US military innovation. Infrastructure and projects
This article continues the discussion of issues started in the previous one - “Military innovation. US Defense Technologies ".
Introduction
Globally, civilian R&D in terms of the amount and size of funding is about 10 times greater than the military.
Most civil R&D in Western countries is financed from private sources. The largest private R&D sponsors, powerful companies, have higher https://topwar.ru/admin.php?mod=editnews&action=editnews&id=186824 R&D budgets than governments can raise for military purposes.
Not least because of the growing importance of civilian R&D, military R&D has undergone significant structural changes in most countries.
Several defense policymakers have acknowledged the growing dependence of the US Department of Defense on civilian technology.
History
What's the point of contacting stories for reasoning about military innovation?
Americans remind their compatriots of this with a quote cut at the entrance to the National Archives.

One of the leading representatives of science in the middle of the last century was Vannevar Bush, a respected engineer and scientific leader who headed the government's Office of Research and Development during the war (his deeds and scientific achievements were mentioned in the previous article).
In addition to the well-known achievements of Bush, there were also lesser known ones, which we discussed in the UFO disclosure series.
On his initiative, after the crash of alien vehicles in Roswell in 1947, the MJ-12 committee was created... Bush was its first leader, who coordinated all research related to extraterrestrial technology and secret reverse engineering programs, during which, among other things, the shape memory material, nitinol (Reverse engineering programs).

For knowledgeable people, this is no secret for a long time, but it seems that this information penetrates into the public sphere, not only through the Internet and Western media.
At VO, we began the discussion even before the publication of the UFO / UAP report announced by Trump and published by Biden (American Unidentified Events Report). Then RT, and last week the Russian TV channel Zvezda, the mouthpiece of the Russian Defense Ministry, joined in the disclosure and discussion of these American secrets.
Bush got President Roosevelt to ask him for a report on how the nation should support science in the postwar period. Bush's 1945 response "Science - Endless Frontiers" became known as a recipe for government support for science.
I will quote a few of his thoughts along the way.
Vannevar Bush. "Science - endless frontiers."
Five years later, the US administration found a common political basis for the creation of the National Science Foundation.
Despite the arguments for the founding of the National Science Foundation, the five-year debate has never once questioned support for science; rather, they have always revolved around the question of how it should be maintained.
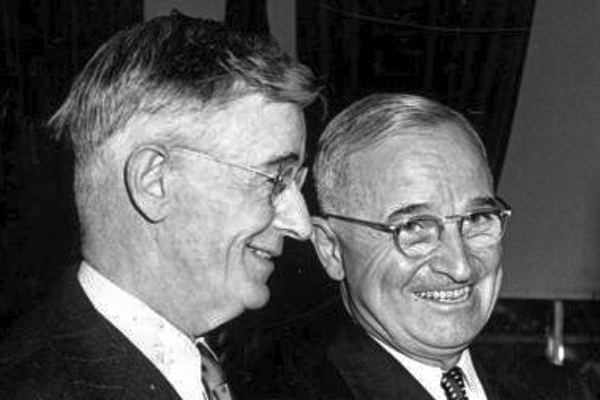

President Truman signed the National Science Foundation bill on May 10, 1950.
The law provided for the creation of a National Science Council of twenty-four part-time members and a director as chief executive officer. All of them were appointed by the president.
By 1950, when the National Science Foundation came into being, there was already a vast, albeit fragmented, state-sponsored scientific research system.
By now, it has acquired the shape developed by Bush (discussed in this and the previous article), in which the National Science Foundation still plays an important role.
Goals. - A National Research Foundation must develop and promote national research and science education policies, must support basic research in nonprofit organizations, must develop scientific talent in American youth through scholarships, and must contract and otherwise support long-term research on military issues. ...
Vannevar Bush. "Science - endless frontiers."
