Air defense tower project Tour Maginot (France)
Despite the presence of the Versailles Peace Treaty, official Paris feared the revival of the military power of Germany. The main and most noticeable consequence of such concerns was the construction of the Maginot Line on the eastern borders of the country. The main construction work was completed in the mid-thirties, and France, as it seemed then, received reliable protection against a possible attack. However, the defense was only on the ground, and therefore it was necessary to organize a fairly powerful air defense.

The proposed view of the "Tower Maginot"
While the French command was making and carrying out plans for the construction of air defense facilities, the production and deployment of guns, enthusiasts came up with alternative ways to protect the country. Among the new ideas came across and extremely bold, including fundamentally unrealizable. The author of one of these proposals was the engineer Henri Lossier. At the end of 1934, he proposed a more than original and bold version of the air defense system to protect Paris from enemy aircraft.
Probably, A. Lossier considered that for the most effective protection of the capital from raids, the airbase with the fighters should be located directly on its territory, but this seriously limited the area of such an object. At the same time, it was necessary to use some way to get the aircraft as fast as possible to the working height, so that they could take a favorable position before the battle and gain advantages over the enemy. Such requirements could be fulfilled only in one way. It was necessary to build a special anti-aircraft tower that accommodates take-off areas.
By analogy with the Line under construction, A. Lossier proposed to call his building the Maginot Tower. Apparently, such a name should reflect the reliability and inaccessibility of the tower with airplanes and anti-aircraft guns, as well as show its strategic importance to the country's security. Finally, it was a tribute to the late Defense Minister Andre Maginot.
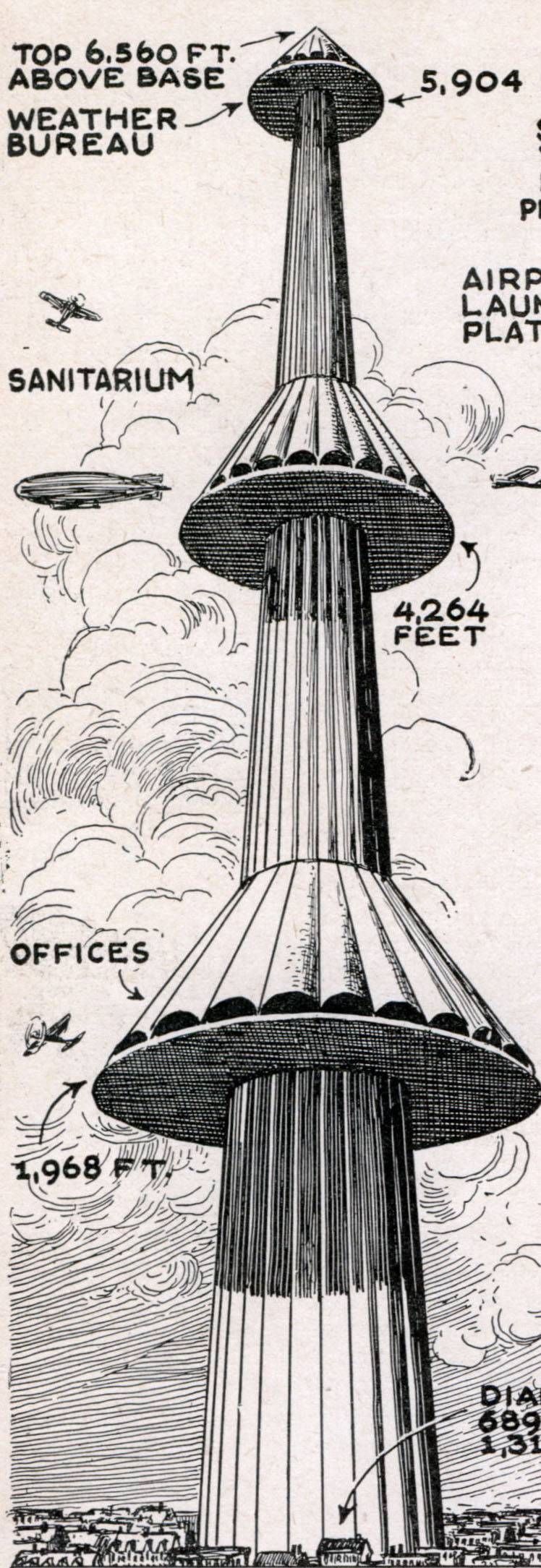
The main idea behind the Tour Maginot project was pretty simple. In one of the districts of Paris it was proposed to build a tower containing several annular take-off areas. Starting from a certain height above the ground allowed fighters to pick up speed already in the air and more quickly find themselves in the path of enemy bombers. Also on the sites should be mounted anti-aircraft guns of different calibers, which, as it was thought, could improve the effectiveness of artillery. The main ideas of the “Maginot Tower” project were fairly simple, but they were proposed to be implemented in a more than remarkable way. The finished airbase-tower was supposed to have enormous size and was distinguished by the extreme complexity of the design.
