Domestic battalion cannon 1915 — 1930
To clarify the situation it is necessary to make an excursion into history. For 80 years, there has been a dispute about Russia's readiness for the First World War. Most Soviet historians argued that the Russian army was badly armed. Despite this, in terms of the number of field guns, Russia was practically not inferior to Germany, significantly surpassing France and England, not to mention the USA and Italy. In terms of the quality of the guns, Russia was slightly inferior or not at all inferior to Germany, but it was superior to the rest of the states. The field guns used the latest systems made in 1902 — 1914, and more than 50% of the guns were generally made in 1910 — 1914 just before the war. By 1 in August 14 of the year the staff of the current artillery staffed by 100%, and the mobilization reserve was staffed by 98%. In the Russian artillery, such an ideal situation never existed, either before 14, or after it. Badly, the Russian artillery was preparing for a confrontation with Napoleon, not Kaiser. On the exercises marched infantry columns, galloping cavalry lava. Sometimes several cavalry divisions were moving in the same lava. Using such tactics of battle, one 76-millimeter battery, using shrapnel for fire, shot the cavalry regiment for half a minute. And our generals, at the suggestion of the French, at the end of the nineteenth century adopted the theory of a single projectile and a single cannon. The 76-mm 1900 and 1902 divisional guns became such a tool (the guns differed only by the gun mantle, therefore only the 76-mm gun of the 1902 model of the year will be considered further, especially since the 1900 guns of the year were stopped year), and the projectile - shrapnel. To bring this theory to the end prevented the Japanese war 1904-1904.
Russian generals made a small correction. In 1907, a high-explosive fragmentation shell was adopted for 76-mm divisional guns. In the divisional artillery, 122 millimeter howitzers of the 1909 and 1910 type were introduced. The 1909 — 1911 created corps artillery, which included 107-mm guns of the 1910 model of the year and 152-mm howitzers of the 1909 model and 1910's. In 1914, Russia entered the war with these weapons.
In Russia, battalion and company artillery did not happen spawn. The regimental artillery was introduced by Tsar Alexei Mikhailovich and completely abolished by Emperor Paul I. The siege artillery (high-powered tools) created under Ivan III was completely eliminated by Nicholas II. Over the twenty years of the reign of Nicholas II, the siege artillery did not receive a single new system. And in 1911, according to the “Highest order”, all the siege artillery regiments disbanded, and the weapons of the 1877 model of the year that were in their arsenal were deposited in the fortress. The formation of new parts of heavy artillery having a new material part was planned to start between the 17 and 21 years.
However, in 1914, a fast, maneuvering war did not work. Machine-gun fire and shrapnel were driven into the trenches of the army of the warring countries. A positional war has begun.
Already 1912 of the year, in the “Direction of the Field Artillery in Combat”, indicated that the artillery commander should “take measures to immediately destroy or silence any specified or noticed machine gun”.
It was quite easy to write this instruction on paper, and it was unclear how and how to actually fight the enemy’s machine-gun fire positions. In most cases, the 76 mm divisional gun was not suitable for this purpose. It was necessary to have a gun that could be transported, or even transferred to the battlefield by forces of one or two, a maximum of three soldiers, which would easily fit in a trench (trench) and could move there freely. Such a gun had to be constantly with the infantry in defense and offense, and, accordingly, to obey the company commander or battalion commander, and not the division commander. In this regard, such artillery was called a battalion or trench.
And in this situation the army was rescued by the fleet. After the Japanese war, several hundred single-barreled Hotchkis 47-millimeter cannons, which at that time had ceased to be an effective anti-mine defense weapon, were removed from the Russian ships. Back in 1907 — 1909, the maritime department tried to fuse the data weapon military department, however, received a decisive refusal. The situation with the outbreak of hostilities has changed dramatically.

Forces of military units or in small civilian workshops for Hotchkiss 47-millimeter cannons created wooden improvised wheel carriages. These guns participated in the battles in the first weeks of the war at Novogeorgievsk, Ivangorod and Warsaw. During the fighting, a serious lack of Hotchkiss 47-millimeter cannons was discovered - high ballistic qualities not required by battalion artillery. The gun with this ballistics had a strong recoil and a heavy barrel. As a result, the overall dimensions and overall weight of the launcher system were large, and the carriage was constantly breaking down.