Federally Funded Research and Development Centers (FFRDC)
The federal government supports research and development (R&D) carried out by a wide variety of actors, including federally owned and operated laboratories, universities, private companies, and other research institutions.
For example, many elements of the iPhone were the result of federally funded research, without which Apple and others would not have been able to create the world we have in communications today.
Vannevar Bush. "Science - endless frontiers"
A special class of research institutions called federally funded research and development centers (or FFRDCs) are owned by the federal government but operated by contractors including universities, other non-profit organizations, and industry firms.
FFRDCs are designed to provide federal agencies with R&D opportunities that cannot be effectively pursued by the federal government or the private sector alone.
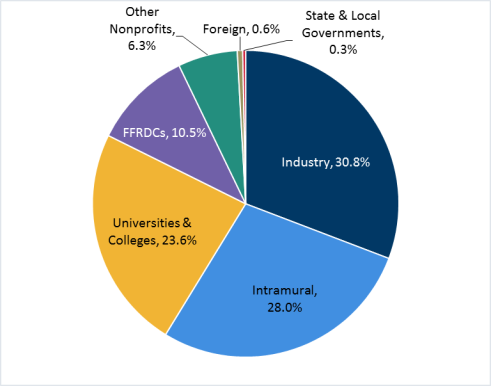
According to NSF, the federal government has pledged $ 141,5 billion in R&D funding in fiscal 2019.
Of all this funding only about 14 percent is directly related to Department of Defense projects. It is difficult to assess the indirect impact on the development of defense and military technologies.
Currently, 13 federal agencies sponsor or co-fund a total of 42 FFRDCs.
The National Science Foundation holds a special place among them.

NSF
The US National Science Foundation has a long history of advancing science and technology through research and innovation. The president's discretionary request for fiscal 2022 includes $ 10,17 billion for NSF.
With a fiscal 2021 budget of $ 8,5 billion, NSF funds reach all 50 states in grants to nearly 2 colleges, universities and institutes. NSF receives over 000 bids each year and awards about 40 new grants. These tranches include support for collaborative research with industry, Arctic and Antarctic research and operations, and US participation in international scientific research.
Since 1982, the administration has advocated significant spending on the Foundation's programs, especially in the physical and life sciences.
The foundation expanded its relationships with industry, government and local sectors, areas not entirely familiar to the agency, which is accustomed to doing business primarily with the academic research community. At the same time, the Foundation encouraged its academic partners to look at industrial knowledge that would be applicable to both industry and science.
Examples of recent NSF programs.
Large projects are in line with NSF's Big Ideas for NSF's Future Investments, including Quantum Leap, Rules of Life, Navigating the New Arctic, and Harnessing the Data Revolution.

Navigating the new Arctic - is it a civilian or a military project?
The question, of course, is rhetorical.
Several projects focus on US national priorities for artificial intelligence and advanced manufacturing. Others are tied to certain communities with daunting challenges to better understand the organisms, systems and resilience of our planet, and to address the pressing challenges of the air we breathe and the production of our food.
Other subjects of innovation infrastructure
IQT - fund
The CIA and government agencies, once the leaders of innovation, realized that they lacked advanced, innovative, and efficient technologies from and beyond Silicon Valley. In-Q-Tel combines government security expertise with Silicon Valley's unbridled curiosity.
Today, In-Q-Tel bills itself as a partner to the US intelligence and national security community, serving eight agencies, as well as the intelligence services and national security communities in Australia and the UK.
Economic Protection Capital Fund
An initiative designed to attract small businesses and startups developing high-risk dual-use technologies. These small businesses and startups are now facing a funding emergencywhich, without bridging financing, could in the near future force them to sell the property to larger defense contractors or private equity firms.
Such an event could stop the development of technologies that the Pentagon urgently needs to acquire.
The approach under consideration for the federal government is to buy shares from small alternative suppliers and actively ensure that critical defense technologies are not stalled.
