German anti-tank grenade launchers Raketenpanzerbuchse 43 "Ofenrohr" (RPzB.43) and "Panzerschrek" (RPzB. 54)
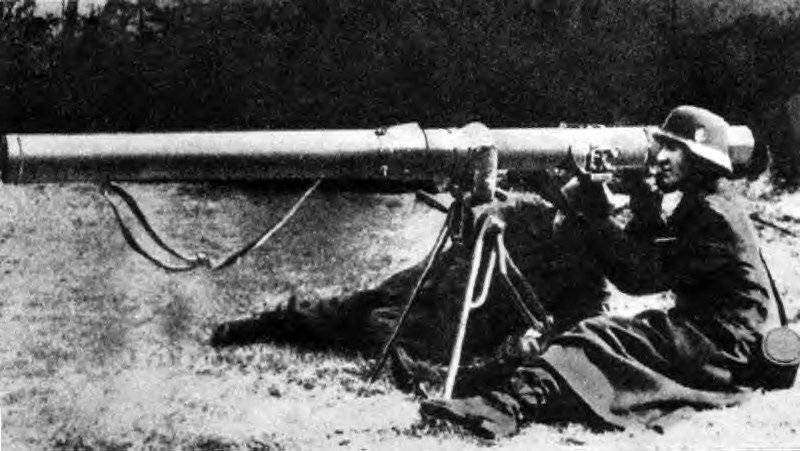
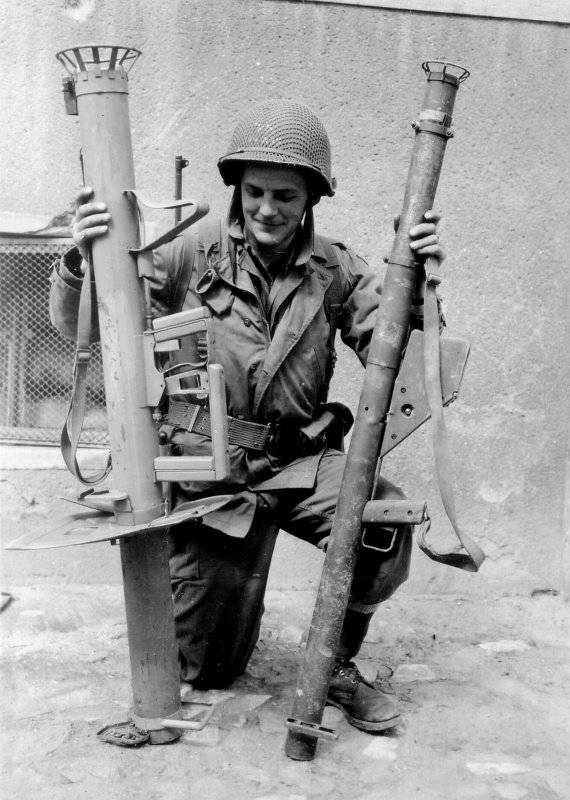
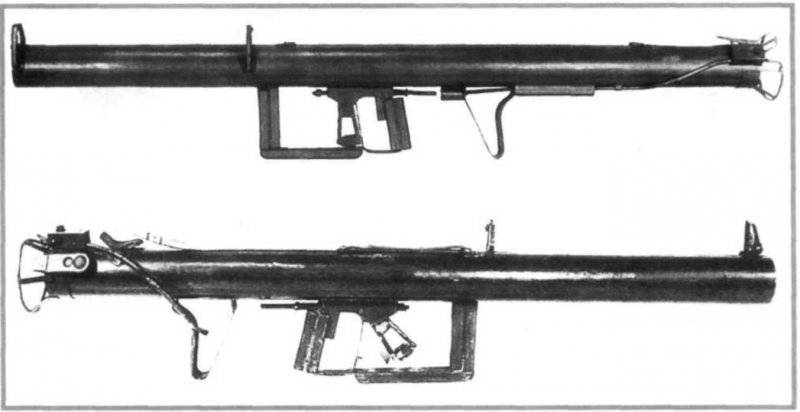
The first model of this weapon, known under the symbol Raketenpanzerbuchse 43 (RPzB.43). The uncommon outer shape of the weapon caused the army to call it Ofenrohr (smoke stack). Unlike R.Wr.43, the new RPG had excellent fighting qualities: high maneuverability (the curb weight of the RPzB.43 was 12,5 kg, which allowed it to be used in infantry combat formations), and the effectiveness of the action of hand-held anti-tank grenade launchers which was significantly higher than other types of similar weapons. The armor penetration rate of the RPzB.43 at a distance of up to 150 meters was 210 millimeters normal and 160 millimeters at an angle of 40 degrees.
