UK and France test sites and test centers on Google Earth images
The UK became the third after the USA and the USSR to possess the nuclear weapons. Naturally, no one was going to carry out test nuclear explosions, fraught with unpredictable consequences, near the British Isles. The place of testing of nuclear charges was chosen Australian territory, which was the dominion of Great Britain.
The first nuclear test was conducted on 3 on October 1952 of the year. A nuclear explosive device was detonated aboard a frigate anchored near the Monte-Bello Islands (the western tip of Australia). The power of the explosion was about 25 Kt.
This test method was not chosen by chance. Firstly, because of its bulky nature, the first British nuclear explosive device was not yet a full-fledged ammunition, that is, it could not be used as aviation the bombs. Secondly, the British sought to assess the possible consequences of a nuclear explosion offshore - in particular, its impact on ships and onshore facilities. This was due to the fact that in those years, when considering a potential nuclear attack from the USSR, the possibility of covert delivery of Soviet nuclear charge to one of the English ports on a merchant ship was taken into account fleet or a torpedo attack with a nuclear warhead.
The explosion literally vaporized the ship. Splashes of molten metal, raised in the air, falling on the shore, caused in several places the fire of dry vegetation. An oval funnel with a diameter of up to 300 m and a depth of 6 m was formed at the explosion site on the seabed.
In total, three atmospheric nuclear tests were carried out in the area of the Monte Bello Islands. Over the past years, there are practically no traces of them on the islands. But the radiation background near the explosion points is still different from the natural values. Despite this, the islands are open to the public, fishing is carried out in the coastal waters.
Almost simultaneously with surface tests near the Monte-Bello Islands in the Australian desert at the Emu Field test site in South Australia, in October 1953, two nuclear explosions were carried out.
Nuclear charges were installed on metal towers, the purpose of the tests was to assess the damaging factors of an explosion on equipment and weapons. various samples of which were installed in a radius from 450 to 1500 meters from the epicenter.
At present, the nuclear testing area at Emu is open to public access, and memorable steles are installed at the site of the explosions.
For several reasons, Emu Field did not suit the British military. It required an area remote from large settlements, but with the possibility of delivering there large volumes of goods and equipment.
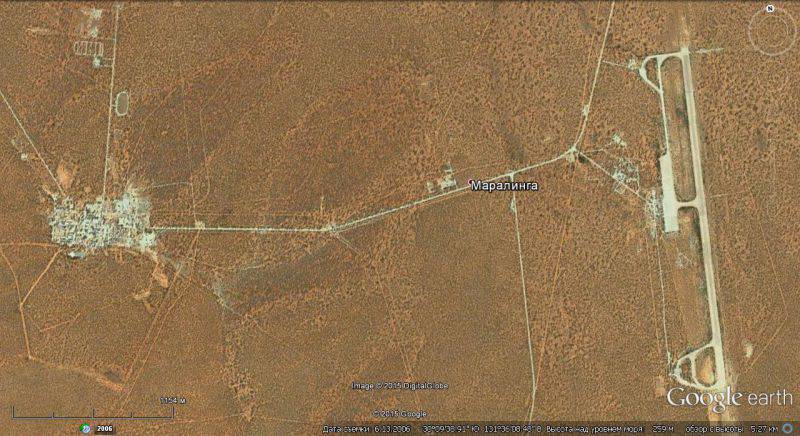
These conditions corresponded to the desert region in South Australia in the Maraling region in 450 km north-west of Adelaide. There was a railroad nearby, and there were runways.
In total, seven atmospheric nuclear tests ranging from 1955 to 1963 CT were conducted in the area between the 1 and 27 years. It also conducted research on the development of safety measures and durability of nuclear charges when exposed to fire or non-nuclear explosions.
As a result of these tests, the landfill has been heavily contaminated with radioactive materials. Landfill cleaning operations were carried out before 2000. More than 110 million dollars was spent for these purposes.
