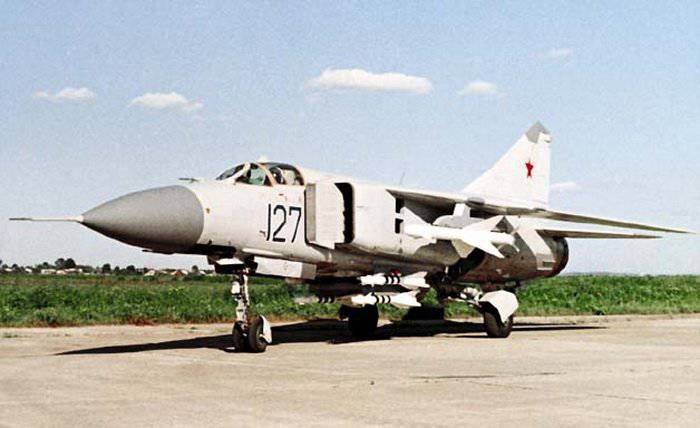
MiG-23ML
In the course of its production, the aircraft was repeatedly improved and modernized. The launch of the lightweight version of the fighter under the symbol MiG-1976ML (product 23-23, L - light) began with 12. This aircraft received a new propulsion unit (TRDF R35F-300 engines), the Sapphire-23ML radar, the TP-23М radar, an advanced automatic control system, an indicator on the windshield of the HPS TSN-17ML, and an identification system, the automatic control system, the indicator on the windshield of the HPS TSN-2ML and the identification system, the automatic control system, the indicator on the windshield of the HPS TSN-XNUMXML and the identification system »SRO-XNUMXM. All these changes allowed to increase the combat capabilities of the machine.
The need to increase the maneuverability and combat capabilities of the fighter was due to the appearance of the X-NUMX generation F-4A, YF-15 and YF-16 machines in the US Air Force, as well as the delay in the creation of Soviet analogs - the MiG-17 and T-29. The MiG-10ML was created as a temporary measure and alternative to the promising MiG-23. The new fighter was able to ease on almost 29 kg. compared to the MiG-1250M. At the same time, it was shortened (forkil almost disappeared), the length of the fuselage was reduced, as the designers abandoned the 23 fuel tank. Despite the fact that the total amount of fuel was reduced to 4 4 l., By reducing the weight and aerodynamic resistance of the structure, the flight range was maintained. The new engines increased the maneuverability of the fighter, providing it with very good acceleration characteristics (in this parameter, the MiG-300ML even surpassed the American F-23).

One of the principal innovations that significantly increased the combat capabilities of the machine was the use of the SOUA - the system of limiting the angle of attack. With the introduction of such a system, the pilot could fly without fear of a plane crashing into a tailspin, and make the most of the existing maneuverable potential of the fighter. This system included a cylinder with a rod, which pushed the control stick forward at precisely the moment when the fighter reached the limit of attack angle for this flight mode. The faster the increase in the angle of attack occurred, the earlier this mechanism worked, which made it impossible for the fighter to dynamically throw at exorbitant angles of attack. Simultaneously with the aircraft MiG 23ML the same system appeared on the machines MiG-23UM and MiG-27.
One of the weak points of the MiG-23ML fighter was its Sapphire-23ML radar. In the main radar viewing mode, the detection range of enemy aircraft was 50-55 km. with manual control and up to 85 km. with automatic guidance from the ground. Based on this, during the Arab-Israeli conflicts and the war in Iraq, when targeting fighters from the ground was impossible (hampered by interference or absent altogether), the enemy, who had F-16 and F-15 fighters, received an advantage during the rapprochement with the MiG-23ML. . Due to the more advanced radar installed on American fighters, they detected the enemy earlier at a distance of 60-70 km. At the same time, the MiG-23 radar target was captured only from a distance of 30-50 km. in the front hemisphere.
