Tanks of England in the interwar period
Mk.VII and Mk.VIII heavy tanks
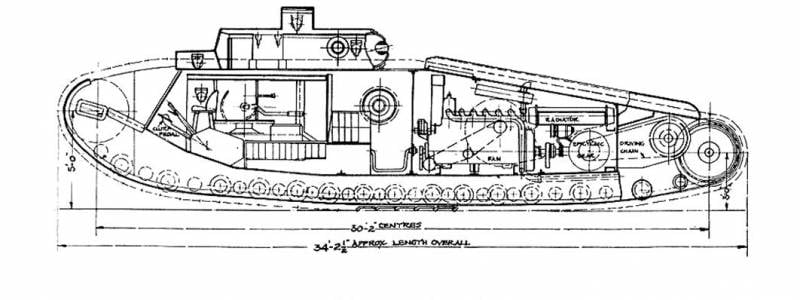
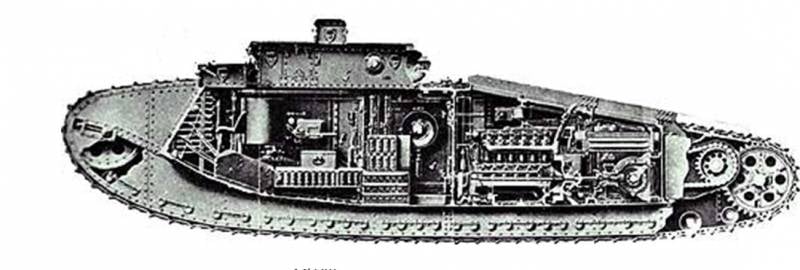
Despite the not quite satisfactory characteristics of the habitability and mobility of "diamond-shaped" tanks of the McNXX-Mc1 family, the development of the line of these tanks was continued. At the end of 5, a batch of Mk.VII tanks was produced, differing from their predecessors by the presence of a hydraulic transmission that provides smooth control of the movement and rotation of the tank. Due to this, the work of the driver was significantly simplified, instead of levers, he drove the car with the help of a steering wheel.
The tank weighed 37 tons, the crew was a 8 man, it was equipped with two 57-mm cannons and five machine guns. The Ricardo engine with a power of 150 hp, providing 6,8 km / h speed and 80 km cruising range, was used as a power plant. Due to the large weight, the ground pressure was 1,1 kg / sq. cm. Only the largest batch of tanks was manufactured, and it was not accepted for service.
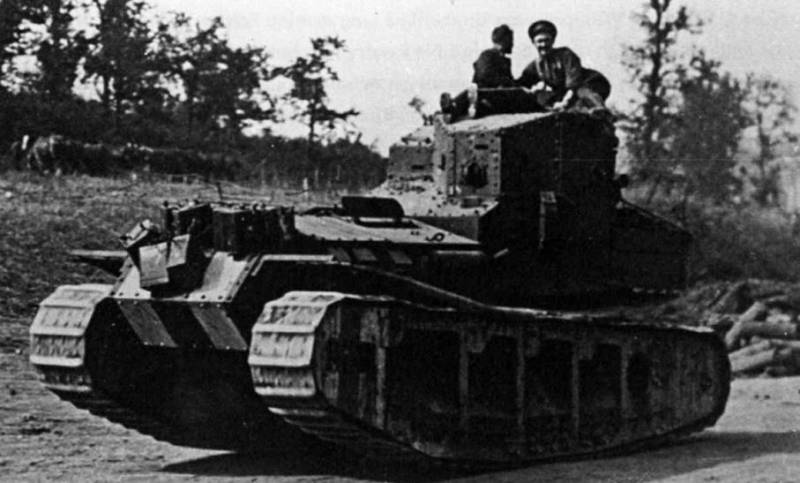
The last of the series of "diamond" tanks was the Mk.VIII, tested in 1919 year. The tank weighed (37-44) t, the crew was a 10-12 man, armed with two 57-mm cannons and up to seven machine guns.
The design of the tank was riveted with two sponsons on the sides, in which guns were installed. On the roof of the hull there was a combat tower, in which two machine guns were mounted in a ball joint, also two machine guns were on each side and one in the front and aft compartments. The tank armor thickness was 6-16 mm.
