Satellites "Condor" and their prospects
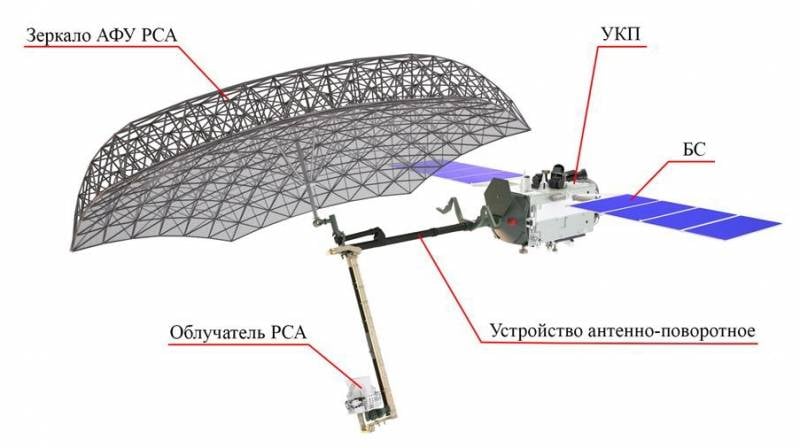
Scheme of the spacecraft "Kondor-FKA" in the working position
The Russian orbital constellation for civil purposes has been replenished with a new spacecraft for remote sensing of the Earth. The Condor-FKA product has been launched into orbit and will soon begin full-fledged work. He will have to carry out radar surveys of the planet's surface as part of various studies. In addition, the launch of another apparatus of this type is planned for the foreseeable future.
scientific grouping
History series of spacecraft for remote sensing of the Earth (KA ERS) "Kondor" dates back to the 2013s, when NPO Mashinostroeniya was developing the basic projects of the future line. In June 2014, the first satellite was launched into orbit, and in December XNUMX, the second one was sent into space. It was reported that two spacecraft are intended for radar monitoring of the earth's surface and oceans, as well as conducting various studies in the interests of the armed forces and civilian structures.
In 2014, the state corporation Roscosmos held a competition for the creation of a new satellite of the series, designated as Condor-FKA. At the end of the year, NPO Mashinostroeniya again received a contract for its development. The association completed the project of the satellite and related facilities, and the creation of a remote sensing radar complex with specified characteristics was entrusted to the Vega concern.
At the turn of the decade, the Condor-FKA project reached the stage of manufacturing spacecraft and preparing for their launch. At the current stage, it is planned to create a constellation of two satellites. This number already makes it possible to ensure the required level of spacecraft presence in the given areas and to fulfill the assigned tasks.
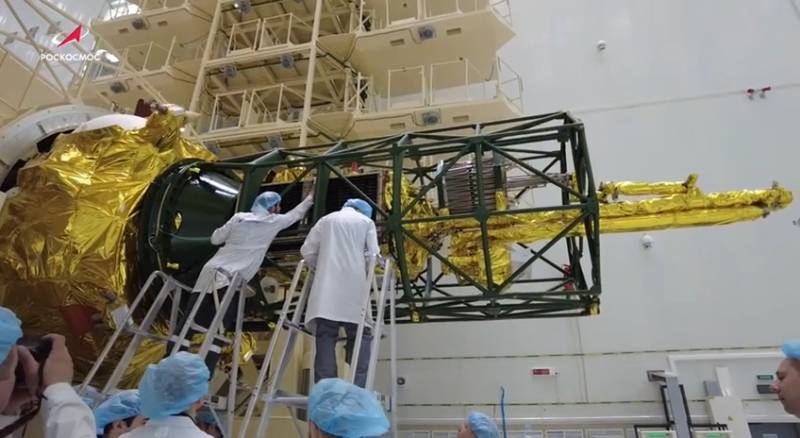

Satellite in the process of being installed on a launch vehicle
In recent weeks, the organizations participating in the project have been preparing the launch of the first spacecraft of a new modification. The launch of the Soyuz-2.1a carrier rocket with the Fregat upper stage carrying the Kondor-FKA product took place on May 27 around midnight Moscow time. A few hours later, Roskosmos announced the successful entry of the device into a given orbit.
Preparations for the second start have already begun. In the next 2024, the second Kondor-FKA remote sensing spacecraft will be sent into orbit, but the exact date has not yet been announced. The second pair of such satellites will be built and launched into space at the end of the decade. In addition, plans have been made for the more distant future. In the coming years, a modernized satellite "Kondor-FKA-M" will be developed. It will start operating around 2030.
In the small class
"Kondor-FKA" is a spacecraft of a small (in size and mass) class, equipped with radar equipment. With the help of the latter, the satellite must carry out remote sensing of the Earth. It is planned to survey the land and the surface of the oceans to collect the necessary information. The tasks of the satellite include the creation of maps, control over natural resources, various environmental studies, information support for various ground operations and events, etc.