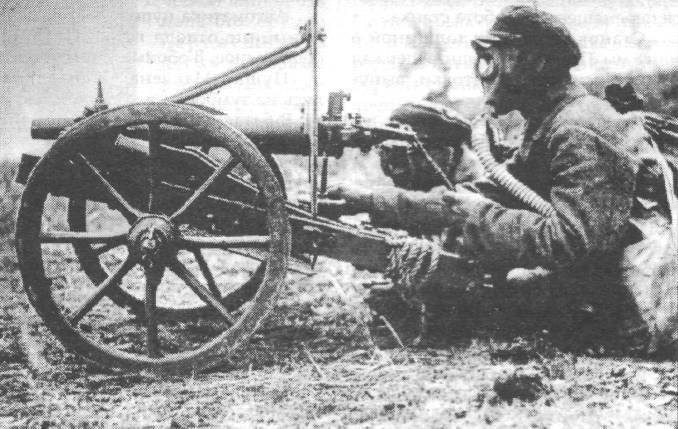

In the battalion artillery, they were forced to abandon Hotchkiss 47-millimeter cannon, although it showed itself well in fixed installations on riverboats, armored trains, and others.
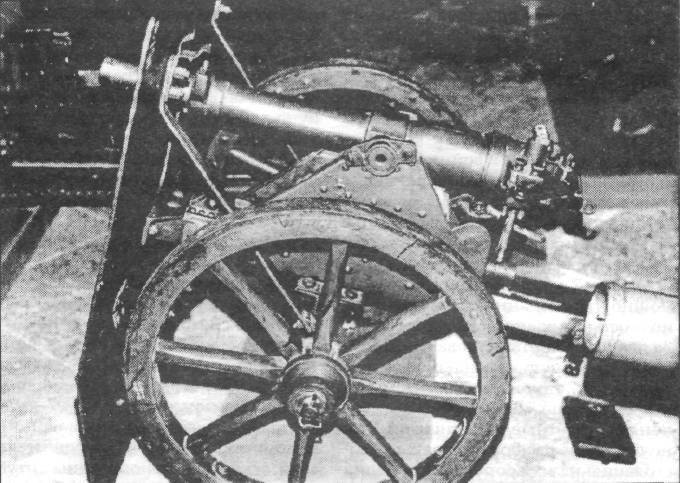
The first specially designed battalion cannon of domestic development was the 37-millimeter cannon of Rosenberg, who as a member of art. Committee, convinced the Grand Duke Sergei Mikhailovich chief of artillery to give him the task to design this system. Rosenberg went to the estate and through the month of 1,5 a project of the 37-mm gun was presented. Without detracting from the merits of Rosenberg, we note that the Soviet designers in the Second World War, while working in the barracks, such projects were made for 48 hours, and sometimes for one day.
As a barrel, Rosenberg used a 37-millimeter regular barrel, which served to shoot a coastal gun. The barrel construction, the muzzle copper ring, the trunnion steel ring and the copper knuckle screwed onto the barrel were included in the barrel construction. Two-stroke piston shutter.
The machine is single-bar, wooden, rigid (without wheel chocks). The recoil energy was partially extinguished with special rubber buffers.
On the lifting mechanism there was a screw fastened to the tide of the breech screwed into the right bed of the sled. There was no turning mechanism. For turning was carried out by moving the trunk of the machine.
The machine was equipped with a 6 or 8 millimeter shield. Moreover, the latter maintained a Mosin rifle bullet fired at full stop.
As you can see, the carriage was cheap, simple and could be made in a semi-handicraft workshop.
The system can be easily disassembled into two parts with a mass of 106,5 and 73,5 kilogram for a minute.
The weapon on the battlefield was transported by three hand calculation numbers. For the convenience of movement by means of parts, a small roller was attached to a trunk bar.
In winter, the system was installed on skis.