The power compartment was located at the back and was isolated from the habitable compartment. All crew members, except the mechanic, were in the fighting compartment and due to the system of creating increased pressure to remove smoke and burning they were in more comfortable conditions than in the tanks of the previous generation. The tank was equipped with an engine power 343 hp, providing speed on the highway 10,5 km per hour and power reserve 80km.
A batch of Mk.VIII in the number of 100 units was jointly manufactured with the United States, where this tank was put into service, was the main heavy tank of the US Army and operated until the 1932 year.
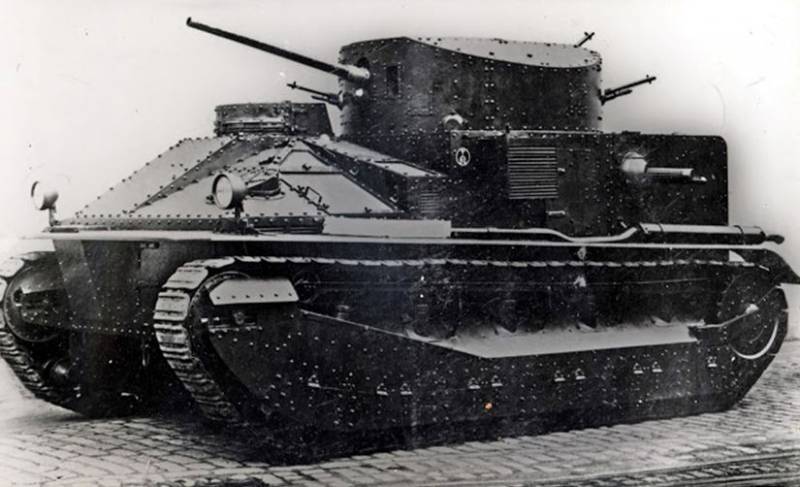
Heavy tank A1E1 "Independen"
At the start of the 20, the diamond-shaped tanks clearly lost the confidence of the military because of a claim to their maneuverability, poor fire maneuverability due to the placement of weapons in sponsons that restricted shelling sectors and poor living conditions. It became clear that the time of these tanks was gone, and they are a dead-end branch. The armies required completely different machines, maneuverable, with strong cannon armament and more powerful armoring capable of providing protection against the anti-tank guns that appeared.
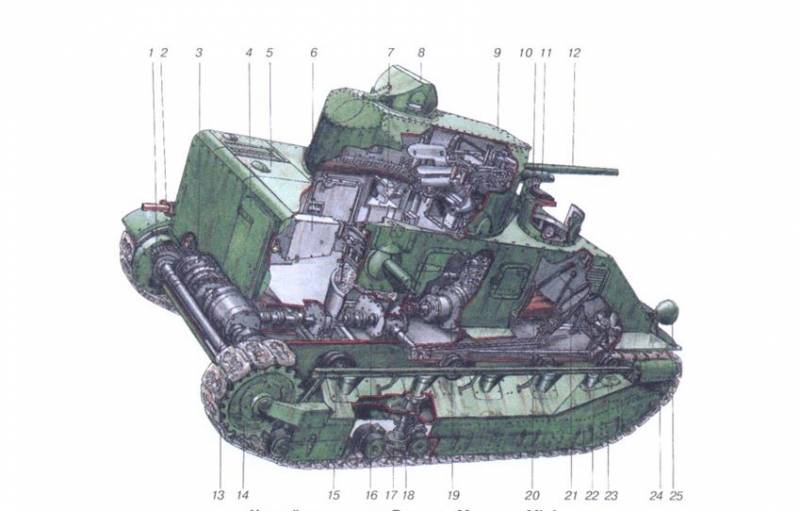
According to the layout, the A1E1 tank was fundamentally different from the "diamond-shaped" tanks, the classic layout was adopted as the basis with the front placement of the combat compartment and the engine-transmission rear. On the hull of the tank was installed five towers, the crew of the tank was 8 people.
The central part of the fighting compartment was set aside for the installation of the main turret with an 47-mm cannon designed to fight tanks and artillery. The tower housed the tank commander, the gunner and loader. For the commander a commander's cupola was provided, shifted to the left relative to the longitudinal axis. On the right was a powerful fan, covered with an armored cap.
In front of the main turret and behind it there were two machine-gun turrets in each, in which one 7,71-mm Vickers machine gun was installed, equipped with a telescopic sight.
