Czech tanks in the armed forces of Nazi Germany and its allies

A sufficiently high level of development of metallurgy and heavy engineering, achieved by Czechoslovakia in the early 1930s, made it possible to start designing and manufacturing tankettes and light tanks. Tracked armored vehicles of Czechoslovak production in terms of security, armament and workmanship fully met the requirements of those years.
After the Czech Republic was declared its protectorate, Germany requisitioned 351 units of armored vehicles, mainly vehicles that were in service with two tank regiments stationed in the Czech Republic. The armament of the third regiment, stationed in Slovakia, went to the army of the Slovak state that declared its independence. Tanks captured by the Wehrmacht, after the annexation of Czechoslovakia, were actively used at the initial stage of World War II. Subsequently, the factories of the protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia carried out orders from the German Ministry of Armaments until the last days of the war.
Wedges
In the late 1920s and early 1930s, the concept of mobile protected machine-gun points was adopted in the armed forces of some states, which should have been relatively simple and inexpensive light tracked two-seater vehicles protected by bulletproof armor.
The most famous machine of this class was the British Carden-Loyd Mk VI tankette, full-scale samples of which and a license for production were acquired by a number of countries.
In 1930, three of these machines arrived in Czechoslovakia for testing. In general, specialists liked the British tankette. However, it was not considered possible to accept the tankette into service in its original form. The selection committee was not satisfied with too thin armor and weak weapons. Czechoslovakia officially acquired a license for the Carden-Loyd Mk VI, and after receiving the entire package of documents, the finalization of the tankette was entrusted to Ceskomoravska Kolben-Danek (CKD).
The height of the wedge hull after revision was increased. A roof with inclined armor plates was attached on top. Frontal armor was increased to 12 mm, sides and stern - up to 8 mm. Viewing slots with triplexes appeared in the armor. The body was assembled using riveting on steel corners. In the middle part of the hull, along its longitudinal axis, there was a 4-cylinder Praga carburetor engine with a volume of 1,95 liters, which produced 30 liters. With. On both sides of it there were places for the driver and gunner, for landing and disembarking of which there were hatches in the roof of the hull. One 7,92 mm machine gun vz. 26 (ZB-26) was mounted opposite the shooter's position, the other was mounted on the right side of the frontal hull plate, and the driver-mechanic fired from it. The ammunition load was 2 rounds.
The mass of the vehicle in combat position was 2,3 tons. The maximum speed was 35 km / h. Cruising on the highway - 100 km. The tankette could cross a ditch 1,2 m wide, a wall 0,5 m high and a ford 0,4 m deep. The specific ground pressure was 0,5 kg / cm². The frontal armor withstood shelling with 7,92-mm armor-piercing bullets from a distance of 125 m, the side armor from 185 m. The frontal and side armor protected against lead-core rifle bullets fired from 50 m.

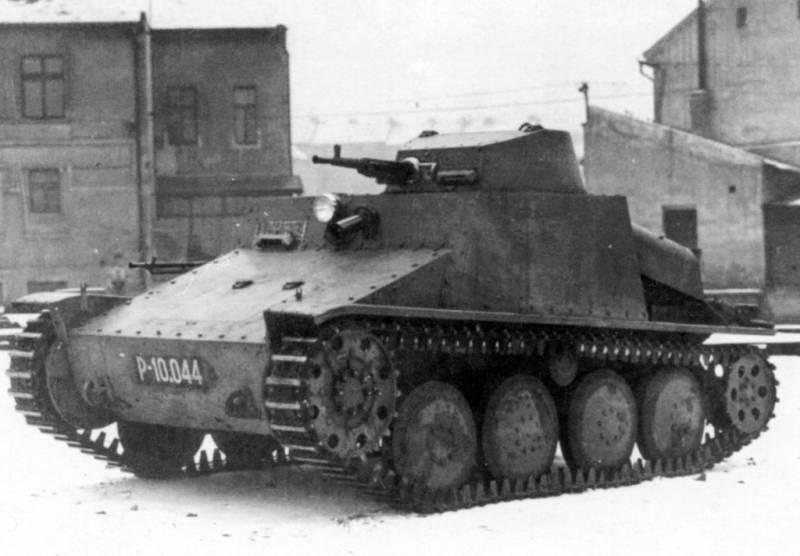
Tankette Tančík vz. 33
In 1933, the tankette was put into service under the designation Tančík vz. 33. After the construction of four prototypes in April 1933, an order was placed for 70 tankettes, completed by October 1934.
In general, the military accepted the tankette favorably. At the same time, they noted a number of serious shortcomings: the machine gun at the disposal of the driver turned out to be practically useless, the shooter could not conduct effective fire at a speed of more than 10 km / h, poor visibility through surveillance devices made the car unsuitable for reconnaissance, the absence of a radio did not allow reliable coordination of actions between vehicles in a platoon or in a larger group.
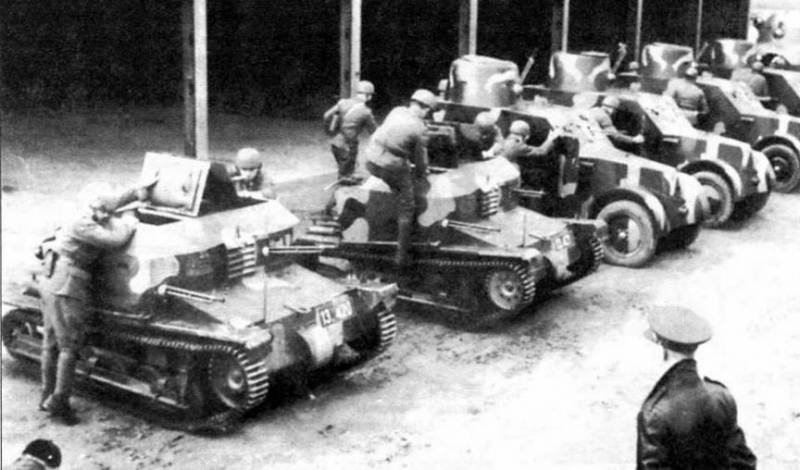

