Armored car-armored rubber "Type 91" (Japan)
The program for the mass development and construction of wheeled armored vehicles for the Japanese armed forces started in the early thirties and quickly gained momentum. In just a few years, a number of enterprises presented a significant number of projects, most of which received approval from the future operator. Commissioned by the army and fleet armored cars with different capabilities and characteristics were created, designed to solve different tasks. Quickly enough, the imperial army formed the requirements for an armored car capable of working on railways.
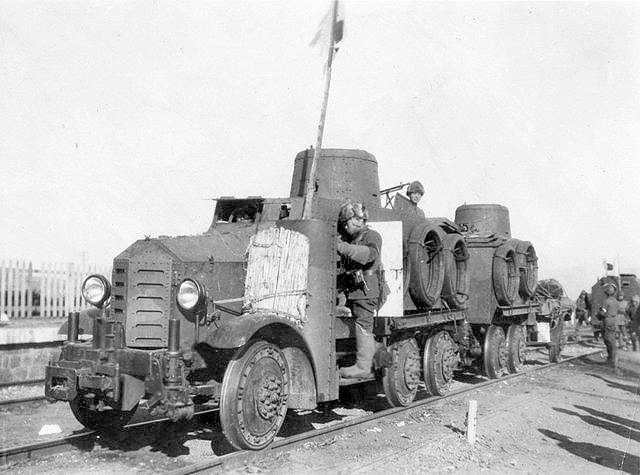
Armored car "Type 91" in the configuration of armored rubber, 1935. Photo Wikimedia Commons
From the available information, it follows that the armored car armored rubber was ordered approximately in 1930 or 1931 year. The development of the project was completed in the same period, and no later than the end of 1931, the finished equipment entered service. It should be noted that some sources indicate other data on the timing of the project. According to these data, the car entered service two years later - in 1933-m.
A certain confusion with the years of engineering development is associated with the mistake of foreign intelligence services. The fact is that third-country intelligence officers, who were watching the development of the Japanese army at that time, designated the new armored car as "Type 93" or "Sumida." The digital designation “93” indicated the 2593 year of the Japanese calendar (1933 year of our era). Under the names indicated by the intelligence, the car appeared in all reference books for many years. More recently, new information about railway armored cars was discovered, which changed the existing picture.
According to newly discovered information, this car wore the official designation "91 Siki Koki Kanisa" - "Transport for wide gauge, type 91". The number in the title denotes the year the technology appeared - 2591 on the Japanese calendar or 1931 on the Gregorian. Together with the correct name, the researchers managed to find some other data about the project.
According to known data, the development of an armored vehicle "Type 91" began in 1930 year. The creation of this machine was commissioned by the design office of the Tokyo plant Ishikawajima, which produced trucks under the brand name "Sumida". Perhaps it was this fact that misled foreign intelligence. The use of proven ideas and solutions, as well as the use of ready-made components allowed us to speed up the work and get the desired result in the shortest possible time.
According to some data, the 91 Type truck, launched in 1931, became the base for the new railway armored car. As in the case of other projects, it was envisaged to abandon various products mounted on top of the chassis, instead of which armored corps should be used. In addition, it was proposed to slightly alter the chassis to obtain the desired capabilities.
The base chassis had a rectangular metal frame with front engine and gearbox. According to known data, the truck “Type 91” was completed with a gasoline engine with a power not more than 45-50 hp. The engine mated with a manual transmission. The drive of the two rear leading axles was carried out through a cardan shaft and a pair of differentials.
As part of the chassis there were three axles with a dependent suspension on leaf springs. The front axle had controls for maneuvering on the highway. It was proposed to equip an armored car with wheels of the original design, which provided movement on roads and railways. The basis of such a wheel was a metal disk, which had a rim and protruding flange. A rubber tire was installed between the flange and rim. Regardless of the configuration of the chassis, the armored car had a wheel formula 6 x4. The front wheels were covered with curved wings. The two rear axles were under the hull, but could be equipped with its own wing.
To go to the railway, the crew should have a simple preparation of the machine. In the front and rear parts of the hull were two pairs of their own jacks, with which the armored car should be hung over the rails. Further, the rubber tires were dismantled, after which the car could be lowered on the track with a 1524 mm gauge. The removed tires were supposed to be transported on the sides of the hull. For efficient operation on the railway, coupling devices and buffers were also provided.