But after that, the debate continued about the security of the area and the long-term health consequences of the aborigines and former military personnel living in the area. In 1994, the Australian government paid financial compensation in the amount of 13,5 a million dollars to the Australian tribe.
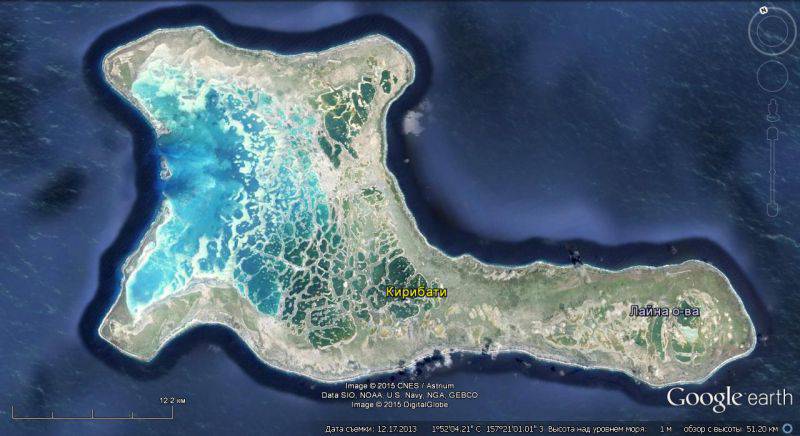
The British in conducting their tests are not limited to Australia. They conducted tests on the islands of the Pacific Ocean. In 1957, the UK conducted three airborne nuclear tests on Malden Island in Polynesia. Until 1979, Malden was in the possession of Great Britain, and from 1979, he became part of the Republic of Kiribati. Currently Malden Island is uninhabited.
In the 1957-1958 years, the UK conducted 6 atmospheric nuclear tests on the Kiribati Atoll (Christmas Island). In May, the first British hydrogen bomb was tested near the island in the atmosphere near 1957.
Kiribati is the largest atoll in the world with an area of 321 km². The number of species of tropical birds found on the island is the largest in the world. As a result of nuclear tests, the island’s flora and fauna suffered great damage.
Later, under pressure from the world community, the UK conducted only underground joint US-British nuclear tests at the site in Nevada. The last nuclear charge the British experienced in Nevada was November 26 1991 of the year. In 1996, the UK signed the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty. A total of 44 British nuclear weapons were tested.
For testing the cruise and ballistic missiles created in the UK, in 1946, in South Australia, in the area of the city of Woomera, construction of a missile range began. The site has 6 launch sites.
In addition to testing military missiles, satellites were launched into orbit from here. The first successful satellite launch from the cosmodrome was carried out on 29 on November 1967, when the first Australian satellite WRESAT was launched into near-earth orbit with the help of the American launch vehicle Redstone. The second successful launch of the satellite and at the moment the latter was carried out on 28 in October of 1971, when the British Prospero satellite was launched into near-earth orbit with the help of the British launch vehicle Black Arrow. This launch was the last, in the future, the spaceport for its intended purpose was not actually exploited.
In July, the 1976, the spaceport was closed, and the equipment was inhibited. A total of 24 launch of three types of Europa-1 launch vehicles (10 launches), Redstone (10 launches) and Black Arrow (4 launches) were made from the spaceport.
The largest British manufacturer of aerospace technology is BAE Systems. In addition to other types of weapons, Typhoon fighters are manufactured at the company's enterprises.
