Armored car Ford FT-B (Poland)
By the middle of 1920, the need to build armored cars became apparent. At the same time, not having all the required production capacity, Poland had to face certain restrictions. However, at the beginning of the summer, a new project of a promising armored car was proposed, which made it possible to organize the construction of machinery at its own enterprises. Soon he received the approval of the military and was accepted for implementation.
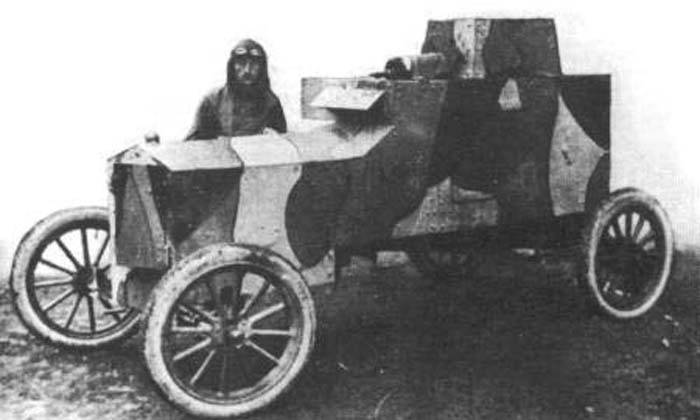

One of the armored Ford FT-B. Photo Aviarmor.net
The author of the new project was the engineer Tadeusz Tansky. He had some experience with automotive technology and therefore could offer a good option for the construction of armored vehicles. Later, after the end of the war, the designer continued to work in the automotive industry and created the first Polish project of a civilian passenger car, brought to the series.
There is a version according to which T. Tansky, starting to develop his own armored car, took into account known information about foreign projects of this kind. So, during the First World War, British engineers attempted to create a light armored car based on the Ford Model T civilian vehicle. Such a project reached the test, but did not interest the British. The commercial chassis did not have high performance, and therefore the resulting armored car could not be effectively used in the war.
T. Tansky could learn about such works and use famous ideas in his new project. In the late tenths, Poland received a number of Ford T vehicles that could be used as the basis for armored vehicles. The British project, if it was known to Polish specialists, showed that such a base would not allow high performance. However, some ideas and solutions made it possible to rely on acceptable parameters of opportunity. In addition, the army urgently needed armored cars, and therefore engineers should not waste time looking for the most successful chassis.
The armored car project was based on the American-made Ford T chassis, which was reflected in its name. The new armored car received several of its own designations at once; he gained fame under the names Ford FT-B, Ford Tf-c and "Model 1920 g."
Like other armored car developers of his time, T. Tansky proposed the easiest way to build machinery. The finished car chassis had to undergo a minor revision, due to the peculiarities of the new units, and then get the original armored corps with crew seats and weaponry. This approach made it possible to produce armored cars even at existing enterprises.
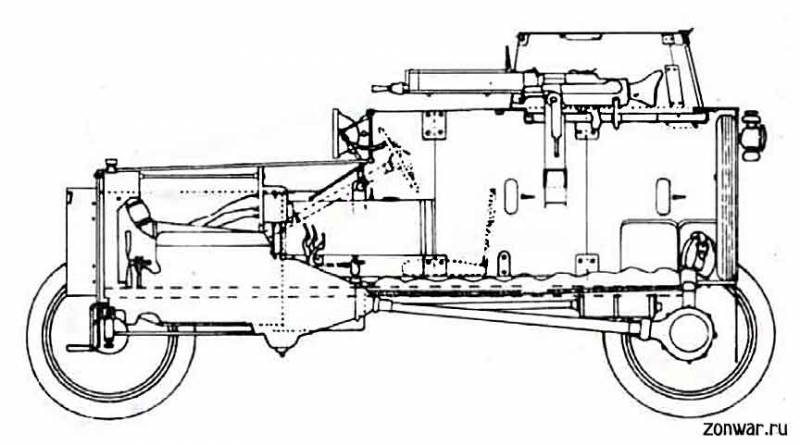
The basis of the car Ford FT-B was the finished American chassis of a passenger car. It was built on the basis of a rectangular frame, in front of which was placed the engine. According to some reports, the frame was slightly modified and strengthened to match the characteristics of the new building. The units installed on it did not change.
As a power plant on the new armored car, a standard Ford Model T engine was used, which developed power up to 22,5 hp. A mechanical transmission with a driveshaft gave out torque to the driving rear axle. Two pairs of wheels were mounted on two bridges. The latter were fixed on the frame with the help of a dependent suspension on the basis of a leaf spring of lateral arrangement. The front axle was equipped with a control mechanism. Used regular-spoke wheels with a porous rubber filler tires.