The grenade launcher, whose mass was 9,5 kg, consisted of an open smooth-bore pipe with three rectangular guides stamped along the entire length. Installed on the trunk: a pulse induction generator, the wiring of which was installed in a metal tube, sights, trigger mechanism, shoulder rest having a shoulder, two handles serving to hold the weapon during firing, a box of plug connector, a spring latch serving to hold the grenade charged position. The wire ring, attached to the breech section of the trunk, protected the channel from damage and contamination. At the same time, it facilitated the insertion of grenades when loading. USM consisted of a spring-loaded trigger lever, the mainspring, impact rod, handle for cocking the rod with a spring and a fuse. The sight consisted of a rear and front sight. The shoulder strap fastened to the pipe was carried.
[
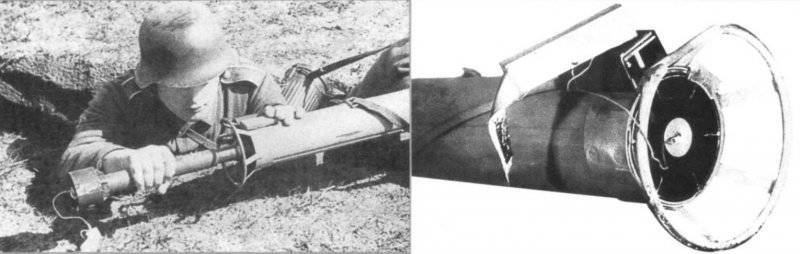
For servicing weapons with breech-loading, a calculation of two people was needed: the gunner and the ammunition carrier, who also served as a loader. Shooting was conducted from the prone position, from the knee, standing. The barrel of a hand-held anti-tank grenade launcher was placed on the shooter’s shoulder, while it was required to move it forward to the limit, after which the target was guided. RPG ammunition was 10 grenades.
Ofenrohr RPzB.43, in many respects resembled the American Bazuku, but was not an exact copy of it, as it had several features, which included:
- caliber 88 mm (American grenade launcher had caliber 60 mm);
- increased firing range to 150 m (in practice, the distance was much shorter);
- the use of an electric induction generator (in the American RPG, dry electric batteries very sensitive to adverse weather conditions were used), this significantly expanded the possibilities of using a grenade launcher in extreme situations;
- more thoughtful loading has increased the practical rate of fire, which could reach 10 shots per minute (in the US 3-4 shot per minute).
In terms of its design, the 88-millimeter caliber feathered cumulative rocket grenade to the Ofenrohr was intended only for combat with armored vehicles and was identical to the R.Pz.Gr.4312 grenade. But there were a number of differences, among which: a smaller mass, a component of 2,4 kg, served as an igniter for an electric igniter, and not a percussion mechanism; the propellant charge was placed in the ammunition itself, and not in the sleeve. Since the igniter of the powder charge is the elektrosistema, inside the nozzle of the combustion chamber by means of lacquer an electric fuse was attached. One conductor electrozapala soldered to the nozzle, the second was connected to the plug (pin connector) mounted on a wooden block. The grenade was equipped with an instant-action fuse KZ-5095 / 1, a non-safety type. The same fuse was used in universal (rifle and hand) grenades and on a cumulative 3,7 cm StielGr. Patr.41. KZ-5095 / 1, unlike other fuses, was supplied with an additional safety check, which was removed before loading. In garnet, diglecol powder was used as a propellant charge. The weight of the bursting charge was 662 grams. The initial speed of the grenade is 115 meters per second. Ring-joined stabilizers formed the walls of the nozzle. For firing from RPzB.43, the so-called “seasonal grenades” were used - in winter conditions (from -40 to + 15 degrees) the Arctic grenade was used RPzB Gr.4322 arkt., In summer (from -5 to + 50 degrees) reactive cumulative grenade RPzB Gr.4322. Shooting was also allowed for the winter version of a grenade in the summer, however, with a lot of dispersion. Externally, these grenades differed, in addition to markings, also with the inscription “arkt” on the tail part of the “winter” ammunition applied with white paint. In RPzB.43, in addition to combat grenades, they used the RPzB.Gr. practical grenade. 4329 Ex and training RPzB.4320 Ub. Pomegranate had a dark green color.