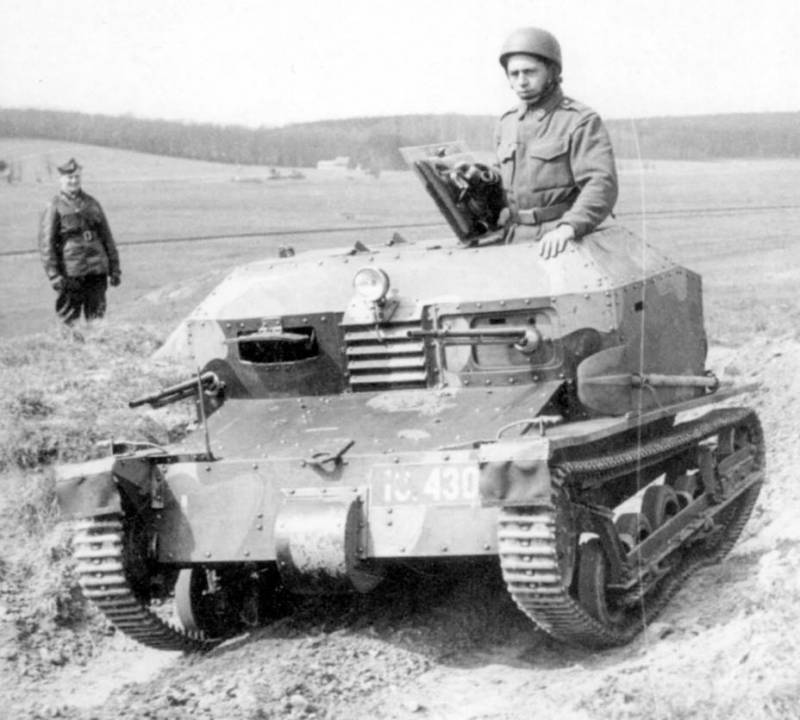
Initially tankettes entered the 1st Tank Regiment. It consisted of two battalions - tank and cavalry. In the tank battalion, two companies were equipped with tankettes, and the third with light tanks of French production FT17. Subsequently, tankettes were in service with three tank regiments of the Czechoslovak army: in the 1st - 24 vehicles, in the 2nd - 16, in the 3rd - 30. After the supply of tanks armed with cannons began in the second half of the 1930s , wedges began to be used for training purposes, and in 1938 they were transferred to infantry units.
The Germans were not impressed with the characteristics of the tankette Tančík vz. 33, and the cars in need of repair were scrapped. Approximately ten tankettes served to train driver mechanics, and three dozen machine-gun "tanks" went to Slovakia, where they, being in the rear units, survived until September 1944.
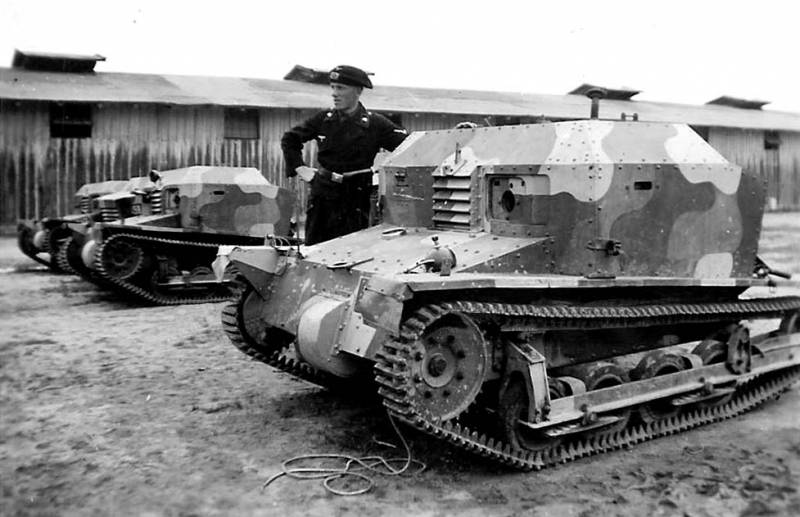

After the suppression of the Slovak uprising, a few surviving tankettes were used by the Wehrmacht to tow 75 mm 7,5 cm Pak 40 anti-tank guns and were lost on the Eastern Front.
Talking about Czechoslovak wedges, one cannot but mention the Tancik Std, developed for export by the Skoda concern. Due to the fact that the vehicle, in addition to the 7,92 mm ZB-30 machine gun, was armed with a 37 mm Škoda ÚV vz. 34 (adapted for installation on armored vehicles anti-tank 3.7 cm kanon PÚV vz. 34), in a number of sources it is called a "mini-ACS". In 1938, Yugoslavia bought 8 tankettes Tancik Std, in the Yugoslav army they received the designation T-32.

Wedge t-xnumx
The tankette had a riveted box-shaped body. The thickness of the frontal armor reached 22 mm, side - 12 mm, feed, roof and bottom - 5-8 mm. In the middle part of the hull there was a cabin, in the frontal sheet of which a 37-mm cannon was installed (angle of fire vertically -10 ° ... + 25 °, horizontally - 20 °) and a machine gun. The engine was located at the rear, the transmission was at the front. On the roof of the cabin there was a commander's cupola with a turret for an anti-aircraft machine gun.
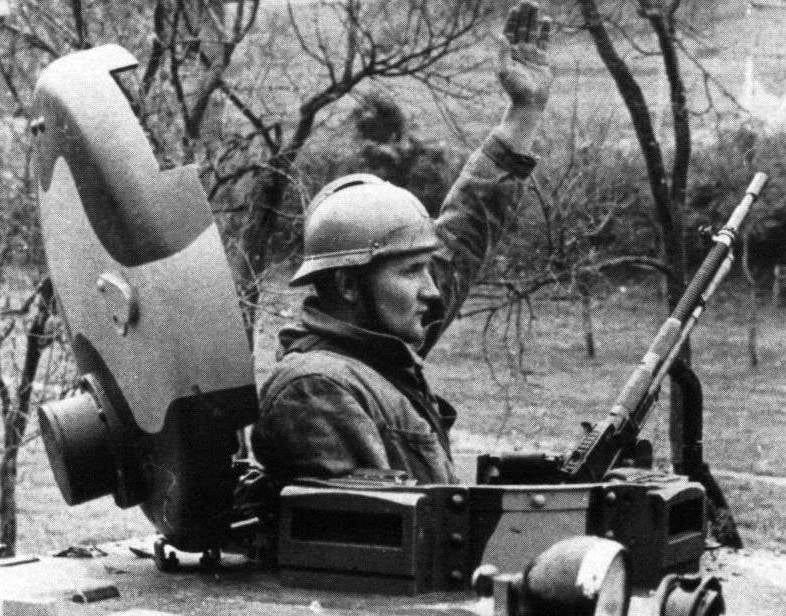