The gun in the campaign was transported:
- in the hull, when two shafts are attached directly to the mast;
- on a special front end, which was made on its own, for example, by removing the boiler from the camp kitchen;
- on the cart. As a rule, 3 paired carts of the 1884 model of the year were released to the infantry units for two guns, one gun was put in two cartridges in the 180 cartridges of cartridges, and on the third carriage there were cartridges of 360.
In the 1915, a prototype of the Rosenberg cannon, adopted under the name "37-mm gun of the 1915 model of the year", was tested. This name did not stick, therefore, in official papers and in parts, this gun continued to be called the Rosenberg 37-mm gun.
Rosenberg’s first cannons on the front appeared in the spring of 1916. The old trunks ceased to be enough and Obukhovsky Plant ordered XA from 22 in March 1916 of the year, ordered to make 37 barrels for 400-millimeter guns of Rosenberg’s 1919. By the end of 342, 58 stem was sent from the order from the factory, and the remaining 15 were ready for XNUMX percent.
By the beginning of 1917, the 137 cannons of Rosenberg were sent to the front, the 150 should have gone in the first half of the year. According to the plans of the command, each infantry regiment was to be equipped with a battery in the 4 trench guns. Accordingly, 687 guns were required for the 2748 regiments, and 144 guns were required for monthly replenishment.
Alas, these plans were not implemented due to the collapse of the army in February 1917 and the subsequent collapse of the military industry with some delay.
1916 units were shipped to Russia from the USA in 1917 — 218. McLean 37 millimeter cannon, also used as battalion artillery.
The automatic cannon implements the principle of exhaust gases. Power was supplied from the holder capacity 5 cartridges.
Maclean's gun was installed on the wheeled and tumbov carriage. In the battalion artillery, guns were used only on a hard wheeled carriage. Recoil devices were absent. Swivel and lifting mechanisms screw.
The gun in the stowed position was towed by a horse-drawn pod with a front end, in which 120 cartridges were placed. A shot from McLain's 37 mm gun is interchangeable with a shot from other 37 mm guns (Rosenberg, Hotchkiss and others).
During World War I, German tanks did not appear on the eastern front even once. At the same time, during the Civil War, France and England supplied the armies of Wrangel, Yudenich and Denikin with more than 130 tanks.
The tanks were first used in March 1919, the Denikin Volunteer Army. Tanks of the White Guards were a significant psychological weapon against parts of the unstable morally. However, the command of the whites used the tanks tactically illiterate, without organizing their interaction with the infantry and artillery. In this regard, tank attacks against militarily-minded units, mainly ended with the seizure or destruction of tanks. During the war, the Reds captured 83 tank white.
The civil war was the very maneuverable war for which Russian generals prepared. On the battlefield reigned supreme three inches (76-mm gun model 1902 of the year). The battalion and corps artillery was rarely used, heavy artillery was used more than once, if we disregard the heavy guns installed on riverboats and armored trains.
In the warehouses of three-inch was more than used by the Red Army. And 76-millimeter shells for the 1918 year, there were several tens of millions. They were not spent even during the Second World War.
Whether it is necessary to say that during the Civil War the three-inch was the main anti-tank tool. Usually, firing was conducted with a shrapnel projectile having a remote tube mounted on the impact. This was enough to penetrate the armor of any tank in service with the White Guards.
The Artillery Directorate (AU) of the Red Army in 1922 — 1924 carried out something like an inventory of artillery property, which was inherited after the Civil War of the Red Army. The property included the following 37-millimeter guns (trench and automatic anti-aircraft guns of Maxim, Vikkers and Maclena, which are fundamentally different types of guns, are not considered in this article): Rosenberg's 37-millimeter cannon has fallen into disrepair , about two dozen 37-millimeter French guns of Puteau having “native” gun carriages and 186 bodies of Gruzonverke 37-millimeter guns, which the Artillery Directorate decided to convert them into battalion guns i. There is no information about where the bodies of the guns of the German Gruzonverke factory came from.
