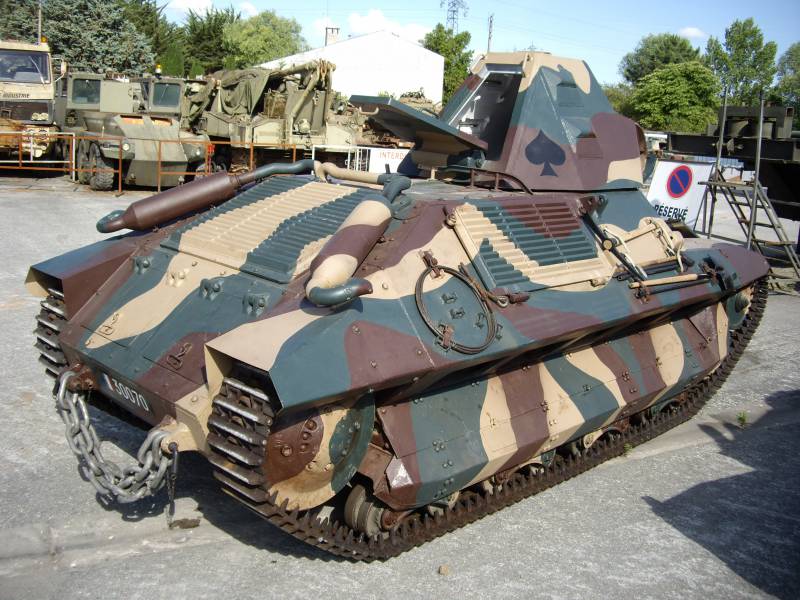
French light tank support FCM 36
The French tank FCM 36 favorably differed from its contemporaries by the sloping arrangement of the armor plates, they were located at rational inclination angles. In this case, the tank hull was welded, and the thickness of the frontal reservation was brought to 40 mm. Also, the installation of a diesel engine, which allowed to significantly increase the cruising range of the tank, was almost undoubtedly compared to the other tanks of those years (225 km), to the undoubted advantages of the combat vehicle.
At the same time, the infantry FCM 36 had obvious drawbacks, which included a low movement speed - up to 24 km / h (on the highway). But most of all the questions were caused by its armament - the short-barreled 37-mm SA18 cannon turned out to be completely ineffective in fighting enemy tanks, as manifested in the battles of World War II. Against German tanks with armor thickness over 20 mm, this weapon turned out to be completely useless. At the same time, the low maximum speed no longer corresponded to the realities of a modern war of maneuver. Even the French themselves at long marches because of low-speed threw these tanks not under their own power, but by road, FCM 36 were transported on special heavy trailers.
History create FCM 36
Strange as it may seem, another company, Hotchkiss, owes its birth to one of the most interesting French tanks of the interwar period. It was she who, in 1933, proposed to develop a better armored and cheaper infantry escort tank. In response to this proposal, a competitive task was drawn up, which was sent at once to several French design teams. The most intense competition was between the Hotchkiss H-35 and Renault R-35 tanks, which were seen as real candidates for mass production. But another player, less dangerous, intervened in the race to create a new light tank.
This player was the company FCM (Forges et Chantiers de la Mediterranee) from the south of France, from Toulon, which had a long tradition of developing armored combat vehicles. Since 1921, the famous heavy tank 2С was produced here, assembled in a small batch - in total 10 units. Later, the plant's team, led by engineer Budro, was engaged in creating a transmission for the new French heavy tank type Char B. In 1934, the company received an offer to engage in a more promising business. It was about developing a new light tank, which was intended to accompany infantry in combat.
The technical task for the creation of a new tank was issued by the French military. Boudreau in a fairly short time managed to prepare a preliminary draft of the new infantry tank. Already in March, 1934, a wooden model of a future life-size combat vehicle was presented to representatives of the army commission. The tank really liked the infantry, which wanted first of all to get a well-protected vehicle. The development of FCM just had a significant advantage - according to the project, the armor plates had to be connected to each other at high angles of inclination, which increased the amount of reduced armor and increased its projectile resistance.