Machine-gun turrets were dome-shaped and rotated 360 degrees, each of them had two viewing slots protected by armored glass. The upper part of the tower could lean back up. For the crew’s interaction, the tank was equipped with an internal laryngophone communication system.
The tank was provided with maximum comfort for the mechanic-driver, he sat separately in a special ledge in the tank hull and through the observation tower he was provided with a normal view of the terrain. The tank was equipped with a V-shaped air-cooled engine with an 350 horsepower. and the planetary transmission, thanks to her and the servos, the driver easily controlled the tank with levers and steering wheel, which was used for smooth corners. The maximum speed of the tank reached 32 km / h.
The armor protection was differentiated: 28 mm front forehead, 13 mm bead and stern, 8 mm roof and bottom. The tank weight reached 32,5 t.
The chassis of the tank largely repeated the chassis of the Medium Mk.I tank. On each side there were 8 track rollers combined in pairs in the 4 trolley. Suspension elements and track rollers were protected by removable screens.
The first sample of the tank, which turned out to be the only one, was made in the 1926 year and passed a test cycle. He improved, but the concept of such huge tanks was not in demand and work on it was stopped. Some ideas implemented in the A1E1 tank were later used in other tanks, including the Soviet multi-turret T-35.
Medium Tank Mk.I and Medium Tank Mk.II medium tanks
By the middle of the 20-x in parallel with the development of heavy tanks, medium tanks Medium Tank Mk.I and Medium Tank Mk.II were developed and put into service, characterized by the presence of a rotating turret with weapons. The tanks had a good design, but the front location of the power plant complicated the work of the driver and the speed of the 21km / h tank did not satisfy the military.
[Quote] [/ quote]
According to the layout, the Vickers Medium Mk.I tank was different from the layout of heavy tanks, the driver was located in the cylindrical armored wheelhouse in front of the right. To the left of the driver was the power plant. Behind the driver was a fighting compartment with a rotating turret. For observation were used the viewing slit. The crew consisted of five people: a driver, commander, loader and two machine gunners. The landing of the crew took place through the side hatches in the hull of the tank and through the aft door.
The tank hull had a “classic” design for that time, armor plates with a thickness of 8 mm fastened with rivets on a metal frame.
The power unit used was a V-shaped air-cooled engine “Armstrong-Siddeley” with a power 90 hp. and manual transmission, located behind. With the weight of the tank 13,2 t he developed the speed of 21 km / h and provided a power reserve of 193 km.
The tank’s armament consisted of 47-mm guns with 50 barrel lengths, from one to four Hotchx 7,7-mm machine guns mounted in the turret, as well as two Vikkers 7,7-mm machine guns mounted on the hull sides. To observe the terrain, the commander had a periscope panoramic sight.
The chassis of the tank consisted of small diameter 10 track rollers interlocked in 5 carts, two independent rollers, 4 support rollers, rear driving and front guide wheels on each side. The undercarriage was protected by an armored screen.
Modifications of the Vickers Medium Mk II tank differed in design changes of the turret, the presence of a coaxial machine gun with a cannon, armor protection of the undercarriage and the presence of a radio station.
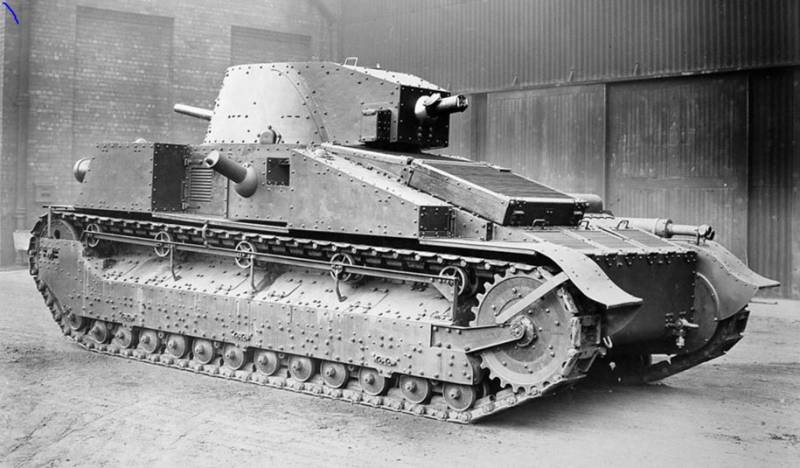
Medium Tank Medium Tank Mk.C
In 1925, the development of a new medium tank began, which received an index of Medium Tank Mk.C. The layout of the car was "classic" with the location of the power plant in the stern of the tank, the control compartment in front and the crew compartment in the center in a rotating turret. An 57-mm cannon was installed in the turret, and a machine gun in the stern of the turret; one machine gun was also placed along the sides of the tank. In the front sheet of the hull was mounted exchange gun. The tank hull was a riveted construction with 6,5 mm armor thickness. On the front plate, the door for the landing of the crew and the projection for the driver’s legs were unsuccessfully placed.