This fund will be modeled on the Central Intelligence Agency's In-Q-Tel and may work in conjunction with the Pentagon's newly created National Innovation Security Capital program, although it will be significantly larger in size and scope.
He will be tasked with acquiring shares in American companies that create capital-intensive technologies of interest to the Pentagon, even at the most risky stages of technology development (when private financiers are unlikely to invest).
NSIC
National Innovation Security Capital (NSIC) has not yet shown itself to be anything epochal.
NSIC is a Department of Defense initiative that allows dual-use equipment companies to advance key milestones in their product development, eliminating the lack of private investment from trusted sources.
defense Department
Consider the research and development organizations of the Ministry of Defense.
The Department of Defense (DOD) supports correspondence research and development on military technologies of interest, and also conducts its own research.
General research and development.
DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) supports but does not conduct R&D for all departments of the US Department of Defense.
There are three types of change that occur in all complex organizations.
First Is systematic continuous improvement that the Department of Defense calls learning and experimentation.
Second is based on building the systems of tomorrow using today's proven methods and technologies. The Department of Defense sees this as evolutionary research and development based on requirements that are practiced, for example, by the Office of Naval Research and the Army and Air Force Research Laboratories.
The third The type of innovation required for any healthy organization is innovation with goals that obsolete and largely replace even the most successful current products and processes.
DARPA also supports research and development on technology useful to the intelligence community, although it is not the only source of technology for this community.
This program has several scientific ramifications and applications.
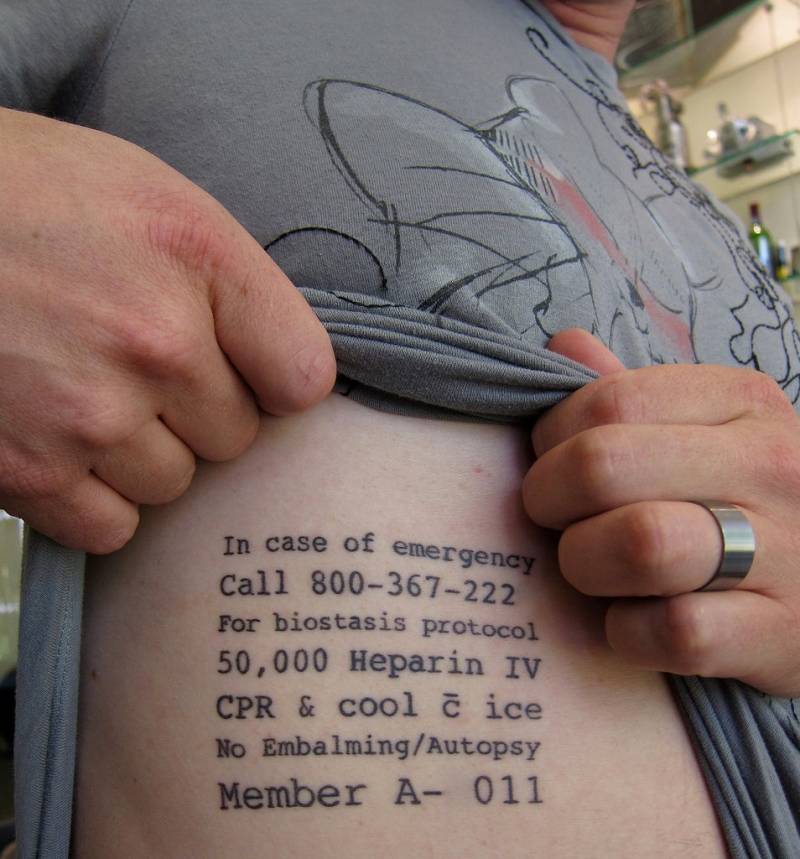
DARPA is studying biostasis protocols that can be triggered in emergency situations.
In fact, DARPA simply wants to put the injured in such a condition to give medical personnel more time to evacuate and heal, which could potentially turn the golden hour of medical evacuations into a golden couple of days.