Grenades were packed two pieces in a wooden box in a fully equipped form. Depending on the type of grenades, the inscription “RMun 4322” or other was put on the box. In addition, a black ring with cruciform light stripes indicated that it was a missile.
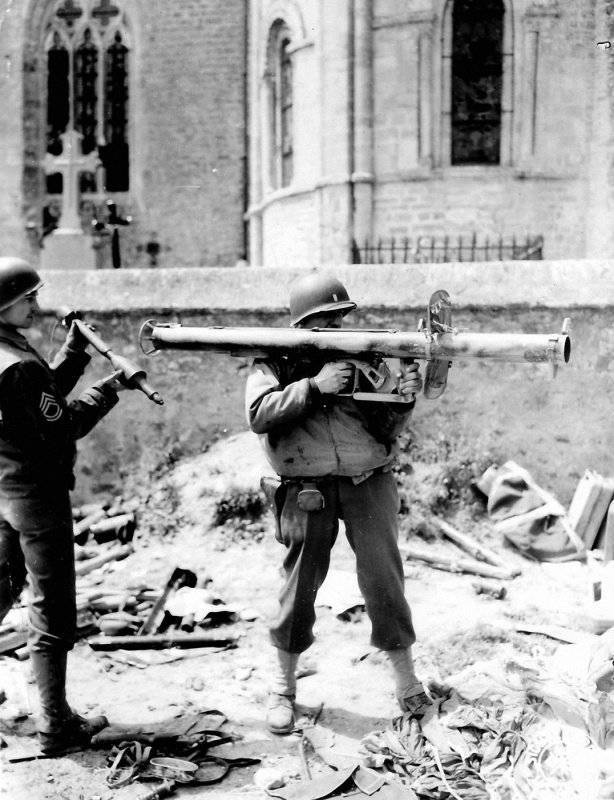
To load the Ofenrohr, it was necessary to remove the safety pin from the fuse, remove the wooden connector connector from the stabilizer and tear off the adhesive tape from it. Then the grenade was inserted from the rear end into the barrel and retracted until it was latched into place with a lock. After that, the plug of the wooden grenade pad was inserted into the socket of the contact box of the grenade launcher. After the RPG was charged, the loader was immediately positioned so that it was not in the zone of action of the powder gas stream. After that came the turn of the gunner. Shooting led from the shoulder. To make a shot, a shock rod was mounted on a combat platoon, which was previously removed from the fuse. After that, the trigger was pressed. Under the influence of a compressed combat spring, the released shock rod moved back and struck the core, which was placed in a pulse generator. When the circuit was closed, the electric igniter ignited, the impulse of which was transmitted to the igniter through special tubes. From the igniter, the impulse was transmitted to the powder charge. The arming of the fuse occurred after the grenade was three meters away from the barrel and when it met the obstacle, the fuse instantly worked, transmitting a beam of fire to the detonating device. Since the burning particles of the charge when fired and during the flight grenades moved in the opposite direction, it was necessary to comply with safety measures. When firing, the instruction on handling a grenade launcher recommended the following: during preparation for a shot, and during firing, care must be taken to ensure that there are no people (charging), combustible materials or ammunition in the danger zone behind the RPG; in order to avoid burns, the gunner himself is recommended to take all precautions when firing: wear gloves on your hands, a mask-mask from a gas mask on your head, and close parts of your body with clothes. To prevent damage to the ears from loud sound, they had to be laid with cotton. In case of misfire, it was necessary to remove the plug from the socket of the wooden box and slightly rotate the grenade one way and then the other way (this is how contact with the barrel is achieved). After that, it was necessary to insert a plug into the socket and press the trigger again.
The aiming point during firing at a distance of less than 75 meters was chosen below the hull of the tank; from 75 to 120 meters - the aiming point was between the turret and the tank control compartment; from 120 to 150 meters - to the tower. During the flanking movement, it was necessary to aim at the front of the tank hull.
