Water ... all around water. About the modernization of the submarine fleet
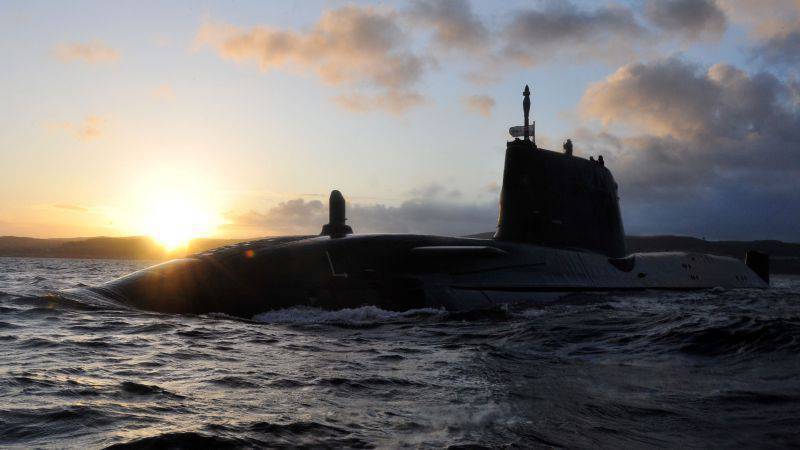

The UK government recently confirmed that BAE Systems will build a total of seven Astute-class submarines to replace the current Trafalgar-class submarines.
Terrible, secretive, versatile, capable of delivering a point or global strike, modern submarines are the preferred weapons platforms for those fleets that can afford it. It is not surprising, therefore, that new submarine construction and modernization programs have become so widespread in the world.
Since the end of the Cold War, fleets with nuclear-powered submarines of the type MPLATRK (multipurpose submarine, nuclear, torpedo, with cruise missiles) have expanded the boundaries of operations for these highly powerful platforms. Previously performed tasks of detecting and tracking enemy submarines, especially nuclear-powered submarines of the type SSBN (submarine, nuclear, with ballistic missiles), they are now regularly working in conjunction with surface warships. Thus, in carrying out its tasks on the open sea and off the coast, the MPLATRK substantially increases the reconnaissance, defensive and attacking capabilities of the fleets.
British fleet
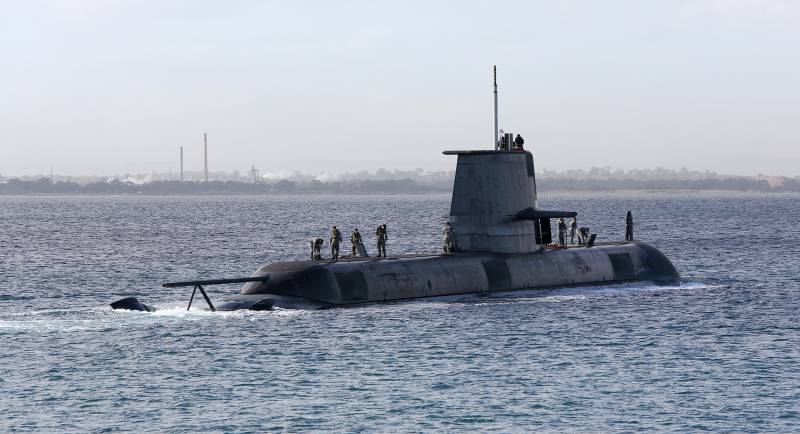
Great Britain is a member of the elite club of those few countries that are armed with both the MPLATRK and SSBNs. As for the first category, the third new Artful Astral MPLATRK was transferred to the British fleet in March 2016. The Ministry of Defense confirmed that BAE System will build a total of seven vessels of this class at its shipyard in Barrow-in-Furness by 2024. Submarines of the "Astute" class, replacing the existing MPLATRK of the "Trafalgar" class, have a displacement of 7400 tons underwater, 97 meters long and 11,3 meters wide. The propulsion system of these MPLATRK includes a Rolls-Royce PWR2 water-water nuclear reactor and a pump-type water-jet propulsion device, which allows to reach a maximum speed of 30 knots (55,6 km / h) under water.
