The system of retaliatory strike "Perimeter"
With the development of nuclear weapons monstrous power principles of global war have undergone major changes. Only one missile with a nuclear warhead on board could hit and destroy the command center or bunker, which housed the top management of the enemy. Here we should consider, first of all, the doctrine of the United States, the so-called "beheading strike." It was against such a strike that Soviet engineers and scientists created a system of guaranteed nuclear retaliation. Created during the Cold War, the Perimeter system took over the alert duty in January 1985. It is a very complex and large organism that was dispersed throughout the Soviet territory and constantly controlled many parameters and thousands of Soviet warheads. At the same time for the destruction of such a country as the United States is about enough 200 modern nuclear warheads.
The development of the system of guaranteed retaliatory strike in the USSR was also started because it became clear that in the future the electronic warfare devices would only be continuously improved. There was a threat that they would eventually be able to block the regular channels of control of strategic nuclear forces. In this regard, a reliable backup method of communication was needed, which would ensure that the teams were launched at all nuclear missile launchers.
An idea emerged to use special command rockets as a similar channel of communication, which instead of warheads would carry powerful radio transmitting equipment. Flying over the territory of the USSR, such a rocket would send commands to launch ballistic missiles not only to command posts of the Strategic Missile Forces units, but also directly to numerous launchers. 30 August 1974, the closed decision of the Soviet government initiated the development of such a rocket, the task was issued to the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau in the city of Dnepropetrovsk, this design bureau specialized in the development of intercontinental ballistic missiles.
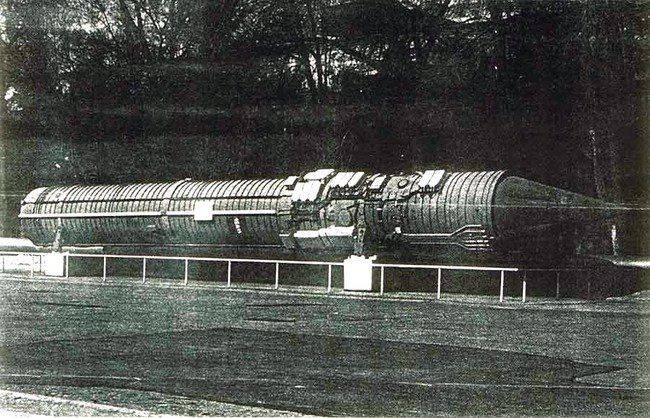
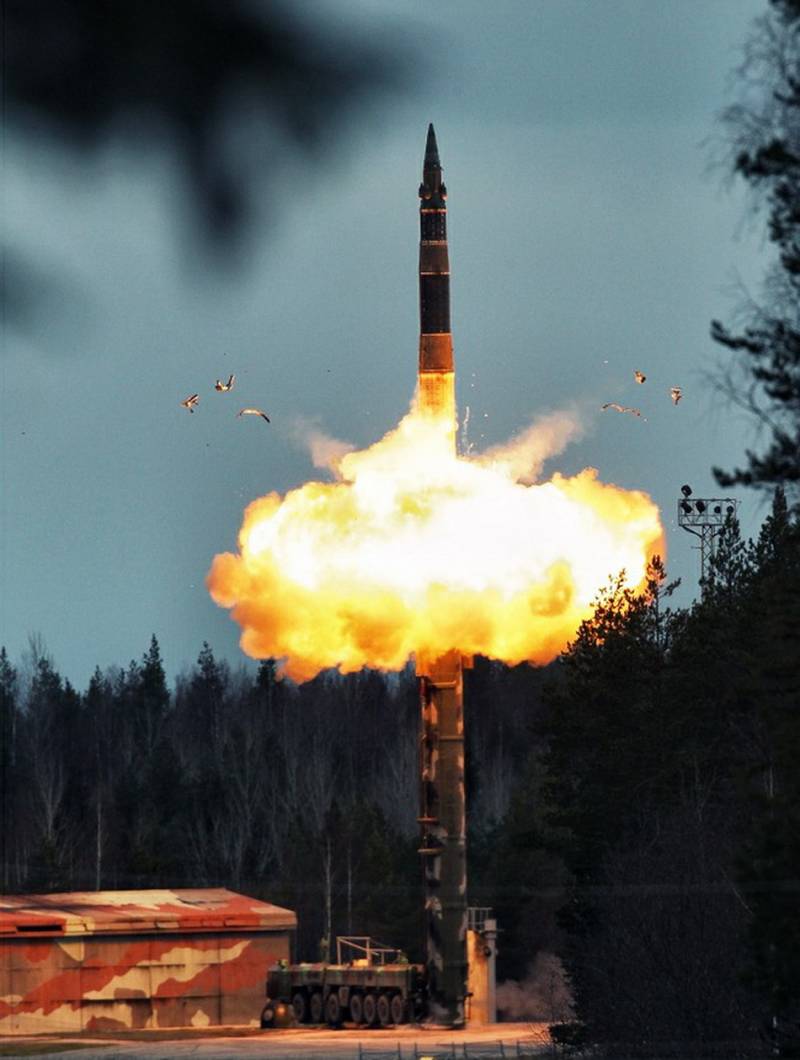
The specialists of Yuzhnoye Design Bureau took the basis of the ICBM UR-100UTTH (according to the NATO codification - Spanker, trotter). The head part specially designed for a command rocket with powerful radio transmission equipment was designed at the Leningrad Polytechnic Institute, and the issue was taken up by Strela in Orenburg. A fully autonomous system with a quantum optical gyrometer and an automatic gyrocompass was used to aim the command rocket in azimuth. She was able to calculate the necessary direction of flight in the process of setting up a command rocket on combat duty, these calculations were maintained even in the event of a nuclear effect on the launcher of such a rocket. Flight tests of the rocket started in 1979 year, the first launch of the rocket with a transmitter was successfully performed on December 26. The tests proved the successful interaction of all components of the Perimeter system, as well as the ability of the head part of the command rocket to withstand a given flight trajectory, the top of the trajectory was at an altitude of 4000 meters at a distance of 4500 kilometers.