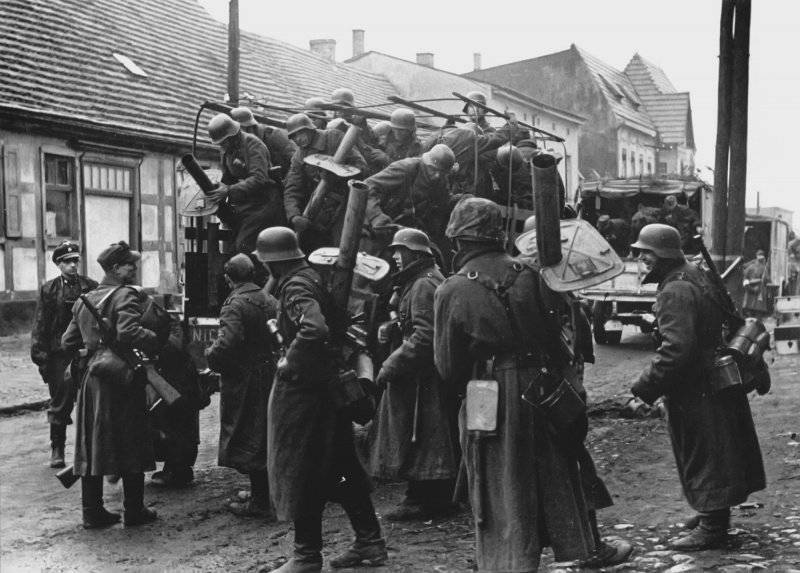
During the transportation of grenade launchers and ammunition on the car used a special two-wheeled trolley to him. The trolley housed up to 6 Ofenrohr anti-tank grenade launchers and several wooden closures for grenades. A grenade launcher in combat was carried by a gunner on a shoulder strap, charging, also playing the role of an ammunition carrier, transferred from 3 to 5 grenades in a special wooden box.
The first successful combat use of the RPG Ofenrohr took place on the Eastern Front in October 1943 of the year. A grenade launcher was sent to the front of the 242. The effective firing range, which equaled from 75 to 150 meters, was several times higher than similar characteristics of Panzerfaust Klein 30m, just adopted by the Panzerfaust Klein 30m grenade launchers, whose range did not exceed 210 meters. At the same time, the armor penetration of Ofenrohr was 140 millimeters versus 150 - 80 millimeters at Faustpatron. These characteristics allowed the infantry to destroy enemy tanks already at a distance from 150 to 80 meters, and not to 300 meters as before. New weapons have become a serious opponent for all types of tanks. At the same time, during their combat operations, a number of shortcomings were found that are inherent in all early models of grenade launchers: the low survivability of the barrel, which burned out after 5 shots and a certain danger for the grenade throwers themselves during the shooting, as the exhaust flames of the grenade ejected from the barrel, even despite the security measures, the gunners were injured. The constant fear of the gunner to injure caused the inaccuracy of aiming, which significantly reduced the accuracy of shooting. In addition, a strong exhaust of powder gases, which formed a whole cloud of earth particles and dust rising during a shot, unmasked the position of the grenade launcher calculation, making it easier to fight it, making it possible to quickly detect a shot flash to destroy the RPG calculation. Front-line experience has shown that the calculation has an extremely limited ability to change the firing position, because when it changes or even changes the direction of fire, there is a danger of hitting the fire of its soldiers, who are behind the calculation. In closed areas, such as in the woods, using the Ofenrohr hand-held grenade launchers was almost impossible. In addition, another Ofenrohr negative feature was already revealed during the first combat use - you cannot fire from short distances, because when fired from a distance of less than 30 grenade meters or did not work or the cumulative jet did not cause any damage to the enemy armored vehicles. In connection with this empirical way, it was established that the fire must be made from a distance of more than 100 meters. For the simplified design of sighting devices (aiming bar and rear sight), front-line soldiers also had certain complaints, since they were designed for firing at frontal targets. This led to the complication of calculations during the fire on moving tanks, narrowing the combat capabilities of weapons, which had much greater potential. The probability of destroying a moving tank (especially if it was moving at high speed) from a distance of 5 meters was extremely low. During mobile forms of combat, wearable stockpiles of ammunition (up to XNUMX units) were limited, and transportation to the front line with the use of a transport cart in combat was difficult.