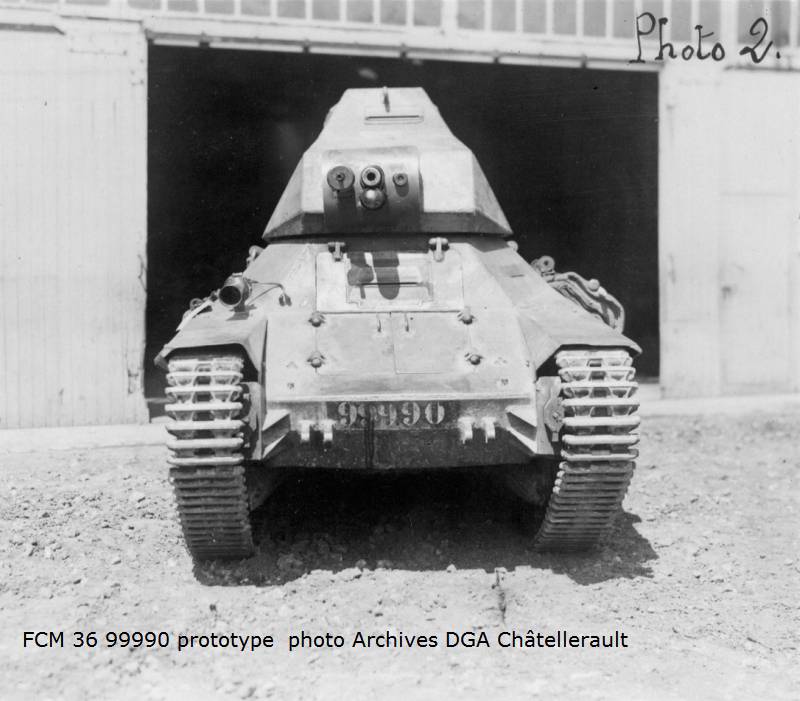
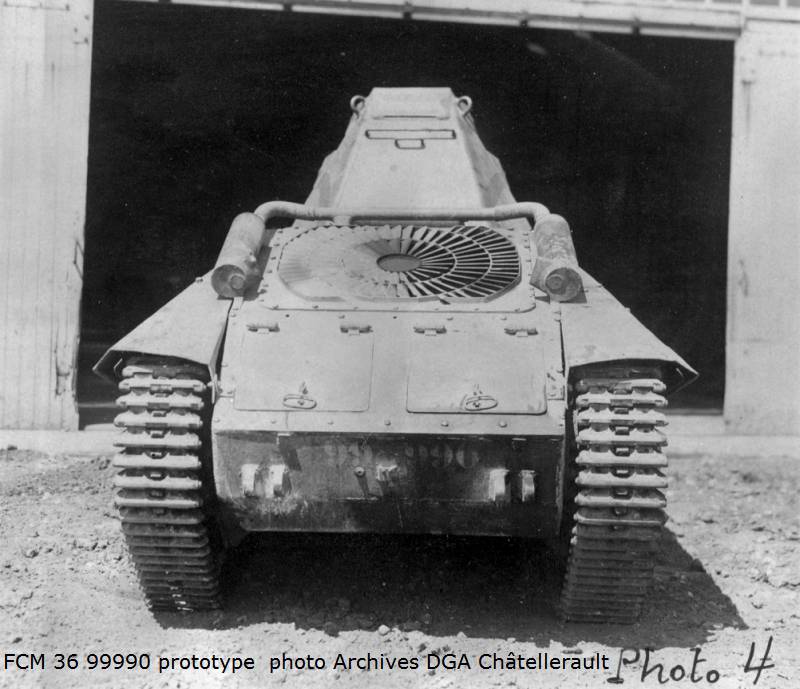
A little more than a year passed, and the first prototype of the light tank, designated FCM 36, was presented to the French military commission in Vincennes. The design of the tank from Toulon was more complicated than that of the R-35 and H-35. According to the technical assignment, the thickness of the frontal and side armor of the tank was 30 mm, which was to provide reliable protection from the fire of large-caliber machine guns, as well as small-caliber guns - 20-25 mm, while German 37-mm "beater" type PaK 35 / 36 at close range combat could well hit the tank in the side, if it was located at a right angle. In this regard, Boudreau decided to use the inclined arrangement of armor plates, in order to let the projectile flashing the armor turn out to be as long as possible. This led to the complexity of the design of the combat vehicle, which, in turn, adversely affected the manufacturing process and the cost of the FCM 36. However, the tank developed by the Toulon company, in general, could not be called simple.