In November 1984, a command rocket launched from near Polotsk was able to transfer a command to launch a silo launcher in the Baikonur region. The P-36М (according to the NATO SS-18 Satan codification) that took off from the ICBM mine, after working off all the stages, successfully struck the target in the given square at the Kura test site in Kamchatka. In January 1985, the Perimeter system was put on alert. Since then, this system has been modernized several times; currently, modern ICBMs are being used as command missiles.
The command posts of this system are likely to be structures that are similar to the standard rocket bunkers of the Strategic Missile Forces. They are equipped with all necessary control equipment and communication systems. Supposedly, they can be integrated with the missile launchers of command missiles, but, most likely, they are spaced apart over a sufficiently large distance to ensure better survival of the entire system.
The only widely known component of the Perimeter system is the command missiles 15P011, they have the index 15А11. Rockets are the basis of the system. Unlike other intercontinental ballistic missiles, they should fly not towards the enemy, but over Russia, instead of thermonuclear warheads they carry powerful transmitters that send a launch command to all existing combat ballistic missiles of various bases (they have special command receivers). The system is fully automated, while the human factor in its work has been minimized.
The decision to launch command missiles is made by an autonomous command and control system - a very complex software package based on artificial intelligence. This system receives and analyzes a huge amount of very different information. During combat duty, mobile and stationary control centers on a vast territory constantly assess a lot of parameters: radiation level, seismic activity, air temperature and pressure, monitor military frequencies, fixing the intensity of radio traffic and negotiations, monitor data from the missile attack warning system (SPRN), and also monitor telemetry from the monitoring posts of the Strategic Missile Forces. The system monitors point sources of powerful ionizing and electromagnetic radiation, which coincides with seismic disturbances (evidence of nuclear strikes). After analyzing and processing all the incoming data, the Perimeter system is able to autonomously make a decision on delivering a nuclear retaliatory strike against the enemy (naturally, the first persons of the Defense Ministry and the states can activate the combat mode).
For example, if the system detects multiple point sources of high-power electromagnetic and ionizing radiation and compares them with seismic disturbance data in the same places, it may come to the conclusion of a massive nuclear strike on the territory of the country. In this case, the system will be able to initiate a retaliatory strike, even bypassing the "Kazbek" (the famous "nuclear suitcase"). Another scenario is that the Perimeter system receives information from the EWS about missile launches from the territory of other states, the Russian leadership is putting the system into combat mode. If, after a certain time, the command to shut down the system does not come, it will itself launch ballistic missiles. This solution eliminates the human factor and guarantees a retaliatory strike against the enemy, even with the complete destruction of the launch calculations and the highest military command and leadership of the country.