Nano-doctor robots in human bodies
In Vivo Nanoplatforms Program.
Imagine entire pharmacies inside each soldier, floating in their bloodstream, ready to deliver medicines at any time.
The DARPA In Vivo Nanoplatforms program calls for the placement of persistent nanoparticles within organisms, especially in the military, but potentially also among civilians in populations vulnerable to infection.
The idea is to have sensors inside people that could provide very early detection of diseases or injuries, especially rapidly spreading infectious diseases.
This is what they call "in vivo diagnostics". Other groups will also receive "in vivo therapeutics", additional nanoparticles that can deliver highly targeted drug directly to appropriate infected or injured cells and tissues.
Human modification
For many years, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency has remained largely out of sight for most Americans, as their research projects are rarely covered in the mainstream media.
In the domestic media, references to DARPA are mainly associated with the news on the development of advanced weapons.
What does medical, biological and genetic research have to do with this?
DARPA often describes the controversial technologies it develops as advances in medicine and healthcare.
For example, in 2018, a group of European scientists accused the DARPA Insect Allies program of being in fact a dystopian biological program. weaponsin which insects will inject genetically modified viruses into plants to attack and devastate the food supply of the target country.
Recently, some of DARPA's human biology and biotechnology projects at its BTO have received massive PR boost from the current coronavirus crisis, with recent reports even claiming that the agency "could create better hopes for stopping Covid-19."
Most of these technologies, which have received positive media coverage thanks to Covid-19, were developed several years ago.
These include DARPA-funded platforms used to produce DNA and RNA vaccines, classes of vaccines that have never been approved for human use in the United States, and includes the injection of foreign genetic material into the human body.
The latter is of particular concern (although they are all alarming), as DARPA also has a project called Advanced Tools for Mammalian Genome Engineering, which, despite having the word “mammal” in its name, is specifically aimed at improving the “usefulness of human artificial chromosomes”. which DARPA describes as "a fundamental tool in the development of advanced therapeutic agents, vaccines and cellular diagnostics" (and who said that humans are not mammals).
Another potential application that DARPA is actively exploring is its BioDesign program, which explores the creation of synthetic organisms that are created immortal and programmed with a "kill switch" that allows a synthetic but organic block to "shut down" at any time.
This has led some to speculate that such research could open the door to the creation of "human replicants" used for warfare and other missions, such as those that appear in the science fiction movie Blade Runner.
In addition, reports on DARPA's efforts suggest that this bi-directional technology will be used to "blur the perception of soldiers" by "distancing them from emotional guilt for the war," a move that will set a dangerous precedent and will undoubtedly lead to a noticeable spike in war crimes.

Of course, these are only recognized potential "military" applications for such technology. Once this technology moves from the military to the civilian sphere, as has been the case with several DARPA inventions in the past, there will be a great temptation to use them for "remote control", "thought control" and / or programming thoughts and experiences, both domestically and beyond.
But several academic teams under contracts with DARPA are already working on this. They periodically report on their work and write scientific articles. Their approaches and results are so unusual that they cause serious fears for the future of all mankind.
Examples of recent DARPA programs

Expanding the capabilities of the UAV.
One of the newest DARPA programs, the Collaborative Operations in Denied Environment (CODE) program, is designed to expand the capabilities of existing US UAVs to conduct long-range combat against highly mobile land and sea targets in contested, rejected and constantly changing combat environments.
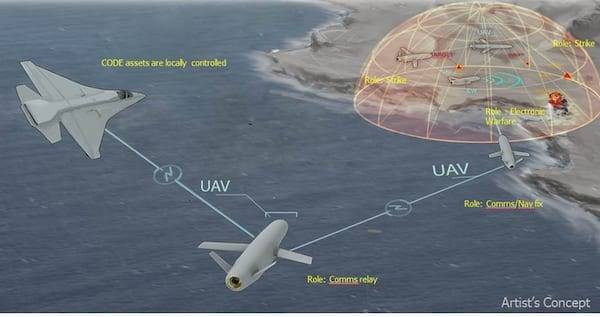
Artistic concept of manned and unmanned aerial vehicles working together. DARPA Image
If the program proves successful, the resulting collaborative autonomy technology could allow groups of unmanned aerial vehicles to work together under the control of one person, rather than through the existing system of continuous monitoring by the pilot and sensor operator, each supported by numerous analysts.