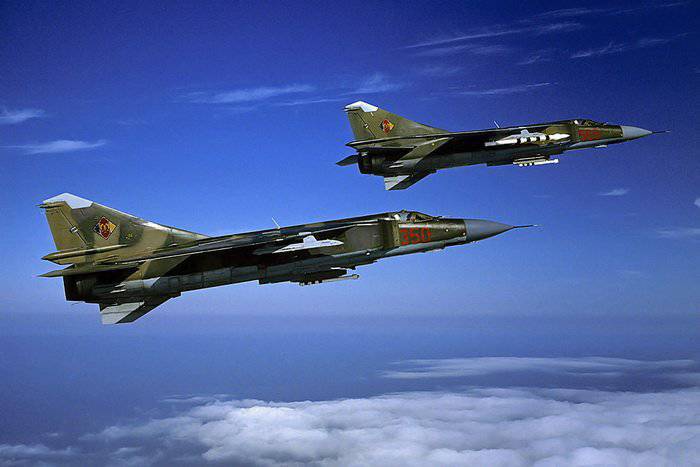
The MiG-23ML fighter was serially produced for the needs of the USSR Air Force from 1976 to 1981, the aircraft was built for export until 1985. According to combatant pilots, some of whom conquered in the Middle East, the MiG-23ML could already be called a full-fledged, truly combat fighter.

Description of construction
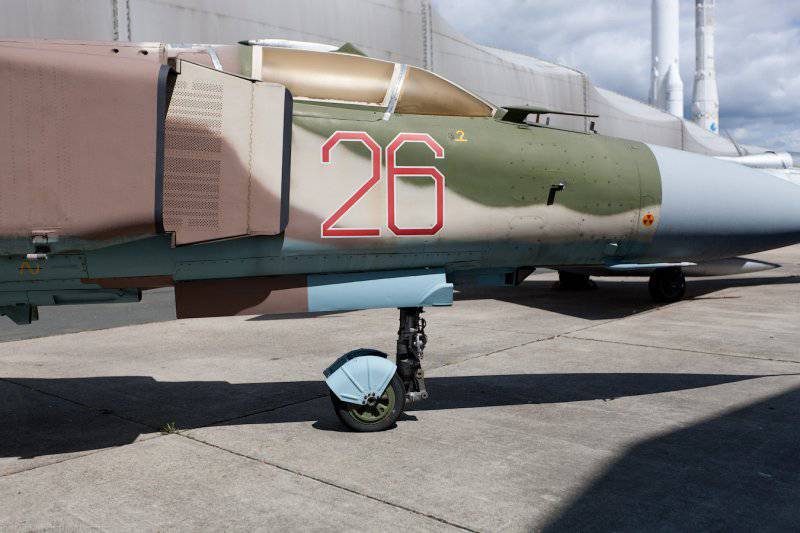