According to A. Lossier's calculations, the optimal combat capabilities would be shown by the construction of a total height (including the foundation) 2400 m. The mass of such a tower was 10 million tons. For comparison, the famous Eiffel Tower has a height of 324 m and weighs "only" 10,1 thousand tons. Nevertheless, as the inventor believed, it was this design that could provide the required potential. First of all, it allowed to raise the takeoff sites to a sufficient height.
The prospective “Maginot Tower” was supposed to stay on the ground with a reinforced concrete foundation extending to a depth of 400 m. On the ground surface, the designer placed the tower itself with a diameter of the lower part of 210 m and three additional large hangars around it. Between the hangars were additional triangular supports of the appropriate dimensions. The tower was supposed to be a tapering structure with a maximum height of 2000 m, made of reinforced concrete with a metal lining. At the height of 600 m, 1300 m and at the top, it was proposed to place three conical expansions that accommodate take-off areas, equipment storage rooms, etc.
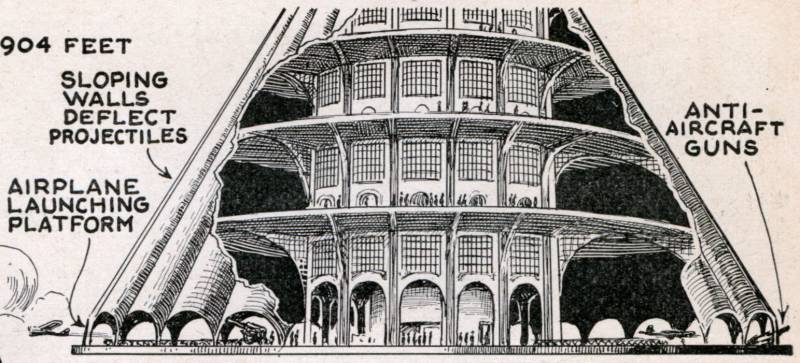
The huge mass of the design led to its special configuration. In the lower part of the wall, the towers were supposed to have a thickness of 12 m. As we climbed up and reduced the load, the thickness gradually decreased to tens of centimeters. The large thickness of the walls solved the problem of weight, and also became the real defense against bombs or artillery shells.
For the basing of aircraft A. Lossier proposed a very original design with the logical name “airfield”. At a given height around the main structural element of the trunk of the tower should arrange a ring platform with a radius of about 100-120 m over the radius of the tower. From above it was covered with an armored roof in the form of a truncated cone, assembled from a large number of curved sections. It was assumed that such a roof would protect aircraft and personnel from enemy bombs: they would simply slide down and explode in the air or on the ground. Under the roof of the "airfield" it was possible to fit several other ring platforms. For obvious reasons, the number of such platforms and the available volumes depended on the size of the armored cone. Most of the place was inside the bottom, while at the top was the least large.