As for the sensory system of Astute class submarines, they install the standard 2076 Stage-2 kit manufactured by Thales, as well as the non-penetrating type CM010 optic mast of the same manufacturer. The Artful MPLATRK was the first submarine equipped with a Common Combat System (CCS) combat system developed by BAE Systems, which should be installed on the first two submarines of this class, built earlier, since they were still serviced by commercial software. As for weapons, submarines of this class carry UGM-1O9E Tomahawk Btock-IV surface-to-surface ballistic missiles by Raytheon and Spearfish heavy torxes from BAE Systems. The British fleet should include four more submarines of this class: Audacious, Anson, Agamemnon and Ajax. According to the 2013 House of Commons, these ships are scheduled to be commissioned every two years from 2018 to 2024. The cost of the project has been revised several times since its approval by the government in 1997, but judging by several figures from the British Ministry of Defense published since 2011, the total construction cost of boats of this class appears to be around 11,9 billion dollars.
US Navy
Like the British Navy, the US also has MPLATRK and SSBNs in service. The US Navy is currently replacing its Los Angeles-class MPLATR fleet with new Virginia-class submarines. A total of 48 submarines are planned to be built, their construction is divided between General Dynamics Electric Boat and Huntington Ingalls Industries Newport News. According to Congressional Research, each submarine will cost $ 2,7 billion. As for the characteristics of boats of this class, they are equipped with a Knolls S9G nuclear reactor, connected to a pump-type jet propeller from BAE Systems, which allows a speed of at least 35 knots (64,8 km / h). The armament complex includes 12 UGM-109E missile launchers and four launch tubes for 28 Raytheon Mk.48 torpedoes. Integrated sonar system with strictly classified technical characteristics includes an active / passive nasal antenna array AN / BQQ-10 from Lockheed Martin, as well as towed sonars TB-34 from Lockheed Martin, RB-33 from Chesapeake Science and on-board fiber-optic antenna arrays. To date, 12 submarines taken into service, the latest John Warner was transferred to the fleet on August 1, 2015. The thirteenth Illinois submarine in this class was launched in October 2015 and is scheduled to be transferred to the fleet on October 29, 2016 (the event happened, everyone reported it news agencies). In December 2008, five more submarines were ordered, four of which, Washington, Colorado, Indiana and South Dakota, are under construction and the fifth Delaware is in the process of being booked. Based on the schedule for the implementation of the existing stages of the program, these first four submarines can be launched sometime in May, September, November and October 2017 and transferred to the fleet one year after these dates. The construction of the South Dakota submarine has not yet begun.
France
Along with the United Kingdom and the United States, France is also updating its MPLATRK fleet through the purchase of Barracuda-class submarines with a tonnage of 5300 tons, which are being built by the DCNS shipyard. For the French fleet, the first Suffren submarine of the six planned is being built. It is expected that the submarine "Suffren" will be transferred to the fleet in 2017 year, and the last submarine "De Grasse" in 2029 year. The French Senate in 2013 estimated the cost of the entire program at about 7,8 billion dollars. These submarines will be equipped with Areva-Technatrome’s K-15 nuclear reactor and a pumping water jet propulsion unit that will allow the speed of at least 25 nodes (46 km / h) to be developed under water. The armament of nuclear submarines of this class includes sea-launched cruise missiles SCALP (Systeme de Croisiere Autonome a Longue Portee-Emploi Genera) - MBDA company SM-39 Block-2 “Exocet” multi-purpose autonomous long-range cruise missile also from MBDA and heavy torpedoes F-21 manufactured by DCNS. Weapon systems, sensors and tactical information are processed by the DCNS / Thales SYCOBS combat control system, which integrates all sensors (including the integrated set of Thales S-Cube hydroacoustic stations, collision avoidance sonar with (underwater) obstacles Seaclear and two optic masts from Sagem), processing loaded external tactical data, weapon launch and control systems, as well as communication and navigation systems.
