Nuclear submarines - carriers of cruise missiles: reality and prospects
The first cruise missiles designed to be placed on submarines were the P-5 and P-6 missiles, developed in the late fifties and early sixties. The missiles were housed in airtight containers and intended to launch from a surface position.
Subsequently, this direction received significant development, as a result of which, at the time of the collapse of the USSR, the submarine fleet had such highly efficient anti-ship missiles as Granit P-700, for hitting surface ships, and C-10 Granat strategic cruise missiles with nuclear war part, to destroy ground targets.
The main carriers of anti-ship missiles P-700 "Granit" are currently nuclear-powered submarines with cruise missiles (SSGN) of the 949A project. Each of these submarines carries 24 rockets. Due to the impressive dimensions of the Granit missiles, the SSGNs of the 949A project have an underwater displacement of 24 000 tons, which is comparable to the displacement of strategic missile carriers with ballistic missiles.
By the time of the collapse of the USSR, the development of new missiles, such as the P-800 Onyx supersonic anti-ship missile (3М55) and the Caliber missile family, including the 3М-54 and КР 3М-14 missiles for the destruction of ground forces, were close to completion. . Also in the complex "Caliber" includes rocket-torpedoes (RT) 91Р1.
A distinctive feature of the new missiles was that they were initially considered for use from different types of carriers. Modifications of the PKR / KR / RT "Caliber" are placed on surface ships, submarines and ground carriers. Rockets P-800 "Onyx" are also adapted for aviation carriers. The smaller damaging capabilities of these types of missiles, due to the reduction in their dimensions, compared to the P-700 missiles, should be compensated for by the possibility of placing a larger number of missiles on carriers.
Also, the press is actively discussing the appearance in the near future in service of the hypersonic 3M22 Zircon rocket. In the case of its appearance, and compliance with the real characteristics of the declared, the fleet can get effective weapon for the destruction of surface ships of the enemy.
Termination of the Treaty on Intermediate-Range and Shorter-Range (DRDM) can lead to the emergence of other types of missiles. Despite the fact that the action of the INF squadron on the fleet did not extend, its cancellation may intensify the development of ballistic missiles with a range of several thousand kilometers, and their further “snagging” can lead to the appearance in the Russian Navy of analogs of the Chinese ballistic missile DF-21D designed to destroy surface ships.
Since the Granit P-700 missiles are no longer being produced, their shelf lives are coming to an end, and the submarines of the 949A project have not yet exhausted their resources, it was decided to re-equip the SSGNs of the 949А project to accommodate Onyx and KR family "Caliber". Each upgraded submarine of the 800AM project will receive launchers for 949, to accommodate the specified types of missiles.
It is not known for certain how many SSGNs of the 949А project will be upgraded to the 949AM project, according to one data these will be four submarines, according to others all eight units that are in service with the Russian Navy.
There are polar points of view, according to which modern anti-ship missiles are invulnerable weapons that have transformed aircraft carriers into floating coffins, and vice versa that anti-ship missiles are unable to penetrate the aircraft carrier strike group (AUG) - most of the missiles will be destroyed by air defense, and the rest will lose their targets because of for interference.
Most likely the truth lies somewhere in the middle. The question is how much RCC is needed to destroy a group of surface ships. Agree that it is one thing to release the 24 "Granite" on the ship junction of Japan or Turkey, and another - on the full-fledged AUG of the US Navy. In addition, it is doubtful that the leadership of the Soviet Navy was so incompetent that it made a serious bet on rocket weapons.
Submarines, especially nuclear ones, can be considered one of the most effective carriers of anti-ship missiles. The maximum range of use of modern anti-ship missiles is about five hundred kilometers. For attacking the anti-ship missiles, for example, on an aircraft carrier strike group, it was supposed to concentrate significant surface forces or direct an air group as part of several regiments of the Tu-22М3. Such large groups can be detected by the enemy at a considerable distance, after which the latter will apply active countermeasures — he will lift deck-based aircraft into the air, turn on air defense radars, change course.