The lower part of the curved roof element, in contact with the platform only at two points, was to form an opening 45 m wide and 30 m high. It should have been closed by mechanically-driven armor gates. Through many of these gates around the platform, it was proposed to produce airplanes from the “airfield”. In addition, they could be used as ports for artillery. The lower platform, along the perimeter of which there were many gates, was a take-off platform, while other platforms under a conical roof could be used for storing and preparing aircraft for departure.
To move the aircraft "Tower Maginot" was supposed to have several large freight elevators. Their mines of large cross-section were inside the tower and passed through its entire height, providing free access to ground hangars or to any platforms of high-altitude “airfields”. Passenger elevators and simple flight of stairs were also envisaged.
Part of the volume inside the trunk of the tower, located between the protected hangars, it was proposed to give for various rooms and objects. So, next to the hangars of the first conic expansion, it was planned to place various cabinets for commanders, command posts of aviation and artillery, etc. Inside the second cone could be its own hospital. In the third, which had the smallest size, it was necessary to equip the weather station. Certain objects, such as workshops, etc., could be “lowered to the ground” and placed in lower hangars.
The main "weaponsThe object of the Tour Maginot were to become fighter aircraft. The dimensions of the elevators, hangars, take-off areas and gates were determined taking into account the dimensions of the technology of that time. In terms of size, the advanced air defense tower was compatible with any existing or prospective fighter aircraft of France or foreign countries.
The combat work of the aviation with the "Maginot Tower" was to be based on unusual principles, but it was not particularly complex. The duty units of the fighters were asked to keep on take-off sites in combat condition. The announcement of the approaching enemy aircraft was followed by the opening of armored gates. Using small platforms "airfields", the aircraft could run and gain some speed. Leaving the site, they were able to increase their speed by reducing, while maintaining sufficient height. It was assumed that in just a few seconds after the launch, the plane would pick up the speed and altitude necessary for the fight.
However, the own "airfields" of the tower were not intended for landing aircraft. After completing the departure, the pilot was supposed to land on a separate platform at the foot of the tower. Then it was proposed to roll the plane into the ground hangar and place it on the elevator, returning it to the initial take-off area. After the required maintenance, the fighter could fly again.
A. Lossier calculated that at least the several dozen planes could be in the “Tower of Maginot” proposed by him. By more dense placement in storage hangars or on take-off areas, this number could be increased in a noticeable way, having received a corresponding increase in the combat qualities of the entire air base tower.
To further enhance the potential of the air defense tower, the project author suggested placing anti-aircraft artillery at different sites. On stationary installations it was possible to mount any existing implements, including maximum calibers. Depending on the chosen configuration and the "balance" of artillery and aircraft, the Tour Maginot could hold dozens or hundreds of guns. It was argued that the load even from large-caliber guns are not a problem for the construction of the tower. A simultaneous shot in one direction from 100 cannons with a caliber 84 mm could cause the top of the tower to vibrate with an amplitude of just 10 cm.
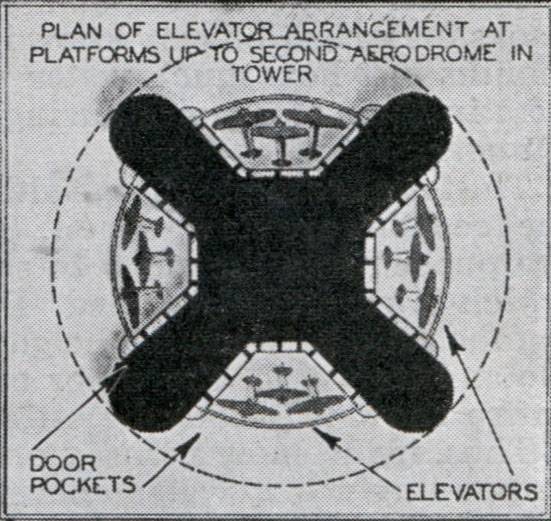
Aircraft Lifts
It is important that engineer A. Lossier understood what the construction of a tower a couple of kilometers in height would lead to. According to calculations, the wind load on the structure could reach 200 pounds per square meter. ft (976 kgf / m2). Due to the large size of the tower would have to experience a load of hundreds of tons. However, the total pressure on the surface was insignificant compared to the total mass and structural strength. As a result, even with a strong wind, the top of the tower should have deviated from the initial position of everything on 1,5-1,7 m.