In battle, the commander loaded and aimed the gun, and the driver had to fire from a machine gun. Carburetor 6-cylinder air-cooled engine power 60 HP With. could accelerate a car weighing 4,8 tons to 40 km / h. In terms of its ability to overcome obstacles, the T-32 tankette was slightly superior to the vz. 33.
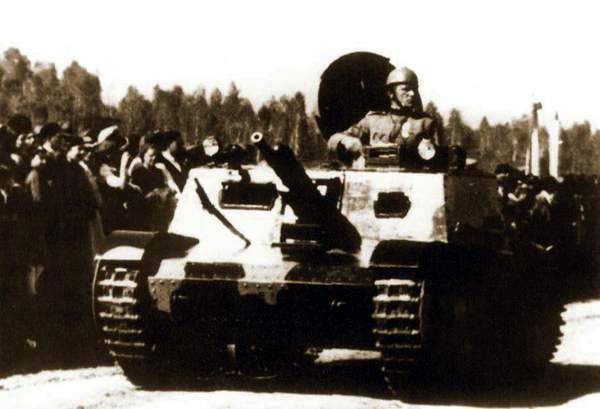

Tankette T-32 at the pre-war parade
In fact, the T-32 tankettes in the Yugoslav army were the only type of armored weapons capable of fighting German tanks. The French-made FT17 and R35 tanks, armed with 37-mm SA18 cannons from the First World War, could not oppose the German armored vehicles. But in the end, the T-32s also failed to provide noticeable resistance to the invaders. There were too few of them, and, besides, the quartermasters did not deliver armor-piercing shells. Most of the Yugoslav tankettes were destroyed, and several captured vehicles served in the Wehrmacht occupation units in the Balkans under the designation Pz.Kpfw.732 (j).
Another export model of Czechoslovak production is the AH-IV tankette, developed by the Prague company CKD. According to reference data, 157 vehicles were built for foreign customers, which were delivered to Iran, Romania, Sweden and Ethiopia.
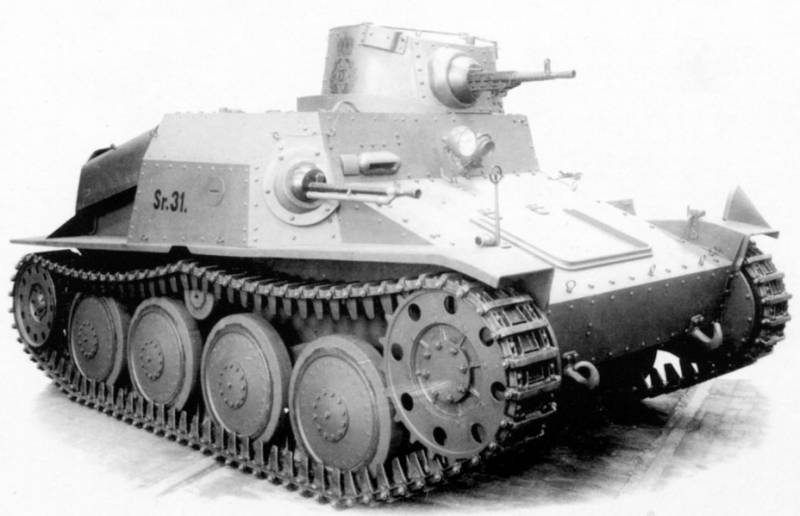

Wedge heel AH-IV
As with previous models, the AH-IV's armored hull was riveted. The frontal armor had a thickness of 10 mm, side and stern - 8 mm, roof and bottom - 6 mm, tower - 12 mm.
Taking into account the experience of operating wedges vz. 33, a turret with a 7,92 mm TK vz. 37 (ZB-53), which had a tape feed. Another machine gun vz. 26 magazine-fed rifle was located to the right of the driver, who fired from it using a thin cable designed for remote control.
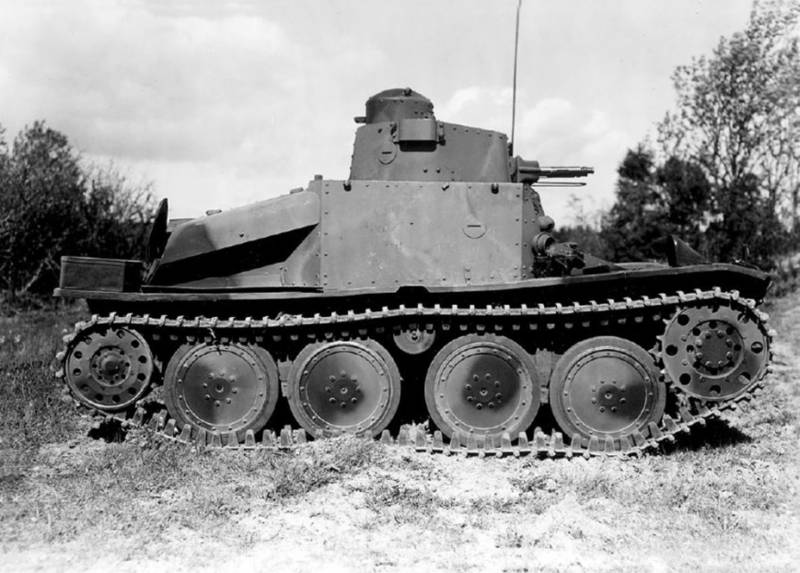

The machine weighing 3,9 tons was driven by a liquid-cooled carburetor engine with a capacity of 55 liters. With. Maximum speed - up to 45 km / h. The tankette could overcome slopes up to 35 °, a ditch up to 1,5 m wide, a wall 0,6 m high, a ford up to 0,5 m.

For us, within the framework of this publication, wedges purchased in 1937–1938 are of interest. Romania in the amount of 35 units and received the designation Carui de Recunoastere (reconnaissance tank) R-1. Tankettes were intended to reinforce the Romanian cavalry brigades. Organizationally, each brigade included a motorized cavalry regiment, in the reconnaissance squadron of which there were four R-1s. Also, light armored tracked vehicles with machine guns in the Romanian army were used to guard headquarters and deliver messages in the front line. They took an active part in the fighting on the Eastern Front: in Bessarabia, near Odessa, in Ukraine, in the Crimea, in the Kuban and near Stalingrad. The last R-1s were destroyed or captured by the Red Army in 1944.
Light tanks
The first Czechoslovak tank armed with a cannon mounted in a rotating turret was the LT vz. 34 (company designation P-II), developed by CKD in 1931-1933. and officially put into service in July 1935.
Although the light tank LT vz. 34 was originally considered as an intermediate option, designed to accumulate the necessary experience and train personnel, for the mid-1930s it was not bad. In 1934–1935 CKD manufactured 50 tanks.
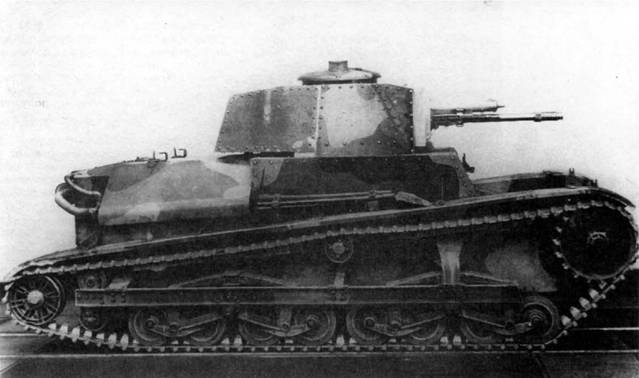
Light tank LT vz. 34
The combat vehicle weighing 7,5 tons was armed with a 37-mm cannon ÚV vz. 34 (Skoda A3), which, by the standards of those years, had good armor penetration and was capable of hitting any serial tank that existed at that time with an armor-piercing projectile.