Armored car "Type 91" should have received protection of the traditional look. A riveted armored body with differentiated protection should have been mounted on top of the chassis. The frontal parts of such a body had a thickness of 16 mm. Some front sheets were less thick - 11 mm. Boards were made of 8-mm sheets. The roof and some other units had a thickness of 6 mm. The armored turret corresponded to the hull in its level of protection.
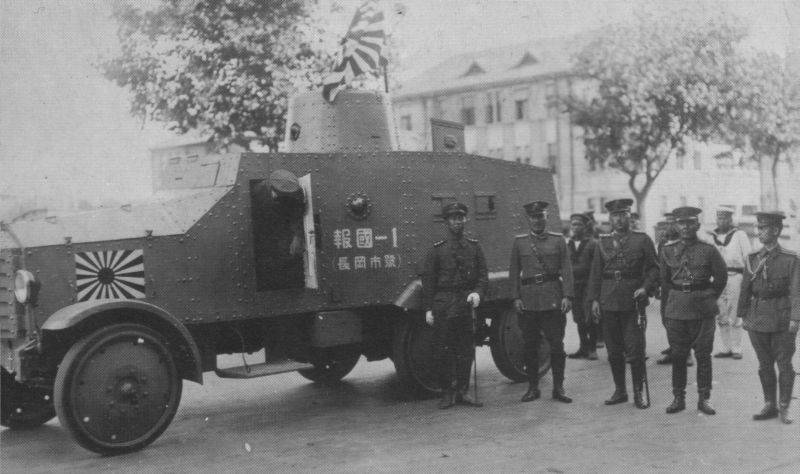

"Type 2591" in Manchuria. Photo Aviarmor.net
Side chassis frame covered with rectangular armor plates of small thickness. Over such a reservation was located the main building. It is curious that the 91 Type differed from other Japanese armored cars of its time with the greater complexity of the hull forms in general and the bonnet in particular.
The engine was covered with a large armored hood of complex shape. Front radiator closed wedge-shaped frontal unit with horizontal slots. On the march his flaps opened, improving ventilation. In combat, the frontal unit was closed, protecting the power plant. Behind the flap was a diverging vertical side. They had hatches for access to the engine. The roof of the hood was formed by three oblique trapezoidal parts. In the back of the hood there was a large inclined sheet mated with the frontal part of the habitable compartment.
The front part of the habitable compartment, which accommodated the driver and commander, was distinguished by a smaller width and rectangular contours. Then the hull expanded, obtaining a maximum cross section that did not change to the very bottom of the forage. The latter was located with some inclination forward. From above, the crew was defended by a horizontal roof with a large sloping section.
The 91 Type machine tower was distinguished by its simplicity of design. It was proposed to fasten several curved parts forming a conical bead on the frame. In its front and rear parts were cutouts with rectangular sheets for the installation of weapons. Also, the tower received a horizontal roof with a large hatch.
The new armored car was to carry only small arms. The tower provided for the installation of a single machine gun rifle caliber. The preserved photographs show that the main weapons Machine was machine gun "Type 92" caliber 7,7 mm. Large ammunition to the machine gun was located on the racks of the fighting compartment.

Bronedresina on the railway. Photo Aviarmor.net
According to various sources, the armament complex of the vehicle also included additional 91 Type machine guns in 6,5 mm caliber, or the crew was asked to use personal weapons. Apply additional rifle systems should be using airborne embrasures. On the sides of the fighting compartment were placed three such devices, equipped with movable armor covers. The tower and six embrasures made it possible to simultaneously fire at several targets, including in different directions. It is known that some armored cars instead of front embrasures of a simplified design received ball installations.
The crew of an armored vehicle-armored rubber "Type 91" consisted of six people. It included the driver, the commander and the four arrows. The driver was located in front of the habitable compartment. Next to him was the commander. Other crew members worked in the fighting compartment and had to use weapons. Access to the car was provided by a pair of side doors, placed at the level of the commander and driver seats, as well as a swing door. With a certain skill, an armored car could also be reached through the hatch of the tower. Behind the tower in the roof there was an additional rectangular hatch.
The armored car was equipped with advanced means of observation. The driver and the commander could follow the road through the front hatches, covered with movable covers. In a combat situation, observation was carried out through the cracks in the latter. Also, a couple of viewing slots were in the side doors. The review from the fighting compartment was provided by onboard embrasures and slots. The tower was equipped with a pair of hatches for mounting weapons and side slits.