In turn, anti-submarine defense (PLO) at the turn of about five hundred kilometers is much less effective. The carrier group is accompanied by one or two multi-purpose hunter submarines. With all the desire, they will not be able to control the area over 785 000 square kilometers. If the actual range of the P-800 missiles is 600 km, then it is necessary to monitor the water area of over one million square kilometers.
Anti-submarine helicopters at such a range do not work, their line is 20-30 kilometers. Deck planes PLO carry out anti-submarine defense at a distance of about 200 kilometers. Thus, the detection of a submarine at the turn of 500-600 kilometers can only be carried out by P-8A “Poseidon” PLO aircraft based on ground airfields.
Due to the difficulty of detecting enemy submarines at such a distance, the main means of countering anti-ship missiles surface ships are anti-aircraft defenses that ensure the physical destruction of the incoming missiles, and jammers designed to deceive missile guidance systems.

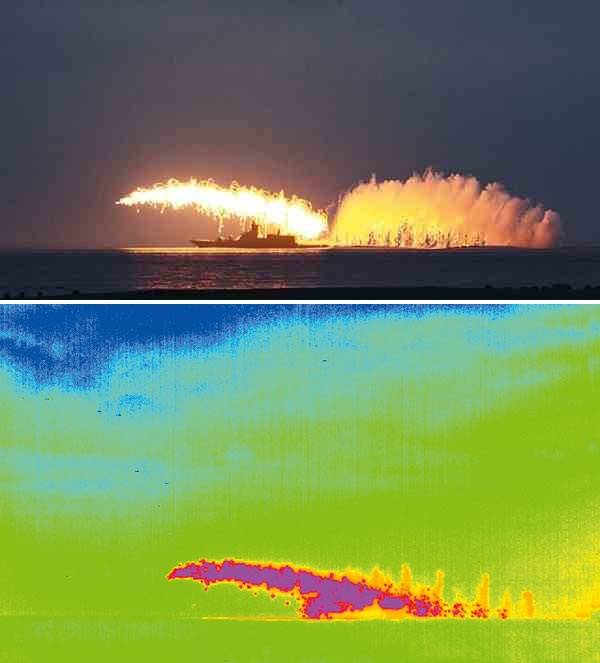
It should be noted that at present the capabilities of air defense have increased markedly. This is due to the adoption of anti-aircraft guided missiles (SAM) with an active radar homing head (ARGSN). The presence of such missiles in combination with the possibility of issuing target designation by long-range radar detection aircraft (ARLO) and fighter aircraft, allows air defense systems of surface ships to fire at low-flying anti-ship missiles, which are below the visibility level of the shipborne radar. This significantly increases the chances of AUG to reflect the impact. Gas-dynamic control is also being actively implemented, allowing the missile defense system to maneuver with overloads over 60g, which increases the probability of hitting high-speed maneuvering anti-ship missiles.
In turn, anti-ship missile measures are applied to reduce visibility, reducing the detection range of surface ships by DRLO and radar aircraft. According to unconfirmed data, own anti-jamming tools can also be placed on the anti-ship missiles, designed to disrupt the enemy’s anti-aircraft missiles. Another way to increase the likelihood of an enemy air defense breakthrough is to increase the speed of the missile. This method, presumably implemented in the Zircon rocket, allows to reduce to a minimum the time allotted to the ship to repel an attack. In general, the competition of the sword and shield continues.
The main problem that impedes the use of long-range CRP, is the issuance of target designation. For this, the MKRTS Legend system was deployed in the USSR — a system of global satellite-based maritime space reconnaissance and target designation. The MKRTS Legend system included passive US-P and active US-A reconnaissance satellites. US – P passive reconnaissance satellites are designed for electronic reconnaissance, the US-A active reconnaissance satellites included a radar capable of scanning the surface from an orbit of 270 km. This system is currently decommissioned.