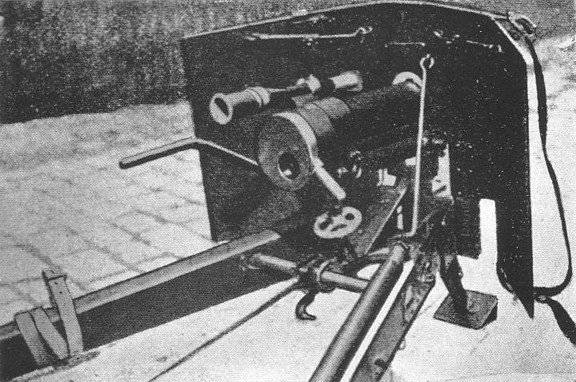
At the end of 1922, the Artillery Directorate ordered to urgently create a simple carriage designed to lay Barrels for Gruзonwerke. Such a carriage was developed by the famous Russian artilleryman Durlyakher.
AU 4 of August 1926 of the year prescribed that the Moscow plant Moststyazhart 186 Durlacher launches be made for Gryuzonwerke guns in Moscow. All 186 gun carriages the factory manufactured for 1 in October 1928, of which 102 was removed from the factory.
The barrel of the new system is similar to the barrel of Rosenberg, but the carriage had some fundamental differences. The barrel of the system consisted of a barrel tube, fastened with a barrel casing equipped with trunnions. A vertical wedge gate was placed in the housing. Opening and closing the shutter was carried out manually. Ballistic data and ammunition gun Grushonverke match gun Rosenberg.
In contrast to the Rosenberg machine, the Durlecher machine tool was made of iron, however, it was built according to the Durlecher machine scheme created at the end of the 19th century for heavy coastal and serf guns. The gun was rigidly connected with the upper machine, which rolled back along the bar of the lower machine after the shot. Inside the upper machine, the recoil devices were placed — a spring-loaded knurling rod and a hydraulic rollback brake. Screw lifting mechanism.
Wooden wheels had a metal tire. The weapon on the battlefield was moved by two calculation numbers. In the back of the beam there was a metal roller providing ease of movement by hand.
The gun in the stowed position was transported on a steam carriage, since carriage on wheels had a negative effect on the gun carriage and, especially, on its wheels.
If necessary, the system could be disassembled into the following parts: a bar with an axis, a shield and a pair of wheels - 107 kg; machine, having a lifting mechanism - 20 kg; barrel - 42 kg.
The Artillery Directorate in 1927 decided to replace the worn wooden machines of the Rosenberg 37-mm cannon with Durlacher iron-made machines. 10 January 1928, the first Rosenberg cannon mounted on the Durlächer machine was tested on the test site with a hundred shots. After testing, Durlächer’s carriage was slightly modified and July 1 of the year, Mastyazhart, received an order to produce Durlächer's modified 1928 carriages. By the middle of 160, the factory produced 1929 gun carriages.
By order of the Revolutionary Military Council in September 1928, the 37-mm Gryuzonverke and Rosenberg guns were temporarily put into service on the Durlächer carriages.
Simplifying the reality can be noted that the development of art. armament in the USSR in 1922 — 1941 was conducted by campaigns, and depended on the leadership hobbies.
The first campaign was the development of battalion cannons in 1923 — 1928. It was believed that with the help of battalion guns of caliber 37 — 65 of millimeters it is possible to successfully destroy tanks at distances up to 300 meters, which was quite fair for tanks and armored vehicles of the time. To fight with tanks should have been involved three-inch divisional and regimental artillery. At the beginning of the 1920-s, for lack of the best, 76-millimeter cannons of the 1902 model of the year were introduced. In this regard, in the 1923 — 1928 years in the Soviet Union efforts to create specials. TAP was not undertaken.
The caliber of the battalion guns ranged from 45 to 65 millimeters. The choice of calibers was not accidental for battalion artillery. It was decided to abandon the 37 mm guns, since the 37 mm fragmentation shell had a weak effect. In this regard, they decided to increase the caliber and have two shells for a new gun - a light armor-piercing projectile that was used to destroy tanks and a heavy fragmentation fragment designed to destroy machine guns and manpower of the enemy. In the warehouses of the Red Army there were a large number of 47-mm armor-piercing shells designed for the 47-mm guns of Hotchkiss. When grinding the leading corners of the shell, its caliber became equal to 45 millimeters. Thus, a caliber of 45 millimeters arose, which until 1917 was neither in the army nor in navy did not have.
