Hide from Thermal Imager: New Materials for Soldier Equipment
Progress in the field of surveillance equipment does not stand still and imposes new requirements for camouflage. Particularly difficult in this context is the protection of personnel from optical systems operating in the infrared range. Currently, there is an active search for technologies and materials abroad for solving such problems, and in addition, full-fledged products have already been created that are ready for practical use.
Physics of the phenomenon
The human body is constantly generating heat. At rest, the body of an average adult produces approx. 100 W, and under load this figure can increase significantly. Body heat is transferred to clothing and surrounding objects. As a result, they all stand out in the infrared range and can be detected with a thermal imager.
Depending on various factors, the entire silhouette, open areas of the body, or even exhaled warm air can "glow" in the infrared range. In addition, heated objects of the environment can reveal the fighter, weapon and items of equipment, etc.

The main way to protect a person from a thermal imager is to shield the generated heat. You need some kind of uniform or various accessories that can trap IR radiation and prevent it from getting into the lens of surveillance equipment. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure light weight, flexibility and ease of handling with such a screen.
Alternative technologies are also being considered. So, one of the modern projects provides for the reduction of heat generation. As a result, the masked object ceases to stand out against the background of the terrain and there is no need for screening or heat removal.
New technologies for protection against thermal imaging surveillance are at various stages. Some of them are already used in the production of commercial products, while others have not yet gone beyond the laboratory. At the same time, it can be expected that the latter will also reach practical application in the future, and scientific organizations will be engaged in the next projects of this kind.
TVC series
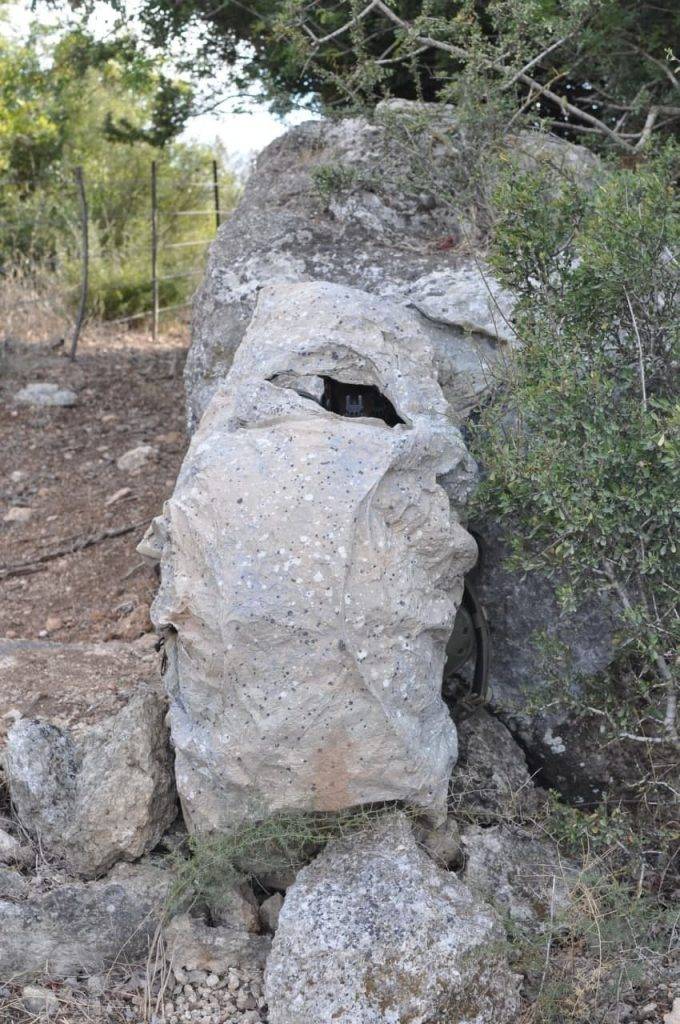
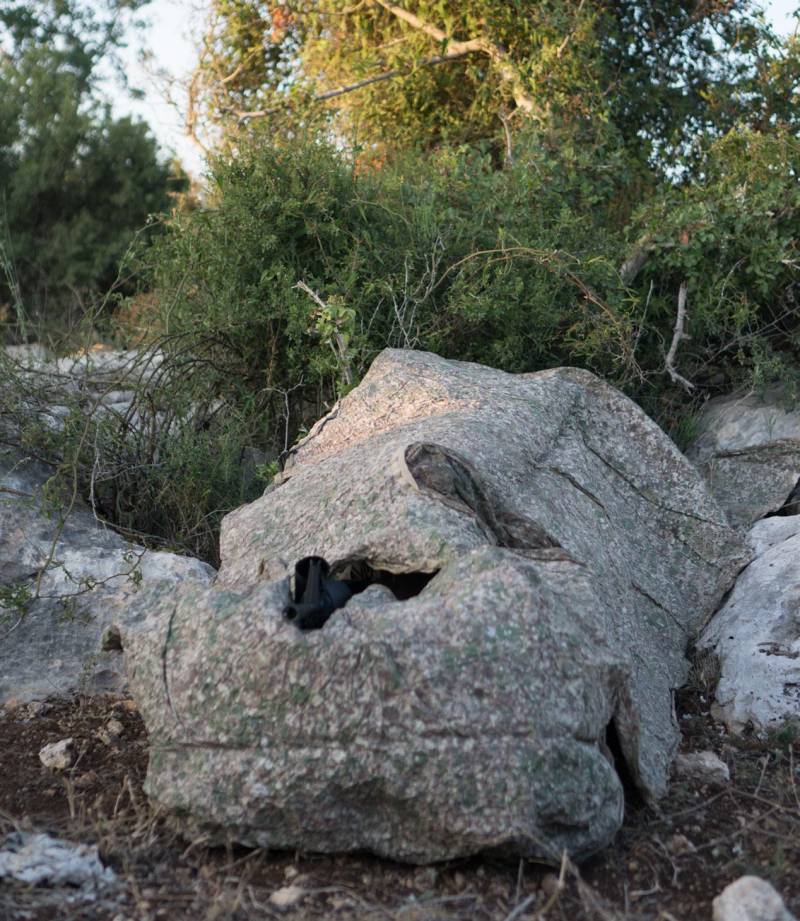
The greatest commercial success in the fight against thermal imagers has been achieved by the Israeli company Polaris Solutions. Several years ago, she introduced her TVC (Thermal Visual Concealment) technology, on the basis of which a lot of different concealment means of various kinds were then developed.
TVC is a visible and infrared camouflage material. The exact composition and architecture of such a material was not disclosed, but it is reported that it uses polymers, microfibers and metal particles. According to various sources, TVC is a multilayer structure, each layer of which is designed to solve its own problem. So, the outer one carries optical camouflage, while the inner ones are responsible for keeping warm. As you can tell, TVC is an exclusively passive system and only works by shielding radiation.
There are three material options: TVC50, TVC100 and TVC150. They differ from each other in density, which affects the weight of the finished product. So, the least dense material TVC50 weighs 490 g per square meter, and for TVC1 this parameter reaches 150 g. Probably, materials of different densities also differ in performance.
TVC material is available in the form of sheets of the required sizes. Also in the Polaris Solutions catalog there are a lot of products made of such material. Awnings, items of uniforms, etc. are offered. Sheet TVC can be equipped with special frames, with the help of which artificial landscape elements are created - stones, bumps, etc. Depending on their needs, the customer can choose the color.
Some of the samples from Polaris Solutions have already been put into practice. The first customer for these products was the Israel Defense Forces. Its units are already using various means of combined camouflage. So, about a year ago, it was announced about the imminent start of purchases of the Kit 300 product. It is a TVC sheet with dimensions of approx. 2x2 m weighing only 500 g, having all the necessary camouflage functions. It is proposed to be used as a wearable cape, awning, etc.