According to one of the developers of the Perimeter system, Vladimir Yarynich, it also served as an insurance against the top leadership of the state making a hasty decision on a nuclear strike based on unverified information. Having received a signal from the EWS, the first persons of the country could launch the Perimeter system and calmly wait for further developments, while being absolutely certain that even if everyone who has the authority to issue an order for a retaliatory attack is destroyed, a retaliation will not succeed to prevent. Thus, the possibility of deciding on a nuclear strike in the event of inaccurate information and false alarm was completely excluded.
Rule of four if
According to Vladimir Yarynich, he does not know a reliable method that could disable the system. The control-command system "Perimeter", all its sensors and command missiles are designed to work in the conditions of a real nuclear attack of the enemy. In peacetime, the system remains at rest, one can say it is in a “dream”, without ceasing to analyze the vast array of incoming information and data. When the system is put into combat mode of operation or in case of receiving an alarm signal from SPRN, Strategic Rocket Forces and other systems, monitoring of the sensor network is started, which should detect signs of nuclear explosions that have occurred.
Before launching the algorithm, which supposes the “Perimeter” to strike back, the system checks for the presence of 4 conditions, this is the “rule of four if”. Firstly, it is checked whether a nuclear attack has really occurred, the sensor system analyzes the situation for nuclear explosions in the country. After that, it is checked by the presence of communication with the General Staff, if there is a connection, the system is disconnected after some time. If the General Staff does not respond, the Perimeter requests Kazbek. If there is no answer here, artificial intelligence transfers the right to make a decision about a retaliatory strike to any person in command bunkers. Only after checking all these conditions, the system begins to act itself.
American equivalent of "Perimeter"
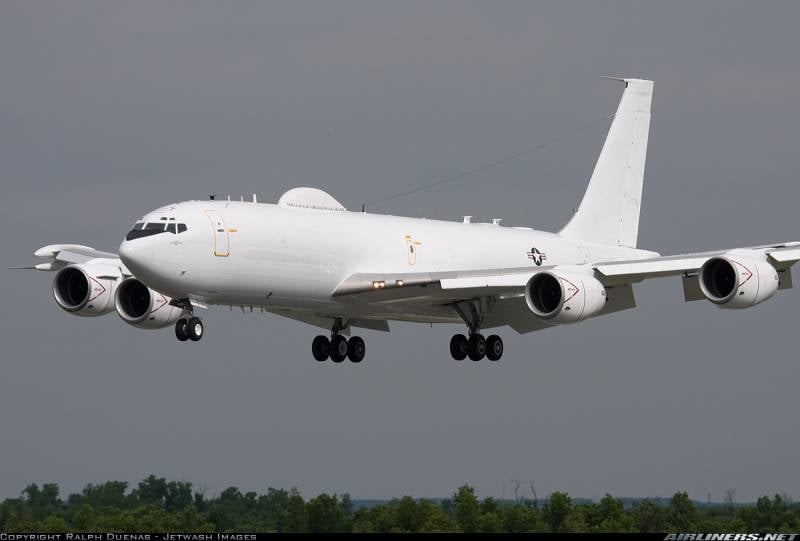
During the Cold War, the Americans created an analogue of the Russian system "Perimeter", their duplicate system called "Operation Looking Glass" (Operation Through the Looking Glass or simply Through the Looking Glass). She was put into action already 3 February 1961 of the year. The system was based on special airplanes - the US Air Command Command Air Command Command, which was deployed on the basis of eleven Boeing EC-135C aircraft. These machines were continuously in the air for 24 hours per day. Their combat duty continued 29 for years from 1961 of the year to 24 of June of 1990. The aircraft flew in shifts to various areas over the Pacific and Atlantic Ocean. Operators operating aboard these aircraft controlled the situation and duplicated the control system of the US strategic nuclear forces. In the event of the destruction of ground centers or their decommissioning by other means, they could duplicate commands to launch a nuclear strike. 24 June 1990, the continuous combat duty was discontinued, while the aircraft remained in a state of constant combat readiness.
In 1998, the Boeing EC-135C was replaced by new Boeing E-6 Mercury aircraft - control and communications aircraft created by Boeing Corporation based on the Boeing 707-320 passenger aircraft. This machine is designed to provide a backup communication system with nuclear-powered submarines with ballistic missiles (SSBN) of the US Navy, and the aircraft can also be used as an air command post of the United States Strategic Joint Command (USSTRATCOM). From 1989 to 1992, the US military received 16 of such aircraft. In the 1997-2003, they have all been upgraded and are now operated in the E-6B version. The crew of each aircraft consists of 5 people, in addition to them, there are also 17 operators on board (a total of 22 people).
