The anti-missile appearance of San Antonio as part of enhancing the survivability of American AUG: a new challenge for the Russian Navy
Widespread promising anti-ship missiles, as well as other high-precision weapons in the Armed Forces of Russia, China and Iran, it had a very negative impact on the defensive capabilities of the US Navy, which, even with the most powerful naval personnel, are not able to dominate in the immediate vicinity of the maritime borders of the Eurasian superpowers.
Remarkable is the fact that the first American warship with the AEgis CMS, the CG-47 USS “Ticonderoga” missile cruiser, launched its military service 23 on January 1983, and in March of the same year, the most powerful Russian PKRC R -700 "Granit" with supersonic anti-ship missile 3М-45 with a range of 600 km. By that time, American intelligence was already aware of both the “Basalts” and the developed “Granites”, so the whole concept of the Aegis system can be considered as an asymmetric response to our anti-ship complexes with elements of advanced artificial intelligence.
But the vaunted BIUS “Aegis”, developed for AUG anti-aircraft defense against massive enemy EIA attacks in a difficult jamming environment and PLO, had serious technological flaws that were preserved in all subsequent versions, which ultimately made the system vulnerable by the beginning of the 21st century. Initially, the Ticonderoga RKR class (CG 47 — 51) was equipped with the SM-2 airborne SAM system with a dual inclined Mk26 PU, which severely limited the fire performance and survivability of the ship as a whole. For example, one Mk26 oblique-type PU has an extremely low rate of fire (5 s), as well as additional 2 seconds to reload Mk26 with anti-aircraft missiles from underdeck weapons storage. This disadvantage almost completely eliminated all the advantages of the high capacity of the Aegis system, which is capable of consistently firing 18 air targets with simultaneous illumination (accurate auto-tracking) of 2-4-s of them. Two PU McNUMX, installed on the first five Ticonderoga class cruisers, allowed to realize the rate of fire only around 26-3 c, which absolutely did not allow fully reflecting the massive missile attack of the PCRC of the Basalt and Granit type, the missiles of which fly at speeds up to 4M at low enough heights.
Later, the flaws were smoothed out by equipping the Mk41 with the most advanced universal built-in launchers (UVPU). Their performance exceeds the Mk26 by about 5 times, and their rate of fire is 1 with. Nasal and stern UkPU Mk41, installed on the "Ticonderog" and "Arley Burke", allow approximately 8-10 with release on targets to 16 SAMs of the type RIM-67D or RIM-156A, with two Mk26, this procedure was spent in less than one hour. During this time, for example, the shock train from 48 CRP 24-3 Granit launched from MAPL Ave 45A Antey overcomes from 949 to 21,2 km (depending on the profile and airspeed, 34 - 1600 km / h) It is worth noting the extremely high vulnerability of the Mark 2600 when anti-ship and other elements of the WTO enter the ship (even if it breaks at a certain distance from the ship): the guide pylons are the suspension points for the 26-ZUR, their rotating platform, and the elevator drive mechanism are out ship hulls, i.e. open air. All TPK modular TLU Mk2 below deck, and even if several of them are damaged, the rest will continue to function.
But even though the performance and survivability of the new launcher was increased, other disadvantages of Aegis related to the radar architecture of the BIUS have made themselves felt.
The Mk99 fire control subsystem of the SM-2 / 3 anti-aircraft missile systems is the basis of the Aegis BIUS anti-aircraft and anti-missile capabilities. The principle of its operation is based on the energy and transmission capabilities of the MRLS AN / SPY-1A / B / D, as well as on the accuracy of the auto-tracking (illumination) of the AN / SPG-62 continuous-radar radars. The use of the latter is the main disadvantage of Ajis, which has passed from the 20 to the 21 century. Most modern ship MRLSs use only one antenna post to track their targets and further defeat the most priority of them. These include such multifunctional RLC as the Dutch APAR and the Russian "Polyment". In the pyramidal superstructure of the European frigates of the type “Saxony”, “Ivar Huitfeld”, “De Zeven Provinsien”, as well as the Russian SC Ave 22350 “Admiral Gorshkov”, there is an antenna post with four-sided AFAR that accompanies and hits targets without the help of any specialized light stations and radar "searchlights", limiting the direct channel of the air defense system. The active phased arrays of APAR and Polyment work in the centimeter wavelength range, and therefore another important task is being solved: noise immunity when tracking and capturing air targets against the background of the water surface. The decimeter MRLS AN / SPY-1A (S-band) has serious problems in working on low-altitude targets, and therefore, when targeting SPG-62 illumination radar, errors often occur in determining the exact location of the target, which is near the radio horizon.