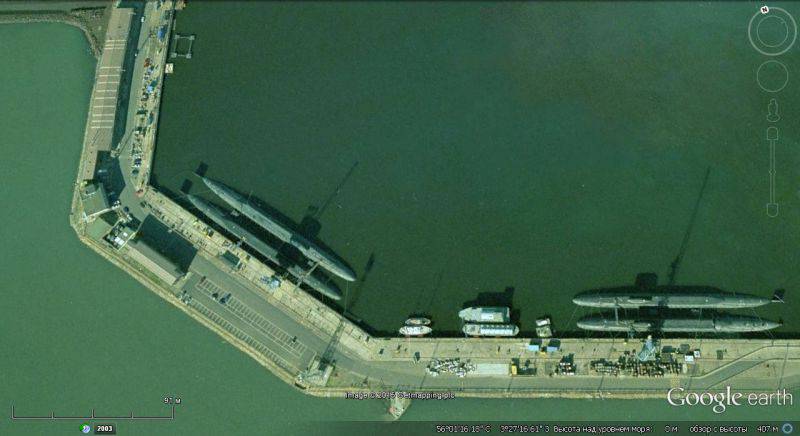
Tests and testing of the combat use of British Typhoon fighters are held at Keningsbay air base.
Not far from the border with Scotland, to the north of the village of Gilsland is a large aviation ground. In addition to the models, there are mobile Soviet radars on this range: P-12 and P-18, as well as Soviet-made air defense systems: Osa, Cube, C-75 and C-125 with operational guidance stations.
It is obvious that all this technique was received by the British from new allies from Eastern Europe.
In the central part of Great Britain, on the territory of the former air base adjacent to the North Laffenheim settlement, British military pilots are working out bombing strikes on the runway.
Judging by the diameter of the craters, quite large bombs were used here.
13 February 1960 France conducted the first successful test of a nuclear device at the test site in the Sahara desert, becoming the fourth member of the “nuclear club”.
In Algeria, in the area of the Oasis Reggan, a nuclear test site was built with a research center and a campus for research personnel.
The first French nuclear test was called "Gerboise Bleue", the power of the device was 70 CT. In April and December of the year 1961 and April of the year 1962 in the Sahara, three more atmospheric atomic explosions are carried out.
The test location was not chosen very well, in April 1961, the fourth nuclear device was undermined with an incomplete division cycle. This was done to prevent its capture by the rebels.
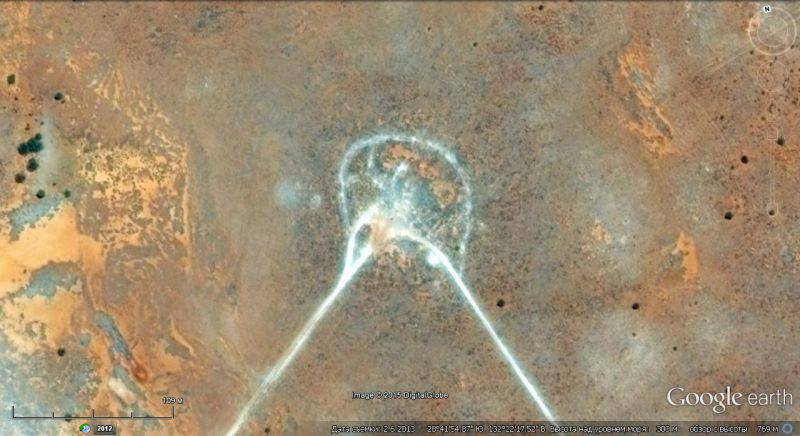
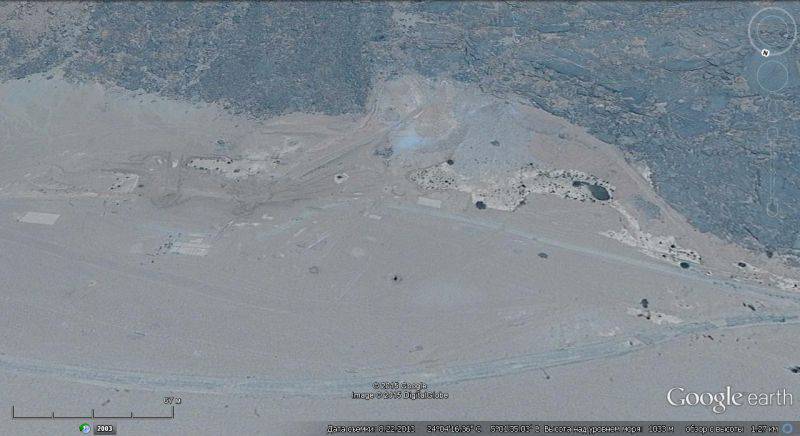
In the southern part of Algeria, on the Hoggar granite plateau for conducting underground nuclear tests, a second test site and a Yn-Ekker test complex were built, which was used until the 1966 of the year (13 explosions were carried out). Information about these tests is still classified.
