814.pdf
http://www.telenir.net/transport_i_aviacija/aviacija_1999_04/p5.php
- Sergey Linnik
- French aviation elegance. Part 1
French aviation elegance. Part 2
French aviation elegance. Part 3









Information