The UAV can travel to its destination, find, track and identify targets, and then provide recommendations for coordinated actions to the mission leader.
Exotica
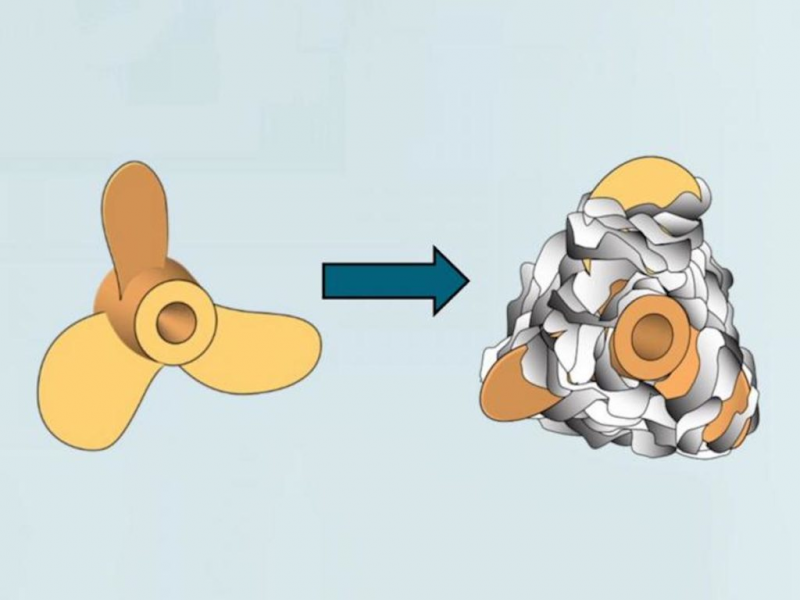
Blocking ship propellers
Since the author is not an expert in this area and is not able to understand this complex technologist, further the project's formula is literally translated (it turned out funny).
Quote from the US NAVY contract.
Present contract for ongoing research support and further development the production of filaments and yarns from spider silk and cowfish slime using transgenic silk worms; and the bacterial production and expression of spider goat milk and silk and curry mucus proteins.
The program develops next generation occlusion materials for a more comprehensive solution.
These next generation materials include synthetic mucus and ginger silk proteins that provide improved swelling, adhesion and strength properties not available in today's commercial products.
These materials are obtained from natural products and will be more sustainable.
That is, it is planned to wind not just mucus on enemy screws, and the mucus is environmentally friendly.
DARPA has partnered with the University of Michigan, Utah State University and Chapman University to investigate the properties of occlusion and "to produce synthetic intermediate filament proteins from hagfish mucus and recreate natural mucus-like behavior."
Experts at the University of Utah have identified alternative uses for synthetic spider silk proteins, including strong sponges and underwater adhesives, which have many properties that can be useful for "non-fatal vascular arrest."
New Quakers
For all domestic submariners and scouts of the late XNUMXth and early XNUMXst centuries, it remains an unsolvable mystery: the nature, goals and objectives, the meaning of existence and the "system of Quaker functioning."
Although none of them understood the concept of this system and its beneficiaries were not identified.
Previously, we could sin on the machinations of the Americans.
But, as available and inaccessible sources show, the Americans were in the same bewilderment and at the initial stage even suspected Russian special means of underwater reconnaissance of "croaking".
Now, perhaps, they figured it out (judging by the formulation of the problem thoroughly) and since November 2018 they have been implementing the program Persistent Aquatic Living Sensors (PALS).
