Project antisubmarine anti-submarine defense boat ACTUV (USA)
The development of submarines makes special demands on anti-submarine systems. New complexes designed to search for enemy submarines should have a number of special characteristics that will allow you to effectively perform the tasks. One promising innovation in this area is the use of remote control systems or fully autonomous machines. It is expected that anti-submarine anti-submarine boats will be able to significantly improve the potential of fleets in the fight against enemy submarines.
Since the beginning of 2010, the DARPA agency and a number of related organizations have been developing a project for a promising anti-submarine system built using crewless boats. Such equipment will have to carry a set of special equipment and conduct patrols of specified water areas. In case of detection of suspicious objects, information about them should be transmitted to the control panel, and then to the anti-submarine defense complexes responsible for the destruction of submarines. It is expected that all work will be completed before the end of the current decade, and the first crewless new model boats and a set of other equipment will be transferred to the US Navy already in 2018 year.
The development of a promising anti-submarine complex is carried out within the framework of the ACTUV program (ASW Continuous Trail Unmanned Vessel - “PLO Unmanned Vehicle for Long Work”). The main goal of this project is to create and test an unmanned boat suitable for performing search tasks for a long time. The main prerequisite for this is the serious limitations of the ships and submarines of the "traditional" design. It is expected that the lack of crew and automation of all processes will eliminate the shortcomings inherent in the "habitable" technology.
The main requirements for the ACTUV complex are the maximum possible cruising range and the possibility of a long patrol in a given area. A crewless boat with special equipment must travel several thousand nautical miles at a single refueling station and remain operational for several weeks or months. The boat must operate in a completely autonomous mode, and on the commands of the operator.
Initially, the ACTUV program was divided into four phases, during which it was planned to carry out various works. So, until the middle of 2012, it was supposed to carry out all the necessary preliminary studies, and then form the exact technical look of a promising anti-submarine complex. From the middle of the 2012, the 2 3 and 4 stages were to begin. The purpose of the second stage was to develop the project, the third - the construction of prototype boats and related equipment, the fourth - the testing and refinement of the prototypes of the complex. The beginning of the fourth stage was planned for the middle of 2015.

The formation of the appearance of the promising PLO ACTUV complex was completed in the summer of 2012. In mid-August, DARPA signed a contract with Science Applications International Corporation or SAIC (now Leidos Holdings). In accordance with this agreement, SAIC / Leidos must implement the second, third and fourth phases of the ACTUV program. For the execution of the work the company will receive 58 million dollars.
At the same time, some details of the requirements for the new anti-submarine system were revealed, as well as the specifics of the SAIC company's offer. A prospective complex should have a set of equipment suitable for searching various types of submarines, including modern non-nuclear ones, which have some means for reducing noise and other factors of visibility. The unmanned boat should continue on duty for 60-90 days. The bulk of the work complex should conduct independently. The operator will be involved in the tasks only in some cases.
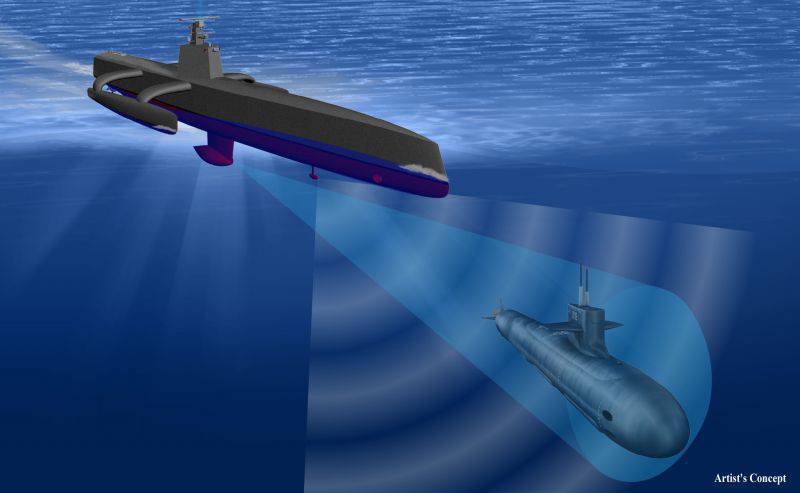
SAIC proposed using a sonar station, an optical-electronic system with a thermal imaging channel, a radar station and a number of other systems as part of the ACTUV complex. Such a set of equipment is expected to allow the ACTUV boat to monitor the waters and detect the submarines of the likely enemy. In order to improve the performance, a promising boat is proposed to be built according to the “trimaran” scheme. Such an architecture of the case should provide the optimal ratio of various characteristics.
