Under barrel grenade launcher TKB-0121
Recall that in 1963, an employee of the Tula Central Design and Research Bureau of Sports and Hunting Weapons (TsKIB SOO) V.V. Rebrikov proposed the original construction of a mortar for throwing fragmentation grenades, which was fixed directly under the barrel of the AKM assault rifle. In 1966, this proposal received the support of the Main Missile-Artillery Directorate, as a result of which experimental design work was launched with the Iskra cipher.
The TKB-048 / Iskra, an experienced grenade launcher with a fragmentation-cumulative TKB-40 / OKV-047 fragmentation grenade, was put to the test at the end of the decade, and showed an ambiguous result. For technical and administrative reasons, it was not taken into service, and the fate of the entire direction of grenade launchers was in doubt.
Despite the failure of JAG-40, the staff of TsKIB SOO maintained an interest in a promising concept. In the near future, this interest led to the emergence of a new project, developed taking into account the developments and experience of Iskra. V.N. Telesh proposed a new version of a grenade launcher with a different ammunition, devoid of the shortcomings of TKB-048. Such a project of infantry weapons received the working designation TKB-0121. As it turned out in the future, it was a purely experimental development, which did not have to get into the troops. For this reason, no other designations were assigned to it according to the type of the GRAU index, etc.
The previous “Spark” had several noticeable problems of a constructive and ergonomic nature. However, some ideas of this project have been successful and could be used to create advanced weapons. At the same time, the new TKB-0121 was supposed to differ most seriously from TKB-048. In particular, to improve ergonomics, it was decided to abandon the pistol layout and arrange all weapons devices in one line.
The TKB-0121 was a single-shot weapon for a special shot with a fragmentation grenade using a self-propelled loader and trigger mechanism. The project again used the idea of a grenade with a flying sleeve, which made it easier to work with a grenade launcher and speed up its reloading. With the help of a special bracket, the grenade launcher was planned to be suspended on an AKM or AK-74 type automatic weapon. Considering the experience of the previous project, the designers of TsKIB SOO took into account the risks of negative impact of recoil on the weapon design.
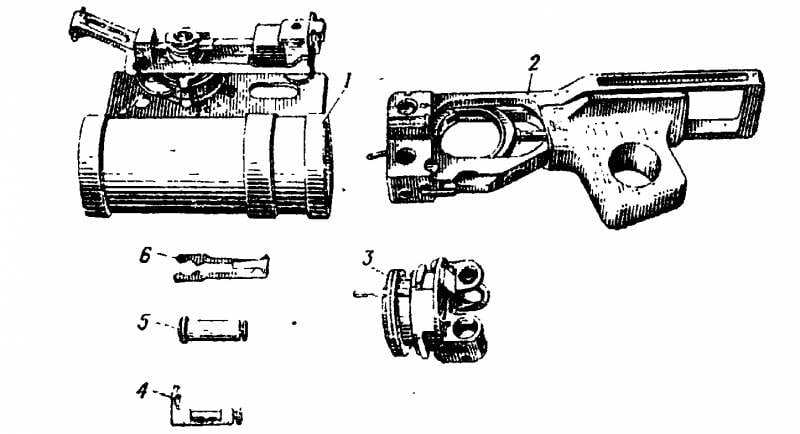
The front part of the grenade launcher was a block formed by the barrel and bracket for mounting on the weapon. Actually, the barrel was made in the form of a tubular part with a threaded internal bore caliber 40 mm. The length of the barrel - about 230-240 mm. Apparently, the barrel for the experienced TKB-0121 was machined from a polygonal blank, as a result of which there was a pair of faceted belts of different widths on its cylindrical outer surface. They were used to connect with the bracket.
Behind the breech was placed in the barrel breech, made in the form of a separate removable parts. It was a low glass, on the bottom of which there were fastenings for connection with other weapons devices. So, it provided for mounting parts for the firing mechanism. In the center of the bottom there was a hole for a spring-loaded drummer, responsible for the ignition of the propellant charge.
The grenade launcher's trigger mechanism was placed in a separate rectangular case fixed behind the breech. On the top and bottom of the case there were bevels for weight reduction. In the front of such a body, holes were made for the pins fastening the weapon. In the same place on the left side of the movable flag located fuse. Immediately behind him was a large window, inside which was located the trigger. Instead of the rear wall in the USM case, a second bracket was mounted for mounting on the machine.
The TKB-0121 grenade launcher got a simple, but curious hammer-type firing mechanism that worked on the principle of a pick-up when pressing the trigger. In front of the case was a swinging trigger with a mainspring, connected with a moving trigger with a hook. At the time of the shot the trigger had to interact with the drummer and carry out the shot. The fuse box blocked the movement of the trigger and did not allow to make a shot.