And this is no longer a fantasy, but an OCD stage!
The Biotechnology Division of the Advanced Research Projects Agency of the United States Department of Defense is creating prototype sensor systems using underwater organisms such as plankton and shrimp ...
DARPA's terms of reference for this work says that we are talking not only about known species of marine animals and plankton, but also "modified" ones.
It also says about controlling the group behavior of certain types of plankton using physical fields, including from airplanes, drones and, possibly, from space.
At the first stage, the teams demonstratedthat marine organisms can sense the presence of an underwater vehicle (or an interfering factor) in their environment and respond with an output signal or other observed behavior.
At the second stage, teams develop artificial detection systems for observing, recording and interpreting the response of organisms and transmitting the analyzed results to remote end users in the form of classified alerts.
- noted Dr. Lori Adornato, PALS Program Manager.
As an important step towards this goal, DARPA has awarded Phase 2 contracts with four separate organizations to advance the PALS concept.
The system will analyze changes in acoustic signals emitted by the natural response of the biota of the coral reef ecosystem to avoid predators, which may offer an indirect mechanism for detecting and classifying underwater vehicles in near real time.
The preliminary results are also known, but this is a separate topic that, for various reasons, will not be widely discussed in either the American or domestic media.
I can only say that Quakers will become nutcrackers or crackers.
And, perhaps, one of the colleagues - divers already hears them.
Research and development in the Air Force and Navy
In addition to DARPA-wide R&D, the military services support external R&D and conduct their own R&D on technologies that meet their service needs.
The Office of Army Research, the Office of Naval Research (ONR) and the Air Force's Office of Scientific Research support correspondence work, while the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), the Army Research Laboratory, and the Air Force Research Laboratory are responsible for internal research and development.
ONR and NRL

For 75 years, ONR has been pursuing its mission of planning, stimulating and encouraging scientific research by sponsoring basic research.
This fundamental research provides the foundation for discoveries and innovations that are now being used by the entire world: improvements in cell phones, GPS systems, vaccines, nanotechnology, semiconductors, and more, made possible by projects sponsored by ONR.

Examples of recent ONR programs
Mobile anti-submarine war surveillance system or AMASS
The ONR's goal is to ultimately develop "a resilient, deep-sea, active anti-submarine warfare system capable of detecting new emerging submarine threats at great distances."
The ASW Affordable Mobile Surveillance System (AMASS) program is to design, build, demonstrate and build a resilient deep-sea active ASW system that can detect new emerging threat submarines over long distances.
Most interestingly, ONR is asking for proposals that include buoys and attached sonars that can fit in a standard shipping container and that crews on board can deploy directly from there into the water.

Space technology from the Navy
All space technologies and patents, the rights to which belong to Salvator Pais, the US Department of Defense and the US government, are also born in laboratories under the auspices of ONR. The author wrote about this in detail in the article Space technologies. Levitation in the US Navy.
I will remind you is:
• high-frequency generator of high-frequency gravitational waves;
• room temperature superconductor;
• generator of electromagnetic "force field" (capable of deflecting asteroids);
• an apparatus using a device for reducing inertial mass (an aircraft with UFO characteristics);
• small-sized thermonuclear reactor.
Other ONR projects
• Research, development and technical support of specialized aerospace systems.
• Geospace research and development in the field of remote sensing and modeling.
• Laser for remote sensing of active turbulent mixed ocean layer.
Obviously, in addition to purely scientific tasks, this technique will allow the detection and classification of underwater objects.
Small business participation

Research and development carried out by small businesses under the special government programs Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) and Small Business Technology Transfer Research, STTR).
Grantee projects must have the potential for commercialization and meet the specific research and development needs of the US government.
Approximately $ 2,5 billion is allocated annually under this program.
The US Department of Defense is the largest agency in this program, with approximately $ 1 billion in SBIR grants annually.