It is also known about another type of shipborne multifunction radar. Its representative is the Japanese-Dutch FCS-3A, installed on the Japanese destroyers of the Hyogo type and the destroyers of the Akiozuki type URO (“19DD”). Antenna post of this MRLS consists of 8 AFAR antenna patterns (2 antenna arrays to the side). The Big AR operates in the C-band of decimeter waves and is intended for viewing and targeting small multichannel on-load tap-changers. Small radar works in the X-range, and is designed to "capture" and fire targets. But unlike the American SPG-62, the Japanese radar of illumination is multichannel and is represented by a compact AFAR. This suggests that FCA-3A are able to provide defense against a massive strike with low-flying anti-ship missiles.
Later, improved versions of the Aegis main radar - AN / SPY-1B / D / D (V) appeared, which received new software and design solutions, which increased the noise immunity and the range of viewing angle of elevation. This allowed us to consistently accompany and hit some low-flying targets, as well as the WTO, diving at AUG with angles up to 85-90 degrees. Undoubtedly, the system has improved performance, but the overall radar architecture and its principle of operation remain the same: only 3-4 SPG-62 do not allow Aegis to hit multiple low-altitude and high-speed targets with low ESR. Therefore, the US Navy continues to search for the most appropriate and economically viable solution that allows the Aegis to successfully confront modern PKR. After all, a complete replacement of the radar complex on the 102's Aegis ships will cost hundreds of billions of dollars and is unlikely to pay for itself, as the era of ships like the promising low-profile Zumwalt class destroyers will soon come.
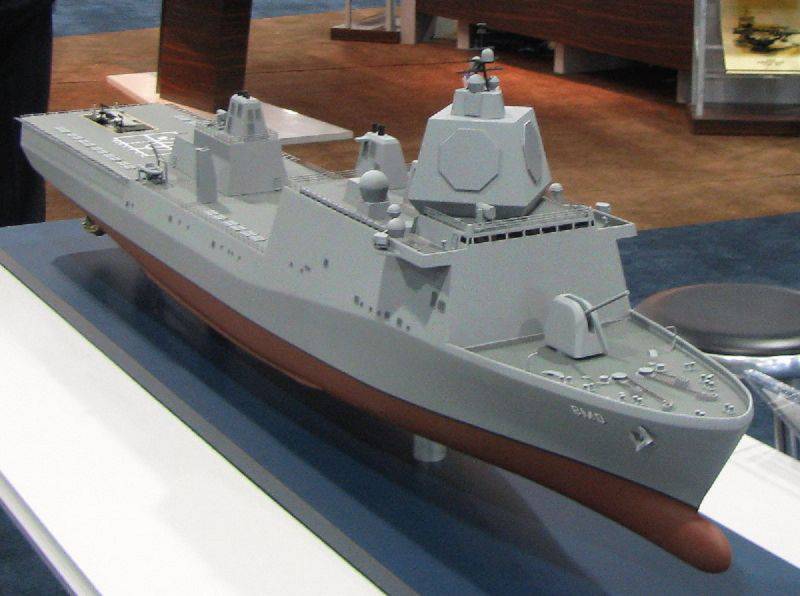
And one such decision is reflected in the topic of recent consultations between the US Navy command and the American leader in naval shipbuilding, Huntington Ingalls Industries (HII). Meeting between representatives fleet and the first persons HII was held on January 15, 2016 during the symposium of the US Navy Association. The technical and organizational issues of the development and construction of a heavy missile defense ship based on the LPD-17 San Antonio class landing helicopter-docking ship were agreed. The decision is very bold, given the multi-billion-dollar estimated cost of re-equipping several existing 25000-ton military transports into anti-missile super-cruisers or building new ships, but the game is worth the candle.
