Machines on a combined course in military and peacetime
History of the Russian Railway Troops takes the beginning of 6 August 1851. It was then that Nicholas I approved the "Regulations on the management of the St. Petersburg-Moscow Railway", according to which for its protection and operation 14 separate military workers, two conductor and " telegraph company ".
In modern conditions, the Railway Troops of Russia carry out technical cover, rehabilitation and barrage of railways in order to ensure the combat and mobilization activities of various branches of troops of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. In addition, they are assigned the functions of building (both in wartime and in peacetime) new ways of communication and increasing the survivability and throughput of existing railways, as well as performing tasks in accordance with the international treaties of the Russian Federation.
We should also mention the bridge. Even the usual small bridge to build is a problem. And the military railway workers erect bridges, which then go trains. And for the construction of these bridges, they are allocated years, and literally several hours, for this there are special machines for driving piles, and there are floating ones that even work in the middle of the river.
And if there is a need to repel the raid on the highway of terrorists or saboteurs, and for this there is a corresponding equipment, special units and everything you need. Military railroaders know how to conduct technical reconnaissance and mine clearance. That is why they are always among the first to arrive at the scene of accidents and disasters on railway transport. Only in the summer of 2005, they were involved three times in the aftermath of man-made and other disasters in Russia. These are railway accidents in the Tver region, in the Krasnodar Territory, and the explosion of a Moscow-Grozny passenger train.

The fighters are firing from the AK from the body of the “Ural”, equipped with railway skating rinks, and the soldiers cover only the sides of the cargo platform. You can see how the soldiers then parachuted directly on the rails and sleepers from the height of the 1,8 meter. At the forefront of this battle group is the UAZ automobile, equipped with railway guide rollers. However, it lacks protection.

The analysis of the presented materials makes it possible to assert that the samples shown cannot fully correspond to the equipment necessary for conducting combat operations against railroad terrorists, primarily due to the lack of gunmen. weaponsthat is not inferior in power to the weapons of a probable enemy and the corresponding defense. At the same time, the equipment that met the necessary requirements was already in service with the railway troops and could be present and future.
Vehicles that combine the possibility of movement on roads, off-road and railway tracks, in scientific and technical literature are called "machines on a combined course." It is quite natural that much attention was paid to such machines in Russia.
In the Russian Empire, and later in the USSR, the territories were developed, as a rule, with the help of railways: inexpensive construction and transportation. At the cost of titanic efforts (BAM, Transsib), the railroad workers were able to cover the country with a network of highways from east to west from Vladivostok to Kaliningrad and from south to north from Kushka to Murmansk and Salekhard. The construction of paved roads came in second place with a considerable delay. So, for example, the Far East still does not have a reliable road for communication with the central regions of the country.
These circumstances prompted the designers to think about the creation of vehicles that will be able to move on highways, rough terrain (off-road) and railway routes. Especially acute need for these vehicles experienced Railway troops. It should be noted that in the USSR even in the pre-war and military periods there appeared samples of vehicles capable of traveling on roads and railways. All samples were created on the basis of armored vehicles, which were mass-produced for the Red Army. The main feature of these armored vehicles was that the size of the wheelbase was comparable to the railway track. This simplified the development of devices for the movement of armored vehicles on the railway track.
So, on FAI-ZhD armored vehicles there were voluminous bandages with flanges mounted on the wheels during 30 minutes by the crew. The same time it was required for crews of BA-6zh, BA-10zh, BA-20zh, BA-20Mzhd and BA-64В vehicles to replace the standard wheels with metal wheels (disks) with flanges. On the BA-10, there was a hydraulic lift used to go from normal to railway and back.
Serial production of armored cars turned in the 1946 year shortly after the end of the Second World War. These vehicles were replaced by the BTR-40 and the BTR-152, which are characterized by increased maneuverability and ability to transport infantrymen equipped with light armor to protect them from shrapnel and small arms fire. However, on the basis of the data of armored personnel carriers, no modifications were made with the provision of a railway line.