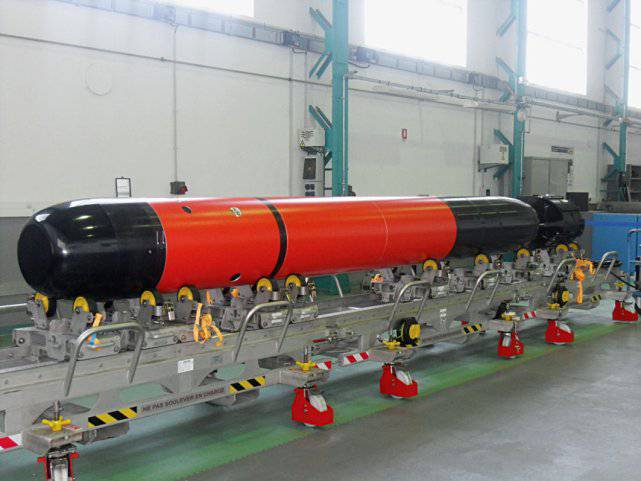

Heavy torpedo F-21
The Virginia-class MPLATRKs of the US Navy, which are replacing the Los Angeles-class MPLATRKs, are intended for coastal and deep-sea operations. The production of these submarines will go at least until the year 2043
Russia
The first MPLATRK "Severodvinsk" of the new project "Ash" was transferred to the Russian fleet after many delays due to insufficient funding in June 2014 of the year. Its construction at the Sevmash shipbuilding plant began in 1993 year. The second submarine of this class, the Nizhny Novgorod, entered service in the 2016 year. According to existing plans, five more submarines of this project should be built, but at the moment four of them are under construction: Kazan, Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk and Arkhangelsk. The last submarine "Perm" should be laid in 2016 year. The submarines of this project with a tonnage of 14021 ton, 120 meters in length and 15 meters in width have an onboard water-cooled nuclear reactor developed by the OKBM. Afrikantov, allowing you to develop speed under water 35 nodes (64,8 km / h). According to open sources, the first submarine of this project has been successfully tested at a depth of 600 meters. The submarine armament complex includes eight vertical-launch launchers capable of launching the P-800 Onyx anti-ship missiles developed by the NPO Mashinostroyenia, the 3M-54 Caliber-PL missile developed by the Novator Design Bureau and the X-101 sea-launched cruise missiles OKB "Rainbow". For the first time in the practice of Russian shipbuilding, ten 533-mm torpedo tubes are located behind the central post section. The spherical hydroacoustic station, which occupied the entire nose, did not allow to place the torpedo tubes traditionally in the nose, which is one of the most noticeable distinctive features of this project. They are located at an angle on the side in the area of the fence of sliding devices. The cost of each submarine is estimated at 1,6 billion dollars.
The search and attack submarine of the Kilo project is currently in service with eight countries. The construction of the submarines continues as Algeria ordered the newest submarines of the 636 Kilo project.
Diesel submarines
In addition to nuclear-powered submarines, more and more attention is being paid to traditional diesel submarines (DPLs), especially with regard to the leading fleets of the Middle East and North Africa. For example, two submarines of the 636E Varshavyanka project developed by Rubin Design Bureau must be supplied to the Algerian Navy in the 2018 year; they will join the four previously delivered submarines of the 636 Kilo Project and the 877EKM Project. The main task of the Kilo family of submarines is to combat surface and submarine vessels in relatively shallow waters. According to the general opinion, these submarines are quite silent, since the frequency of rotation of the propeller shaft was reduced to significantly reduce the acoustic signs of visibility. In addition, an air-independent power plant (WES) was developed for these boats, but there is no information that it will be installed on Algerian submarines. The wind turbine uses fuel cells in combination with the oxygen production system, which allows the boat to stay under water for a long time and also to move very quietly due to the fact that it does not depend on the cooling pumps, which create considerable noise. The first two boats must be delivered by the end of 2018 of the year.