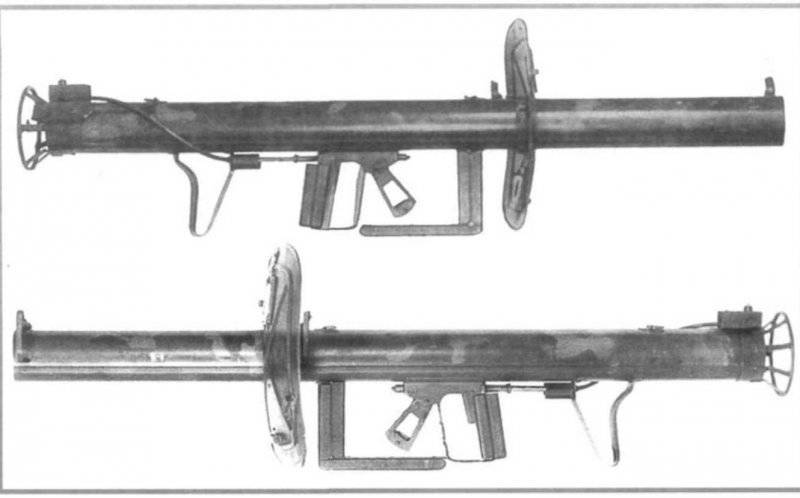
Already in the first months of the use of RPGs on the Eastern Front, the need to further improve the RPzB.43 grenade launchers was proved. In this regard, 12 August 44-th year in service with battalions and companies tank fighters, which are introduced in the infantry divisions of the state 1944 year, enters the upgraded RPzB. 54 Panzerschrek ("Thunderstorm for Tanks"). From RPzB.43 PRzB.54 differed in that in order to protect the hands and head of the shooter from burns during the shot in the design of a grenade launcher introduced a removable light metal shield, fastened between the sight and front sight. In the shield for targeting there was a window covered with glass, and on the back of the shield there was a box in which spare glasses were placed. A safety bracket was installed under the muzzle of the barrel, which did not allow laying the weapon directly on the ground when lying down. The designers took into account the extremely important factor of proper aiming. As for choosing the lead (moving the aiming point in the direction of the target), it was necessary to determine the distance, speed and course angle of the target, some changes were made to the sight design: the target bar was equipped with five slots designed for frontal targets moving with speeds up to 15 kilometers (when attacking tanks that are in the front line and interacting with infantry) and 30 kilometers (if success is developed on a favorable terrain for tanks), and from various courses. This greatly increased the capabilities of the German PRG in the fight against enemy tanks. At the same time, we took into account the experience of using "seasonal" ammunition. It was possible to make corrections to the position of the front sight, taking into account the temperature from -25 to + 20 degrees. This greatly influenced the accuracy of the fire.
First of all, RPGs began to enter German units on the Western Front in Italy, France, Holland and Belgium. By the fall of 1944, the Germans managed to achieve that there was up to a kilometer of the front to the 40 Panzerschreck and Ofenrohr. By December 44, the 107 450 RPG was released. In the 1 March Wehrmacht, the 45 had 139 700 hand-held anti-tank grenade launchers Panzerschreck and Ofenrohr. According to the new field regulations of Germany, one anti-tank platoon was created in all infantry companies, which consisted of two sections, consisting of six people each armed with three grenade launchers. This organization gave the grenade throwers a maximum of personal initiative in battle, which soon brought its results, since the personnel of the tank destroyers was aimed at the destruction of tanks. The fire from hand-held anti-tank grenade launchers was conducted intently - by a platoon or a detachment. Prior to 1944, each infantry division had anti-tank companies armed with 9 - 12 anti-tank guns, and after the RPGs began to receive RPGs, the firepower of these units increased dramatically. In the companies of the anti-tank weapons of the infantry regiment in the new states there were only three anti-tank guns, two platoons had an 36 RPG or only one Panzerschreck in the number of 54 units. The platoon of “tank destroyers” consisted of three sections of six grenade launchers and a control section with a light machine gun. The squad included a commander, 12 grenade throwers and a wagon. The detachment commander had an automatic rifle (submachine gun), the gunner had a pistol, and all the rest had 98 carbines. In total, the 48 manned personnel of the platoon of tank destroyers numbered, 18 RPG Panzerschreck and Ofenrohr, 19 pistols, 4 submachine gun (submachine gun), MG.42 light machine gun and 24 carbine. The instructions of the German command recommended supplying tank destroyers with Faust launchers and smoke grenades. Now, in the 44 state, the anti-tank company of the infantry division, in addition to anti-tank guns, had an 130 Panzerschreck, another 22 unit was in reserve. Along with the "faustprony", RPG data began to form the backbone of the PT defense.