The situation changed dramatically at the end of the 1960-ies due to the exacerbation of relations between China and the Soviet Union. Within a short time, military infrastructure was created in the border areas. In the conditions of weak development or absence of the road network in the region, the main emphasis was placed on the use of railway tracks. However, their defense has become a daunting task. In the sparsely populated taiga or steppes with rare villages and stations, not only open railway legs were vulnerable, but also a huge number of crossings, tunnels and overpasses. For the protection, reconnaissance, emergency transfer of repair brigades and motorized infantry needed an effective and mobile tool.
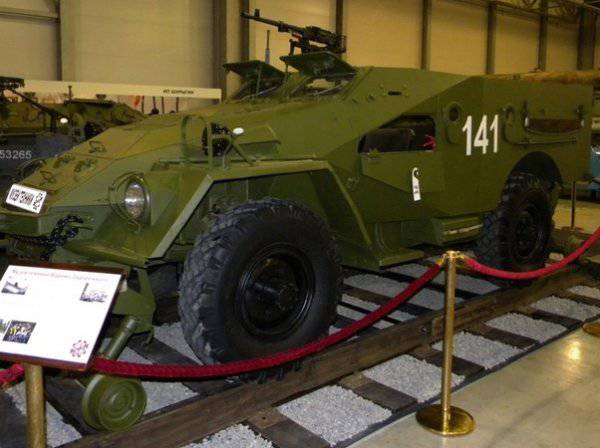
It was decided to use the main developments of the war, tested in 1943 year on a prototype BA-64G equipped with a device for a railway course. To create a new car at the combined course, they took the BTR-40 as the basis. One of the main factors in choosing this car as the base was that the wheel track of the car was close to the size of the railway track. This made it possible to use the wheels of the car as propellers while the car was moving along railway tracks. At the same time the speed of the car on the railway could reach 80 km / h. The front and rear of the car had folding frames equipped with spring springs and steel frames, rollers arranged in pairs. Rollers had internal flanges. When pressed to the rails, they prevented the BTR from the railway track immediately. To get off the track, it was necessary to raise the rollers. To replace the course it took from 3 to 5 mine. A prototype was manufactured and tested in the 1969 year. The machine was mass-produced under the designation BTR-40ZHD.
At the same time, it was decided to build four armored trains for the Trans-Baikal Military District. The composition of each armored train included a reconnaissance company having eight BTR-40ZhD. For the transportation of these vehicles, the armored train had four conventional railway platforms, which were loaded by a pair of BTR-40ZhD.
At the beginning of the 90-s, these machines served in the Far East of Russia. In 2003, the 15 BTR-40ZD, in a renewed operational state, was located on the territory of the 38 Research Test Institute of the Russian Ministry of Defense.
Do we need such machines today?
It turns out and not only for military purposes.
The author of the published article in 1997 discussed these problems in Moscow with specialists from the scientific and technical committee of the railway troops. It was a time of “local conflicts” that swept across the territory of the Russian Federation. Then it was about the difficulties faced by the repair brigades of military railway workers and the losses among the personnel. After sabotage, the GAZ-66, whose tent did not protect against the fire of terrorists, was mainly used to repair the railways. In addition, the cars did not have weapons to repel the attackers.
Railway engineers showed their achievements in the field of creating vehicles with a train at the base of an all-wheel drive car with the wheel formula 6x6, but it did not suit them. The machine shown on 6 in August 2005 of the year apparently marked the completion of the development started in the middle of 90-x. The appearance of this sample confirms the need for cars on a combined course with an increased carrying capacity, dimensions and weight.
It turned out that the constructive solutions that had been implemented earlier had exhausted themselves. The preservation of the auto-wheel track, close to the railway, in the case of an increase in the mass of the car did not provide lateral stability during the passage of bends on the highways. A different approach was required. An example of a successful solution of this task was the development of the design department of special equipment of the Gorky Automobile Plant, headed by A.G. Masyagin.