Thus, it turned out that even before the creation of the 45-millimeter battalion cannon, there was an armor-piercing projectile, whose weight was 1,41 kilogram.
For battalion artillery, two 45-millimeter cannons of “low power” designed by F.F. Lender and A.A. Sokolov, as well as the duplex development of Lender, which consisted of an 45-millimeter cannon of "high power" and an 60-millimeter howitzer, and an 65-millimeter howitzer P.A. Durlahera.
60- and 65-millimeter howitzers were actually cannons, since their elevation angle was small. The only thing that brought them closer to howitzers was the small length of the barrel. Probably, the designers called them howitzers, based on certain service circumstances. All guns had unitary loading and were equipped with iron carriages with rollback along the axis of the bore. All guns in the traveling position were to be transported with the help of a pair of horses behind the wheel of a primitive front end.
The barrel for the experimental low-power 45-millimeter cannon of the Sokolov system was manufactured at the Bolshevik plant in the 1925 year, and the carriage was made at the 7 (Red Arsenal) plant in the 1926 year. The system was completed in 1927 year and immediately transferred for factory testing.
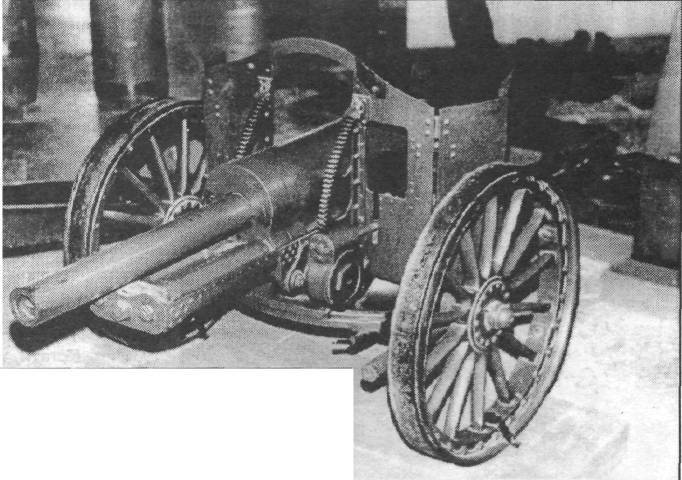
The barrel of Sokolov was fastened with a casing. Valve wedge vertical semi-automatic.
Nakatnik - spring, recoil brake - hydraulic. Lifting gear sector. A large angle of horizontal guidance equal to 48 ° was provided by sliding beds. In fact, it was the first domestic artillery system with sliding beds.
The system was intended for firing from the wheels. The wooden wheels had no suspension. On the battlefield, two or three calculation numbers easily rolled over the cannon. If necessary, the system is easily disassembled into seven parts and transferred to human bags.
In addition to the towed version of the Sokolov cannon, a self-propelled version called the Arsenalets-45 was developed. The self-propelled artillery installation on the design of the chassis was called the installation Karataeva. Arsenalts-45 had a super-original design and had no analogues in other countries. It was a tracked self-propelled artillery installation - midget. The length of the ACS was about 2000 mm, height 1000 mm, and the width of the entire 800 mm. The swinging part of the gun Sokolov changed slightly. Reservation installation consisted only of the front sheet. The self-propelled gun was installed horizontal four-stroke engine power 12 hp The tank capacity was 10 l., Which was enough for 3,5 hours of travel at a speed of 5 kilometers. The total mass of the installation - 500 kilogram. Ammunition - 50 cartridges.
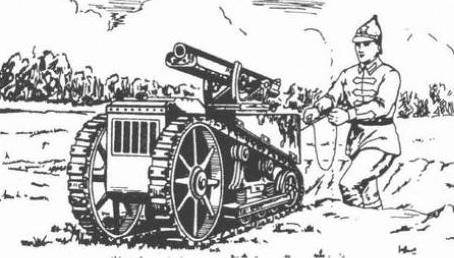
Installation on the battlefield was to be controlled by the Red Army, going from behind and move by self-propelled. On the march self-propelled installation was transported in the back of a truck.