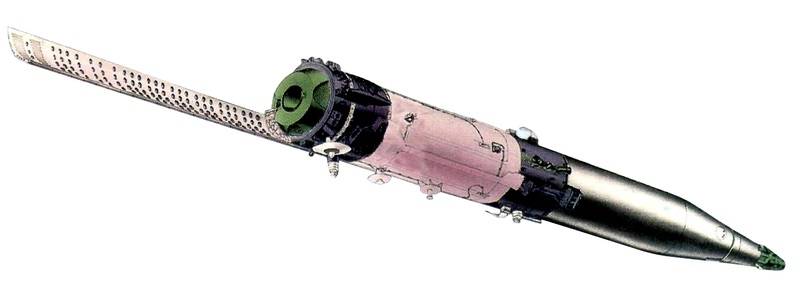
It should be noted that the altitude of the 270 km orbit makes the MKRTS Legend satellites vulnerable to modern US and Chinese anti-satellite weapons.
In exchange for MKRTS Legend, the Liana space reconnaissance system is being commissioned, which includes the Lotos-S (14F145) and Pion-NKS (14F139) satellites. The Lotos-S satellites are designed for passive radio intelligence, and the Pion-NKS for active radar reconnaissance. Permission "Pion-NKS" is about three meters, which allows you to detect ships, made with the use of technologies reduce visibility.

According to various data, the orbit of the satellites of the Liana system is at an altitude from 500 to 1000 km. If so, they can be destroyed by SM-3 Block IIA missiles, with a hit zone that is up to 1500 km high. The SM-3 rockets and launch vehicles are available in the United States in significant numbers, and the SM-3 rocket cost is likely to be lower than the Legend satellite MKRTS system and the cost of putting it into orbit. On the other hand, it is necessary to take into account that only the USA and, to a lesser extent, the PRC, have such anti-satellite capabilities. In other countries, the possibilities for the destruction of objects in space are absent or limited. In addition, it is possible that Russian military satellites can counteract the destruction by jamming and / or adjusting the orbit.
In addition to satellite intelligence, reconnaissance aircraft AUG in the USSR were used by reconnaissance aircraft Tu-95РЦ and Tu-16Р. At the moment, these planes are decommissioned. In addition, the huge effective area of dispersion (EPR) of these planes made it easy for NATO aircraft to detect them. In the event of a conflict, all the crews would likely be suicide bombers.
What opportunities for delivering massive PKP strikes will Russia have in the future? Unfortunately, the prospects are foggy. After the last SSGN 949AM’s withdrawal from the Navy, the maximum number of anti-ship missiles (32 missiles) will be carried by multipurpose nuclear submarines (MCPNP) of the 885 Severodvinsk project. These boats are planned to release only seven units in two fleets.
There is no reliable data for the Husky project. According to one information, this type of submarines will be carried out in different versions - a multi-purpose hunter boat, a carrier of cruise missiles, and even a boat carrier of ballistic missiles. On the other hand, it will be the YKSSP of the “Ash” type, but at a new technical level. In any case, so far there is no information that a SSGN will be created on the 70-100-150 CR / PCR base on the Husky.
The surface fleet has even less possibilities. In spite of the fact that almost pleasure boats are equipped with launching boats for CR / PKR, their total number is small. To organize a massive attack, the PCR will have to collect a whole “mosquito pack”. Seaworthiness and cruising range of corvettes, rocket boats and diesel submarines are limited.
The possibilities of aviation are bigger, but not by much. Each departure of a strategic bomber-missile carrier is monitored by NATO forces, what can we say about the departure of a dozen bomber bomber bomber simultaneously. In the case of the outbreak of hostilities, there is a chance that they will be intercepted before reaching the line of launching the missiles.
Do you need a SSGN for Russia? If we consider the need to counter the CBG or AUG of developed countries, then yes. The modern echeloned defense of the naval compound will be difficult to break through with a volley at thirty, and possibly at sixty PKR. In addition, given the shortage of multi-purpose SSNs, all YCSSLs of the Yasen type will most likely be involved in the task of covering strategic missile carriers. Prospects for the Husky project are vague, especially given the habits of our industry to shift deadlines.