The customer was the UGZD (Gorky Railway Administration), headed at that time by O.Kh. Sharadze From the side of the UGZD, scientific and technical support of the project was carried out by the doctor of technical sciences Z.M. Slavinsky. Management hoped to solve the problems inherent to electrified railways with the help of a new car. High electrical tension, difficult weather conditions, wear of electrical equipment are the reasons for the high probability of malfunctions in the power grid. These malfunctions are difficult to predict, and their consequences often lead to train stoppages. An autocar carrying a repair crew sent after a stopped train cannot always get to the place of the accident. It was necessary to have a vehicle with a combined stroke, which would be able to get to the scene of the accident and deliver equipment for repairing the railway power grids.
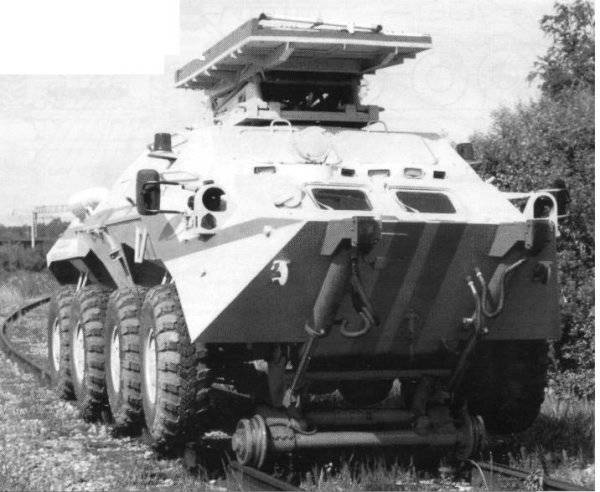
Experts UGZHD together with the designers of GAZ, analyzing the situation, decided that the armored personnel carrier BTR-80, which in 80-e was developed on GAZ, is most suitable for the creation of the vehicle as a base.
The BTR-80 maximally meets the requirements of maneuverability and has a high speed. Flexible production technology of these armored vehicles allows you to adapt its body to accommodate repairmen and the necessary equipment. The broad gauge of the BTR-80 eliminates the possibility of overturning while driving on the highway. However, for its installation on the railway track and movement on it, an additional drive was needed. Designers have proposed two options for solving this problem: an autonomous drive to the railway rollers or a drive to the rollers from the wheels.
The manufacture of prototypes and further serial production was carried out by the Arzamas engineering plant, which at that time was headed by V.I. Tyurin. Technical support was carried out by A. D. Mintyukov.
To test both versions of the drive, it was decided to make two prototypes. At the initial stage, unrealized corps of military vehicles based on the BTR-80 were used. They cut holes for the windows, and installed a lifting tower on the roof, designed by specialists from the Samara Trolleybus Repair Plant. The tower had a platform for 2 — 5 people and was able to rise to the height of the repair of electrical networks.
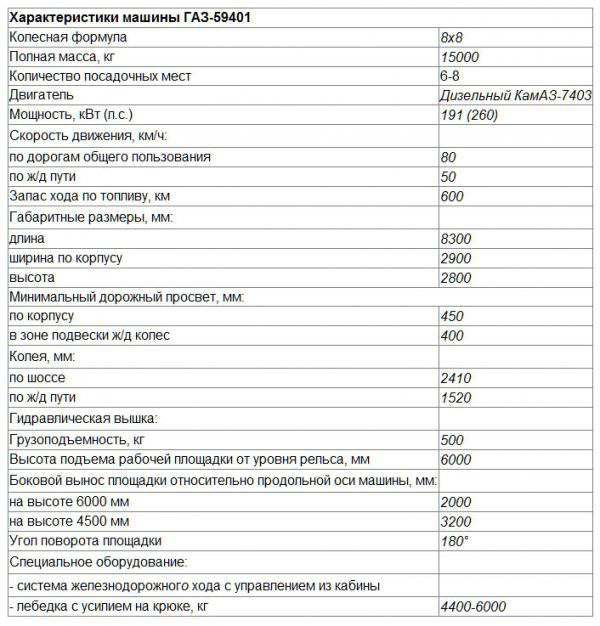
Characteristics of the armored personnel carrier BTR-40ZHD
Wheel formula 4x4
Combat weight, kg 5800
Length, mm 5200
Width, mm 1900
Height, mm 2230
Ground clearance, mm 276
Maximum speed, km / h: on the highway 78 by rail 50
Overcoming obstacles: angle of elevation 30 ° roll 25 °
pit width, m 0,75
Wade depth, m 0,9
Crew (landing), people 2 (8)
Autonomous drive of the first prototype was realized by installing a hydrostatic transmission. This solution was proposed by NATI experts (Moscow). The hydraulic pump was located in the power transmission compartment and was brought from the transfer case, which, due to the absence of a water jet, had a selection capable of passing engine power through itself. The hydraulic pump was connected with a hydraulic motor located behind the rear of the housing on the flange of the gear drive gear, converted from the armored personnel carrier bridge, using pipelines, connectors in the rear wall of the hull, as well as flexible hoses. The driven axle gearbox were connected to the supporting railway rollers.