The layout of the tank FCM 36
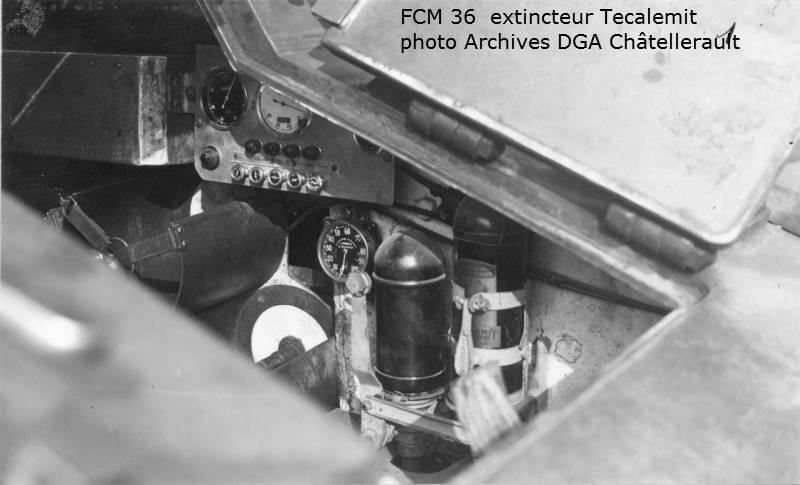
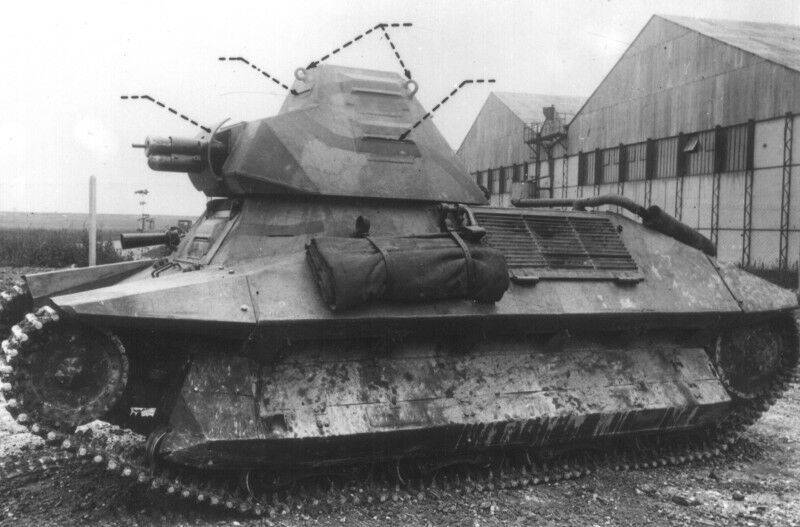
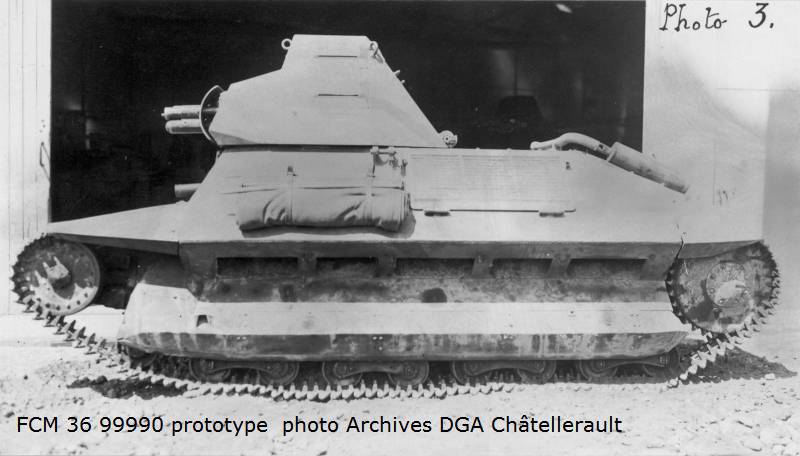
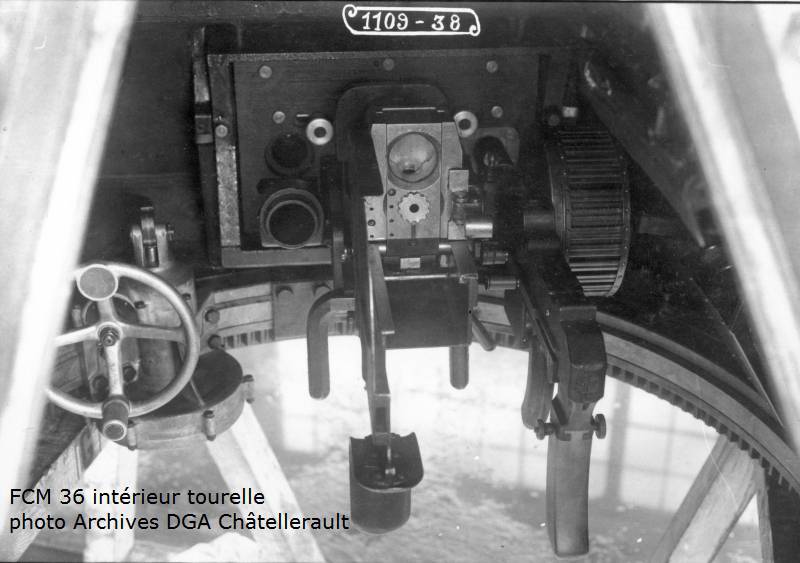
The layout of the FCM 36 infantry tank was “classic.” In front of the case was the place of the driver, behind him was the commander of the combat vehicle, which simultaneously served as the shooter and loader. At his disposal was an old short-barreled 37-mm SA18 cannon and a 7,5-mm machine gun paired with it. Semi-automatic rifled gun Puteaux SA 18 was created during the First World War. The gun had a total length of 21 caliber - 777 mm. This gun was installed on one of the best tanks of the First World War - Renault FT-17, but for the second half of the 1930-ies the gun was clearly outdated. Armament tank FCM 36 was located in a single tower, which was made in the shape of a truncated pyramid, it had 4 viewing devices. The general mask for guns and machine guns allowed to direct weapons in a vertical plane ranging from -17 to + 20 degrees.