As a power plant was used aviation 110 hp Sunbeam Amazon engine, with a tank weight of 11,6 tons, it reached a speed of 32 km / h.
The crew was a 5 man.
In 1926, the tank was tested, but, despite a number of successful design solutions (classic layout, rotating turret and high speed), the tank was not accepted for armament due to weak security. Nevertheless, the customer for the tank was found, it was acquired by the Japanese and created on this base its medium tank Type 89.
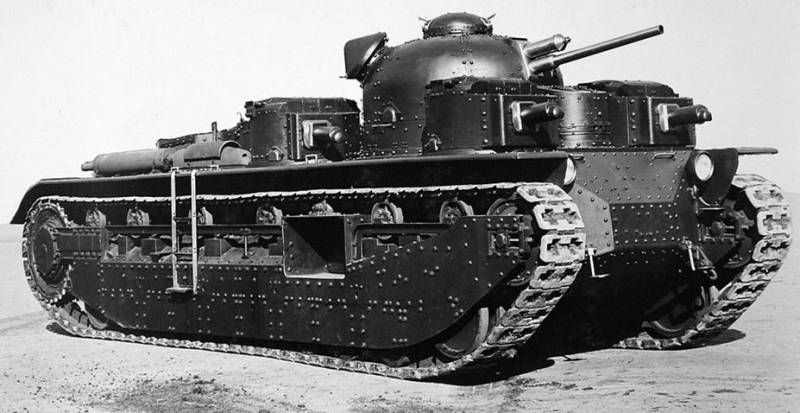
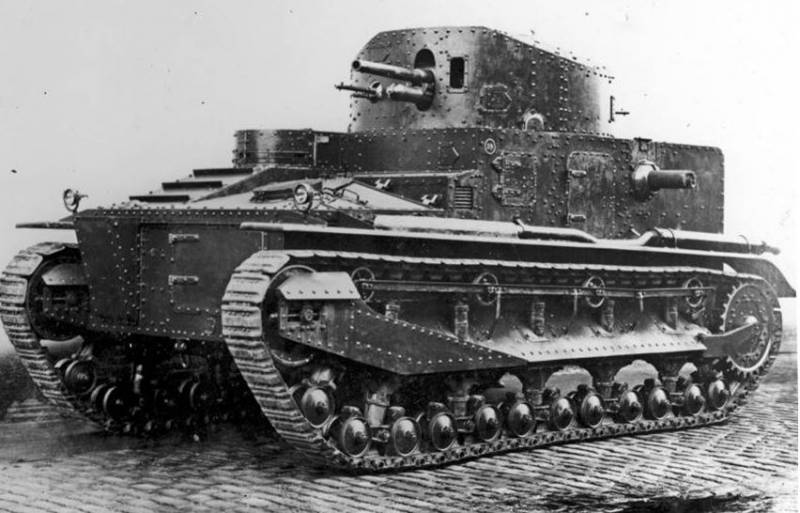
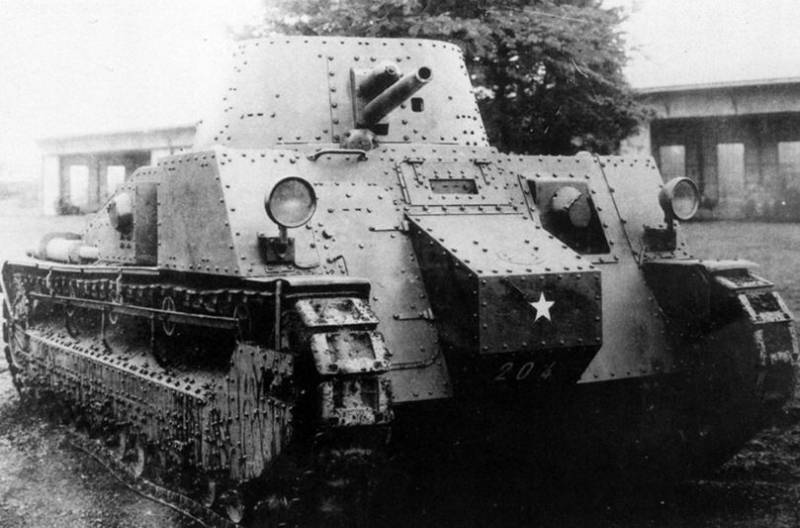
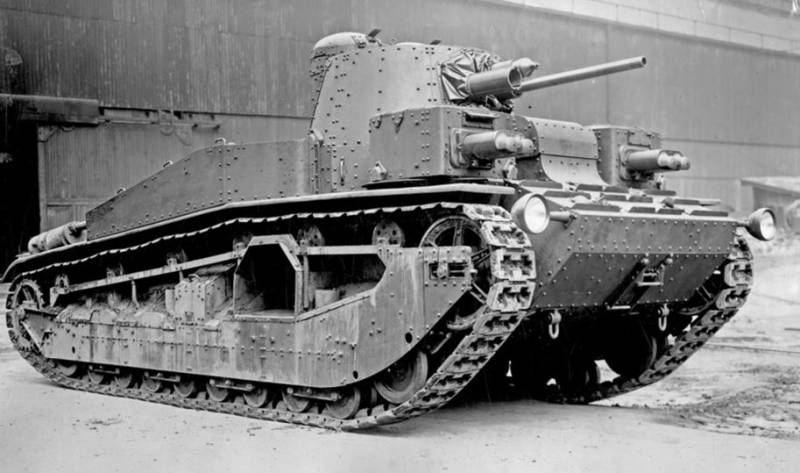
Medium Tank Medium Tank Mk.III
The experience and groundwork of the Medium Tank Mk.C tank was used in the development of the Medium Tank Mk.III medium tank with a cannon turret in the center of the tank and two machine gun turrets on the tank hull, each turret had two machine guns with one machine gunner. On the central tower there were two commander towers. Then in the machine-gun towers they left one machine gun each and removed one commander's turret.
The thickness of the frontal armor was 14 mm, and the sides of the 9 mm.
As a power plant, the Armstrong-Siddeley V-engine 180 hp was used, providing a speed of up to 16 km / hr with the weight of the 32 tank
In 1928, an improved version was created with a Thornycroft RY / 12 diesel engine with 500l.s power, which received an index of Medium Tank Mk.III А3. On tests, the tank showed good performance, but because of the outbreak of the financial crisis, the tank was not put into service.