The order for the manufacture of self-propelled artillery installation issued in 1923 year. The chassis and the swinging part of the guns were manufactured by plant number 7. The installation was completed in August 1928 of the year, and in September began factory testing.
During the tests, the ACS overcame up to 15 °, and also maintained 8 ° roll. At the same time, the passability of the ACS was very low, and often the engine was gloh. The system was vulnerable to enemy fire.
In 1929, they tried to refine the self-propelled artillery gun, however, it ended unsuccessfully. Then the Arsenalts chassis was thrown into the plant shed No. 7, and the trunk and sled in an experimental workshop. AU Red Army in May 1930 of the year transferred materials on the manufacture and testing of the system to the OGPU. There is no information about the further fate of Arsenalts.
The main competitor of the gun Sokolov was 45-millimeter cannon low power system Lender. Design began in 1923 year at AKB Kosartop. September 25 1925 of the year with the "Red Putilovts" signed a contract for the manufacture of low-power 45-millimeter cannon Lender. The completion date was set to 10 December 1926 of the year. But since Lender fell ill, the work was delayed, and the gun was actually finished at the beginning of 1927.
According to the project, the main method of firing was fire from the rollers, but if necessary, the fire could be fired from the walking wooden wheels. There was no suspension.
Designed two versions of the gun - folding and folding. In the latter version, the gun could be disassembled into 5 parts, for carrying on human bags.
On the battlefield, two or three calculation numbers were rolled on the wheels on wheels or on rollers. In the stowed position, the system was transported behind the wheel end of a pair of horses. In semi-assembled form, the cannon was transported on a tavern-carriage.
Under the leadership of Lender, in the Kosartop battery, in parallel with the development of a low-power 45-millimeter cannon, a battalion duplex was installed, mounted on a unified carriage on which a high-power 45-millimeter cannon or a 60-mm howitzer could fit. The trunks of the systems were pipe and casing. In this case, the weight of the bodies and the external dimensions of the casing of both guns were the same, which made it possible to impose them on the same sled. Both guns had vertical wedge paddles with 1 / 4 automatics. Some documents erroneously indicate semi-automatic shutters.
The spring chain, the rollback hydraulic brake, the cylinders of recoil devices were placed in the cradle under the barrel, and when the rollback was fixed. Since the swinging part was unbalanced, a balancing spring mechanism was introduced. Lifting gear sector. Combat axle crankshaft, sliding bed.
The main method of firing both systems was shooting from the rollers, but it was possible to fire from the walking wheels. Interestingly, the walking wheels consisted of a metal circular ring and a metal roller. During the transition from the rollers to the wheels on the rollers they wore circular rings.
Both systems on the skating rinks had a shield, but the shield was not worn with the traveling wheels.
For carrying people in packs, both systems were disassembled into eight parts. In the stowed position and on the battlefield, the movement of the system was similar to Lender’s 45 millimeter cannon.
65-millimeter howitzer Durlyahera produced 1925 — 1926 of the year at the factory number 8 (named. Kalinin, Podlipki).
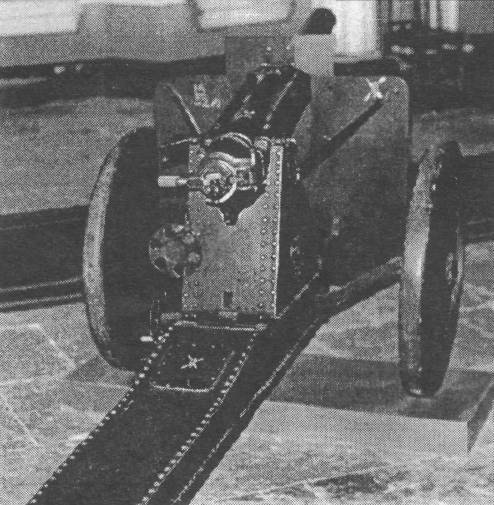
Howitzer barrel - barrel and casing. Piston valve. Knuckle hydropneumatic, hydraulic recoil brake. Single-gang carriage. Shooting was conducted from the wheels, which were both combat and marching, the system was not separable. Metal wheels with rubber tires. There was no suspension. The system in a combat position was transported by the forces of calculation, in the marching position - by two horses behind a wheeled front end.