In addition to the gun, the turret had a 7,92 mm machine gun in a ball mount, and another such machine gun was mounted in the front plate. The ammunition load was 60 shots for the gun and 2 rounds of ammunition. Crew - 000 people.
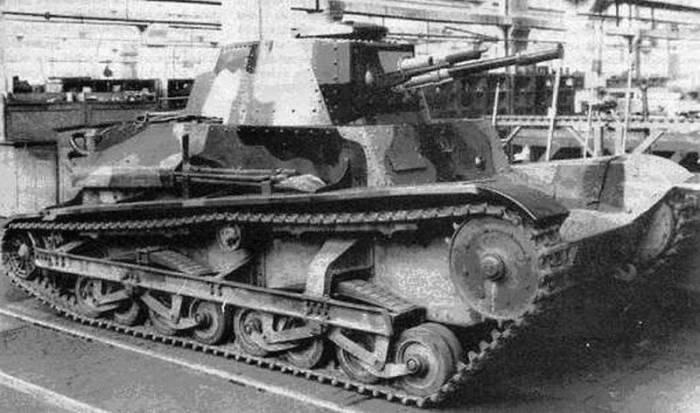

The hull of the tank was assembled from armor plates on a frame made of corners with the help of bolts and rivets. On the roof of the tower there was a commander's cupola with four viewing devices. The thickness of the frontal armor was 12-15 mm, the side - 10 mm, the stern and roof - 8-10 mm, the tower - 15 mm. According to the assurances of the manufacturing company, the side armor provided protection against armor-piercing rifle bullets fired from a distance of more than 75 m.
Carburetor 4-cylinder liquid-cooled engine with a capacity of 62 liters. With. provided speed on the highway up to 30 km / h. Fuel range - up to 160 km. The tank could force a slope up to 27°, a wall 0,8 m high, a trench 2 m wide and a ford up to 0,8 m deep.
By January 1936, most of the LT vz. 34 was distributed among three tank regiments of the Czechoslovak army. At the time of its creation, this combat vehicle was considered one of the best in the world, but after the start of operation in combat units, the military considered that the LT vz. 34 does not meet modern criteria: mobility was low, relatively thin armor provided protection only from light infantry weapons, and all this was aggravated by frequent breakdowns. An attempt to transfer tanks LT vz. 34 to the reconnaissance units of the infantry divisions did not cause understanding among their commanders.
By March 1939, more than two dozen LT vz. 34 was part of the 3rd Panzer Regiment stationed in the vicinity of the town of Turchanski Sveti Martin in northern Slovakia. The Wehrmacht command rejected the vehicles captured by the Germans and sent them for scrapping. The leadership of the Waffen-SS protested against this, wanting to use them to transfer Croatia and reinforce infantry units.
About a dozen LT vz. 34 participated in the Slovak Uprising of 1944. Almost all of them were humiliated in battles with the Nazis. At the final stage of the war, the Germans used several captured tanks as fixed firing points. There is also information that tank turrets removed from decommissioned vehicles were used in long-term defensive structures.
At the time of the annexation of the Czech Republic, the most valuable acquisition of the Wehrmacht was 244 light tanks LT vz. 35, developed by Skoda. The production of these armored tracked vehicles was carried out by Skoda and CKD from 1936 to 1938. A total of 298 tanks were built.
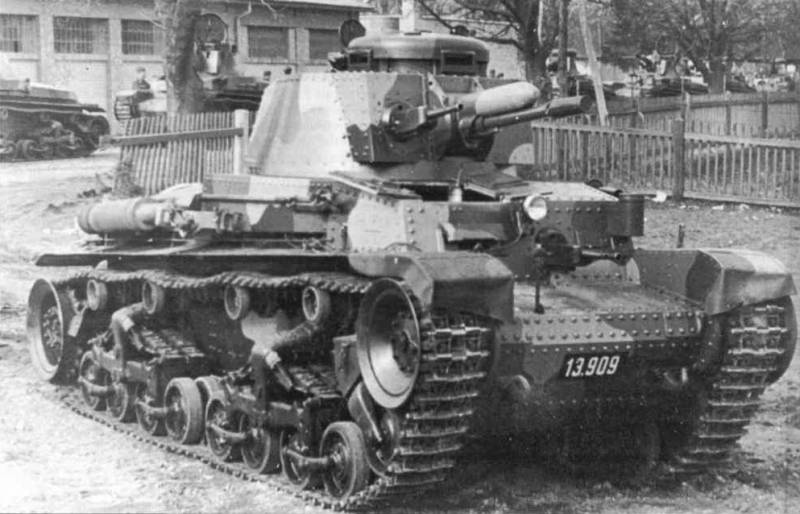