The site of the nuclear tests was selected area Taurirt-Tan-Afella, located on the western border of the mountain range Hogtar. During some tests, a significant leakage of radioactive substances was observed.
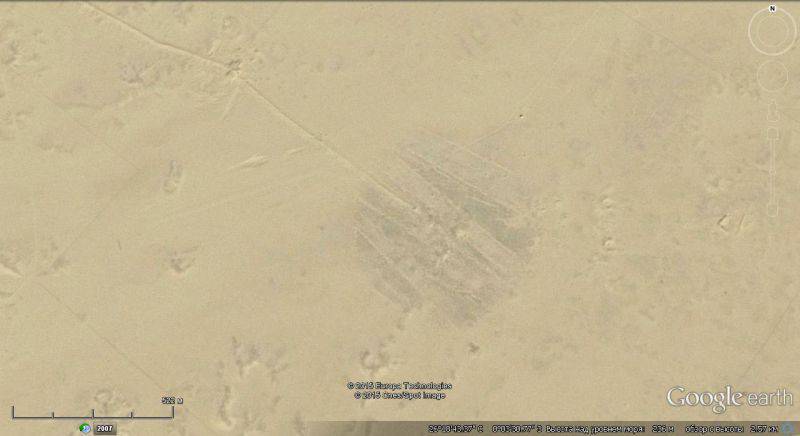
The test codenamed "Beryl" was particularly famous,
held 1 May 1962 of the year. The real power of the bomb is still kept secret, according to calculations, it ranged from 10 to 30 kilotons.
Satellite image of Google Earth: the site of underground nuclear explosions in the area of Mount Taurirt-Tan-Afella
But it seems that due to an error in the calculations, the power of the bomb was much higher. Measures to ensure tightness at the time of the explosion turned out to be ineffective: a radioactive cloud dispersed in the air, and molten rocks contaminated with radioactive isotopes were thrown out of the adit. The explosion created a whole stream of radioactive lava. The length of the stream was 210 meters, the volume of 740 cubic meters.
Nearly 2000 people were evacuated from the test area in a hurry, more than 100 people received dangerous doses of radiation.
In 2007, journalists and representatives from the IAEA visited the area.
After more than 45 years, the radiation background of rocks ejected by the explosion ranged from 7,7 to 10 miliber per hour.
After Algeria gained independence, the French had to transfer the nuclear test site to the atolls of Mururoa and Fangatauf in French Polynesia.
During the period from 1966 to 1996, 192 nuclear explosions were carried out on two atolls. On Fangatauf, 5 explosions on the surface and 10 underground were carried out. The most serious incident occurred in September 1966, when the nuclear charge was not lowered into the well to the required depth. After the explosion, it was necessary to take measures to deactivate part of the atoll of Fangatauf.
Underground explosions caused volcanic activity on the Muroroa Atoll. Underground explosions caused the formation of cracks. The zone of cracks around each cavity is a sphere with a diameter of 200 — 500 m.
Because of the small area of the island, explosions were carried out in wells located close to each other and were interconnected. Radioactive elements accumulated in these cavities. After the next test, an explosion occurred at a very shallow depth, which caused the formation of a crack 40 cm wide and several kilometers long. There was a real danger of a split and separation of rocks and the release of radioactive substances into the ocean. France still carefully conceals the real damage to the ecology. Unfortunately, that part of the atolls, where the nuclear tests were carried out “pixelated” and are not visible on satellite images.