Despite this, the progressive ideas of this tank were used on other tanks. The armament scheme with two machine-gun turrets was used on the Vickers Mk.E Type A light tank, on the Cruiser Tank Mk.I and the German Nb.Fz.
This experience was also taken into account in the Soviet tank building, the Soviet purchasing commission in 1930 acquired a number of samples of British tanks, with the Carden-Loyd Mk.VI being the basis of the Soviet T-27 tank shoes, and Vickers Mk.E as the basis for the T-26 light tank , and the ideas laid down in the tank Medium Tank Mk.III were used to create the Soviet medium tank T -28.
Light tanks
After the not quite successful use in combat of the first heavy tanks, the military set the task of creating a light "cavalry" tank. So the first light English tank was the Mk.A "Whippet". After the end of the war in England, a whole family of light tanks was created, which found application in the English army and the armies of other countries.
Light tank Mk.A. "Whippet"
Light tank Mk.A “Whippet” was created at the end of 1916 of the year, mass production was launched only at the end of 1917 of the year, and he took part in hostilities at the end of the war in 1918.
The tank was supposed to be with a rotating tower, but with its production problems arose, and the tower was abandoned, replacing it with a casemate felling in the stern of the tank. The crew of the tank was three people. The commander was in the wheelhouse on the left, the driver was sitting in the wheelhouse on the seat on the right, and the machine gunner was standing behind and servicing the right or stern machine gun.
Four 7,7-mm Hotchkis machine guns were taken in a tank, three were mounted in ball units and one was a spare. Landing was made through the aft door.