Light tank LT vz. 35
Compared to LT vz. 34 model LT vz. 35 was more in line with the requirements of the military, who wanted a light tank capable of reconnaissance, providing close support to infantry and cavalry, and also acting independently.
When designing LT vz. 35, the developments obtained during the creation of the previous sample were used. Just like on LT vz. 34 armor plates were attached to steel corners with riveting. The thickness of the frontal armor of the hull and turret was 25 mm, side armor - 16 mm, bottom and roof - 8 mm.
The armament remained the same - a 37-mm cannon and two rifle-caliber machine guns. One machine gun was mounted in the frontal part of the hull, the other in the turret. The turret machine gun could be guided both together with the gun and independently of it. Horizontal guidance was carried out using the shoulder rest of the gun or using a rotary mechanism. Ammunition: 78 shots and 2 rounds. On the roof of the tower there was a commander's cupola with a hinged hatch.
The curb weight of the tank reached 11 tons. The Skoda T-11 carburetor engine with a capacity of 120 liters. With. could accelerate on the highway to 34 km / h. Fuel tanks with a capacity of 135 liters provided a cruising range of 190 km.
In general, compared to LT vz. 34 tank LT vz. 35, with the same firepower, had greater security, its frontal armor could withstand hits from large-caliber 12,7-mm bullets. It was also possible to increase the reliability of the main units and the resource of the chassis.
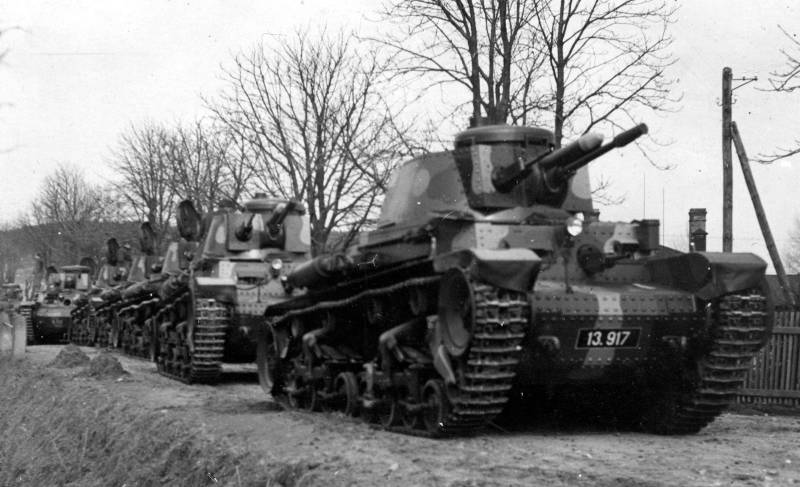

After the Germans occupied the Czech Republic and Moravia in March 1939, the LT vz. 35 received the designation Panzerkampfwagen (3,7 cm) "LT.Sk.35", and from January 16, 1940 - Panzerkampfwagen 35 (t), abbreviated as Pz.Kpfw.35 (t).
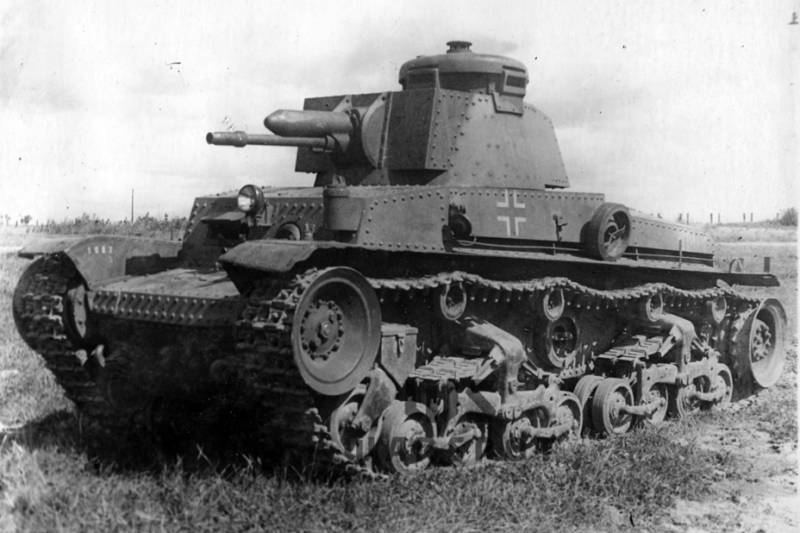

To bring the LT vz. tanks up to Panzerwaffe standards. 35 have been modified. German Fu 2 or Fu 5 radio stations were installed on them, working in telephone mode, and the primitive internal light signaling was replaced by a tank intercom. By reducing the ammunition load, a fourth crew member, the loader, was introduced. Changes were made to electrical and lighting equipment.
In the aft part of the tank, on the fenders and the roof of the MTO, mounts for fuel canisters appeared. Some of the vehicles were converted into command vehicles, giving them the designation Pz.Bef Wg, 35 (t). All command tanks were equipped with a gyrocompass. A second Fu 7 radio station with a whip antenna was added to the tanks of the company commanders, to accommodate which they abandoned the course machine gun. The tanks of the battalion commanders and the vehicles of the regimental headquarters received an additional Fu 8 radio station with a loop antenna mounted in the rear of the hull. On these tanks, from the turret armament, only a machine gun was left. The cannon was dismantled and replaced with a wooden mock-up to maintain its unaltered appearance.
Modified captured tanks were equipped with units of the 1st light division: the 11th tank regiment, the 65th separate tank battalion and the 82nd communications battalion. After the capture of Poland, the 1st Light Division was reorganized into the 6th Panzer Division. In addition to it, the reconnaissance battalion of the SS division Totenkopf received six tanks. As of June 22, 1941, the 6th Panzer Division had 160 Pz.Kpfw.35(t). Regarding the reconnaissance battalion of the SS division Totenkopf, sources differ, there could have been four or five Pz.Kpfw.35 (t).
By the summer of 1942, most of the Pz.Kpfw.35(t) tanks were lost or needed to be repaired. Due to their low combat value, in July 1942 they were decommissioned and sent to the Skoda factory for conversion into Mörserzugmittel 35 (t) artillery tractors. According to reference data, 49 linear tanks were converted into tractors.
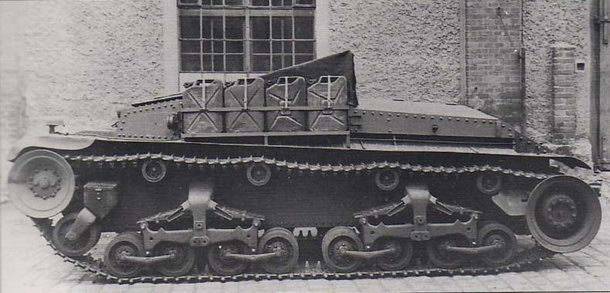
Artillery tractor Mörserzugmittel 35 (t)
The turret and all weapons were dismantled, a hook was welded to the stern, which made it possible to tow trailers and guns weighing up to 12 tons. The turret shoulder strap was covered with a canvas awning. The turrets removed from the Pz.Kpfw.35(t) tanks were placed on the fortifications of the Atlantic Wall and were used to arm armored trains.
In addition to the Germans, the LT vz. 35 were in the armies of Slovakia, Romania, Bulgaria and Hungary.
Slovakia received 52 LT vz. 35 and 27 of them as part of the "Mobile Brigade" were involved in the attack on the USSR. The Slovaks mainly provided protection in the front line, and their combat losses in armored vehicles were small. Severe frosts of the winter of 1941–1942 negatively affected the technical reliability of LT vz. 35, and all surviving Slovak LT vz. 35 went home. According to Czechoslovak sources, at least eight tanks took part in the Slovak Uprising in 1944.
Romania ordered 126 LT vz. 35 in August 1936, adopting them under the designation R-2. At the same time, some of the cars were assembled under license in Romania. Unlike LT vz. 35, produced in the Czech Republic, the Romanian-made tanks had a simplified manufacturing technology (the bent rear sheet of the turret, for example, was replaced by two straight ones).