A novelty of the tank was the use of the Berliet 4-cylinder diesel engine manufactured by Berliet, initially it was an HP 91 power unit. Although its power was weaker than that of the engine of the H-35 tank, FCM 36 significantly exceeded other combat vehicles in this indicator as the power reserve - the 217 reserve of a liter fuel tank was enough for 225 kilometers when driving on the highway. In addition, cheaper diesel fuel had a lower fire hazard, which was also very important.
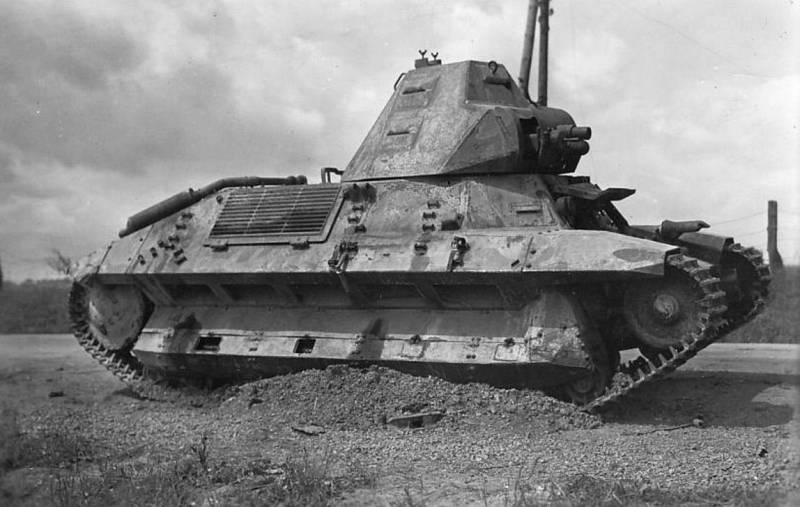
The undercarriage of the Toulon tank was not particularly simple. Applied to each side, it consisted of 9 track rollers, 8 of which were combined into 4 carts, as well as 4 support rollers, rear drive and front guide wheels. The rollers of the tank, as well as the external elements of the transmission, were almost completely closed by a bulwark of a different shape. The bulwarks had 5 cutouts designed to dump dirt from the upper tracks of the tracks. The prototype of the tank also had front “wings” of a specific configuration. The design of the tracks was partially borrowed from the heavy French tank B1. It was not the best choice of designers, but they will find out about it later.