More than half of the Defense Department awards go to firms with fewer than 25 employees, and a third to firms with fewer than 10 employees.
One fifth are minority or women-owned businesses.
SBIR
The Small Business Administration (SBA) has overall control over its implementation. Those US ministries and departments are involved in mandatory participation in it, for which the volume of budgetary expenditures directed to third-party organizations (external executors) for R&D (Extramural R&D) exceeds $ 100 million per year.
At the same time, the minimum amount of equity participation in the SBIR program for such ministries and departments is determined annually as a percentage of their annual expenditures intended for R&D by outside organizations.
The work under the SBIR program of the military department is formalized by a contract between the US Department of Defense and the main executor - a small business organization. The lead executor of the project has the right to conclude subcontracts with co-executors of the work (with organizations or individual citizens).
SBIR projects involve 2 mandatory stages of work and one final, but optional.
The first stage may contain a technical concept check and the development of proposed solutions. The duration of this stage is no more than 6 months (up to 8 months on Air Force orders) and cannot be extended. The marginal cost of work on the first stage should not exceed $ 150 thousand (up to 2010 - $ 100 thousand), and for the second stage - $ 1 million (up to 2010 - $ 750 thousand).
As a rule, second stage is divided into two sub-stages, each lasting 10–12 months. The first sub-stage is basic and involves obtaining results that allow you to evaluate or confirm the effectiveness of the selected research area (or development), as well as make a decision on the advisability of opening the second sub-stage.
The third stage work within the SBIR project of the US Defense Ministry opens only if a non-governmental source of funding is found interested in finalizing the results obtained to the level of an industrial design of weapons and military equipment (or civilian products) for the purpose of its subsequent commercial sale (commercialization).
Every year, the US Department of Defense SBIR program initiates ~ 8-9 thousand projects, the list of which is published twice a year (in October and May).
As the analysis has shown, the annual projects of work under the SBIR program of the US Defense Ministry cover almost all areas of development of defense research and development.
STTR
Another form of government cooperation with small business organizations is implemented in the American program "Small Business Technology Transfer Research - STTR". Within its framework, research and development projects are carried out by small business organizations (head performers) in conjunction with universities and industrial research and development organizations (co-performers).
The Small Business Technology Transfer Program (STTR) uses a similar approach to the SBIR program to enhance public-private partnerships between small businesses and non-profit research institutions in the United States.
The main difference between the SBIR and STTR programs is that the STTR program requires a company to have a research partner institution that must be awarded at least 30% of the total grant allocated.
Those US ministries and departments are required to participate in the STTR program for which the volume of budgetary expenditures allocated to third-party organizations (external executors) for R&D exceeds $ 1 billion per year.
Examples of recent SBIR programs
Examples of the most important research and development projects carried out under the SBIR program include the following:
- creation of diesel aviation engines (LOLS horsepower per cylinder) for small-sized UAVs;
- creation of high-speed (speed over 8-10 knots) unmanned underwater vehicles (Unmanned Underwater Vehicle, UUV) - weapons carriers.
List of SBIR Hall of Fame Laureates 2020
A few examples from this list.
New radars
For Colorado Engineering Inc. (CEI), small business, owned by womenHeadquartered in Colorado Springs, Colorado, Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) funding has enabled the company to develop technological breakthroughs in a variety of military and commercial radar applications.
SBIR funding has enabled CEI to develop technological breakthroughs in a variety of military and commercial radar applications.
The AN / SPS-49 (V) Surround Surveillance Radar provides long-range aerial search capability for a variety of ships and serves as an integral component of Cooperative Interoperability (CEC) and Ship Self-Defense System (SSDS).
Geospatial exploration
In all mobile, web, desktop and airborne planning applications, flexibility is built into the technology - in addition to being used for civilian purposes, these tools help mission planners, engineers, and operators to define and tune systems, constraints, and planning goals. This customer and end-user focus has helped the company expand its customer base and expand into new directions.