This version of the drive had several advantages. When driving on the railway track, automobile wheels did not rotate. This reduced power loss, and the quality of the tread and tire wear did not affect the process of creating traction. However, significant shortcomings were identified. Only the rear rollers were leading. This reduced the traction characteristics of the car (the existing theoretical possibility of installing a second hydraulic motor in the front unnecessarily complicated the design). Wiring high pressure hoses (around 400 kgf / cm2) outside the machine could cause them to be damaged when driving over rough terrain. In addition, the prototype could not solve the issue of creating a high performance braking system.
During the creation of a prototype with a drive from automobile wheels, the designers of GAZ studied all known samples having a similar drive. At the same time, they paid attention to the fact that the previous cars had a mismatch of the direction of rotation of the auto wheels to the direction of rotation of the railway rollers and, consequently, the direction of the vehicle. This discrepancy may cause an accident at the time of the car’s derailment. The process of entering the rails was also considerably complicated. For cars with such a drive forward movement was carried out on the reverse gear. This made it difficult to disperse and significantly limited the speed of movement. In addition, there was no suspension of railway rollers, which is necessary for a comfortable and safe ride while driving on a railway track at speeds up to 100 km / h. In addition, the systems developed earlier necessarily included the fixing units of the railway rollers in the position of movement along the rails (hydraulic shut-off devices or mechanical stoppers).
The development of the original design of the chassis, which provided the car with the ability to move along the railway track, was done by Yu.S. Prokhorov and I.B. Kopylov under the direction of V.S. Meshcheryakov.
The device works like this. To transmit the rotation to the rollers, automobile wheels of the rear and front axles are used, having wide-profile tires of the KI-126 brand. Developed lugs KI-126 tires provide high speed and good road performance on roads with a hard surface and a weakly bearing soil.
When driving on roads, the back and front frames are pressed against the frame of the car and fixed. At the same time, all the structural elements that are necessary for driving on the rails do not impair the car’s passability, since they are located above ground clearance.
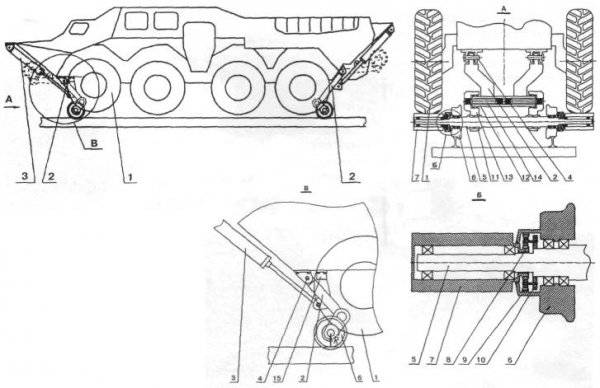
Railway track system: 1 - automobile pneumatic tires; 2 - front and rear frames; 3 - hydraulic cylinders; 4 - fingers; 5 - axis; 6 - railway skating rinks; 7 - videos; 8 - drive gears of planetary gears; 9 - driven gears; 10 - drove; 11 - rubber bushings; 12 - pins; 13 - balancers; 14 - torsion bars; 15 - stops
When putting on a railroad track, a car enters it in such a way that the pneumatic tires are positioned with the same clearance on both sides of the rails. After that, the frames are retracted by hydraulic cylinders, turning on the fingers, and run with rollers against the rails, lifting the vehicle above them. In this case, the drive rollers are pressed against the pneumatic wheels. The outer surface of the rollers has longitudinal trapezoidal grooves.