The trials of the light tank FCM 36, which took place in 1935, brought more disappointment than optimism. The total mass of the new combat vehicle exceeded the permissible 10 168 kg, and in terms of mobility and maximum speed the tank significantly lost to its main competitor - Renault R-35. 9 June 1935, the prototype was returned to the manufacturer, where the developers facilitated the design of the hull, and also altered the transmission, tower and tracked tracks. To facilitate access to the engine compartment its roof could be closed easily removable panel. Two repeated test cycles were conducted on September 10 - October 23, and also December 19 1935 of the year - May 14 of the year 1936. The French army was not thrilled with the new tank, but agreed to put it into service, with one condition - the maximum thickness of the armor would be brought to 40 mm. Since there was no time left for such a revision, instead of designing a new hull, the designers decided to simply add an 10 mm armor steel sheet over the existing hull. In this form, the prototype was demonstrated 9 June 1936, the selection committee, which declared it the best of the infantry tanks presented, but still preferred the R-35 tank.
As a result, the French army placed an order for 100 tanks (at a price of 450 thousand francs per unit), giving them the official designation Char leger Modele 1936 FCM. Perhaps the number of ordered serial tanks could turn out to be large, but the price of the tank and its overweight, coupled with low-speed characteristics, had a very big influence on the fate of this initially promising combat vehicle.
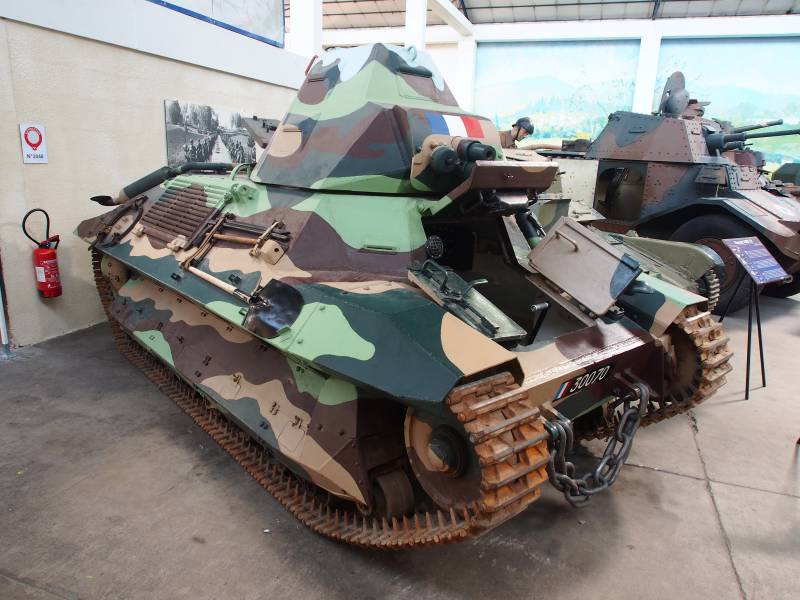
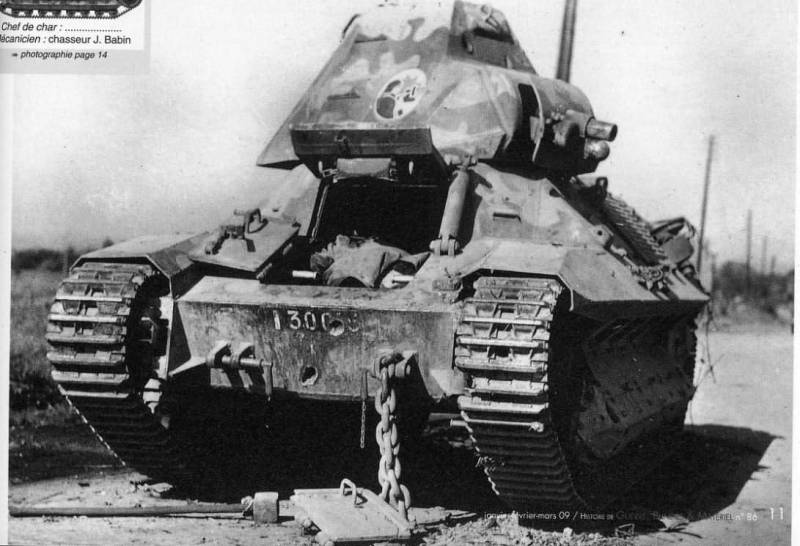
The FCM 36 production tanks were somewhat different from the prototypes that were tested. First of all, the company from Toulon replaced the tower. Unlike the prototype, it acquired a characteristic superstructure, which was designed to observe the battlefield (something like a commander's turret), which made the outlines of this combat vehicle even more futuristic. The bow section of the tank hull was also completely changed, becoming more “broken” rather than flat, as it was, for example, in the famous T-34. The low dynamics of the combat vehicle was attempted to be improved by installing a more powerful engine of the same company Berliet, its power increased to 105 hp. However, in the end, the power density of the serial machine still amounted to just 7,6 hp / t, which was far from an outstanding indicator. Managed to undergo changes and the chassis of the tank. First of all, the tracks were changed, the grip to the supporting surface of which was significantly improved. In addition, the front "wings" were dismantled, which weakly defended the chassis and prevented confident movement in snow and mud.