In the new project TsKIB SOO provided for the use of the original mounting system on the weapon, taking into account the errors of the Iskra ROC. With the help of bolts, a long U-shaped bracket was fastened on the corbel rims. In its side surfaces there were holes for weight reduction. During installation on the machine, the bracket had to be put on the trunk from below and fixed in place with a set of stops. The bracket was placed under the gas block of the machine, directly in front of the forearm. Any modifications of the serial machines for the use of TKB-0121 were not required.
The main arm of the grenade launcher was supplemented with a rear frame, the task of which was to protect the wooden forearm from impacts and damage. Behind to the case of USM attached milled block of complex shape, formed by a pair of basic elements. On top of it was placed a symmetrical pentagonal frame with a central window. On the back side of this frame set a small rubber pad. This structural element had to rest on the forearm and receiver of the machine gun from below, and the pad prevented scratches or chips from impact.
At the same time with the frame there was a vertical element, on which a handle was fastened to the bottom with the help of rivets. It was made in the form of a rectangular part with rounded edges and a beveled upper surface. Apparently, such an inconvenient design of the handle was temporary and was not intended for use in subsequent versions of the project.
In front of the left of the bracket placed a sight, designed for shooting with large elevation angles. The sight included a fixed plate with markings for firing at different distances. In connection with the experimental role of the product, the sight had the conditional marks “1”, “2” and “3” instead of a full scale with distances. On the support screw was installed swinging bar with front sight and entirely on the front and rear parts. On the bar was the simplest cam mechanism that controlled the position of the front sight. With its help, an amendment to the derivation was automatically made in accordance with the range of the shot.
The total length of the TKB-0121 grenade launcher reached 350 mm. The presence of a large bracket and side sight increased the diameter of the weapon. However, the linear layout of the product allowed to keep dimensions at an acceptable level. Weight - no more than 1,5-1,7 kg. The initial speed of a grenade at a shot could reach 75-80 m / s. Due to this, depending on the angle of elevation, it was possible to attack targets at distances to 350-400 m.
The grenade launcher was supposed to use new grenades equipped with so-called. flying away sleeve. The ammunition had a metal case with a rounded head, inside which were placed the fuse and explosive charge. At the bottom of the sleeve it was proposed to install a cylindrical sleeve. In its bottom there were several holes for the release of powder gases. In the center there was a cap. Grenade caliber - 40 mm. Length - about 100 mm. Mass - 250 g with 48-gram charge. Used shock fuse with self-destruct.
The principle of operation of the TKB-0121 grenade launcher was quite simple. Before the shot, it was necessary to put a grenade through the barrel. At the same time her sleeve was inside the breech. Then it was necessary to disable the fuse, unlocking the trigger. The existing sight provided the aiming of the weapon at the target, after which the trigger should be pulled. Moving back, he pulled the trigger behind him, squeezing the mainspring. In the rearmost position, the trigger was released and hit the drummer, executing a shot.
Powder gases broke through the membrane of the bottom of the liner and forced the grenade to leave the barrel. The sleeve was removed from the grenade launcher along with the grenade, and therefore preparation for a new shot could begin immediately after the previous one. With proper training of a fighter, the rate of fire could exceed 5 rounds per minute.
The overall architecture of the GP-25 serial grenade launcher is a drawing from the instruction manual. This design was developed in the project TKB-0121
In the 1971-72 years, TsKIB SOO produced prototypes of the new rifle grenade launcher and conducted their tests. In addition, a promising model was demonstrated to representatives of the GRAU. The previous project "Iskra" with a certain time has lost the support of this department, which led to a temporary halt to work in a new direction. The new TKB-0121 avoided this fate and immediately managed to interest the army. Soon there was a recommendation to finalize the design.
It should be noted that the interest in the project V.N. Telesh could be associated not only with the tactical and technical characteristics of the proposed weapon. In the late sixties, a part of the American army received an automatic-grenade launcher system, which included an M16 rifle and an XM148 grenade launcher. Later, the production of a similar system with the M203 grenade launcher was launched. The complexes of two types passed military tests in Vietnam, where some of them became the enemy's trophy. Naturally, the captured weapons soon fell into the Soviet Union and were studied by our military.
After reviewing the foreign developments, the Soviet command wished to receive a similar sample. The already existing Iskra product didn’t show itself well, and the new TKB-0121 grenade launcher looked very interesting and promising. However, he did not overestimate. Special comparative tests were organized, during which JAG-40 and TKB-0121 were simultaneously evaluated. According to the results of these checks, new conclusions were made, which determined the further development of domestic grenade launchers.