The trajectory of the rollers when rotating frames intersects vertical planes that pass through the axes of the fingers. Thus, the frames are pressed against the stops by the reaction force R on the rollers of the vehicle mass. This ensures the fixing of the frames in the position necessary for movement along the railway rails without the use of additional fixing elements in the construction. In this case, the cylinders are not subjected to loads that are associated with movement on rails. The constant pressing force on the pneumatic wheel drive rollers is ensured by the fact that the axes of the drive rollers, trunnions and pneumatic wheels are in the same plane. Pneumatic tires when moving along the railway rails are located at a height of 10 centimeters from the top level of the rails. This ensures unhindered passage of the vehicle arrows and crossings.
The movement on the railway track is carried out by means of the pneumatic wheels of the vehicle, which transmit the rotation to the drive rollers and then to the rollers through the planetary gearbox. The direction of rotation of the rollers and pneumowheels is the same. Braking is carried out by working brake system of a car through pneumowheels. When moving, the balancers, in which the axes of the rollers are fixed (through rubber bushings), can swing on the pins, twisting the torsions. Thus, the suspension of the car while driving on rails is ensured. In addition, rubber bushings reduce vibration loads.
During removal of the vehicle from the railway tracks, the frames are rotated on the fingers with the help of hydraulic cylinders and fixed in the upper extreme position. At the same time the car goes down and becomes on pneumowheels.
This option allowed to reduce the transition time from one version of the move to another to 2 minutes.
Tests of both samples were carried out in different weather conditions. The railway system was tested in the Nizhny Novgorod Region on the territory of the Railway Troops test site, where there were sections of the route that were extreme in their parameters (turning radius, debris, elevation angle, etc.). All obstacles both cars successfully overcome.
The second sample on a straight horizontal section developed the speed of 100 km / h. However, taking into account the existing restrictions, it was recommended to operate these cars at a speed of no more than 50 km / h.
Although both samples stood the test, it was decided to start mass production of the second option: it had a cheaper and simpler design, better traction and dynamics, and a reliable braking system. There was no effect of tire wear on the performance of the car.
Unfortunately, there was a tragedy at the testing stage. Because of the ridiculous accident, N. Maltsev, a leading test engineer, a very responsible, thoughtful and competent specialist, a sincere and intelligent person, who could do a lot of good and useful things, received a serious injury (which later led to death).
For mass production, they took as a basis the hull of a floating car-bus having a comfortable interior, a ventilation system, convenient doors for entry, and an increased glazing area. The car, which received the designation GAZ-59401, was additionally equipped with a radio station, which is used on the railway, as well as with a special light signaling system.
During the test, it was found that the machine can be used as a shunting tractor for several cars. Therefore, on serial samples, devices were installed to connect with standard railway train couplings.
The patent of the Russian Federation for an industrial design was issued for the appearance of this machine at a combined move.
The Gorky Railway in 1997 — 1998 ordered 15 GAZ-59401, which were distributed to almost all territorial departments of Russian railways.
Unfortunately, the plant was not able to establish permanent communication with organizations operating these machines. Information about their operation is not. However, this fact has its positive side. There were almost no orders for spare parts, which means that all systems, and in the first place, the rail system, work well. Of course, 15 machines for AMZ, which has significant production potential, cannot be considered a large number. However, at the time of economic turmoil, lack of government order, and this relatively small number of machines helped the plant and its workers survive.
But the scope of machines with a combined course could be much wider.