In the period from 1927 to 1930, numerous individual and comparative tests of battalion guns were conducted. For example, 29-31 March 28 year NIAP comparative trials 45-millimeter cannons low power Lender and Sokolova, 45-millimeter high-powered guns Lender, 60-millimeter howitzer Lander, 65-millimeter howitzer Durlyahera, 37-mm cannon Puteaux, and also two 76 millimeter recoilless (dynamo-reactive) guns. Although the latest samples showed worse results compared to the classical tools (accuracy, rate of fire, and so on), however, Tukhachevsky, the test leader, liked the PDD most of all. The “brilliant theoretician” on this occasion wrote a historical resolution: “For further experiments on AKUKS, it is necessary to refine the PD in order to destroy the unmasking. End date of completion 1 August 1928 of the year. Raise the question of combining anti-aircraft and anti-tank guns.
In Russia, they always loved martyrs and fools. Tukhachevsky was lucky in both cases, but practically no one knows what damage the whims of the Soviet Union’s defense capability and attempts to combine the anti-aircraft gun with an anti-tank or divisional one caused damage.
All battalion artillery systems caliber 45-65 millimeters fired armor-piercing, fragmentation shells and canister. The “Bolshevik” plant also produced a series of “modular” (over-caliber) mines - 150 pieces weighing 8 a kilogram for 45-mm guns and 50 pieces for 60-mm howitzers. However, the Artillery Directorate, for unclear reasons, refused to adopt above-caliber mines. It must be recalled here that during the Great Patriotic War the Germans on the eastern front rather widely used over-caliber mines (shells) both cumulative (anti-tank) of 37-millimeter cannons, and high-explosive heavy of 75- and 150-millimeter infantry guns.
In general, the tests showed that the 45 — 65-millimeter guns that passed the tests mainly corresponded to the tactical and technical tasks of the first half of the 20-s, but for the 30-s they were rather weak systems, since they could only fight with lightly armored vehicles (up to 15 millimeters) and then at short distances. They could not carry out mounted fires. If the guns on the battlefield were mobile enough, the lack of suspension and the weakness of the carriages precluded movement using mechanical traction, so there were only a couple of horses moving in steps.
All this and the unhealthy fascination of Tukhachevsky with recoilless guns was the reason that they adopted only the 45-millimeter cannon of low power of the Lender system, which was given the official name "45-mm battalion howitzer of the 1929 model of the year". By the beginning of 1930, the AU issued an order for 130 45-millimeter battalion howitzers of the 1929 model of the year, of which 50 plant No. 8 and 80 plant Red Putilovets. Moreover, at plant number 8, it is quite common for foreign guns (Hotchkiss, Bolshevik, Rheinmetall, Maxim and others to assign their own factory index). Thus, the Lender system also received the designation "12-K" (the letter "K" denotes the Kalinin plant). In total, 31-32 passed about a hundred 45-mm howitzers.
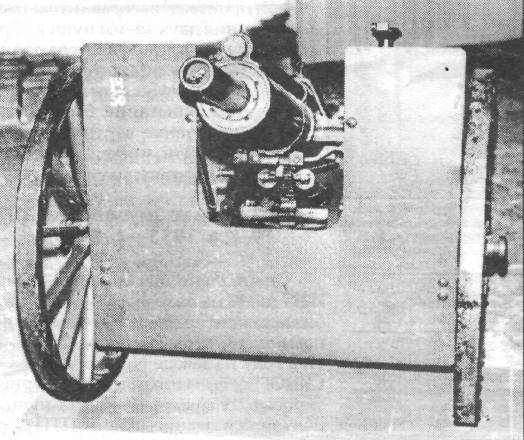
Despite the small number of manufactured 45-mm howitzers, they participated in the Second World War. In 1942, they even released new firing tables for them.

Information