Experts recognized that the TKB-0121 product is not without flaws, but still surpasses the older Iskra. The result was an order to continue the development of the project, taking into account the new wishes of the customer. The further development of the grenade launcher was to deal with TsKIB SOO. For the development of an improved grenade with a flying sleeve to the project attracted the State Research and Production Enterprise "Pribor". Development work on the improvement of TKB-0121 received the code "Bonfire".
According to known data, for a long time experienced TKB-0121 remained in stock at TsKIB SOO. In the mid-nineties, these weapons were transferred to the Tula Museum of Weapons, where it remains to this day. Unfortunately, at a certain point, all the stamps and markings were removed from the weapon, which makes it difficult to recognize it and in due time became a reason for disputes.
Over the next few years, Tula engineers were engaged in improving the existing design. Almost all parts of the TKB-0121 grenade launcher were reworked in a technical or technological sense, although the main provisions and decisions of the project remained unchanged. In the first place, this led to a change in the appearance and ergonomics of the product. Also changed the dimensions of some parts. In particular, the barrel was shortened to 205 mm, as a result of which the total length was reduced to 323 mm.
During refinement, the trunk lost polygonal corners, instead of which small cylindrical appeared. Instead of a large box-shaped body trigger, a smaller part with a larger window under the trigger was now used. There was a simple lever mechanism that blocked the descent without installation on the machine. A hollow plastic grip of a more convenient shape appeared behind the main body. The rear frame, resting on the forearm and receiver box machine, has become longer. The bracket and the sight mounted on it were subjected to substantial processing.
The original design of the 40-mm grenade was changed, but its common features are preserved. At the same time, certain aspects of the product were improved. Also, Pribor State National Production Enterprise developed new versions of ammunition - a “jumping” grenade with an additional charge and a non-lethal shot with a tear gas charge.
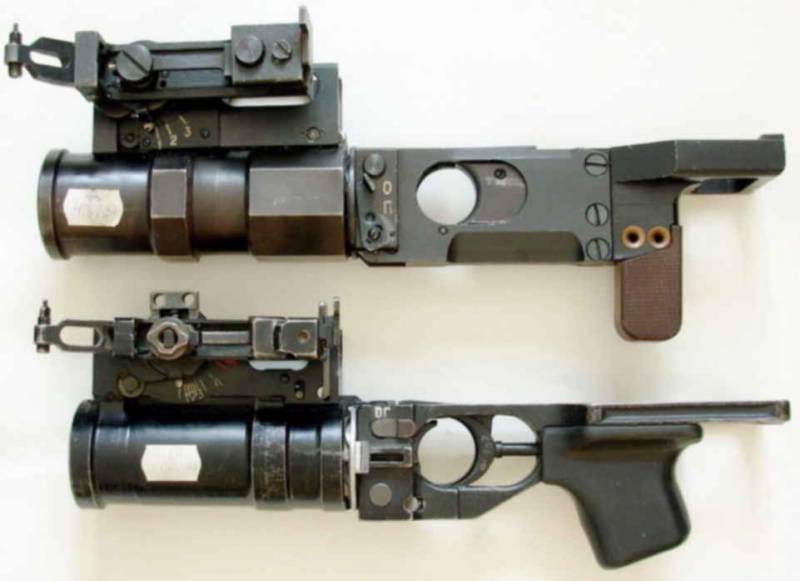
In the mid-seventies, an updated grenade launcher was put to the test and confirmed the design characteristics. In a few years, the weapons passed all the necessary checks, and according to their results in 1978, they were put into service. The updated grenade launcher based on TKB-0121 received the official designation GP-25 "Koster" and the GRAU index 6-X15. The 40-mm grenade was designated 7P17 or VOG-25.
The GP-25 “Koster” grenade launcher has been in service with the Soviet and Russian army for 40 for years, and it is not yet planned to abandon it. Subsequently, an improved grenade launcher GP-30 “Obuvka”, using the same ammunition, was developed on the base of “Bonfire”. Also GP-25 became the basis for the GP-34 product. Several types of grenade launchers are the main weapons of their class in the armies of Russia and a number of foreign countries. Apparently, they will maintain this status in the future.
The first domestic grenade launcher TKB-048 "Iskra" did not live up to expectations and did not enter service. Based on it, an experimental model TKB-0121 was created, which managed to interest the military. In its original form, he, too, did not get into the troops, but he managed to become the basis for a whole line of more successful designs that became the regular armament of the army. All subsequent serial grenade launchers of Soviet and Russian development were based on the ideas of V.N. Telesh, previously applied in the project TKB-0121.
Based on:
http://modernfirearms.net/
http://militaryparitet.com/
http://bastion-karpenko.ru/
http://ak-info.ru/
https://forum.guns.ru/
Manual 40-mm grenade launcher GP-25. Military Publishing Ministry of the USSR, 1983.






Information