The production of a new light tank took place very slowly. The first batch of these tanks, the French military received only 2 May 1938 of the year. A fully supply 100 combat vehicles ended 13 March 1939 of the year. Combat vehicles received registration numbers starting with 30001 through 30100. As a result, the constructors tank from Toulon turned out to be not only the heaviest of "classmates", but also the most expensive. Each FCM 36 cost the French treasury 450 thousand francs, while Hotchkiss H 35 cost just 200 thousand francs. For comparison: for the same money it was possible to purchase one British Infantry Tank Mk.III, two Infantry Tank Mk.I or almost two German Pz.Kpfw.III, with which FCM 36 simply could not fight on equal terms. Such was the price paid by the French for quite progressive elements of the structure.
The battles of World War II showed that FCM 36 could successfully fight with enemy light tanks and armored personnel carriers, but already Pz.Kpfw.III, which he had to face, turned out to be too tough for him. Of course, FCM 36 was no worse than the same Renault R 35, but it wasn’t better either. The effectiveness of the combat use of these tanks corresponded to the issued technical task. Created to support the infantry, they were forced to engage in battle with more advanced enemy tanks. As a result, only the decisiveness of the French tankers was not enough; by the end of the fighting, the entire French army had only 10 operational FCM 36 light tanks.
Performance specifications FCM 36:
Overall dimensions: length - 4,46 m, width - 2,14 m, height - 2,20 m.
Combat weight - 12 350 kg.
Reservations - 40 mm (maximum).
Armament - SA-37 18-mm gun and 7,5-mm machine gun.
Ammunition - 102 projectile and 3000 cartridges.
The power plant is a diesel 4-cylinder Berliet-Ricardo engine with a power of 105 HP.
Power density - 7,6 hp / t.
Maximum speed - 24 km / h (on the highway).
Power reserve - 225 km.
Fuel supply - 217 l.
Crew - 2 person.





Information sources:
http://www.aviarmor.net/tww2/tanks/france/fcm_36.htm
http://warspot.ru/5421-progressivnyy-neudachnik
http://www.chars-francais.net/2015/index.php/engins-blindes/chars?task=view&id=801
Open source materials





Information