Tank R-2 near Stalingrad. November 1942
In 1942, Romania purchased another 26 Pz.Kpfw.35(t) tanks from Germany. R-2 tanks were in service with the 1st Armored Regiment of the 1st Armored Division "Great Romania" and participated in the fighting on the southern flank of the Soviet-German front. They suffered significant losses in the battle for Odessa, and most of them were destroyed at Stalingrad. As of July 1944, Romania had 44 R-2 and Pz.Kpfw.35(t) tanks. After the country joined the anti-Hitler coalition, they took part in battles with German troops.
Bulgaria bought 1940 LT vz. 26. In 35, a batch of 1941 T-10 tanks arrived, originally ordered by Afghanistan and stored after the occupation in a finished product warehouse. Afghan tanks differed from other vehicles of this family in that they were fitted with 11 mm Skoda A-37 guns designed for the LT vz. 7 and differing from the Skoda A-38 in increased muzzle velocity. In 3, after Bulgaria entered the war against Germany, T-1944 tanks took part in battles with the Germans in Yugoslavia. Czech tanks remained in service with the Bulgarian army until the early 11s.
The Hungarian army captured two LT vz. 35 in 1939 during clashes on the border with the Czech Republic. After the tanks were tested, the Hungarians tried to legally purchase Czech-made tanks, but they were refused. Captured LT vz. 35 in 1941 were repaired at the Skoda plant, after which they were used for training purposes until 1943.
The best Czechoslovak tank developed in the interwar period and mass-produced during the German occupation is the LT vz. 38. As was often the case with models of equipment and weapons adopted by the Czechoslovak army, its appearance was preceded by the creation of a series of export tanks.
In 1935, CKD developed the Praga TNH light tank for sale to foreign customers, in which early developments were implemented. This vehicle weighing 8,2 tons was armed with a 37 mm cannon and two 7,92 mm machine guns.
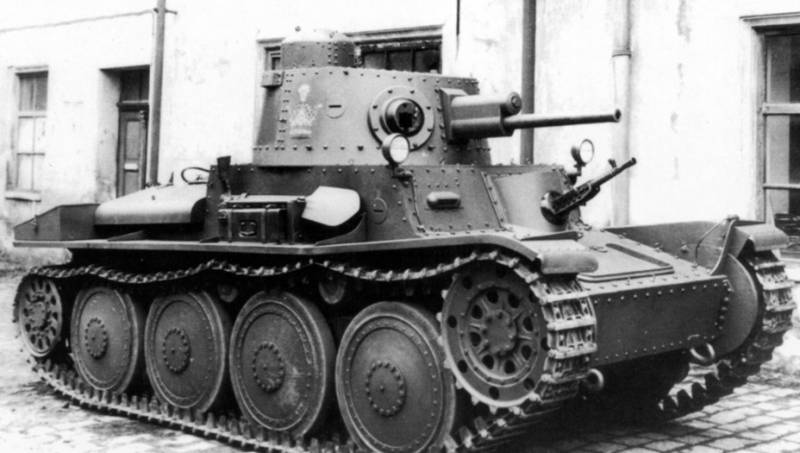

TNH light tank prototype
The buyer of TNH tanks was Iran, which ordered fifty units in 1935, under the same deal it was planned to supply fifty AH-IV tankettes. Due to problems with the fragility of the armor plates, the contract was slowed down, and export tanks went to Iran in 1937.
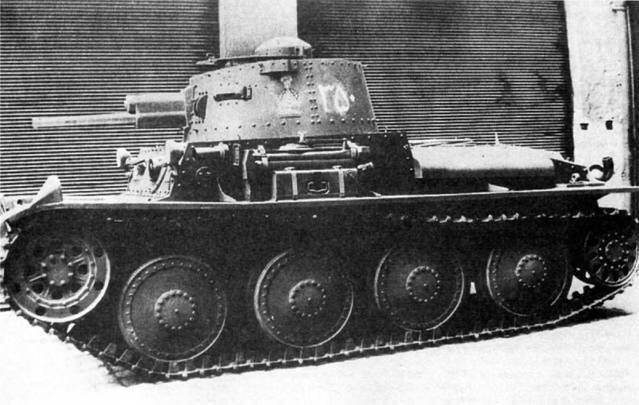

The delay allowed for some improvements. Iranian tanks were equipped with Praga TN 100 carbureted engines with a capacity of 106 hp. with., providing speeds up to 37 km / h. The machines received radio stations, the machine-gun installation in the hull changed, as well as viewing devices. The undercarriage has undergone refinement. Ammunition consisted of 60 artillery rounds and 3 rounds of ammunition. Armor thickness - 000-8 mm.
The modification developed for Peru was designated LTP. This model differed from TNH in a different arrangement of the transmission, drive wheels and the Swedish 6-cylinder Scania-Vabis 1664 engine. With. provided LTP with an impressive power density of 125 liters. With. per ton. The maximum speed on the highway reached 17,1 km / h.
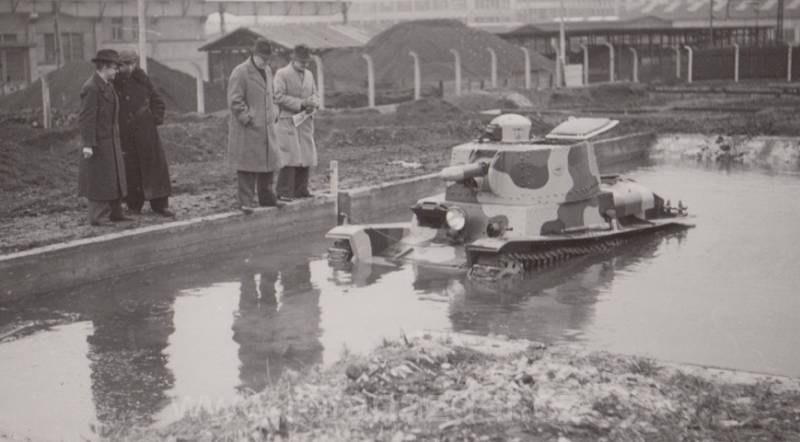

Tests of the LTP tank prototype
With a mass less than that of LT vz. 34, the LTP tank was armed with the same cannon and coaxial machine gun, and was equal in armor thickness to the LT vz. 35. In 1937-1938. the Peruvian army received 24 tanks, which were operated until the second half of the 1980s.
The variant built for Switzerland is known as the LTH or Panzerwagen 39. An order for 24 vehicles was placed in December 1937. The differences from the LTP were more powerful armor (reaching 32 mm), engine and armament.