T. Tansky designed the original armor corps that matched the capabilities of the existing chassis. Protection of the crew and the engine was assigned to the armor sheets of two thicknesses. The frontal projection, the sides and the stern were covered with 8-mm steel, while the roof and the bottom should have the thickness of the entire 3 mm. The origin of the steel used in the construction of serial equipment is interesting. According to some reports, this sheet armor was previously released by the German industry and was intended to protect the trenches. After the end of the First World War, part of the stock of such armor went to Poland, and soon found use in the construction of armored cars.
The limited carrying capacity of the existing chassis led to the formation of a specific look of the armored hull. This unit was supposed to differ in small size and reduced volumes. Nevertheless, even with such restrictions, T. Tansky managed to get the maximum possible results. In particular, the armored car turned out to be equipped with a full-fledged rotating turret.
The engine and gearbox were covered with an armored hood, consisting of 8-mm sheets. There was a vertical frontal sheet with an opening and swing doors. Behind it were vertical sides, noticeably diverging in the rear. On top of the engine covered with a lid of a pair of inclined sheets. The latter could recline to the side, opening access to the power plant. The front part of the sides of the engine compartment was distinguished by a greater height, due to which it covered a certain part of the frame behind the front axle.
Inhabited housing compartment differed simple form. It was made in the form of a large rectangular box, assembled from several armor plates on a metal frame. The vertical partition between the engine and the habitable compartment passed into the upper frontal sheet. On the sides there was a pair of vertically arranged sides. A horizontal roof was placed on top, equipped with a device for mounting the tower. Behind the car defended the vertical feed sheet. The horizontal bottom of such a body was mounted directly above the frame. The small width of the armored box allowed to do without any arches under the rear wheels.
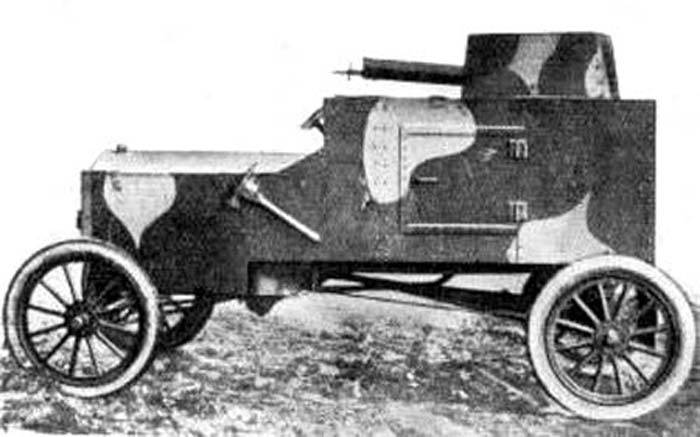
Side view. You can consider the units of the chassis and transmissions. Photo Aviarmor.net
A new tower of characteristic pentagonal shape was developed. It had a trapezoid frontal sheet with an embrasure for a machine gun, with which the inclined diverging sides were mated. Behind the arrow covered the wedge-shaped structure. The horizontal roof of the tower had a large hatch.
The armament of the Ford FT-B armored car was to consist of one machine gun placed in the turret. The design of the front embrasure of the tower ensured the installation weapons with a large barrel water cooling jacket. Thus, the car could be armed with any machine gun of the Maxim family. According to some reports, serial armored cars carried German-made MG 08 machine guns. Regardless of the type of weapon installed, the gunner of the armored car could turn the turret in any direction. The embrasure design allowed shooting with different elevation angles. The ammunition consisted of 1250 cartridges in tapes. Boxes with ribbons were placed on the racks of the fighting compartment.
The armored body of the construction of T. Tansky, created taking into account the possibilities of an affordable passenger car, did not differ in large volumes. As a result, the crew of the new armored car was supposed to consist of only two people. In front of the habitable compartment fit the driver. He was asked to follow the road with a rectangular viewing hatch in the front plate. In a combat situation, the flap was closed with a lid with a slit. Behind the driver in the conventional fighting compartment was the shooter, in charge of which was a machine gun. The shooter could monitor the situation with the help of the embrasure viewing device, the top hatch of the tower and the viewing slots.
Access to the car was provided by three hatches. Two of them had a rectangular shape and were located on the sides of the hull. The third hatch was located in the roof of the tower, and it could only be used with a certain skill. Anyway, due to the limited size of the hull, the use of all hatches was associated with certain difficulties. In the side doors and behind them were provided small embrasures with flaps, designed for firing personal weapons. It should be noted that these embrasures were not proposed by the designers. They were originally present at the infantry armor casks used in the construction of equipment.
The dimensions and weight of the prospective armored car were determined by the capabilities and parameters of the existing chassis. The Ford FT-B had a length of 3,25 m with a width of 1,55 m and a height of 1,73 m. The combat weight was only 1350 kg. Specific power over 16,5 hp per ton allowed us to obtain acceptable driving performance. On a good road, an armored car could accelerate to 45-50 km / h. Power reserve - 250 km. At the same time, the existing chassis seriously limited cross-country maneuverability.