As the power plant used two engine power 45l.s. each, they were in the front of the hull, and the gearbox and drive wheels in the back, where the crew and weapons were located.
The hull was going to be riveted and bolted at the corners from sheets of rolled armor 5 — 14 mm thick. The security of the frontal part of the cabin was somewhat increased by the installation of armor plates at constructive angles of inclination.
Chassis was with a stiffer suspension, assembled on armored frames along the sides of the hull. The tank weighed 14 t, developed speed on the highway 12,8 km / h and provided a power reserve of 130 km.
On the basis of the Mk.A small batches of tanks Mk. B and Mk.C with a 57-mm cannon and three machine guns. On some samples, an engine with a capacity of 150l.s was installed. Tanks Mk.A (Mk. V and Mk.S.) were in service with the British army until 1926.
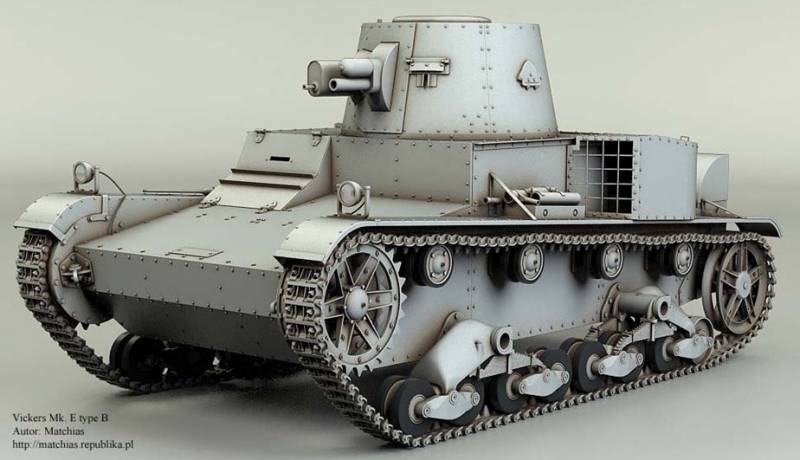
Light tank Vickers Mk.E (Vickers six-ton)
The Vickers Mk.E light infantry support tank was developed in 1926 and tested in 1928. It was produced 143 tank. The tank was developed in two versions:
- Vickers Mk.E type A - a two-tower version of the “trench cleaner” with one machine gun in each turret;
- Vickers Mk.E type B - single-turreted version with a cannon and a machine gun.
In a constructive respect, all the Mk.E tanks were almost identical and had a common layout: the transmission in front, the control compartment and the fighting compartment in the middle part, the engine compartment in the back. The crew of the tank 3 man.
In front of the hull housed a transmission, which occupied a rather impressive compartment. Behind it, in the middle part of the body, a characteristic under-case box was installed, which became the hallmark of all the “six-ton Vickers”. Inside the box was the crew, the driver's seat was on the right side. In the right tower was the place of the commander, in the left machine gunner. The standard weaponry consisted of two 7,71-mm Vickers machine guns.
In the modification of the type in weapons included 47-mm cannon and 7,71-mm Vickers machine gun. Gun ammunition consisted of 49 shots of two types: high-explosive and armor-piercing. An armor-piercing shell pierced a vertically mounted armor plate up to 30 mm thick at a distance of 500 meters, and this tank posed a serious threat to other tanks.
The tank weight was 7 t when booking the 13 mm hull forehead, 10 mm hull sides and stern, 10 mm turret hulls, 5 mm roof and bottom. On individual modifications of the Type B tank, a radio station was installed.
The Armstrong-Siddeley “Puma” hp 92 air-cooled engine was used as a power plant, which often overheated and failed. The tank developed the speed of 37 km / h and provided the course for 120 km.
The undercarriage of the tank was a very original design, consisting of 8 supporting rollers blocked in pairs in 4 trucks, with each pair of trolleys having a single balancer with suspension on leaf springs, 4's supporting rollers and a fine-grained track 230 mm wide. Driving scheme was very successful and served as the basis for many other tanks.