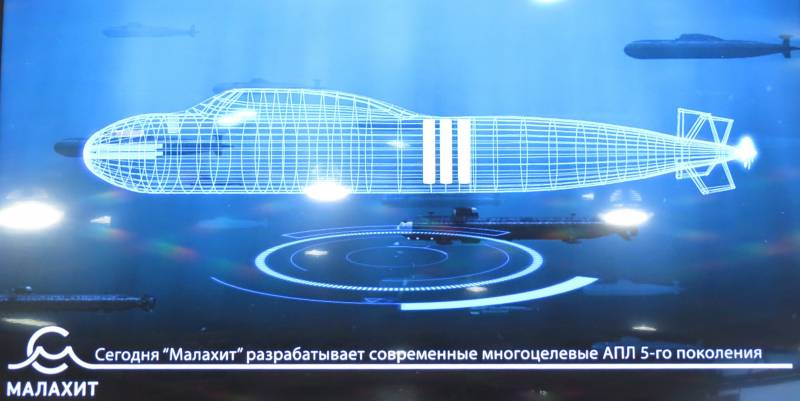
What can be offered in this situation? Implement a new generation of SSGNs based on SSBNs of the Borey type 955A project, and possibly also of the 955B project. An example of processing SSBNs in SSGNs is available - they are American SSBNs / SSGNs of the Ohio type, and they were reequipped from ready-made boats. Despite the fact that the number of carriers of the Kyrgyz Republic from the US fleet is greater than that of all the fleets of other countries combined, they considered such a modernization expedient, and they actively use these boats.
The SSGN is not required to conduct an underwater war with enemy's submarines or to attack surface ships with torpedoes (although it can), therefore the 955А / B project looks optimal for creating a replacement for SSGN of the 949А / AM project.
In the coming years, the construction of a series of eight SSBMs of the Borey type will be completed (with the possibility of increasing the series by another two units). After that, on the liberated stocks, the SSGN can be laid on the basis of the 955А / B project. Spent during the construction of SSBN technology will allow to implement the project in the shortest possible time. The cost of the SSGN should not exceed the cost of the Borey-type SSBNs, and it may be reduced by increasing the series (most of the equipment will be unified with SSBNs). Even now, the 955A SSBN is cheaper than the 885 MTsPL project, so building four SSGNs does not greatly affect the construction program of multi-purpose SSNs (you still need to build many more).
Ammunition of the KR / PKR of a single SSGN based on the 955А / B project is expected to be on the order of the 100-120 КР / КР in the vertical start installations (УПП), i.e. one and a half times more than in the 949AM project, with the same displacement.
The required number of SSGNs for the Russian Navy can be estimated at four to eight units (two to four for the Northern Fleet and the Pacific Fleet). Thus, there will be a smooth transition from the SSGN of the 949А / 949AM project to the SSGN based on the 955А / B project. It should also be noted that the 949 / 949А project was an uncompromising fighter with AUG, while the capabilities of the 949А and SSGN-based SSGNs will be much wider.
What tasks can solve the SSGN as part of the Russian fleet?
1. Destruction of warships and enemy ships operating as part of formations and groups, as well as singly. The first and obvious purpose is the fight against AUG. A volley in the 200-240 RCC with two SSGNs will "break through" any air defense. To ensure a similar launch density without a SSGN, all seven “Ash trees” from two fleets will be required. The surface fleet, without air cover, is unlikely to be allowed on the range of RCC launch to AUG. If the Zirkon PKR turns out to be as good as they are told about (8 Makhov on the entire flight path), then it is possible that a single SSGN will be enough to destroy the AUG.
2. Fight against KUG. Other countries' fleets that have weaker fleet support capabilities than the United States are much more vulnerable to a massive RCC attack, since will not be able to provide over-the-horizon guidance on anti-ship missiles. In other words, fleets of countries such as Japan, Turkey, and Norway can be shot by the anti-ship missiles from a long distance with almost no punishment (with target designation, to which we return later).