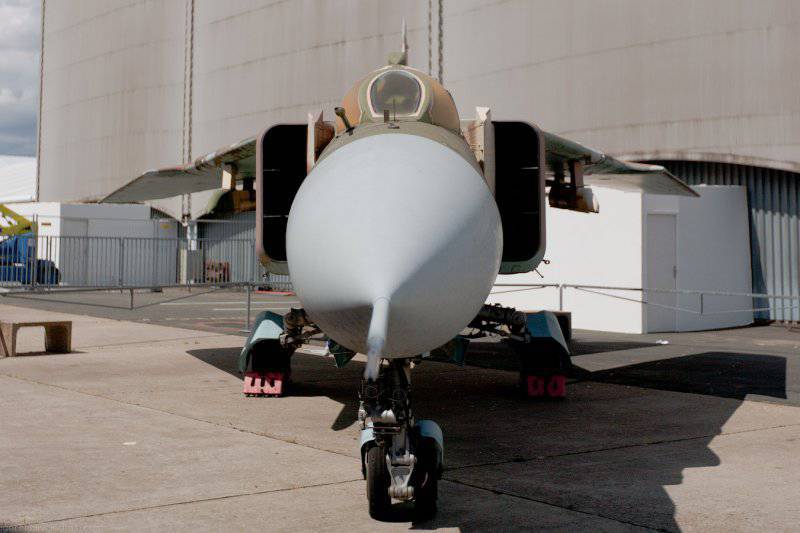
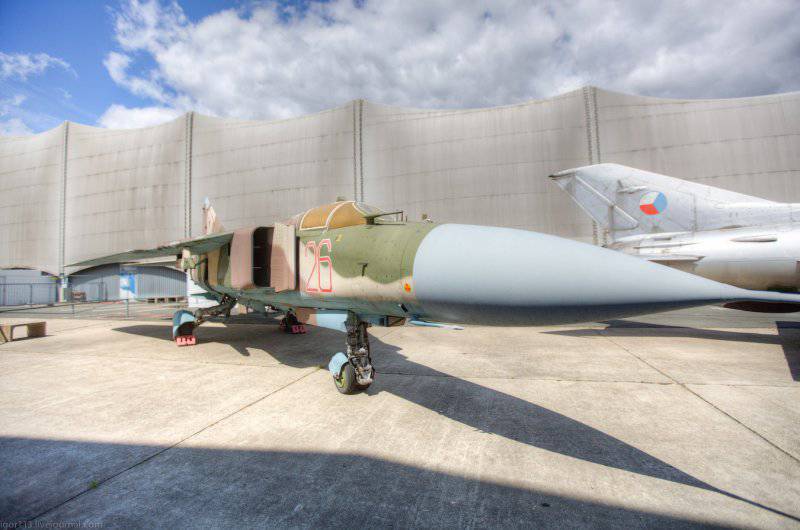
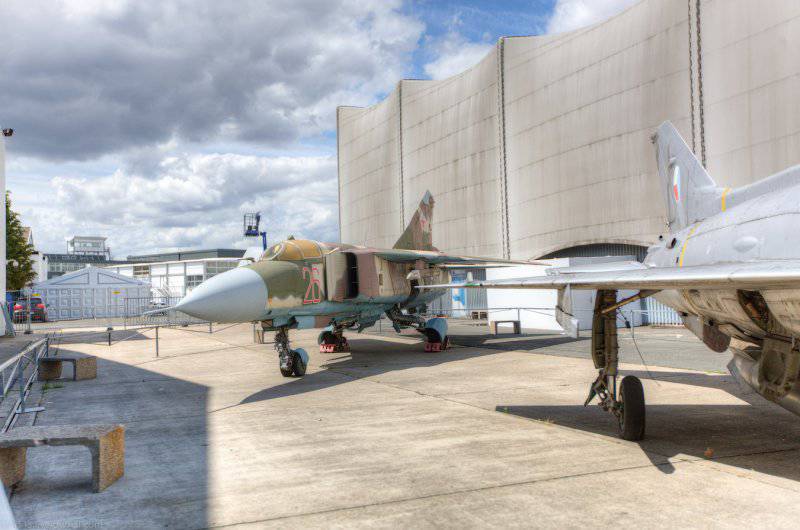
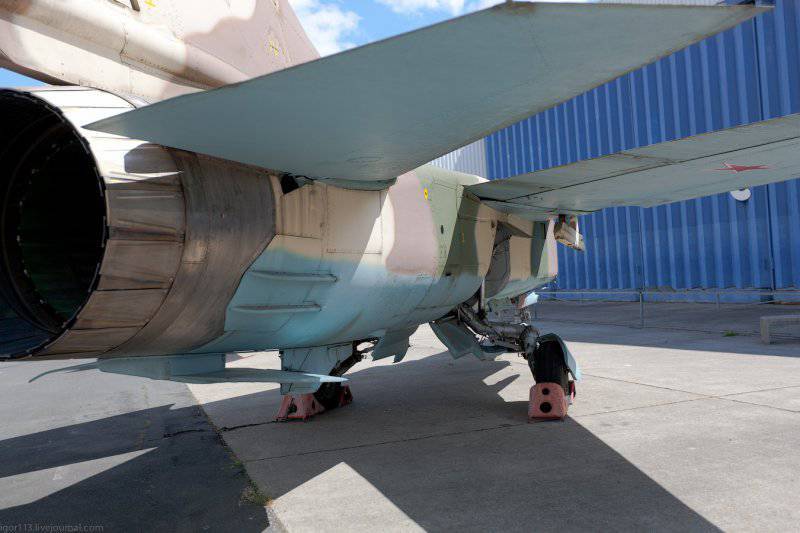
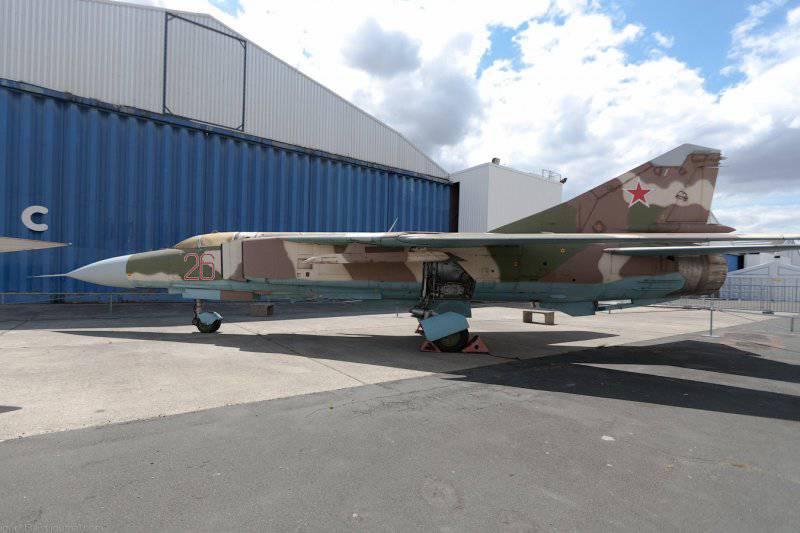
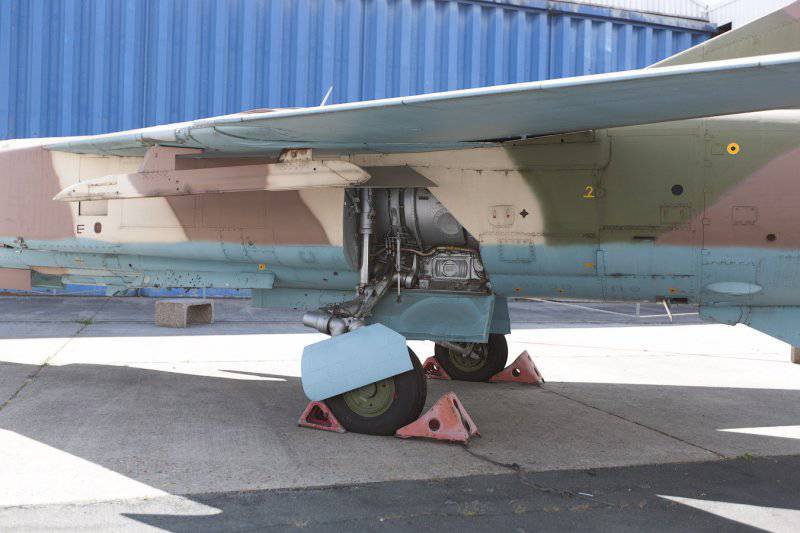
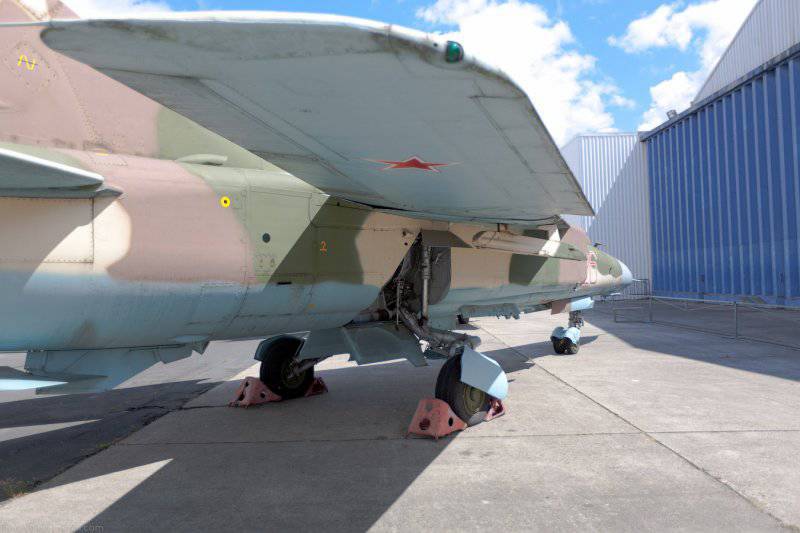
The MiG-23ML fighter is a high-wing aircraft with a variable sweep wing and all-round horizontal tail. The aircraft fuselage has a semi-monocoque design. Its nose includes a sealed compartment of electronic equipment and radar, a front landing gear compartment and a cockpit. Behind the cockpit are air intakes, fuel tank No. XXUMX, equipment compartment and gun compartment, main power compartment aka fuel tank No. XXUMX, engine compartment and tank No. XXUMX. The tail of the fighter has an 1 air brake section, an afterburner, and hitch assembly assemblies.