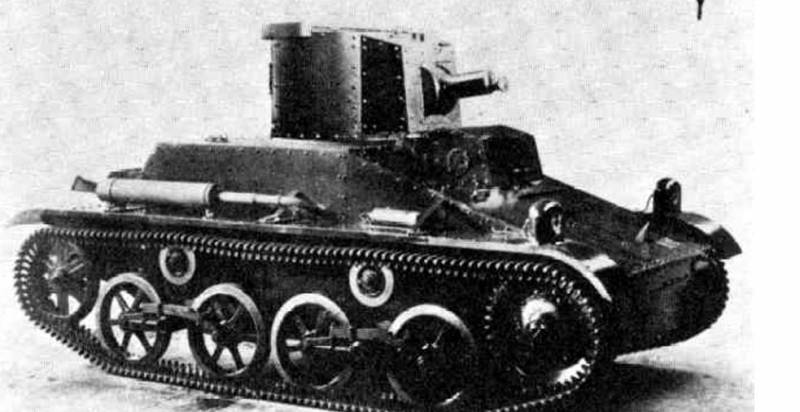
Light tank Vickers Carden-Loyd ("Vickers" four-ton)
The tank was developed in 1933 year as a "commercial" tank, from 1933 to 1940 was produced exclusively for export. A single-revolving tower of a cylindrical or faceted structure, displaced to the left side, was installed on a riveted case with a tilted frontal sheet.
The engine compartment was located to the right, and to the left behind the partition the command and control compartment. Transmission and engine power 90 HP located on the right in the bow of the hull and ensured the speed of the tank 65 km / h. The driver’s seat and the traffic controls were located on the left; there was an armored cabin with a viewing slot above the driver’s head.
The crew of the tank - 2 man. The fighting compartment occupied the middle and rear of the tank, here was the place of the commander - the arrow. Armament tank 7,71 mm machine gun Vickers. The survey from the commander's seat was provided through the cracks with bulletproof glass in the sides of the turret and with the help of a machine gun sight.
The thickness of the armor of the tower, forehead and sides of the hull 9 mm, the roof and bottom of the hull 4 mm. The chassis is blocked, on each side there are two two-roller balancing carts suspended on leaf springs. With a weight of 3,9, the tank could reach speeds on the highway up to 64 km per hour.
Depending on the requirements of the customer, the tanks differed in design and characteristics. In 1935, a batch of tanks that received the T15 index was shipped to Belgium. Machines differed conical turret and the Belgian version of weapons, consisting of 13,2-mm Hotchkiss machine gun and anti-aircraft 7,66-mm machine gun FN-Browning.
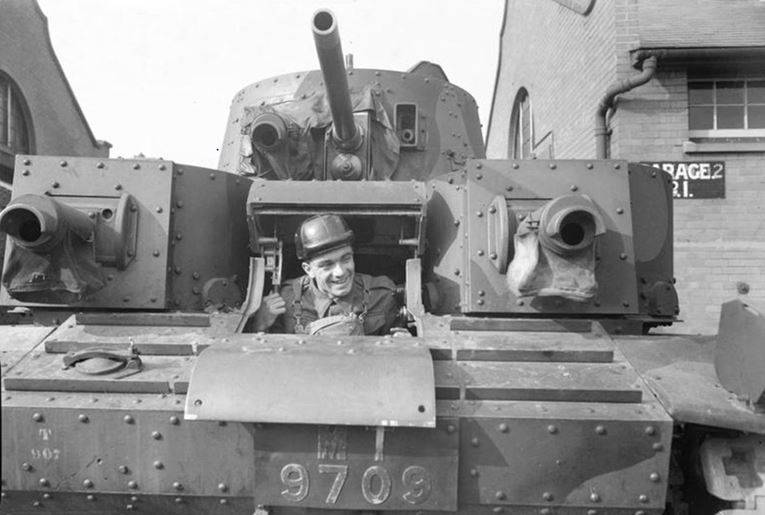
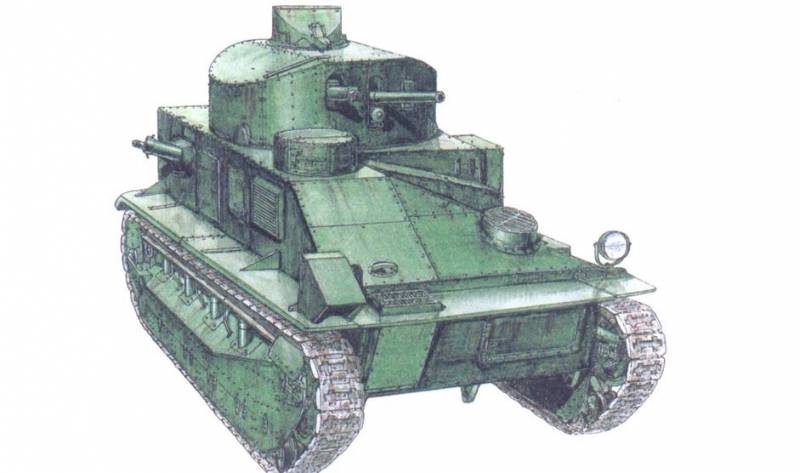
Light tank Mk.VI
The final model of the series of light tanks, developed in the interwar period, was the light tank Mk.VI, created in 1936 year based on the experience of developing light tanks MK.I, II, III, IV, V, which were not widely used in the army.