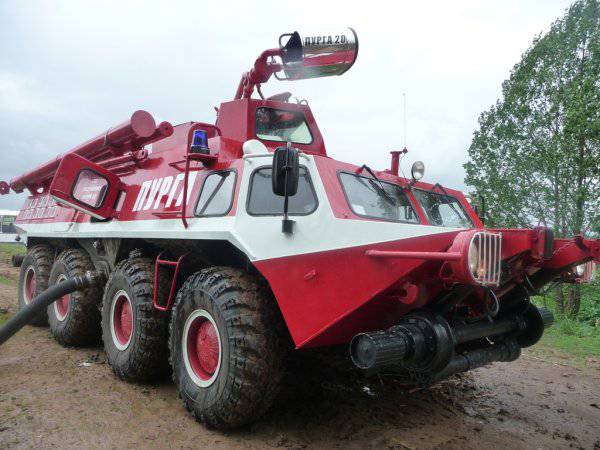
The next object that interested the Gorky Railway was the fire truck on a combined run. The kit of this machine included powder fire extinguishing equipment developed at the St. Petersburg Institute of Fire Engineering under the direction of G.N. Kuprina. This equipment was named "Purga".
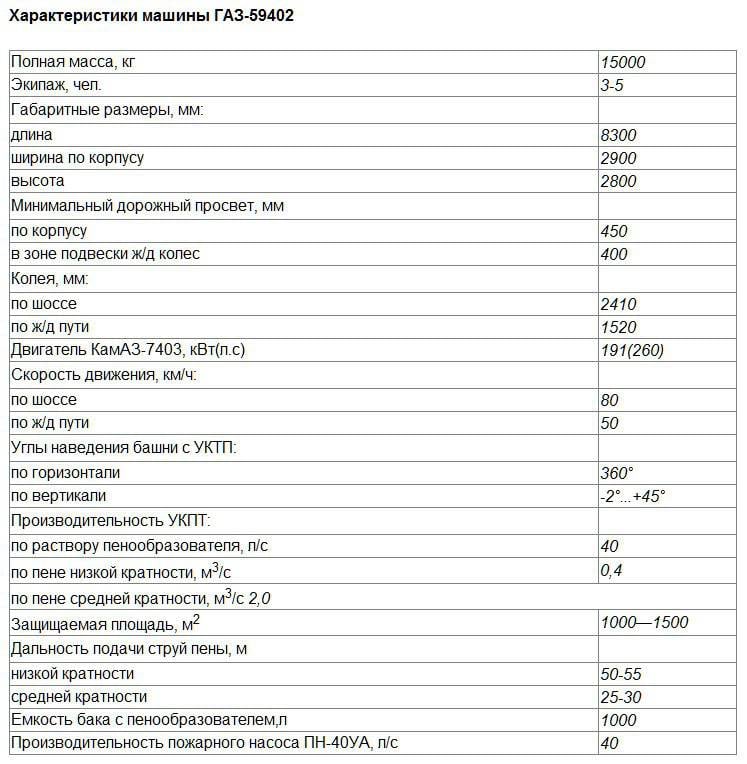
Depending on the performance of the foaming device, a number of installations are included in the “Purgi”. It can be installed on various carriers, including the VAZ-2121 "Niva".
In these installations, water under pressure, which creates a pump, is mixed with a liquid fire extinguishing agent and is supplied to the nozzles located inside the shafts. The mixture during expansion in the trunks forms a flake of substance emitted to a distance of 55 meters.
Especially for this fire engine with a combined course developed a tower installation with four trunks placed in one horizontal line. With the help of the mechanism of guidance, all trunks simultaneously rose in a vertical plane. Movement of trunks in the horizontal plane was carried out by turning the entire installation. The operator, who is inside the installation, had a window located between the pairs of trunks to monitor the terrain.
The tower installation with the Purga system was developed by VB Kuklin and B.N. Brovkin.
The pump, which provided water from a pond or tank, was part of the equipment of this machine. There were hoses, hoses, which allowed for the withdrawal of water at a distance of 50 meters from the reservoir. Inside the car were a reagent tank and space for five members of the fire brigade.
The prototype machine, which received the designation GAZ-59402, many times carried out demonstration extinguishing and demonstrated at exhibitions.