A total of 1960 nuclear tests were carried out in the period from 1996 to 210 in the Sahara and on the islands of French Polynesia in Oceania by France.
At present, France possesses the order of 300 strategic warheads stationed on four nuclear submarines, as well as 60 tactical air-launched cruise missiles. This puts it on 3-e place in the world in the number of nuclear weapons.
In 1947, the construction of the French Rocket Testing Center and later the Hammagir cosmodrome began in Algeria. He settled near the city of Colomb-Bechar (now Bechar) in the west of Algeria.
The rocket center was used for testing and launching tactical and research rockets, including the Diamant-A launch vehicle, which, on November 26, launched the first French Asterix satellite into orbit on November 1965.
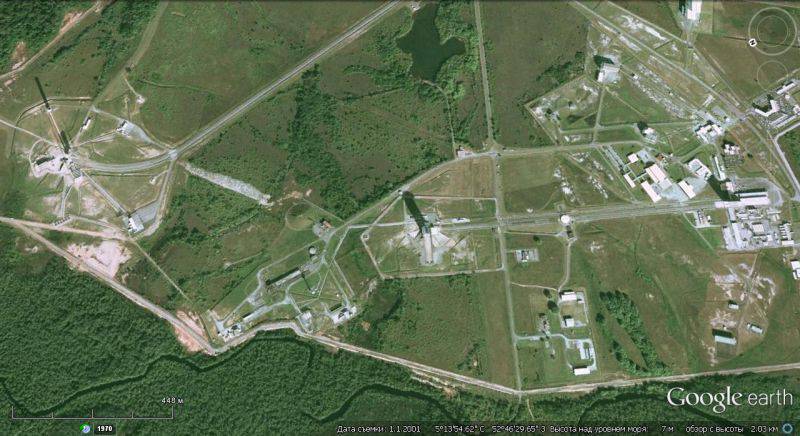
After Algeria gained independence and liquidated the Hammagir rocket center, in 1965, at the initiative of the French space agency, the creation of the Kuru rocket testing center in French Guiana began. It is located on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean, between the towns of Kourou and Sinnamari, in 50 km from the capital of French Guiana Cayenne.
The first launch from the Kourou cosmodrome was performed on 9 on April 1968. In 1975, when the European Space Agency (ESA) was formed, the French government proposed using the Kourou space center for European space programs. The ESA, considering the Kourou space center as its integral part, funded the modernization of the Kourou launch sites for the Ariane spacecraft program.
There are four launch complexes for the launch vehicle at the cosmodrome: heavy class - Arian-5, medium - Soyuz, light - Vega, and rocket-probes.
On the coast of the Bay of Biscay, in the Department of Landa in the south-west of France, sea missile systems are being tested at the Biscarosse rocket testing center. In particular, a special well with a depth of 100 meters is built here, into which a stand is submerged, which is a rocket shaft with a rocket inside and a set of relevant equipment.
All this equipment is used to test missile launches from a submerged position. In addition, a ground launch pad was built for SLBM launches and stands for testing cruise engines.
The French Aviation Testing Center is located in the outskirts of the city of Istres, in the south of France, in 60 km northwest of Marseille. It is here that most of the French military aircraft and air-to-air missile armament passes the entire test cycle.
Testing of means of destruction of ground targets is conducted at the Captier training ground near Bordeaux.