Double action
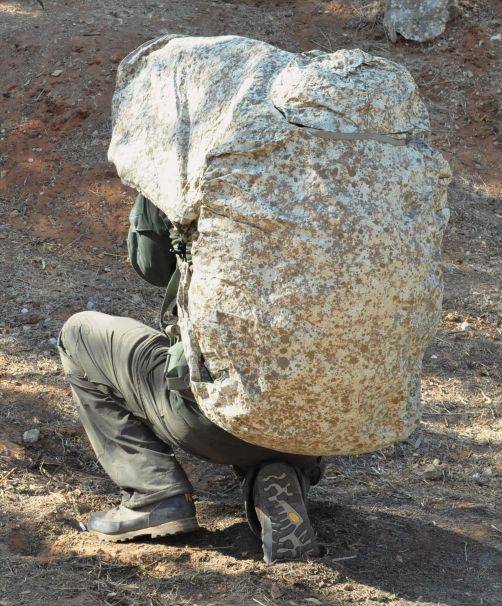
An alternative disguise was presented early last year by the University of California at San Diego and the National University of Singapore. Their original technology offers to shield the protected object and at the same time actively simulate the surrounding background, providing additional masking.
The project of the two universities also provides for the creation of multilayer sheet material, from which elements of uniforms, covers, etc. can be made. In the composition of such a material, various metals and polymers are used. One of the main tasks of the project was the search for optimal materials and their combinations that give the best characteristics.
The outer layer of the experimental material is a heating element in a polymer sheath. The operation of the element is controlled by a microcircuit with an external temperature sensor; power is supplied from a wearable battery. The inner layer is made of a special polymer sandwiched between two flexible plates. This polymer is similar in structure to wax and is able to change its state depending on external temperatures. It performs the function of thermal insulation.
An experimental sample of the new material showed its performance in a wide range of positive temperatures, and also demonstrated high performance. It took about a minute for the outer layer to heat up from +10°C to +38°C. At temperatures below +30°C, the polymer in the inner layer hardened and provided reliable heat shielding from the inside. When heated above +30°C from the external environment or the outer layer, this polymer absorbs energy, melts and does not allow the user to overheat.

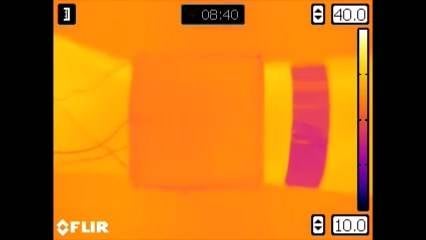
The first results of the US-Singapore project were revealed almost two years ago, and since then no new data has been received. Perhaps the two universities are continuing their research and improving the unusual material. In addition, they could move on to the stage of creating a full-fledged camouflage clothing with acceptable indicators of weight, convenience and duration of work.
Future technologies
Thus, in parallel with the development of observation means, camouflage is also being improved. Thermal imagers capable of dealing with camouflage in the visible range are receiving a worthy response in the form of new materials. At the same time, new camouflage tools of different classes are being developed with various advantages. Screens of a passive type are already being produced, and an active system with adaptation to external conditions has been brought to testing.
It is clear that such technologies will continue to evolve. There will be new materials and principles of work with higher rates. In addition, other countries will be interested in this area, which will lead to the emergence of a mass of new developments of various kinds. Then the finished samples will be supplied to the armies. How they can influence the battlefield is unclear. But it is obvious that the emergence and widespread dissemination of fundamentally new means of camouflage remains only a matter of time.


Information