An air defense tower of the Tour Maginot type, 2 km in height, designed for dozens of airplanes and guns, was designed to protect the French capital. However, Henri Lossey did not stop at this and worked on options for the further development of existing ideas. First of all, now he was looking for ways to increase the starting height of the aircraft. The whole of this turned out to be a further increase in the height of the entire tower as a whole.
The hypothetical dimensions of the “Maginot Tower” were limited by the available materials. Calculations have shown that the use of more durable concrete of new varieties in combination with reinforced reinforcement will make it possible to bring the height of the tower to 6 km or more. The maximum height of the all-metal construction of promising steel grades was determined in 10 km - more than a kilometer above Everest. However, the technology materials of the mid-thirties did not allow such ideas to be put into practice.
The project of the original air defense tower appeared at the end of 1934 of the year and was probably presented to the French military department. In addition, information about the extremely bold proposal came to the press and attracted public attention in different countries. In general, this was the main achievement of the project. The tower-airbase with airplanes and guns became a topic of discussion and a reason for disputes, but no one even thought of building it in Paris or anywhere else.
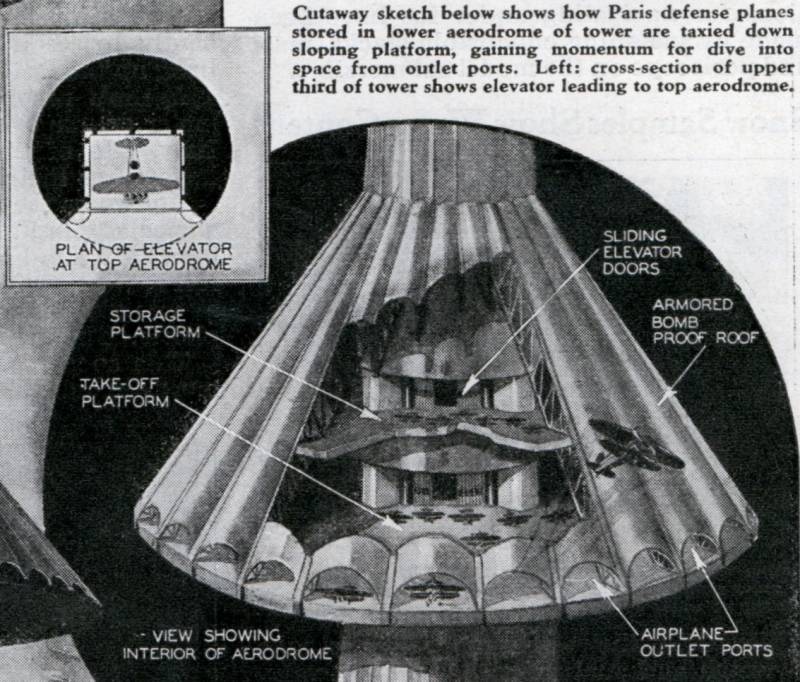
Another image of the "airfield" with the removal of part of the roof. Top left - a version of a smaller elevator for lifting aircraft to the uppermost platform
Actually, all the main problems of the project A. Lossier are visible when it is first considered. And we are talking about the most serious shortcomings, which immediately put an end to the whole idea - without the possibility of its refinement and improvement with obtaining acceptable results. The improvement of certain elements of the tower allows you to solve certain problems, but does not eliminate other disadvantages.