Orbit Logic has over 15 years of experience in developing and implementing advanced mission planning solutions for the aerospace and geospatial markets and continually developing new solutions to meet the changing needs of these industries.
Multimedia drone
A drone that can fly, swim, dive and move between air and water in less than one second - can you believe it?
New Jersey-based SubUAS brought it to life with the Naviator platform, technology developed by Dr. F. Javier Diez and Dr. Marco Maia of Rutgers University with funding from the Business Innovation Research / Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR / STTR) Foundation.
The Naviator platform has many unique characteristics that make it much more flexible than other platforms, including operation without being tied to remote pilot control and the ability to perform autonomous missions.
Naviator drone can operate in the harshest conditions, from snow to rain and sandblasting.
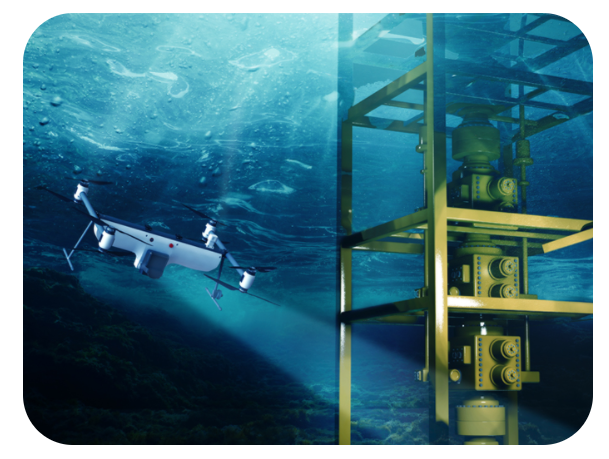

This is the only drone that can work together drones (one for air and one for the vehicle), reducing costs and time while improving safety and adding features that were previously unimaginable.
It has been designed to be neutral buoyant for excellent energy efficiency, range and endurance.
The Naviator can be used for station inspection and hold and carries a variety of sensors.
And we'll end with a long quote from Vannevar Bush's letter to President Roosevelt.
Five basics
There are certain basic principles that should underlie the program of state support for research and education.to ensure that such support is effective and does not prejudice what we seek to contribute.
These principles are as follows:
1. Whatever the degree of support, funds must be stable for many years in order to implement long-term programs.
2. The agency for the management of such funds should be composed of citizens selected only on the basis of their interest and ability to contribute to the work of the agency. They should be people with a broad interest and understanding of the specifics of research and education.
3. The agency must promote research through contracts or grants to organizations outside the Federal Government. It should not have its own laboratories.
4. Support for basic research in public and private colleges, universities and research institutes should provide internal control of policies, staff, and research methods and scope to the institutions themselves. This is extremely important.
5. Ensuring complete independence and freedom in the nature, scope and methodology of research carried out in institutions receiving public funds, and maintaining discretion in the allocation of funds between such institutions, the Foundation proposed in this document should be accountable to the President and Congress.
It is only through this responsibility that we can maintain proper relationships between science and other aspects of a democratic system.
Conclusion
With this latest twist in R&D strategy, the United States runs counter to longstanding trends in the relationship between military and civilian R&D.
Civil R&D has become increasingly dominant in recent years.
Military research and development became more specialized and focused on filling the gaps left by civilian research and development, as well as integrating civilian and military scientific research.
Such support can be extended to individual scientists or selected projects and take the form of, for example, direct financial support, exchange programs, joint sites and joint research programs, or it can include the military in “centers of excellence”.
At least, the existing innovative structure and long-term practice of using its mechanisms give grounds for such assumptions.
PS
The author is quite familiar with the domestic innovation system and its problems, but, despite calls to describe it, he will not do this.
For I will paraphrase from Ecclesiastes:
Facts and reflections, as a rule, prove nothing, unlike concepts that awaken thought and motivate positive change.









Information