Prospective combat vehicle differed relatively large size. Its length reached 6,7 m, width - 1,9 m with a height slightly less than 3 m. The combat weight was 7,7 t. The limited engine performance allowed us to reach speeds of no more than 40-45 km / h. Power reserve - up to 240 km. In the automotive configuration, the new armored vehicle "Type 91" could move on the highway and some rough terrain, overcoming simple obstacles. The highest performance characteristics he had to show on the railways. In particular, it is known about the possibility of acceleration to 60 km / h.
Armored car-bronedrezina was created at the very beginning of the thirties and, after carrying out all the necessary checks, was recommended for use with subsequent supplies to the troops. No later than 1932-33, the Type 91 vehicles went to the territory of China and Manchuria to take part in hostilities. They had to solve a variety of combat and support tasks. The ability to work on roads and railways to some extent increased the potential of technology.
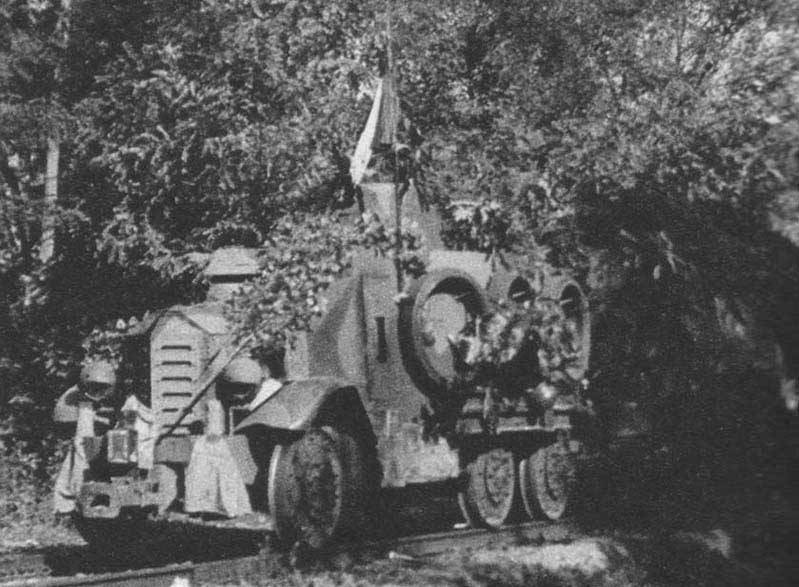
Armored car with disguise. Photo Aviarmor.net
Serial production of armored vehicles with a combined chassis lasted for several years. Different sources mention that the Japanese army received at least 100 and no more than 500 of similar combat vehicles. There are also more courageous assumptions. It can be assumed that the actual number of armored vehicles "Type 91" was noticeably less than some modern estimates. However, in this case, these machines became one of the most numerous armored cars of Japan of its time.
By the beginning of the 1930s, the planned to seize the territories of China and Manchuria had a well-developed network of railways, which provided the new Japanese armored vehicles with high mobility. For the minimum time combat vehicles could arrive in a given area and provide support to ground forces. In addition, the "Type 91" proved to be a very convenient means of patrolling and protecting the railways. Unlike other vehicles, such armored cars did not need separate roads and could protect the paths used for movement.
In the role of reinforcement for infantry or cavalry, as well as in patrolling various areas, 91 type armored vehicles-armored rifles have been used for several years. According to some reports, such technology was able to take part in several full-scale military operations. In particular, armored cars were actively used in the capture of Shanghai in the 1937 year. However, by this time the machines had become outdated and developed a significant part of the resource.
According to various sources, the 91 Shiki Koki Kanis armored cars remained in service at least until the end of the thirties. The emergence of a newer technology with improved characteristics allowed to transfer old cars to secondary roles, but one-time full rejection of them was still not planned. As the use of resource armored equipment was written off and disposed of. Apparently, this process stretched over several years and ended in the early forties. Not a single armored vehicle "Type 91" has been preserved.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the future theater of military operations, the Japanese command ordered the development of various combat armored vehicles. One of such orders involved the construction of an armored car that could move by rail in a regular manner. The appearance of serial armored vehicles "Type 91" significantly increased the potential of the Japanese army and affected the outcome of subsequent hostilities that lasted for several years.
Based on:
http://tanks-encyclopedia.com/
https://militaryfactory.com/
http://voenteh.com/
http://aviarmor.net/
Fedoseev S. Armor of Japan 1939-1945 // Technique for Youth Magazine Library. - M .: "Eastern Horizon", 2003.
Malmassari P. Armored Trains. Seaforth Publishing. 2016.

Information