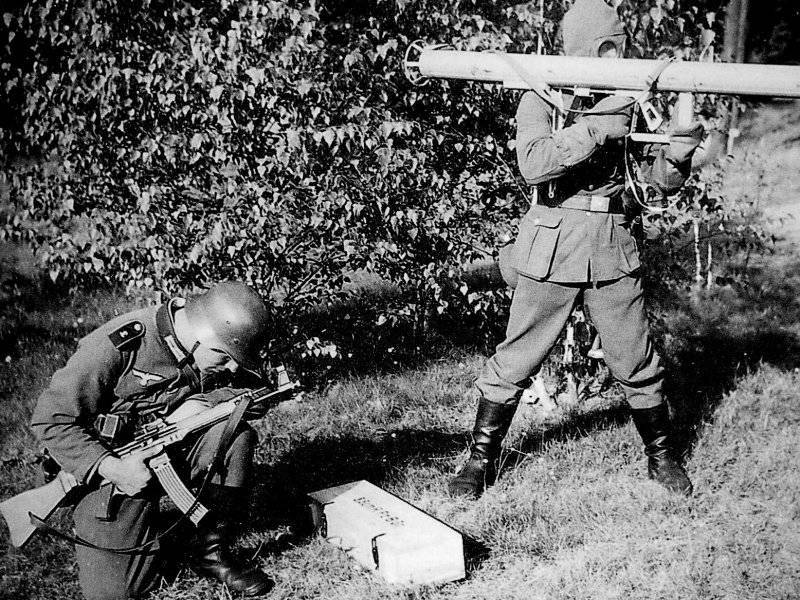
The Germans were able to achieve the greatest effectiveness from the skillful organization of an anti-tank defense system, which combined anti-tank and multi-layer continuous fire zones from all available weapons (small arms, grenade launchers, mortars and anti-tank guns) in front of the front edge, in the depth of defense and on the flanks, aimed at the destruction of tanks and armored vehicles. Tank fighter positions were chosen in tank-dangerous directions, and any shelters were used. If the enemy penetrated into the defense zone, the enemy tanks were destroyed by direct fire from all the available anti-tank weapons, including grenade launchers from the minimum distance. Moreover, in the last months of the war, in order to ensure the defense of the platoon strongholds, they developed special tactics for such groups of grenade launchers. These groups consisted mainly of three people: the commander, the gunner and the carrier of ammunition. The distance between the individual groups did not exceed 150 meters, that is, the most effective range of the Panzerschreck grenade launchers. Grenade throwers with such an arrangement could transfer their maneuver to any threatening direction. The firing positions of grenade launchers in the settlements were chosen in such a way that it was possible to fire along squares and streets. Tank fighter groups were often accompanied by several arrows, which were armed with assault rifles or submachine guns. The task of these fighters included the destruction of infantry, covering the advancing tanks, and tank crews who left the wrecked vehicles.
However, the numerous advantages of the weapon were practically negated by some shortcomings. First of all, this related to the impossibility to destroy tanks from the Panzerschreck and Ofenrohr grenade launchers at a distance of more than 150 meters (due to the difficulty of firing at moving targets) and low effectiveness against enemy infantry, which in turn led to the soldiers managed to find a means of confrontation with similar weapons. It is thanks to these features of using RPGs that have allowed tank assault forces and infantry next to tanks to hit grenade launchers from full-time small arms from a distance from 200 to 300 meters, that is, before calculating the grenade launchers managed to open real fire. So, if in the period from October 43 to the end of June, 44 managed to destroy the entire 642 German grenade launcher, then from July 1944 to January 1945, the losses of the rocket launchers amounted to 12965 units. In this regard, until the end of the war, the German gunsmiths were engaged in the development of hand-held anti-tank grenade launchers. 20 December 1944 of the year, after changes were made to its design, the Wehrmacht adopted a new complex: the Panzerschreck RPzB.54 / 1 anti-tank grenade launcher and the RPzNGR.4992 rocket grenade. In the modernized ammunition used a new brand of quick-burning powder charge, which burned before the projectile had time to leave the barrel. This increased the effectiveness of the weapon itself by increasing the firing range to 200 meters and armor penetration to 240 millimeters.

