The American ESMC / ESMB Mongoose demining system was too complicated.
The development of a new model of engineering equipment for making passes in minefields was launched in August 1994. After analyzing the recent conflicts, the Pentagon came to the conclusion that it was necessary to create a new demining system capable of making a major passage in the shortest time. In accordance with the technical task, it was necessary to create a towed system with a launcher and a means of demining a new type. It had to make passes with a width of at least 4-5 m, leaving no more than 10-12 percent. raw min.
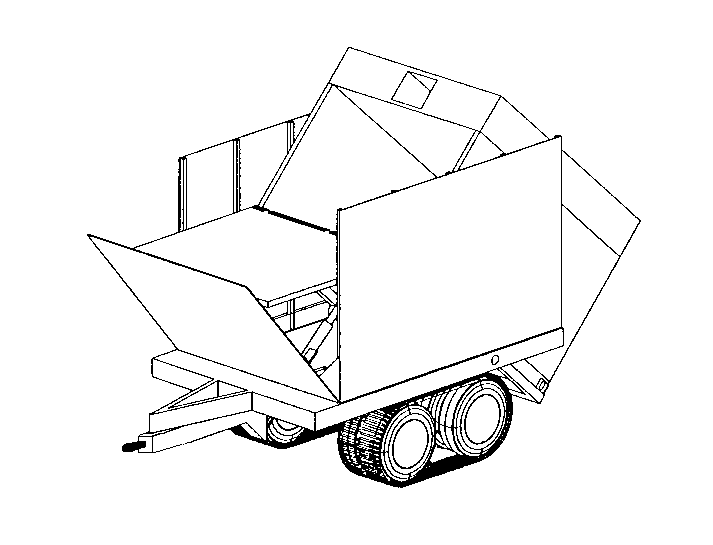
The scheme of the trailer with a container Mongoose. Figure Fas.org
By that time, demining systems based on towing missiles and elongated charges became widespread. Calculations showed that the reactive principle of setting the charge on a minefield is suitable for use in a new project. At the same time, it was necessary to abandon the traditional extended charge in favor of a more complex, but, as it seemed, a more efficient system.
The development of a new model was entrusted to BAE Systems. The demining system was named Mongoose (“Mongoose”) and two designations at once. In some documents, it appears under the name ESMC (Explosive Standoff Minefield Clearer - “Mine Blast Clearing System”), while others use the designation ESMB (Explosive Standoff Minefield Breacher - “Mine Blast Passing Explosion”). Moreover, both designations are equivalent. Due to the uncertain status, the ESMC / ESMB system still does not have an official army designation.
***
The main element of the "Mongoose" is the transport and launch container used for the storage and production of a special ammunition system called ENS. The container has an average size corresponding to the capabilities of the vehicles on the supply. With the help of a trailer the container can be transported by one or another tractor.
To transport the mine clearance system over long distances, it is proposed to use 5-ton class trucks. On the battlefield, a trailer with ESMB / ESMC must go beyond a tank or another secure machine. On the highway, towing speed is limited to 40-45 km / h; on rough terrain, it is recommended to keep half speed and not allow sharp maneuvers.
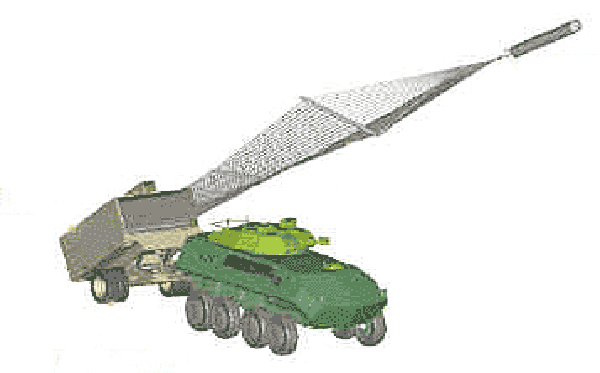
Running the grid in the artist's view. Figure Saper.isnet.ru
The container is a rectangular box of armor steel, which can withstand the hitting of bullets and shrapnel. The front wall of the drawer folds forward and down, allowing all ENS components to exit. Under the roof of the container there is a tubular guide for the towing rocket, the remaining volume is intended for the ENS product. After use, the Mongoose container should be returned to the rear for reloading, after which it can provide clearance for a new pass.
The container is mounted on a support with drives that provide its vertical guidance. Also, the product is equipped with a set of sensors that monitor the position of the trailer and container. Based on this data, the automatic calculates the data for firing.
The system is controlled by the operator console. It is located on the towing vehicle and is connected to the container with a cable. The console provides data processing from the sensors and control of the vertical guidance of the container from the guide. After installing the container at the desired angle, the console starts the launch of the means of mine clearance. He is also responsible for undermining the product ENS. Depending on the need, undermining can be performed immediately or at an arbitrary point in time.
Defeat enemy mines is carried out using the ENS product - Explosive Neutralization System ("Explosive Neutralization System"). It is a network of nylon ribbon. The network length is 82 m, width is 5 m. The mesh cell has dimensions 170 x 170 mm. At the intersection of individual ribbons, lightweight cumulative charges with a mass of about 100 g are placed. On a single ENS grid, 16354 of such devices is located. Control of undermining is carried out using an electric signal. The total mass of one ENS product is 2346 kg.
The cumulative charge from the ENS composition during blasting forms a jet penetrating the ground. The cumulative jet reaches the depth of 120 mm and is capable of striking objects in the ground. The principle of operation of ENS and the whole Mongoose system is based on this.