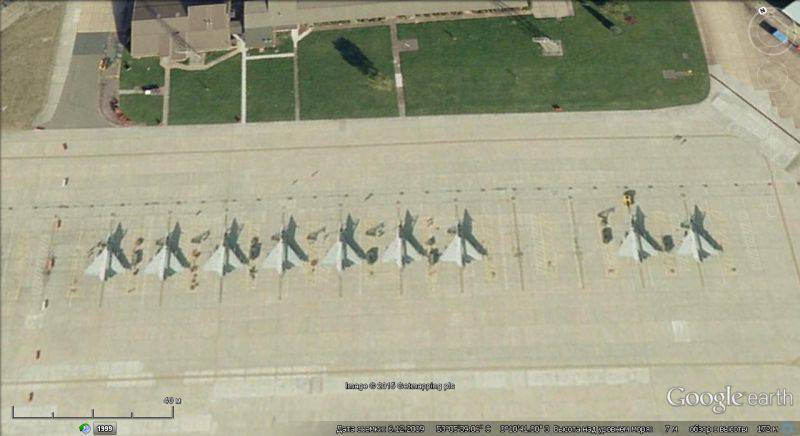
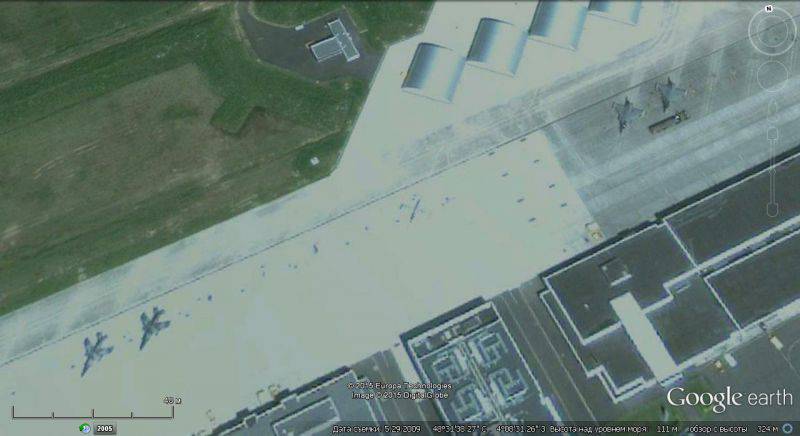
The French Naval Aviation Test Center is located north of the town of Landivisio, 30 km from the naval base Brest.
Google Earth satellite image: Rafale fighter aircraft and Super Etandard attack aircraft at Landivisio airfield
Britain and France are permanent members of the UN Security Council and members of the “nuclear club”. But it is necessary to note in the past a significant difference in foreign policy and the military doctrine of these two countries that are members of the "defensive" NATO bloc.
Unlike the French Republic, Great Britain has always followed a political and military course in the wake of the United States. Possessing formally its own "nuclear deterrent forces", the United Kingdom, after abandoning long-range bombers, became completely dependent on Washington in this matter. After the elimination of the nuclear test site in Australia, all test explosions were conducted jointly with the Americans at the test site in Nevada.
The program to create British ground-based ballistic missiles failed for several reasons, and it was decided to use the resources for creating SSBNs.
All submarine strategic missile carriers of the English fleet were armed with American-made SLBMs. Initially, the English SSBNs were armed with Polaris A3 SLBMs with a range of up to 4600 km, equipped with a scattering-type warhead with three warheads up to 200 Ct each.
At the beginning of the 90-s of the Vangard-type SSBNs, they replaced the earlier resolution-type missile carriers. At the moment there are four such boats in the British fleet. The ammunition of the Resolving SSBN consists of sixteen American Trident-2 D5 SLBMs, each of which can be equipped with fourteen 100 Ct combat units.
France after the withdrawal from NATO in 1966, unlike Britain, was practically deprived of American assistance in this area. Moreover, at a certain historical stage, France was viewed by the United States as a geopolitical rival.
The development of French means of delivering nuclear weapons was largely self-reliant. The French, deprived of American missile technology, were forced to develop ballistic missiles of land and sea bases themselves, having achieved some success in this.
The development of its own ballistic missiles to some extent spurred the development of French national aerospace technology. And unlike in the UK, France has its own missile range and space center.
Unlike the British, the French are very sensitive about the issue of national nuclear weapons. And much in this area is still classified even for the allies.
Based on:
http://www.iss-atom.ru
http://geimint.blogspot.com















Information