3. Violation of sea and ocean communications of the enemy. Destruction of convoys going from the USA to Europe. The attack of convoys by torpedoes will always be fraught with the risk of the loss of submarines from the enemy ASW forces. At the same time, the air defense of the convoys cannot be compared with the air defense of the CUG / AUG, therefore, in the presence of target designation, the SSGN will shoot ships from the convoys as ducks in the dash.
4. Destruction of important military and economic objects of the enemy on the coast and in the depths of its territory. Massive strikes of the Kyrgyz Republic on objects in the territory of the enemy or its military bases in other countries. A volley in 200-240 KR can cause significant damage to the economy of a developed state. Administrative institutions, power stations, bridges, large factories, and so on can be destroyed.
If the CD can be equipped with electromagnetic warheads (and they are real and effective), then striking them at major cities and industrial facilities of the enemy can cause a collapse of the enemy’s economy.
For the military, this means diverting additional forces to protect the bases, a constant stress effect on the personnel.
Another scenario is that the regime has changed in the former “friendly” state, and the loans issued earlier by the Russian Federation have decided not to return. By inflicting periodic strikes by the Kyrgyz Republic on the debtor’s government facilities, it is possible to put a new government before a choice - to pay off the loan, or to manage the country from the bunker. The cost of missiles included in the bill. Why? Israel is bombing neighbors, and nothing, we can also try to do so.
5. The implementation of mine productions. Modern sea mines, designed for use of torpedo tubes from 533 mm, may well be adapted to be placed in the CIP by two pieces per launcher. Thus, a mine attack of one SSGN can be 200-240 min. Close the straits, block the ships in the bays, mine ambushes on the way of the convoys.
6. The landing of reconnaissance and sabotage groups on the coast of the enemy. This task is being solved by modernized Ohio-type SSGNs. With appropriate equipment, it can be solved and SSGN based on the project 955А / B.
7. And finally, in the event of further aggravation of relations with the United States, and the breach of agreements on the limitation of nuclear weapons, the SSGNL can be armed with long-range defense and nuclear weapons. Accordingly, Russia's strategic arsenal can quickly be increased by 400-800 (480-960) warheads.
The task “Ensuring the deployment and combat stability of strategic missile submarines” will also be indirectly addressed. Almost identical appearance and acoustic signatures of the SSGN and Borey-type SSBNs can mislead the enemy's forces by redirecting them to tracking SSGNs instead of SSBNs.
Returning to the vital issue of targeting.
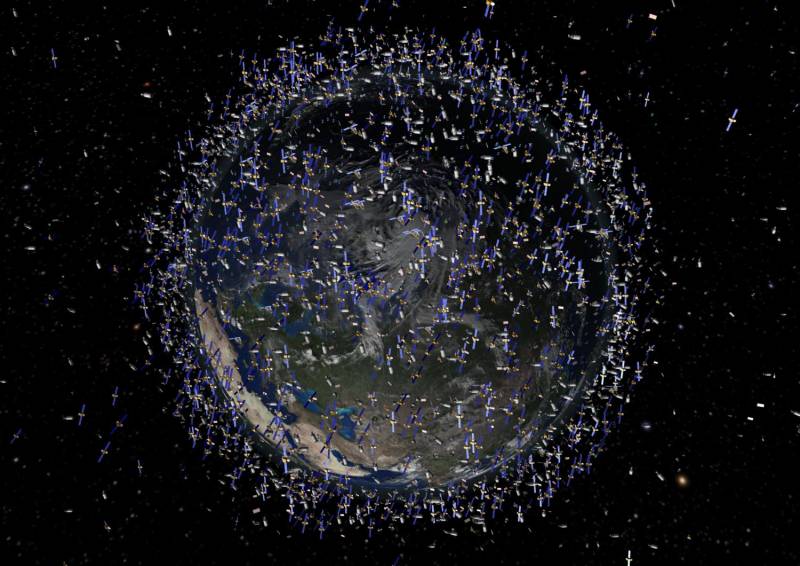
Firstly, it is certainly satellites. The development of the reconnaissance satellite constellation is important in the interests of all types of armed forces.