Also, Russian submarines are in service with the Egyptian Navy. Egypt’s submarine fleet consists of four outdated submarines of the 633 project (NATO’s Romeo classification) built by the Red Sormovo plant, upgraded in the 90s. The UGM-84 Harpoon anti-ship missiles of the American company Boeing are installed on board these submarines. At present, the process of replacing these boats with four Type 209 class submarines has begun. The first submarine of this class, launched in December 2015, was built by the German shipyard ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems (TKMS). Previous submarines of this type were equipped with optoelectronic mast of non-penetrating ISUS-90 type from Atlas Elektronik, as well as passive / active search and targeting sonar station CSU-90 manufactured by Atlas Elektronik and side sonar antennas. These submarines can also be equipped with the MSI-90U Mk.2 combat management system developed by the Norwegian company Kongsberg. This combat control system is also installed on board the Indonesian fleet of the Cakra / Type-209 class fleet and is expected to be installed on board the Chang Bogo / Type-209 class Indonesian submarines.
Israel
Israel, meanwhile, is building up its underwater power as part of a program for developing naval forces, whose tasks now include protecting gas fields on the shelf in the Mediterranean. Three modern submarines of the “Dolphin IV” class, which are being built by a division of the German TKMS, Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft, will be consistently taken to the balance of the Israeli Navy. The total cost of this program is 1,8 billion dollars and is partially subsidized by the German government. The first two submarines, Tannin and Rahav, have already been transferred to Israel, and the third should be delivered in 2017. These submarines have a special neck of secrecy, because they use the technology of wind turbines, which allows you to develop the speed of 25 nodes under water. The armament system includes torpedoes with wire-guided DM-2A4 Seehake from Atlas Elektronik and Boeing’s UGM-84C anti-ship missiles, as well as Triton anti-helicopter missiles manufactured by LFK-Lenkflugkorpersysteme. Submarines are equipped with six 533-mm and four 650-mm torpedo tubes. Devices of larger diameter can launch not only torpedoes and cruise missiles, but also serve as a lock chamber for the exit of naval commandos from the Israeli unit Flotilla 13.
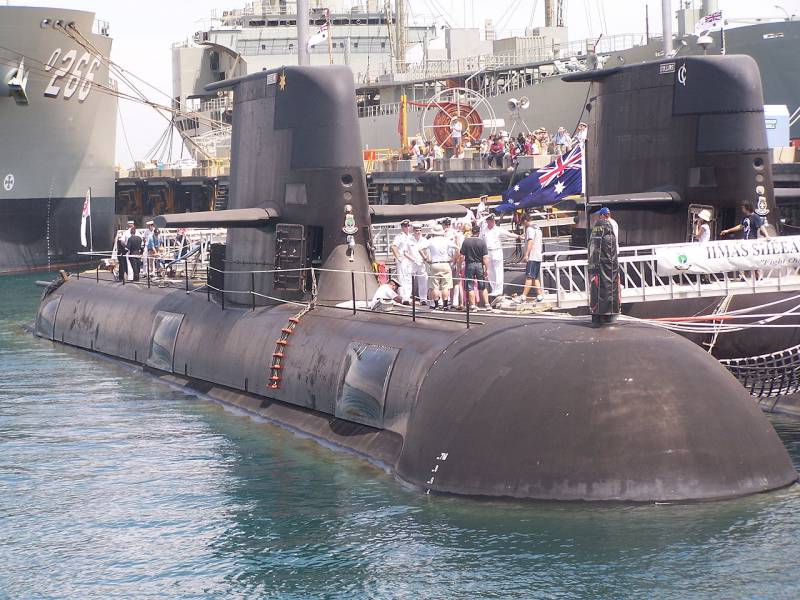
The combat readiness of six Collins class submarines was considered unsatisfactory due to the lack of personnel and technical problems. It is planned to modernize them and, ultimately, to replace them with twelve new DPLs.