The main disadvantage of the Tour Maginot project is the unacceptable complexity and high cost of construction. The inventor has calculated that the two-kilometer tower will require 10 million tons of building materials, not counting the various internal equipment. In addition, especially for such a tower would have to create completely new models of construction equipment, internal equipment, etc. It is terrible to imagine how much a construction program would cost just one such structure for an air defense system and how long it would last. It is quite possible that the construction would take away the lion's share of defense budgets over several years. In this case, it would be possible to improve the protection of only one city.
The reason for the dispute may be the level of protection of the tower. Indeed, the slope and armor of the roofs of the “airfields” made it possible to protect people and equipment from detonating bombs. However, the vitality of a real construct of this kind is questionable. In addition, the air defense tower could become a priority target for enemy aircraft, and the most powerful bombs would not spare it. Concrete and steel could withstand active bombardment - in practice it was not possible to establish it.
You can not worry about the survivability of the main structural element of the tower. A massive bomb strike capable of inflicting fatal damage to the walls of the base of the barrel, which had a thickness of 12 m, at that time would hardly have been within the power of the bomber aircraft of any country. The need to deliver a huge number of bombs while faced with problems in the form of precision unguided weapons and opposition from air defense.
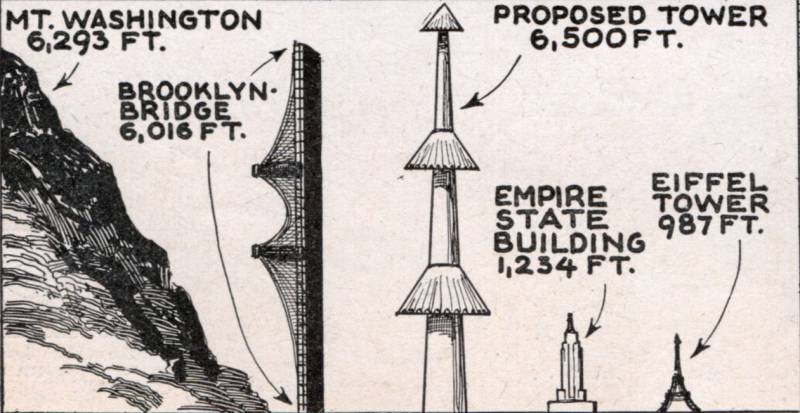
Comparison of various large objects: The Maginot Tower is larger than Mount Washington, Brooklyn Bridge and other high-rise buildings.
Finally, the combat effectiveness of a high tower with its own airfields is doubtful. Indeed, the presence of several elevated take-off areas in theory makes it possible to reduce the time to climb for combat. However, in reality, such problems were solved by much simpler methods: timely detection of approaching aircraft and the rapid rise of interceptors. The take-off of the plane from the ground did not look as impressive as a “jump” from a raised platform, but it allowed at least not the worst results to be obtained.
Placing anti-aircraft guns on the tower had a definite meaning, since it allowed to increase their reach in height and range, as well as to eliminate the negative impact of the surrounding urban development. However, the need to build a two-kilometer tower with three platforms for aircraft and guns eliminates all these advantages. Similar results could be obtained with the help of less high towers, passing the interception of high-altitude targets of aviation.
Naturally, no one began to consider the project of Henri Lossier seriously, not to mention the recommendation for the construction of one or more of the Bazin Maginot. An overly bold project became famous only thanks to publications in the press. However, fame was short-lived, and soon he was forgotten. In the thirties, in France and other countries a great many of the most unexpected and unusual projects of equipment, weapons, fortifications, etc. were proposed. New reports of interesting inventions soon overshadowed the Tour Maginot project.
It is hardly worth reminding once again that any new sample should not only solve the tasks set, but also be technically or economically acceptable. Aircraft "Maginot Tower" design A. Lossier from the very beginning did not meet these requirements, which immediately determined its future. The project instantly fell into the category of architectural curiosities, where it remains to this day, demonstrating how far unlimited inventive courage can reach.
Based on:
Giant Air Tower to Guard Paris // 1935, Jan.
Fort More Than Mile High? // Everyday Science and Mechanics. 1935, Feb.
http://blog.modernmechanix.com/


Information