The new remote sensing satellite has a mass of 1050 kg and is distinguished by a characteristic layout. The device received a rectangular case, on which folding solar panels and a rod-base of the antenna device are fixed. When deployed in orbit, the satellite must open the antenna mirror and other units. The mirror has an effective diameter of 6 m and weighs approx. 100 kg. It is reported that the device is distinguished by the maximum degree of localization - the share of domestic components has approached 100%.
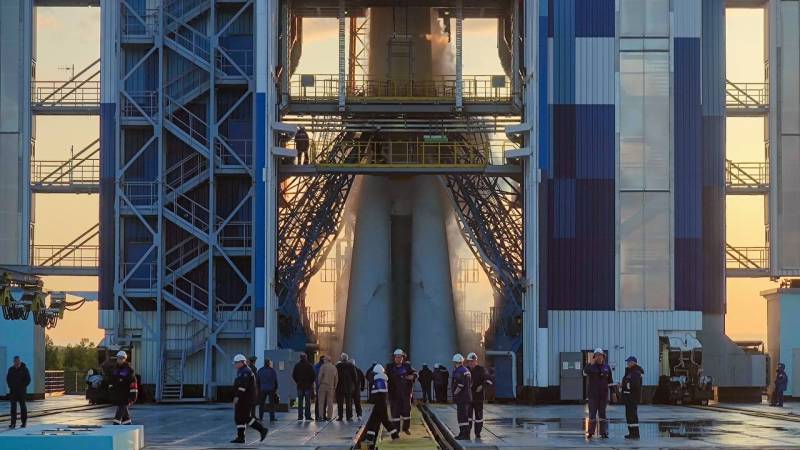

Preparing the rocket for launch
The Kondor-FKA is equipped with a synthetic aperture radar with several operating modes. The radar operates in the S-band with a wavelength of 10 cm and a frequency of 3,1-3,3 GHz. The maximum average power at the input of the antenna device is 250 W. The antenna device is rotatable, which provides a view in the right direction from the track.
There are several modes of operation of the radar. In the survey mode, the satellite surveys a band up to 100 km wide and 500 km long. The resolution is not better than 6-12 m. In the detailed continuous mode (DPR), the capture strip is reduced to 10 km with an improvement in resolution to 2-3 m. The best resolution, up to 1-2 m, is given by the detailed spotlight mode (DPR). In this case, the spacecraft captures only an area of 10 x 10 km. In addition, "Kondor-FKA", alone or in pairs, can operate in the interferometry mode.
The Kondor-FKA satellite is capable of conducting radar surveys of the planet's surface in any mode in the range from 85°N. up to 85°S A constellation of two satellites, depending on the selected survey object and its corresponding orbit, can monitor at least 12 hours apart. A pair of satellites in the LPR mode is capable of taking at least 200 frames per day. In other modes, the performance is much higher, but the resolution worsens. Thus, the OP mode allows you to take up to 1 million pictures per day.
One remote sensing satellite can collect and store up to 96 GB of information per day. Storage time - up to 10 days. In this case, data processing by the onboard means of the satellite is not provided. The data is transmitted to Earth; up to 16 GB is issued for one communication session.
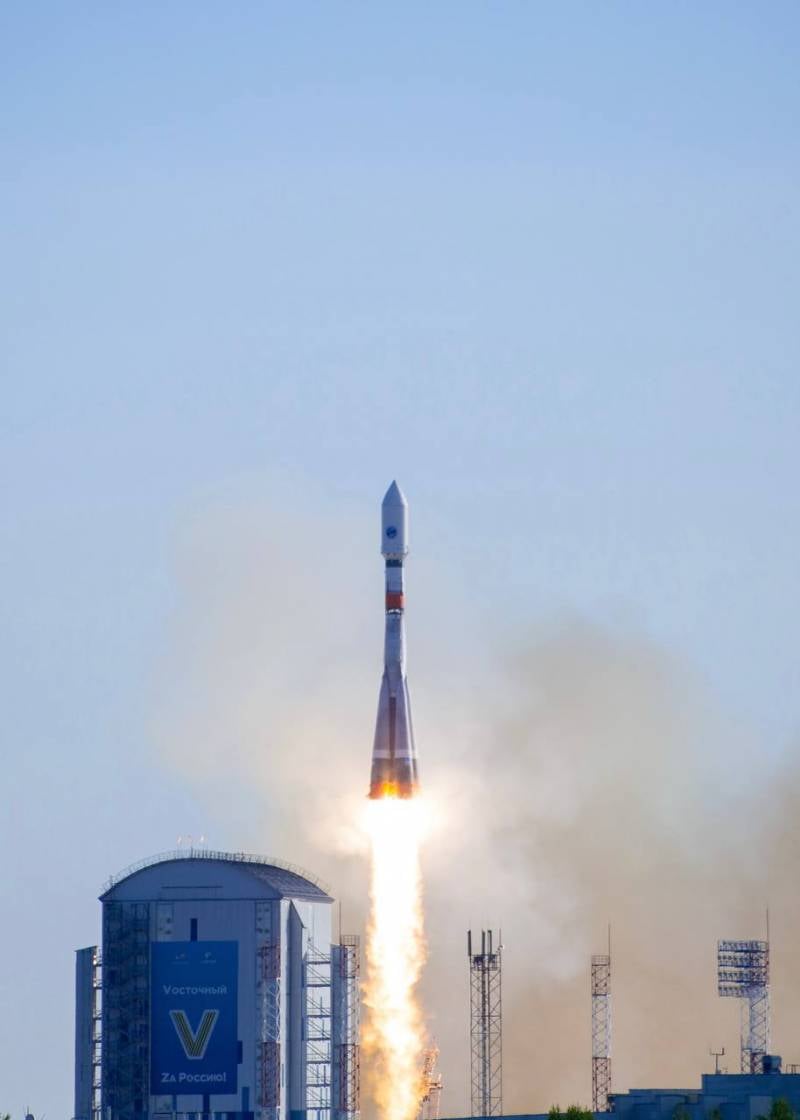

Launch of Soyuz-2.1a with Condor, May 27
Ground facilities of the Condor-FKA complex provide primary and secondary processing of the received information. Both stages of processing take about a day. It takes about 5-10 minutes to process one high-precision radar frame in the LPR mode.