Australia
The Australian Navy is considered to be a highly experienced DPL operator with a strategic location and professional connections with European and Asian fleets. These and some other reasons forced the Australian fleet to begin both the modernization of the existing problem class “Collins” submarines and the program for their replacement. According to a well-known Australian expert in the field of submarine warfare: “Diesel engines of these submarines usually need special attention, there is also a fundamental problem with the fuel tanks of the Collins class submarines, which are not designed to operate in the very salty sea water of the Australian coast ". The shipbuilding company ASC, the manufacturer of the existing six class submarines "Collins", in the next ten years is going to take up closely the construction of new surface combatants. In this regard, the company will have limited opportunities to implement the modernization program for the Collins class submarines, within which, apparently, the batteries, armament systems, communication systems and hydroacoustic stations will also have to be developed. According to one of the senior officers of the fleet: "The politically sensitive issue of the modernization of submarines in Sweden, where they were originally developed, is currently being worked out." The involvement of the Spanish Navantia shipyard to build hulls for two new Canberra-class amphibious ships of the Australian fleet caused many criticisms from politicians who stated that for economic reasons and to ensure safety, all work on these vessels should be carried out in Australia. The transfer of contracts to foreign companies for the construction of Australian submarines is likely to cause serious objections from opposition politicians and trade unions. At the same time, in October 2015, the Kockums shipyard (a division of Saab) proposed the modernization of Australian submarines on the basis of improvements carried out at the Gotland class submarine fleet of the Swedish fleet. Currently, the modernization of the submarines of the Australian fleet, which is expected to end in 2019 year, the company is engaged in Saab.
Along with the planned modernization of the Collins class submarines, the Australian fleet is already looking for a replacement for them. In April, 2016, Australia selected the French shipbuilding company DCNS as the preferred contractor for the Collins class submarine replacement program, designated Project Sea 1000. Negotiations are underway between the Australian Department of Defense and the DCNS shipyard, which should be completed at the start of 2017. Depending on the outcome of these negotiations, DCNS will begin a three-year contract for the construction of new submarines. The project of the French shipyard is a variation on the Barracuda class of submarines, in connection with which it received the designation "Shortfin Barracuda-A1". Traditional nuclear submarines class "Barracuda" are in service with the French fleet. Australia has yet to decide whether to acquire a battle management system from Lockheed Martin or Raytheon. All twelve submarines that the Australian fleet will purchase will be built in Australian shipyards.
The Scorpene class submarines, designed by DCNS shipyard, are in service with four countries. A project is underway to assemble four such submarines in Brazil.
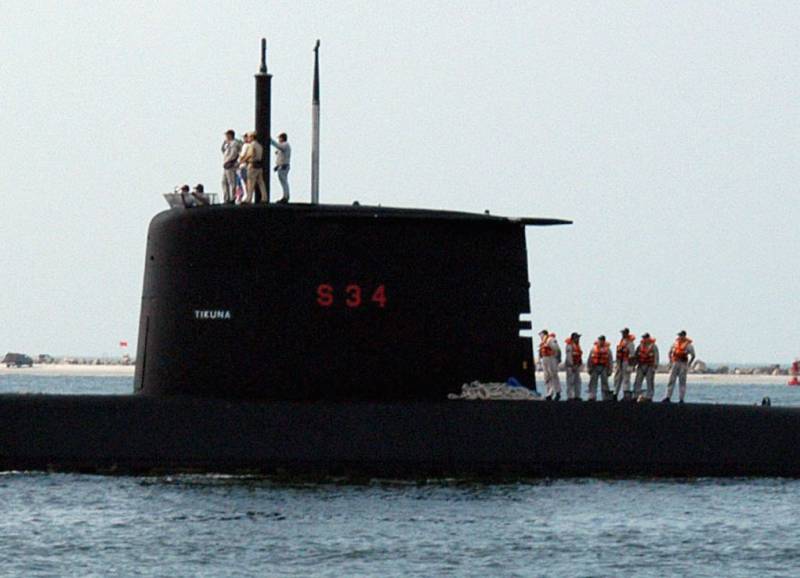
The submarine class "Tikuna" of the Brazilian fleet will be replaced by new submarines in the near future.