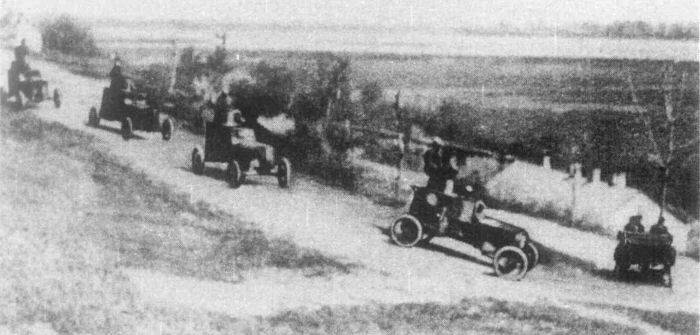
Armored Ford FT-B on the road. Photo Aviarmor.net
The development of the Ford FT-B project was carried out in one of the most difficult periods for Poland. The active offensive of the Red Army led to the loss of large territories, a large number of equipment and personnel, and also threatened to defeat the war. As a result, new armored vehicles had to be produced in a hurry and in the conditions of shortage of components. In this case, the performers, in general, coped with the tasks. So, the project of T. Tansky was approved by the military 12 of June 1920 of the year, and in early July the first production vehicles went to the army.
Serial production of armored cars was established at the factory Gerlach i Pulsing in Warsaw. By this time, the company has mastered the assembly of cars for armored trains and therefore had all the opportunities to start production of other protected equipment. Construction of the first two cars "Model 1920 g." Lasted a decade and a half. After some factory tests, both armored cars went to serve in the 8 Cavalry Brigade. At that time, this compound covered the retreat of the troops near Warsaw. A month later, the army received four more armored cars.
The assembly of armored vehicles of the new type continued until September. During this time, the contractor has manufactured and transferred to the Polish Army 16 or 17 machines. The finished equipment was attached to cavalry units and was supposed to increase their firepower. According to known data, Ford FT-B serial armored cars received an unusual color. They were camouflaged in the form of sand, green and brown spots, separated by curved black lines.
Over time, some of the cars built, in addition to the tail number, received their own names. Crews called them in honor of the stinging and blood-sucking insects - "Wasp", "Mosquito", etc. Apparently, the appearance of such names was associated with the small size and weight of armored vehicles, with the presence of a machine gun, as well as with the characteristic chirping sound of the engine.
All built cars were actively used in battles until the very end of the Soviet-Polish war. The armored cars, which were in fact the means of improving the quality of infantry and cavalry, were constantly transferred to various sectors of the front, where they contributed to the solution of various tasks. In certain situations, the Ford FT-B cars coped well with their work, while in other circumstances they encountered the most serious difficulties. Armored cars regularly returned from combat with various damage. In addition, some of the equipment was destroyed.
Due to losses at the front, the end of the war saw only 12 Polish armored vehicles based on the Ford Model T. After appropriate repair, the vehicles continued their service and remained in the army for the next few years. Already in the early twenties, Tadeusz Tansky proposed to build an additional series of three dozen armored cars, each with a different design. First of all, it was planned to use a larger and more convenient to use tower. The military considered this proposal and decided not to order new armored cars.
Active exploitation during the war and limited potential eventually forced the army to abandon existing armored vehicles. According to known data, the process of writing off a dozen Ford FT-B armored vehicles started in the late twenties and ended in the 1931. All existing machines, obsolete and finally developed their resources, were dismantled and sent to the smelter.
Some sources claim that several such armored vehicles were idle at the sites of units up to the 1939 year. Allegedly, this technique even managed to use in the fight against the advancing troops of Nazi Germany. However, there is no evidence of such information.
During operation, the Polish army was able to identify the strengths and weaknesses of Ford FT-B armored vehicles. It was quickly found that this machine is a typical representative of its class, devoid of any serious advantages or disadvantages. Characteristic pluses were completely compensated by the existing minuses, and as a result, an average armored car was obtained with acceptable parameters and capabilities. The Polish armored car differed from other models of its class, perhaps, only by its small size and minimal combat mass.
The positive features of the armored car were considered relatively high mobility on a good road and ease of maintenance. Protection and weapons, in general, met current requirements for modern light armored vehicles. At the same time, the undercarriage did not always show the desired permeability, the engine in the closed compartment quickly overheated, and the habitable compartment was too close for the crew to work comfortably.
However, the main advantage of Ford FT-B armored cars was the fact of their existence. This technique was created in the most difficult period and was required for the quickest change in the situation at the front. The designers managed to perform the main tasks of this kind and give the Army Polish a sufficient number of new armored vehicles. With all its problems, this technique contributed to changing the situation and contributed to the subsequent victory. However, in the early twenties, the armored cars were morally outdated and demanded a replacement.
On the materials of the sites:
http://tanks-encyclopedia.com/
https://aviarmor.net/
http://derela.republika.pl/
http://zonwar.ru/

Information