Currently, these aircraft are flying in order to meet the needs of the US Department of Defense in the Pacific and Atlantic zones. On board the aircraft there is an impressive complex of necessary radio-electronic equipment for operation: an automated complex for launching ICBMs; the onboard multi-channel terminal of the Milstar satellite communication system, which provides communication in the millimeter, centimeter and decimeter ranges; a complex of super long range of high power, intended for communication with strategic nuclear submarines; 3 decimeter and meter radio stations; 3 VHF radio stations, 5 HF radio stations; automated control and communication system for VHF; emergency tracking equipment. To provide communication with strategic submarines, carriers of ballistic missiles in the super-long wavelength range, special towed antennas are used, which can be produced from the aircraft fuselage directly in flight.
Operation of the Perimeter system and its current status
After being deployed on combat duty, the Perimeter system worked and was periodically used as part of command and staff exercises. At the same time, the command missile system 15P011 with the 15А11 missile (based on the ICBM UR-100) was on alert until the middle of the 1995 year, when, within the framework of the signed START-1 agreement, it was removed from combat duty. According to the magazine Wired, which is published in the UK and the USA, the Perimeter system is operational and ready to strike a nuclear attack in the event of an attack, the article was published in the 2009 year. In December, 2011, the commander of the Strategic Missile Forces, Lieutenant-General Sergei Karakaev, said in an interview with the journalists of Komsomolskaya Pravda that the system “Perimeter still exists and is on combat duty.
Will the "Perimeter" protect against the concept of a global non-nuclear strike?
The development of promising complexes of an instantaneous global non-nuclear strike, on which the US military is working, is able to destroy the existing balance of forces in the world and ensure Washington’s strategic dominance on the world stage. The representative of the Ministry of Defense of Russia spoke about this during the Russian-Chinese briefing on missile defense, which was held on the margins of the first committee of the UN General Assembly. The concept of a fast global strike suggests that the US army is able to deliver a disarming strike on any country and any part of the planet within one hour, using its non-nuclear weapons. In this case, cruise and ballistic missiles in non-nuclear equipment can become the main means of delivering warheads.
AIF journalist Vladimir Kozhemyakin asked Ruslan Pukhov, director of the Center for Strategy and Technology Analysis (CAST), how much the American instantaneous global non-nuclear strike threatens Russia. According to Pukhov, the threat of such a blow is very significant. With all the Russian successes with Caliber, our country takes only the first steps in this direction. “How many such“ Calibers ”can we launch in one salvo? Suppose a few dozen pieces, and the Americans - a few thousand "Tomahawks." Imagine for a second that 5 of thousands of American cruise missiles are flying toward Russia, skirting the terrain, and we don’t even see them, ”the expert noted.
All Russian long-range radar detection stations record only ballistic targets: missiles that are analogs of the Russian Topol-M, Sinev, Bulava, etc. We can track rockets that go up into the sky from mines located on American territory. At the same time, if the Pentagon gives the command to launch cruise missiles from its submarines and ships located around Russia, they will be able to wipe out a number of strategic objects of paramount importance: including top political leadership, headquarters control.
At the moment we are almost defenseless against such a blow. Of course, in the Russian Federation there is and is a double reservation system, known as the “Perimeter”. It guarantees the possibility of delivering a nuclear retaliatory strike against the enemy under any circumstances. Not by chance in the United States called her "Dead Hand". The system will be able to ensure the launch of ballistic missiles even with the complete destruction of communication lines and command posts of Russian strategic nuclear forces. A retribution will still be dealt to the United States. At the same time, the mere presence of "Perimeter" does not solve the problem of our vulnerability to the "instantaneous global non-nuclear strike."
In this regard, the work of the Americans on this concept, of course, cause concern. But Americans are not suicidal: as long as they are aware that there is at least a ten percent chance that Russia can respond, their “global strike” will not take place. And our country can only answer with nuclear weapons. Therefore, it is necessary to take all necessary countermeasures. Russia should be able to see the launch of American cruise missiles and respond to it adequately with non-nuclear deterrent, without unleashing a nuclear war. But so far Russia has no such means. With the ongoing economic crisis and a reduction in funding for the armed forces, a country can save on many things, but not on our nuclear deterrent forces. In our security system, they are given absolute priority.
Information sources:
https://rg.ru/2014/01/22/perimetr-site.html
https://ria.ru/analytics/20170821/1500527559.html
http://www.aif.ru/politics/world/myortvaya_ruka_protiv_globalnogo_udara_chto_zashchitit_ot_novogo_oruzhiya_ssha
Open source materials




Information