Brazil
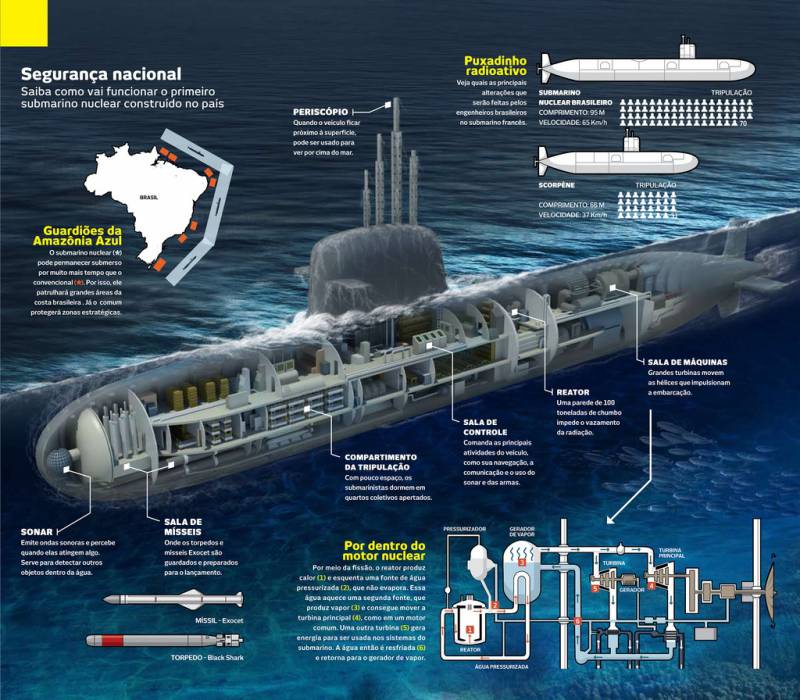
In Latin America, the Brazilian fleet is notable for its power. Currently, the fleet, which has five Type 209 class submarines, is cooperating with the French shipyard DCNS to replace its traditional diesel submarines with nuclear submarines of the class Scorpene developed by DCNS, after which it will join the elite group of countries that have weapons like submarines. According to French media, the total value of the contract is 9,3 billion dollars. “I can confirm that the submarines of the Scorpene class will be armed with heavy F-21 torpedoes, as well as the CANTO electronic countermeasure system,” said DCNS spokeswoman Marion Bonnet. “Most likely, the submarines will be armed with anti-ship missiles, although it is too early to say which ones.” The construction of the first Brazilian submarine of the Scorpene class, mainly of French components, is already underway at the Itagual Brazilian shipyard on the south coast, where the submarine fleet is also being built. The country's leadership states that Brazil needs nuclear submarines in order to ensure the long-term security of the country's long coast and mineral deposits on the shelf. It is likely that today's Brazilian politicians also want to raise the status and influence of the country, especially in connection with the possible permanent membership in the UN Security Council.
The project of the first Brazilian nuclear submarine Alvare Alberto
The construction of the nuclear submarine Alvare Alberto of its own Brazilian development with a submerged displacement of about 4000 tons, which was to begin in the 2015 year, had not yet begun. It is known that the water-cooled reactor 2131-R of Brazilian development, which was made in 2013 year, will be installed on the boat. The model of the reactor determines its placement in the middle part of the body. The French company DCNS will assist in the construction of the hull and will also provide non-nuclear technologies. The commander of the Brazilian fleet has recently confirmed that priority is given to the construction of nuclear submarines. However, Brazil’s economic and political turmoil, as well as corruption charges, are likely to reduce the country's ambitions in building its own nuclear submarines.
All over the world, national concerns about maritime sovereignty, the safety of offshore fields and the protection of maritime communications continue to grow in parallel with the growth of the capabilities of submarine fleets. In this regard, a substantial increase in the number of programs for the construction of new submarines and the modernization of existing submarines is inevitable.
Materials used:
armadainternational.com
www.baesystems.com
www.saabgroup.com
www.naval.com.br
www.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org






Information