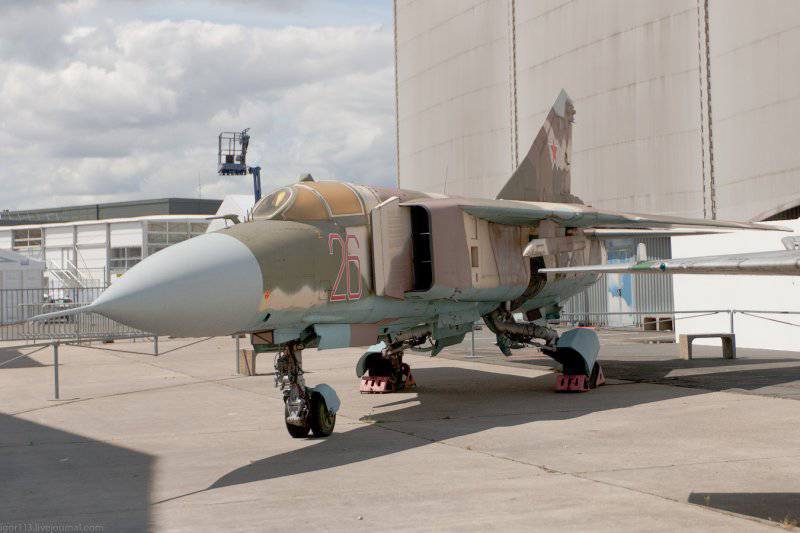
The lantern of the pilot's cabin includes a visor with an electrothermal PIC and a folding part equipped with a pneumatic drive. In order to prevent fogging of the glass of the lantern, inside around the perimeter of its lower part are mounted pipes for blowing hot air, which comes here from the engine compressor. For ventilation of the cockpit while on duty on the ground or while taxiing on the runway, the cockpit can be raised by 100 mm. The review of the pilot back is implemented using a special periscope - viewing device TC-27AMLU, which is mounted on the folding part of the lamp. Inside the pilot's cockpit on the forward arc of the hinged part are 2 mirrors, which are designed to view the planes of the fighter wing.
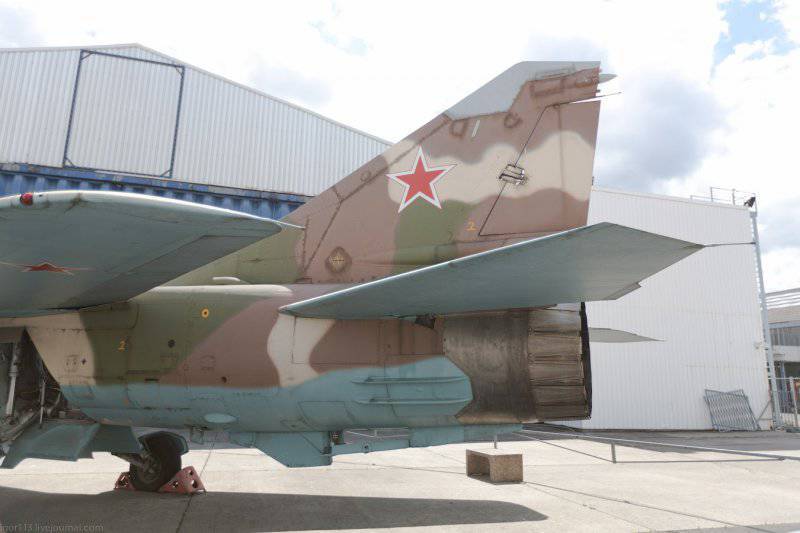
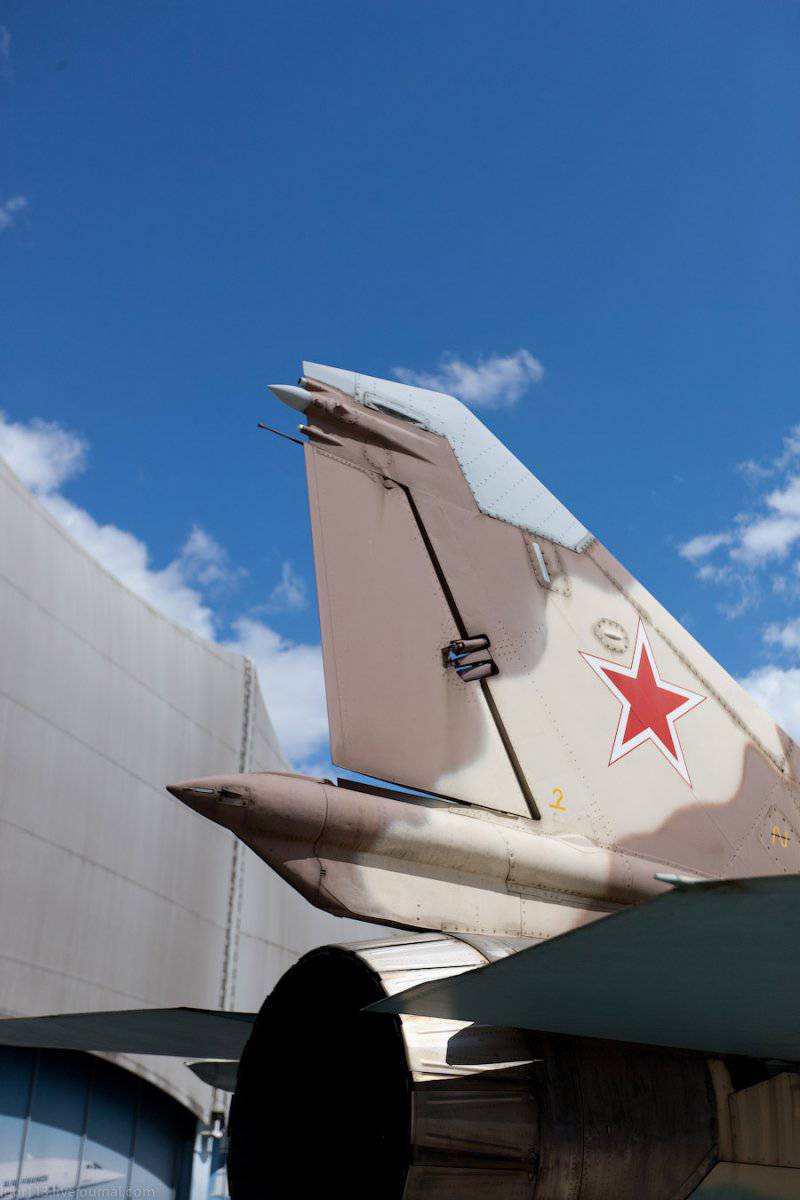
The wing of the aircraft includes 2-e rotary trapezoid console and a fixed part (the angle of sweep of the wing on the leading edge 70 degrees). The fixed part of the wing includes two compartments: the nose, in which there are oxygen cylinders, antennas of the