Light tank LTH
Swiss-made Saurer-Arbon ST1 diesel engine with a capacity of 125 hp. With. could disperse a tank weighing 7,7 tons to 45 km / h. To combat enemy armored vehicles, a 24-mm semi-automatic gun 24 mm Pzw-Kan 38 was intended with a rate of fire of up to 40 rds / min. An armor-piercing projectile with a mass of 225 g and an initial velocity of 900 m/s at a distance of 200 m could normally penetrate 40 mm armor. In addition to the cannon, the tank was armed with two 8 mm Maxim M.38 machine guns. Operation of the Panzerwagen 39 continued until the early 1960s.
The tank, created by order of Lithuania, had the designation LLT. In fact, it was an LTH armed with a 20 mm Oerlikon automatic cannon and two Maxim machine guns. An order in the amount of 21 units was ready in July 1940, but after Lithuania joined the USSR, it was canceled. In August 1940, the unclaimed tanks were bought by the Slovak army and given the name LT vz. 40. After that, they received weapons similar to the LT vz. 38 - 37 mm cannon and two machine guns.
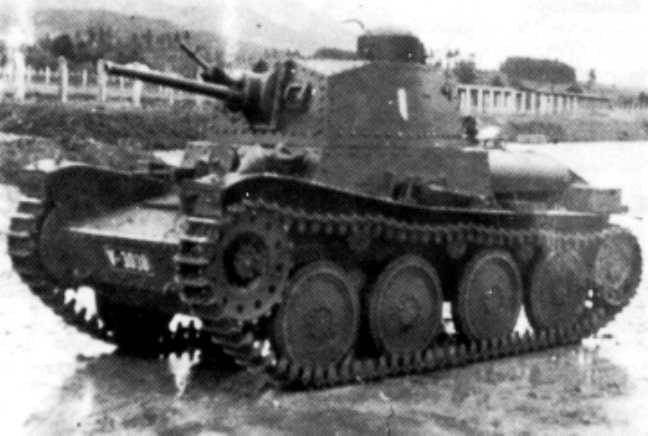

Light tank LT vz. 40
Tank LT vz. 40 had much in common with the LT vz. 38, the differences were in the shape of the turret and commander's cupola, as well as in individual details of the hull and chassis.
Tanks LT vz. 40 as part of the "Mobile Brigade" of the Slovak army participated in the attack on the USSR. Seven tanks were lost in the summer of 1941. The Slovak security division, stationed in Ukraine in August 1942, received a company of seven combat vehicles of this type. At the end of 1942, six tanks took part in the battles in the Caucasus. By April 1943, almost all of them were lost. As part of a separate mechanized regiment, several tanks of this type fought against the Germans during the Slovak National Uprising in the autumn of 1944.
Based on the exported TNH, LTP and LTH tanks, CKD created the light tank LT vz. 38, formally adopted in 1938. But this machine did not have time to enter the units of the Czechoslovak army - on March 15, 1939, the Czech Republic and Moravia were occupied by German troops, and mass production began after the occupation.
In the armed forces of Nazi Germany LT vz. 38 received the designation Pz.Kpfw 38(t). In 1939–1942 the factories of the CKD company, which under the Germans was renamed VMM (Bchmisch Mahrische Maschinenfabrik), produced 1 tanks.
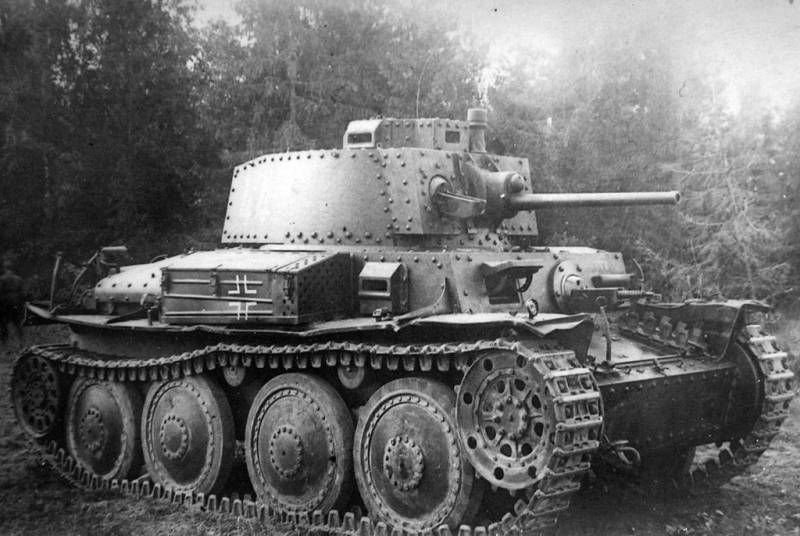

Light tank Pz.Kpfw 38(t)
The vehicles of the first serial modifications: Ausf.A, Ausf.B and Ausf.C were protected by 25 mm frontal, 15 mm side and stern armor, the bottom and roof were 8 mm thick. The tank was armed with a 37 mm Pz.Kpfw 38(t) cannon (tank modification of the Škoda 37 mm A7) with a barrel length of 49 calibers and two machine guns MG 37 (t) (ZB-53). On the variants put into series after the occupation, changes were introduced that were previously applied on the light tank Pz.Kpfw 35 (t) modified according to German standards. Also, due to the reduction of the gun ammunition from 72 to 54 shots, a loader was introduced into the crew.
In combat position, the Pz.Kpfw 38 (t) Ausf.С weighed 9,5 tons. The Praga EPA engine with an HP 125 power. With. provided speeds up to 45 km / h. Cruising on the highway was 200 km. The tank could overcome slopes with a steepness of 28 °, a wall 0,8 m high, a trench 2,1 m wide and a ford up to 0,8 m deep. Line tanks were equipped with a Fu 5 VHF radio.
To increase security, some tanks of the Pz.Kpfw 38(t) Ausf.D modification in the frontal projection of the hull were equipped with a package of two 25-mm armor plates. On the Pz.Kpfw 38(t) Ausf.E, in addition to the 50 mm frontal armor, the thickness of the sides increased to 30 mm. The combat weight of such a tank was 10,14 tons. The Pz.Kpfw 38 (t) Ausf. G modification had homogeneous frontal armor 50 mm thick and side armor 30 mm thick.