The layout of the tank was typical for light tanks of the time. The Meadows ESTL engine with 88l.s power was located in the forward part of the hull from the starboard side. and manual transmission company Wilson. On the left side was the place of the driver and controls. The fighting compartment occupied the central and aft parts of the corps. There were places for the machine gunner and the commander of the machine. The tower was a double, in the stern of the tower was a niche for the installation of the radio station.
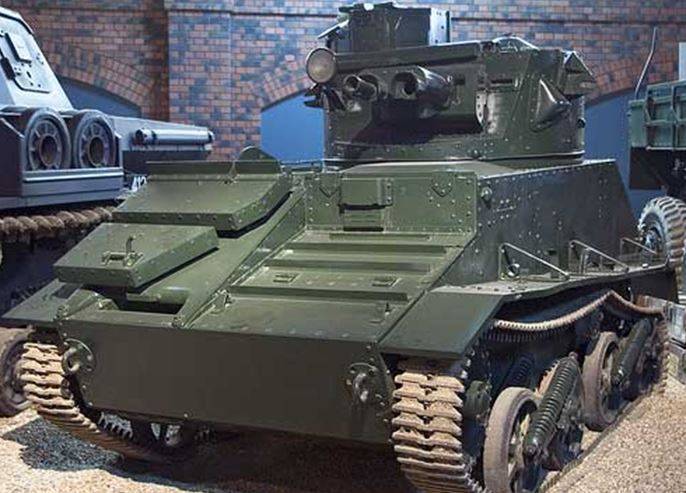

On the roof of the tower there was a round double-wing hatch and a commander's cupola with a viewing device and an upper hatch. A large-caliber 12,7-mm machine gun and an 7,71-mm machine gun coupled with it were installed in the turret. The tank weighed 5,3 t, the crew was the 3 man.
The hull structure was riveted and assembled from sheets of rolled armored steel, the thickness of the frontal armor hull and turret 15 mm, sides of the 12 mm.
The chassis was an original design, on each side there were two trucks with two supporting rollers equipped with a Horstmann suspension system (“double scissors”) and a supporting roller mounted between the first and second rollers.
The drive wheel was in front, the track was a fine-grained width 241 mm. The tank developed a speed of 56 km / h and had a cruising range of 210 km.
On the basis of the tank, several modifications of light tank and military tracked vehicles for various purposes were developed, in total about 1300 of such tanks were produced. Mk.VI was the most massive tank of England in the interwar period and formed the basis of its armored forces.
The state of England's tank park before the war
In the interwar period in England, the program of creating heavy, medium and light tanks was implemented, but only certain types of light tanks became widespread. As a result of the consequences of the Great Depression, the serial production of heavy tanks Mk.VIII and А1Е1 was not launched in England and the production of medium tanks of the Medium Tank Mk.I, II, III series was stopped. On the eve of the war, only mostly light tanks remained in the army (1002 light tanks Mk.VI and 79 medium tanks Medium Tank Mk.I, II).
Before World War II, England was not ready for a modern war, it developed tanks for the previous war. Of the entire generation of inter-war tanks in the European theater of the Second World War, the British army initially used only Mk.VI light tanks in limited quantities, which they quickly had to give up. These tanks were used in secondary "colonial" theaters of war against a weak enemy. During the war, England had to develop and establish production of a completely different class of machines in accordance with the demands put forth by the war.










Information