The main purpose of the ACTUV complex should be diesel-electric and non-nuclear submarines of the enemy. In this case, an important advantage of the complex will be the possibility of a long stay in a given area. Diesel engines require regular ascents to recharge batteries, which should to some extent facilitate their detection. Thus, a set of special equipment will allow the crewless boat to search for submarines both under water and after ascent. In the case of non-nuclear submarines equipped with an air-independent power plant, the ACTUV complex will have to use mainly hydroacoustic station and other means of detecting underwater objects.
In developing the ACTUV project, the need to reduce the visibility of anti-submarine boats themselves was taken into account. This technique should not only find enemy submarines, but also remain invisible to them. Otherwise, the crewless boat can be destroyed before it can transmit accurate information about the location of the found submarine. To this end, the project used some stealth technology. Boats should have a special shape formed by a set of flat surfaces, the hull will be made of materials that are hardly noticeable for radar, etc.
Special requirements were placed on communication systems. Most of the time, ACTUV devices should operate at a great distance from the bases in automatic mode. In a number of situations, the operator should be involved in the operation of the complex. For this reason, a promising anti-submarine system needs two-way communication, suitable for transmitting various information, commands and video signals. In addition, it must be protected from interference from the enemy's electronic warfare systems. It is also necessary to take into account the fact that the leading transfer of the boat can be detected by means of electronic intelligence.
SAIC was tasked to develop a promising PLO complex that meets the requirements. In addition to the requirements relating to the characteristics and capabilities of this technology, the customer asked some restrictions on the cost of the system. One crewless boat, at the request of DARPA, should cost about 20 million dollars.
In March, 2013, it became known that Raytheon would take part in the development of the ACTUV project. The main contractor in the face of SAIC ordered this organization to create a new hydroacoustic station, which should later on become the main means of accomplishing combat missions. The MS3 hydroacoustic system, upon the request of the customer, must have active and passive mode of operation and be fully housed in the hull of the boat. The station should find submarines, torpedoes and various small-sized underwater objects.
A little later, it was announced that SAIC had signed an agreement with OpenClovis Solutions, Inc. The latter is engaged in the development of control systems for various equipment. As part of the ACTUV project, OpenClovis Solutions, Inc. responsible for creating a new version of the SAFPlus platform. According to reports, such a system will manage the interaction of several ACTUV unmanned boats when working together in automatic mode.
In 2013, some changes have occurred at SAIC. The most noticeable is the name change. Under the new name, Leidos, the company continued to work on the program ACTUV. In the summer of 2014, the company's specialists completed the design of a promising anti-submarine system and submitted the project to the customer. In early July, it was announced the imminent start of construction of an experienced boat and a set of related equipment. The construction of an experienced boat was given 15 months.
In parallel with the construction of the prototype boat, Leidos began testing the technology demonstrator. The pilot boat with a length of 32 feet (9,7 m) was equipped with a set of sensors and control equipment. The on-board equipment of the technology demonstrator could work offline or carry out operator commands. It is curious that during the tests of the reduced prototype not only the features of remote and autonomous control were studied. Separately studied the possibility of automation in compliance with the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea. The absence of a crew is not a reason for non-compliance with international norms and rules. Prospective boats ACTUV must follow the rules of navigation. In addition to the demonstrator of technology in such tests, another boat was used, imitating the vessel with which it is necessary to disperse.
In November last year, the tests of the first simplified prototype boat, equipped only with control systems, were completed. During the 42 of the day, experts conducted about 26 thousands of tests, during which the boat ran through various routes, overcame narrow channels and diverged from other vessels on different courses. Used control automation showed its capabilities. During the tests and refinement, it was possible to “teach” the automatics of the boat to correct driving.