Pz.Kpfw 38(t) Ausf.G.
The Pz.Kpfw 38(t) Ausf.S variant, intended for Sweden, was structurally similar to the Ausf.S, but had 50 mm frontal armor. Tanks ordered by Sweden in the amount of 90 units were requisitioned and used by the Panzerwaffe. As compensation, Sweden received a package of documentation for licensed production. Armored vehicles produced in Sweden were designated Stridsvagn m/41.
Several dozen Pz.Kpfw 38(t) early modifications were converted into command tanks. At the same time, instead of a gun, a wooden mock-up was mounted. The command tanks of the company level were equipped with radio stations Fu 5 and Fu 6, battalion and regimental - Fu 5 and Fu 8.
Part of the line tanks during the refurbishment was converted into reconnaissance tanks Aufklarungspanzer 38 (t). A total of 70 units were delivered.
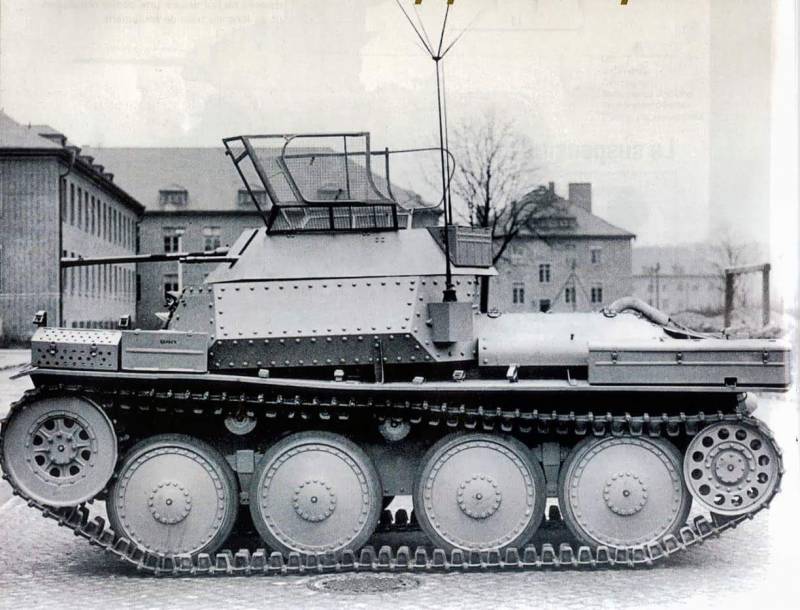
Reconnaissance tank Aufklarungspanzer 38(t)
Praga AE engine with 160 hp. With. improved the mobility of the reconnaissance tank. Instead of a turret with a 37 mm cannon, the caterpillar armored scout received a turret from an SdKfz.222 armored car with a 20 mm 2 cm KwK 38 automatic cannon and a 7,92 mm MG.42 machine gun. The car was equipped with additional radio stations.
By the beginning of World War II, the 38th tank battalion of the 67rd light division of the Wehrmacht was equipped with Pz.Kpfw 3 (t) tanks. On the eve of the French campaign, Pz.Kpfw 38 (t) were part of two German tank divisions in the amount of 230 line and command tanks. As of June 22, 1941, 17 German tank divisions were deployed against the USSR, and five of them were equipped with Pz.Kpfw 38 (t) tanks - a total of 660 units, including command divisions. During the hostilities, tanks produced by the VMM enterprise were continuously supplied to the Eastern Front, which partly made it possible to compensate for losses. In total, in 1941, the Wehrmacht lost 796 Pz.Kpfw 38 (t) tanks.
In the first half of 1942, most of the Czech-made tanks were reduced to the 22nd Panzer Division, which fought in the Crimea, and then in the Volga steppes. By the beginning of 1943, most of the Pz.Kpfw 38 (t) available on the Eastern Front had been destroyed or needed factory repairs. In 1943–1944 the remaining Czech tanks were used mainly for police and training purposes.
By the middle of 1941, Slovakia had 37 Pz.Kpfw 38 (t) tanks, and they took part in Operation Barbarossa as part of the Mobile Brigade. The Slovak security division, which fought against the partisans, had five of these tanks in the spring of 1943. In the autumn of 1943, the Germans handed over 37 used tanks of various modifications that arrived after repairs. Almost all of them were destroyed during the Slovak National Uprising.
To make up for the losses suffered at Stalingrad, Romania in 1943 received 50 Pz.Kpfw 38 (t) Ausf. A, B and C. In the Romanian army they were called T-38 and were transferred to the 2nd tank regiment in the Crimea. By 1944, almost all Romanian T-38 tanks were in a state of scrap metal.
The Bulgarian army received 10 Pz.Kpfw 38(t) tanks at the end of 1943, and they took part in counterguerrilla operations in Macedonia. In the late autumn of 1944, several Bulgarian Pz.Kpfw 38(t) took part in the battles with the Wehrmacht.
Hungary had a fairly large fleet of Pz.Kpfw 38(t) tanks: 105 line tanks and six command tanks. A significant part of the Czech-made tanks was lost during the Soviet Voronezh-Kharkov offensive operation. By May 1943, the remnants of the 2nd Hungarian Army were withdrawn to Hungary. In 1944, Pz.Kpfw 38(t) were used in combat operations against detachments of the Ukrainian Insurgent Army and the Red Army.
At the end of 1942, it became clear to the German command that the Pz.Kpfw 38 (t), due to its low security and unsatisfactory firepower, in its original form had no further prospects for use at the front. In this regard, some of the tanks were converted into ammunition transporters, technical support vehicles, tractors and self-propelled artillery mounts. According to Czechoslovak sources, more than 350 tank turrets removed from the Pz.Kpfw 38(t) were used in long-term defensive structures. Almost half of the towers (150) were placed in the fortifications of Southwestern Europe, 78 were sent to the Eastern Front, 75 to Norway, 25 to Italy, 20 to Denmark and 9 to the Atlantic coast. The weak 37-mm cannon and thin armor of the Pz.Kpfw 38(t) turrets did not give many chances to win in artillery duels with tanks, but the ZB-53 rapid-fire machine guns mounted in the turrets made it possible to effectively repel infantry attacks.
Unfortunately, the format of the site does not allow in one publication to talk about self-propelled artillery mounts created on the basis of Czechoslovak tanks LT vz. 35 and LT vz. 38. This will be discussed in the next part of the series devoted to equipment and weapons of Czechoslovak production, which was available in the armed forces of Nazi Germany and its allies.
Продолжение следует ...
Information