The San Antonio DVKD have important design features that allow: to operate in inaccessible for Tikondero sites of the seas and oceans, to “look” much further than the radio horizon adopted for the early Ages, to maintain the combat stability of the AUG by an order of magnitude longer than it could have done “ Arleigh Burke ", look at enemy radar indicators with ordinary frigates of the Oliver Hazard Perry class or even smaller ships.
A ship of length 208,5 m and displacement 25 thousand tons has significantly larger internal volumes due to the greater length and due to the width of the hull 32 m (2 times wider than Ticonderoga, and 56% more than that of Arleigh Burke "). The huge width of the deck allows you to install 4 UVKU Mk41 modification Mk158, in which the 61 TPK is placed under the SM-2 / 3 SAM, RIM-162 ESSM SAM, LRASM CRM, BGM-109C SC-Tok-shk-kha-kha-kha-kha-kha-cham-ZNXX, and the AHR-UNSX X-ROM. complex "Asroc-VLA". Four such Mk 139 will accommodate different types of 41 missiles, i.e. 244 times as much as the Ticonderoga class (2 Mk 2 on the 41 TPK). The ship turns into a real floating "Aegis-arsenal", adapted to long-term military operations under the blows of hundreds of anti-ship missiles.
The use of the self-defense Mk 25 self-defense container, which represents the quad version of the WPC for the RIM-162A interceptor missile, allows you to fit ESSM missiles into the 2 Mk 41 488 missiles, with a significant numerical superiority of enemy air attack weapons. Add to this number another 61 distant RIM-161A and 61 “Tomahawk” missile in the two remaining Mk 41 - no modern warship with such ammunition is known.
The anti-missile giant based on San Antonio will be managed by the promising AMDR AMDR developed on the basis of the latest AN / SPY-1D (V) modifications integrated into the latest versions of Aegis (BMD 5.1.1. 4 block).
Based on the upper figure with the scheme, you can see that the AMDR MRLS consists of two main elements, similar to the standard version of "Aegis". The detection and tracking radar is performed by 4 large S-band antenna arrays, the backlighting is performed by additional 3 X-band RPNs, but these are not old SPG-62s, but new and powerful AFAR webs, each of which is capable of capturing at least 10 goals.
The AMDR MRLS will surpass all versions of AN / SPY-1, APAR and Sampson in TTX and catch up with the domestic Polymer, as well as the Japanese-Dutch FCS-3A. AMDR has a high energy potential and range. When used in the main “San Antonio” add-on, the AMDR antenna post will be 1,5 — 2 times higher than AN / SPY-1, and therefore the radio horizon will increase by tens of kilometers. The AMDR operators on the new ship will be able to detect more distant targets without retransmitting the tactical situation from the E-2C DRLO aircraft. In addition, new X-band and multi-channel on-load tap-changers of the new multifunctional radar, in contrast to the “ancient” SPG-62, will be able to scan the sea surface for the presence of small radio-contrast targets such as “periscope”, “small landing craft”, etc., which was not available for decimeter S-band AN / SPY-1.
The new BIUS for the AMDR radar will be built on the basis of the latest supercomputers, and therefore the number of air-guided missiles may increase from 22 (in Aegis) to 7 and more than a dozen. The seven-meter “San Antonio” sediment will allow the ship to enter shallow waters, as well as shallow seaports, which will further expand its functionality in marine theaters.
Americans have all the shipbuilding, technological and material capacities for the construction of a large series of such ships in the near future, and therefore it will be very difficult to give an adequate answer. The re-equipment of Admiral Nakhimov into the most powerful shock and defensive instrument of the Russian Navy will certainly make a good contribution to countering the threat from the US Navy's arsenal ships, but this is just a drop in the sea, large-scale construction of 22350 Ave., 885 Ave. "Ash" and other anti-ship surface and submarine cruisers with Onyx, Caliber missiles and more promising products, the production of which must be urgently accelerated.



Information