At the beginning of this year new tests started. This time the platform for the construction of the prototype was the 42-foot boat. In mid-January, one of the most interesting stages of testing took place. An experienced boat independently traveled a distance of about 35 nautical miles, passing from Gulfport to Pascagoula (Mississippi). During this voyage, the boat independently determined its location and the necessary route. In addition, automatics in accordance with all existing rules avoided collisions with other vessels and other objects.
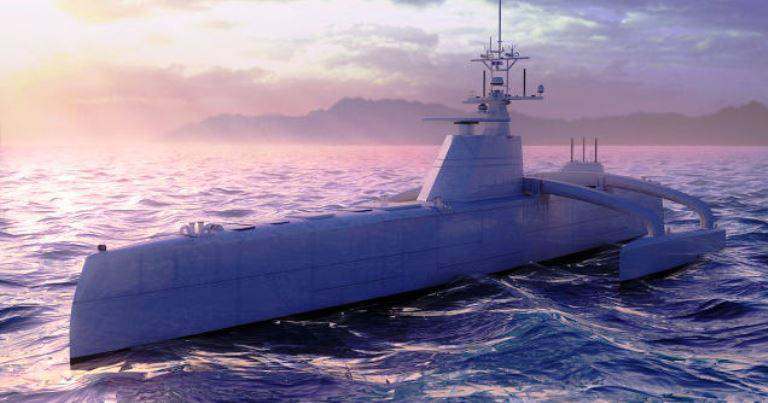
To date, the overall appearance and composition of the equipment of a promising anti-submarine boat has been fully determined. In addition, the main technical tool of the ACTUV complex got its own name - Sea Hunter (“Sea Hunter”). Most of the information about this boat, in particular the exact composition of the target equipment, remains classified. However, some data has already been published.
The ACTUV Sea Hunter boat will have an elongated body length of 130 feet (about 40 m). To reduce radar visibility, the hull will have a shape formed by several rectilinear panels. Most of the equipment will be located inside the case. Part of the equipment should be rendered on a small superstructure. It will have a small size and shape formed by several planes. To enhance the seaworthiness, the boat is a trimaran with small onboard outriggers installed on horizontal beams. It is expected that this design will allow to maintain acceptable performance in the presence of a sufficiently long and narrow body.
On the superstructure of the boat will be placed equipment to monitor the surface situation. For this purpose it is planned to use an optical-electronic system with a video camera and a thermal imager, as well as, possibly, a radar station. In the underwater part of the hull should be located antenna hydroacoustic station. The MS3 station itself should have two modes of operation: passive and active. In the first, it will only receive signals, in the second, it will work on the principle of a sonar.
Characteristics of the "Sea Hunter" have not yet been announced. It is only known that such a boat will be able to patrol for 60-90 days and overcome over 3300 nautical miles without refueling and maintenance. It can be assumed that during the patrol the anti-submarine boat will move at a speed of no more than 5-7 knots. This will increase the cruising range and duration of patrols due to fuel economy, and also not interfere with the operation of the sonar station with the noise of its own propellers.
According to some information, the automation of the anti-submarine boat will control all the processes, as well as do part of the work for the operator of the complex. In particular, it will be able to analyze the noise of the detected submarine and determine its type, giving out to the console not only the coordinates of the detected target, but also its other parameters. Thus, the participation of the operator in the work of the complex can be reduced to the necessary minimum.
Leidos is currently completing the construction of the ACTUV Sea Hunter pilot boat. Tests of this prototype should start in the summer of 2015. Since the operation of some systems has already been studied using previous prototypes, the main task of the testers will be testing and testing the target equipment - hydroacoustic station, communications equipment, etc. The holding of the fourth stage, during which it is planned to test and refine the prototype of a full-fledged anti-submarine boat, is given several years. The first serial ACTUV Sea Hunter is planned to be built and transferred to the naval forces in 2018.
On the materials of the sites:
http://darpa.mil/
http://navaldrones.com/
http://defense-update.com/
http://globalsecurity.org/
https://leidos.com/
Information