For maximum performance, both satellites will operate in circumpolar sun-synchronous orbits. Altitude - 500-550 km. In this case, the orbits will be shifted relative to each other by about 9°. Due to such orbits, it will be possible to obtain the best results both in the single operation of the vehicles and in the joint solution of problems.
Clear perspectives
The first remote sensing spacecraft "Kondor-FKA" has already entered the estimated orbit and is preparing to start full-fledged operation. Over the next few weeks or months, it will begin to film selected areas of the planet and transmit the collected radar images to Earth. Next year, a second similar device will be put into operation. Such a grouping will be able to perform all the intended tasks.
With the help of one or two new spacecraft, Roskosmos will be able to conduct various surveys of certain parts of the earth's surface or the World Ocean. It is assumed that such activities will be carried out in the interests of civil structures - scientific, commercial and other customers. However, the involvement of "Condors" in military intelligence is not excluded, but within the limits of their capabilities.
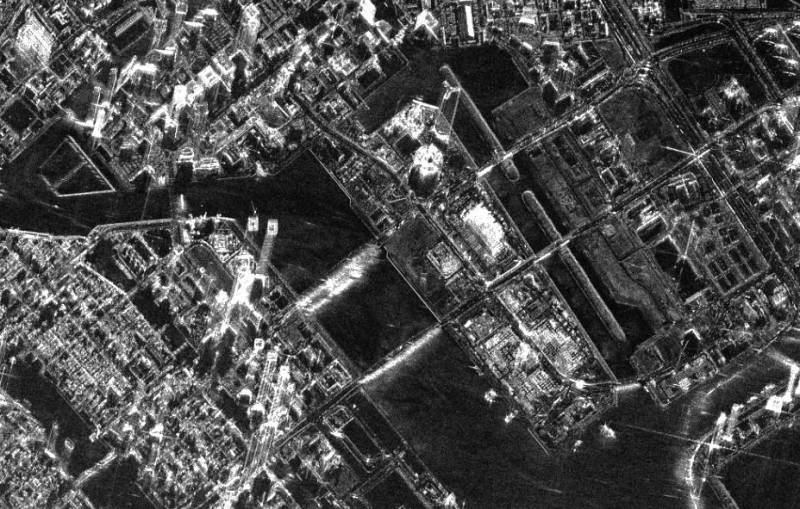

Radar image of the city obtained by the Condor satellite of the first model
In general, a new type of spacecraft is capable of solving a variety of tasks. It is expected that it will be used to compile and/or refine maps of different areas. It is also possible to use a satellite to monitor the situation in different situations. The possibility of tracking the ice situation on the Northern Sea Route, tracking forest fires, etc. is mentioned.
"Kondor-FKA" carries out remote sensing using a radar station. This means that it can perform its work at any time of the day and with virtually no restrictions on weather conditions in the survey area. In this regard, it is much more convenient and efficient than satellites with optics.
The modern radar from the Vega concern is distinguished by high performance and allows you to shoot large areas with high resolution. In addition, a high intensity of work is provided with the possibility of issuing a large number of frames. At the same time, the ground part of the complex is built on the basis of modern computing tools, which makes it faster to process data and transfer it to consumers.
New generations
It is known that the previous satellites of the Condor series and their services enjoyed a certain popularity among civilian customers. The new generation of similar devices is distinguished by improved technical and operational characteristics, and will also not be left without orders. Therefore, it can be expected that immediately after the start of full-fledged operation, the first Condor-FKA will begin active work on shooting different regions of the planet.
At the same time, the development of the civil orbital constellation will not stop. The second Condor of the new model is already being prepared for flight, and it is planned to develop the next project, again aimed at increasing the main parameters. Such satellites will appear by the beginning of the next decade, but for now the main task is the deployment of the current generation of remote sensing satellites - and it is being successfully solved.
Information