"Mongoose" on trial. Photo Globalsecurity.org
From the transport and launch container, the ENS network is extracted using an unguided solid fuel rocket towing vehicle with a mass of 270 kg. Before starting it is on the guide inside the container. The rocket through the lock connects to the network with a cable. The use of a brake cable connecting the network and the launch canister is also envisaged.
***
To make the passage in the minefield, the tractor must bring the trailer with the ESMC / ESMB container to the specified position, after which the operator prepares to launch the grid with charges. At the command of the operator, the rocket leaves the container and pulls the net behind it. At a distance of about 150 m from the starting position, the brake cable causes the rocket to unhook the grid, after which it lies on the field. All charges are detonated automatically or at the operator’s command.
16354 cumulative jets, being formed at a distance of no more than 150-170 mm from each other, are able to literally dig up the ground and hit objects in it in an area comparable to the size of the ENS grid. It was argued that this method of demining has significant advantages over the traditional extended charge and other means of clearing minefields.
The developers assumed that a cumulative jet is capable of destroying a mine lying in the ground or, if it gets into its charge, causes detonation. Due to this, the ENS system could deal with mines of various types and for any purpose. Also guaranteed guaranteed defeat of explosive devices with a diameter of more than 170-200 mm: regardless of their position, such a mine would fall under one or two shaped charges.
***
The development of the ESMC / ESMB Mongoose system was completed only in 1999. After that, the project moved to the stage of construction and testing of prototypes. The first stage of the ground tests was carried out by 2000-2001 years, and after it was decided to refine the existing system. In 2002, new tests were carried out, according to the results of which “Mongoose” got into the field regulations of FM 20-32, describing the means and methods of dealing with the explosive barriers. Adoption of the system was planned for 2004-2005 years.
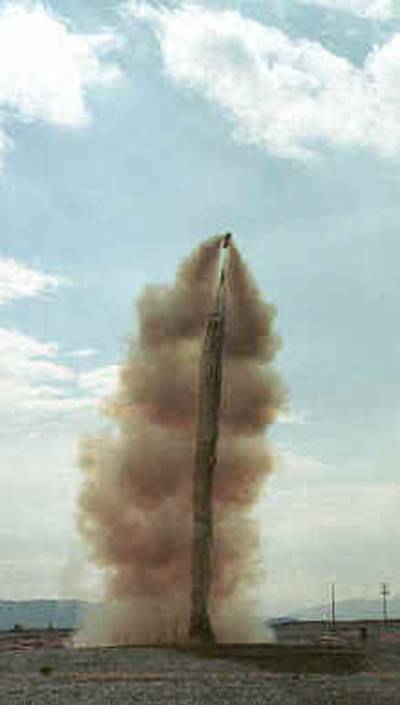

Grid ENS in flight. Photo Globalsecurity.org
After the first stages of testing and finalizing the demining system, Mongoose and the ENS network were put into trial operation, which began in the middle of the last decade. The US Army received a small number of new systems designed for heavy engineering battalion companies. Each company was to operate six units of the Mongoose, two in each platoon of its composition.
According to available data, the ESMC / ESMB reactive demining system has not yet been put into service and retains the status of a promising model undergoing military trials. Apparently, the "Mongoose" will not be adopted and will not be put in a series. Existing samples will develop their resource and in the foreseeable future will be written off as useless. It is no longer a question of replacing other demining systems.
The reasons for this result are well known. Even at the stage of the first tests, problems arose that, apparently, could not be solved with the further development of the project. The ESMC / ESMB system has two characteristic disadvantages directly related to the ENS network design. Without their elimination, obtaining the desired characteristics is simply impossible.
The first problem is the extreme difficulty of correctly laying a soft net with charges. If this product does not unfold in flight in the correct manner and does not lie flat on the ground surface, the dimensions of the cleared area will be less than necessary. In addition, the creases and unnecessary bends of the mesh, which prevent the proper placement of cumulative ammunition, are not excluded.

The principle of defeat min. Figure Saper.isnet.ru
During the tests, it was found that a cumulative jet, even with a direct hit, cannot always destroy or disable a mine in the ground. With a direct hit of the jet into the fuse, the mine was neutralized. The defeat of the detonator provoked an explosion; the same happened with the minimum distance between the mine and the grid charge. The latter worked as a consignment note, destroying a mine by a shock wave and provoking an undermining of its charge. The damage to the hull and the main charge of the mine by a cumulative jet did not always lead to detonation.
According to available data, after the use of one ENS network, on the test minefield remained about 10-15 percent. explosive devices in combat readiness. This did not meet the requirements of the military, and therefore the project was repeatedly finalized in order to increase efficiency. As is now clear, BAE Systems, even after a long process of fine-tuning, was not able to fully resolve all issues and get rid of the identified deficiencies.
***
The development of a promising reactive demining system ESMC / ESMB Mongoose started almost a quarter of a century ago. The trial operation of this system has been going on for 15 years. With all this, the "Mongoose" has long had no chance of officially entering service and ensuring the re-equipment of all engineering units of the American army. In fact, all the problems of this system appeared at the beginning of the last decade, and then there were reasons for negative forecasts.
Over the years, the situation has not changed, and Mongoose has retained all its flaws. This system will not be able to exit trial operation, and in the future, manufactured samples will only be written off and recycled. A new original method of demining turned out to be too difficult for normal implementation and closed the road to the troops for an interesting model of engineering equipment.
Based on:
https://globalsecurity.org/
https://fas.org/
http://saper.isnet.ru/
FM 20-32. Mine / Contermine Operations. Headquarters, Department of the Army, Washington, DC, 2001.
Engineering Systems Handbook. Ft. Leonard Wood, Mo .: May 2001.
Information