The design of the machine had the following features:
- wheel formula 8x8;
- centralized tire pressure adjustment system;
- independent torsion wheel suspension;
- hydraulic shock absorbers;
- differentials of high friction bridges;
- heat insulation, heating and ventilation systems;
- the system of the railway course controlled from the cabin;
- filtering unit;
- self-pulling winch;
- protected sealed enclosure that allows you to approach the fire source to a distance of 50 meters and extinguish explosive objects;
- rotary tower installation, equipped with a system of combined extinguishing fires (water plus fire extinguishing agent) "Purga";
- pump PN-40UA which is driven by the transmission of the machine.
In addition, the specialists of the UGZD have worked on a complete set of machines for maintenance of the railway track. It was assumed that this machine would be equipped with a powerful hydraulic manipulator of the company “LOLLIFT”, which would have a brush-cutting head at the end of the boom, allowing to cut small trees (trunk diameter up to 50 mm) and bushes in the area of alienation under the railway track without leaving the machine. Also provided special equipment for the repair of rails, sleepers, ways, etc. However, the leadership of the UGZD soon came to other people, and the joint work with JSC AMZ and JSC GAZ described above did not continue.
In order for all original solutions providing a combined course to be more widely used, the following can be recommended.
1. In addition to the active sales of mass-produced cars based on the BTR-80, it was necessary to work out the use of other high-traffic vehicles as the base chassis. For example, the structure of the holding "RUSPROMAVTO", except for OJSC "Arzamas Machine-Building Plant" and OJSC "GAZ", includes OJSC "Automobile Plant" Ural ". “Urals” have proven themselves on the roads and roads of Russia. They were used by the transport service of the Railway Troops. Despite the fact that military engineers proposed their own version of equipping the Ural with a railway line system, the device from GAZ, which was tested on the basis of the BTR-80, will also have advantages when installed on Ural vehicles. For civil service conditions, it is also important that on these machines the width will not exceed 2500 millimeters, which meets the safety requirements of the vehicle. Probably, the cost of such cars will be significantly less than that of GAZ-59402 and GAZ-59401.
2. For machines with a combined course created on the basis of the BTR-80, there is a slightly different future. Russian railway troops do not currently have their own fighting vehicles. Therefore, the development of OAO GAZ would have come in very handy. After all, from the entire family of armored personnel carriers, created by the designers of this plant, it would be possible to create a machine that would best meet the needs of the Railway Forces.
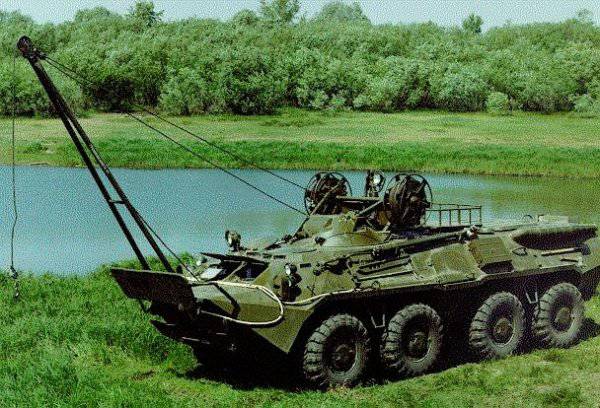
Apparently, we need a machine at a combined move, which has a set of equipment for carrying out repair work on railways, a crane installation, welding equipment, comfortable conditions for the repair crew, with protection and the ability to repel an attack. In this case, a serial armored vehicle BREM-K, equipped with a railway system, could be used. This would allow to eliminate all the disadvantages that appear when using a civilian car as a base vehicle.
The designers of OAO GAZ many times turned to the leadership of the railway troops with proposals to create a car on a combined run. These appeals, unfortunately, remained unanswered. But since the question of equipping the Russian Armed Forces with equipment that has advanced and progressive capabilities and characteristics is very relevant today, interest in the joint work of specialists and managers of railway troops on the one hand and designers and manufacturers of military equipment on the other will increase in the near future.







Information