Protection of satellite constellation from destruction can be solved in several ways.
1. Equipping satellites with defensive systems - traps, jamming devices, advanced means of evasion / orbit correction. Perhaps this has already been implemented.
2. Increasing the orbit of satellites in order to minimize the probability of their being hit by “cheap” means of missile defense.
3. Development and deployment of low-orbit groups from compact, cheap but numerous satellites, following the example of satellite Internet projects. Output them bundles of 5-10-20 devices. Each individual satellite will yield to its “big” counterparts, but in the group they will solve problems no less effectively. The goal is to make the destruction of the satellite more expensive than bringing a new one. It will also allow the satellite constellation to be more resilient to the failure of one or more satellites.
There should also be a reserve of satellites to ensure the possibility of rapid replenishment of the orbital group. They can be placed in advance in the mines of ballistic missiles or in the mines of the SSBNs in a state of high readiness for launch.
Regardless of the reality of the creation of the SSGN, the development of space intelligence is of paramount importance for all the armed forces of Russia.
The second effective option for reconnaissance and target designation is the creation of long-range reconnaissance unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) by analogy with the Triton MC-4C UAV.
UAV MC-4C Triton is designed to collect information, surveillance and intelligence. Flight radius is about 3700 km, flight altitude more than 18 km, autonomy 24 h. During one flight, it is able to control an area of 7 million square kilometers.
Russia has a significant lag in the part of the UAV, however, promising models are gradually emerging. In particular, the heavy-class Altair UAV, developed by JSC NPO OKB named after MP. Simonov. Flight range will be 10 000 km, ceiling 12 000 m. Flight duration 48 hours.
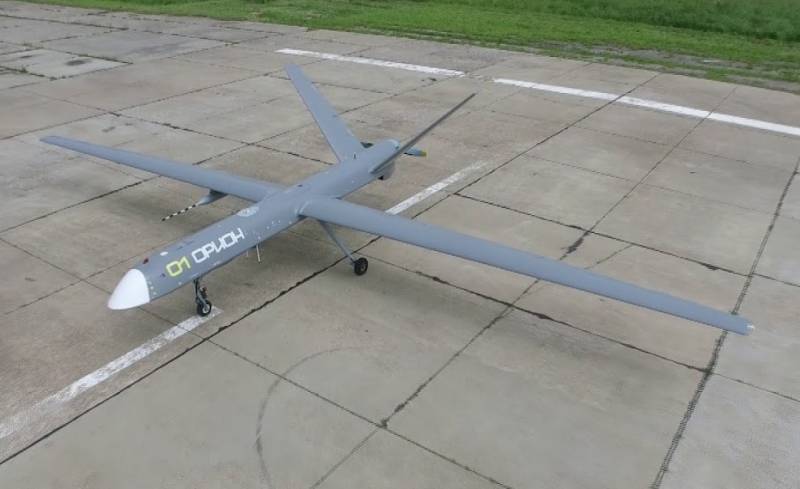
Another interesting model is the Orion UAV, developed by Kronstadt (AFK Sistema). The radius of the flight will be 250 km, the ceiling 7500 m. The duration of the flight 24 hours.
It should be noted that an important problem of all Russian UAVs is the lack of high-speed satellite communications, which often limits the flight range and capabilities of the UAV for the transfer of reconnaissance data.
Summarizing, we can say that the presence in the Russian Navy of four or eight SSGNs with effective missile weapons, with a developed target designation system, will create a threat to any surface fleet of a potential enemy, any military base around the world. And this threat cannot be ignored, since in this case, no actions to inflict non-nuclear strikes on the territory of the Russian Federation, destroy ships under the flag of the Russian Federation or block the straits are guaranteed not to go unpunished.












Information