radiation warning station, pylon attachment points, the defendant of the friend or foe system and the central compartment, which serves as the main power element of the wing. It is attached to the console, and at the same time it is a container for storing fuel. The wing of the MiG-23ML is a two-spar. The vertical tail of the aircraft includes the rudder, keel, ventral ridge. Fighter chassis tricycle, provides operation of the machine with concrete and soil runways. In case of landing at speeds up to 320 km / h, the PT-10370-65 parachute can be used.
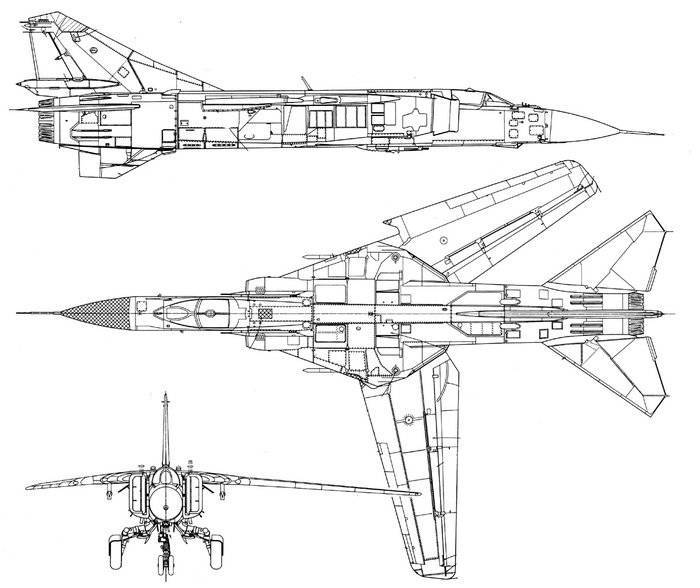
The power plant of the MiG-23ML fighter consists of an afterburner turbojet P-35-300 engine. Aircraft side air intakes are adjustable with variable configuration wedges. The inlet area of the air intakes is maximum with the landing gear released and minimal during supersonic flight modes. The fighter engine launch system on the ground is autonomous from the TC-11 turbo starter. During the flight, the engine is started from autorotation, at high altitudes of flight, oxygen is used to start the engine to start the engine.
The fighter’s fuel system consists of three (on previous fighter models four) fuselage and 4 (formerly 6) wing fuel compartments. The total fuel volume of 4 liters. In addition, it is possible to use 300 PTBs: 3 under-fuselage with a capacity of 1 liters., And 800 underwing on 2 liters. The aircraft uses fuel aviation kerosene of the following grades: T-1, TS-1 and RT. Refueling centralized under pressure for all fuel tanks with the exception of outboard ones is carried out through the refueling receiving unit located on the port side of the aircraft. At the same time, open fueling of fuel tanks through their filler necks is also possible.
The aircraft is equipped with fire-fighting equipment, which includes a fire alarm system, which includes 5 ionization sensors located in the engine compartment, as well as a fire extinguishing system, which is represented by 3-liter UBSH-3-1 fire extinguisher and collector-expander. The aircraft is equipped with an air conditioning system that is used to maintain the optimum air temperature and pressure in the cockpit and in some compartments with avionics. At flight altitude up to 2 000 meters, the fighter cockpit is freely ventilated, after which the pressure drop gradually increases, reaching at flight altitude in 9-12 km. 0,3 values kgf / cmg, this value is maintained until the aircraft reaches the practical flight ceiling.
Aircraft armament includes 23-mm automatic cannon GSH-23L (200 ammunition shells, 3400 fire rates per min / min). In addition, it is possible to install on the MiG-23ML two similar guns in special containers UPK-23 / 250 with ammunition in 250 shells. To destroy airborne targets, the aircraft can use up to 2-x medium-range missiles P-23Р (with semi-active radar guidance), P-24Р (radio command and semi-active radar guidance), P-23T with a thermal homing head, P-24Т (TGS), which are suspended on fixed parts of the wing. As weapons short-range 2-XR UR P-13М, Р-13М1 or 4-Р Р-60 or Р-60М are used on the ventral nodes of the suspension.
Possible upgrade
RAC "MiG" in order to fully disclose the significant potential of front-line fighters MiG-23, as well as fighter-bombers MiG-27 has created a program of modernization of fighters, which takes into account the specific requirements of different customers. These programs provide for the installation on the fighter of a number of new avionics systems, as well as expanding the range of weapons used by introducing new models. A new aircraft armament control system can be based on a multifunctional radar or include an additional system in its structure, which is intended to issue radio-correction commands to the modern air-to-air UR and to form a flight task.
The composition of avionics of the modernized fighter can include modern information display systems, including a multifunctional display and an indicator on the windshield, a helmet-mounted target designation system for the pilot. Communication and navigation systems, video registration, radio counteraction, registration, control and processing of incoming flight information are also upgraded.

The composition of the weapons of modernized fighters can include modern guided missiles, such as the RVV-AE, P-73E and P-27Р1. At the request of the customer, the fighter can be adapted to the use of other types of air-to-air and air-to-ground guided missiles.
Flight performance of the MiG-23ML:
The wingspan is 14,10 / 7,78 m., The length of the fighter is 16,7 m., Height is 5,0 m.
Wing area - 37,27 / 34,16 square. m
Aircraft normal take-off weight - 15 600 kg., Maximum take-off - 20 100 kg.
Fuel supply - 4300 l.
Engine type - two TRDDF P-35, unforced traction - 8 850 kgf., Afterburner - 13 000 kgf.
The maximum speed is 2500 km / h.
Practical range - up to 1450 km.
Ferrying range - 2 360 km. with 3 PTB.
Practical ceiling - 17 700 m.
Crew - 1 man.
Armament: 1 23-mm gun GSH-23L, combat load up to 2 000 kg., On 5 suspension nodes.
Information sources:
-http: //www.airwar.ru/enc/fighter/mig23ml.html
-http: //www.dogswar.ru/voennaia-aviaciia/samolety/4700-frontovoi-istrebitel.html
-http: //www.migavia.ru/military/MiG_23_27.htm
-http: //ru.wikipedia.org
Le Bourget Museum













Information