Unlike its predecessors, the advanced grenade launcher had a less complex loading system, in which the contact of the electric igniter was installed opposite the electrical contact of the grenade tail. To increase maneuverability, the length of the weapon was reduced to 1350 millimeters, which greatly improved operation in combat conditions.
Increasing the production of RPG firms Meuzelwitz and HASAG allowed in the 45-th year to create specials. brigades of tank destroyers, which were often recruited from representatives of the "Hitler Youth" and armed with Panzerschreck. Also, a number of grenade launchers were transferred to equip the Volkssturm (for arming the battalions of the first two sets, 40260 Panzerschreck and Ofenrohr grenade launchers were needed). Subdivisions and units of Volkssturm and Wehrmacht, armed with grenade launchers, were primarily used for anti-tank defense of the most important objects. In the same year, mechanized units of the German infantry received a RPzB.54 / 1 grenade launcher mounted on a Sd.Kfz.250 / ll light armored personnel carrier, which greatly influenced the growth of firepower. In addition, in the last months of the war, the Panzerschreck was installed on the T-IV chassis and Volkswagen VW-Kubelwagen vehicles with increased maneuverability. Simplification of the production of these weapons has reduced the cost of grenade launchers to 70 brands, that is, to bring labor costs to a level that was comparable to the material costs of creating one of the most popular types of Wehrmacht weapons - the StG-44 assault rifle.
On 1 March 1945 of the year, according to the OKN, in the German armed forces in the troops there were - 92728 RPG Panzerschreck and Ofenrohr with 541500 projectiles to them. There were also 47002 grenade launchers with 69300 grenades in their arsenals. In total, the 314895 88-millimeter RPGs Panzerschreck and Ofenrohr were delivered to the Wehrmacht during the Second World War Reich World War, of which 289151 RPzB.43, RPzB.54 and 25744 - RPzB.54 / 1, and also 2218400 and XNUMX - RPzB.XNUMX / XNUMX, and also XNUMX and XNUMX - RPzB.XNUMX / XNUMX, and also XNUMX and XNUMX - RPzB.XNUMX / XNUMX, and also XNUMX and XNUMX - RPzB.XNUMX / XNUMX, and also XNUMX and XNUMX - RPzB.XNUMX / XNUMX, and also XNUMX and XNUMX - RPzB.
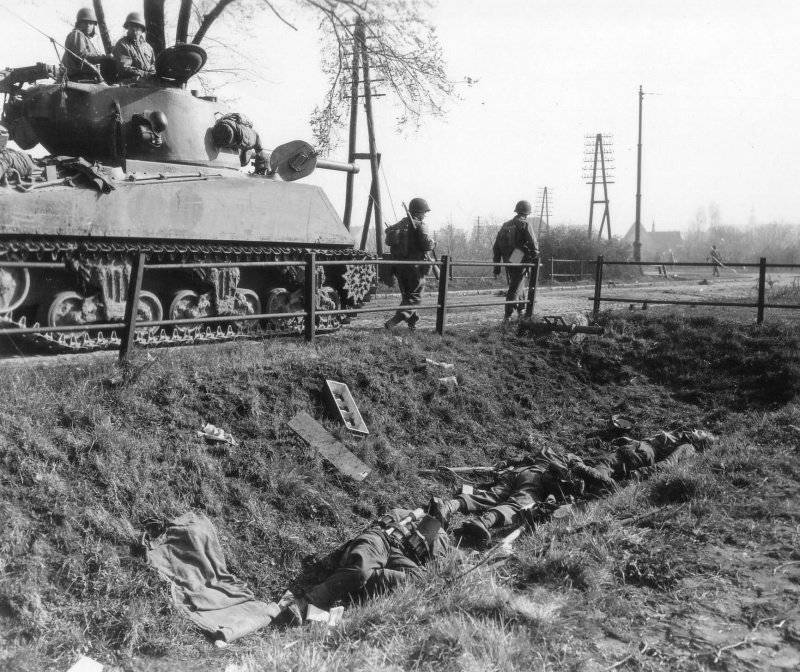

This powerful, but at the same time quite cheap and simple weapon, played a significant role in the last battles, having multiplied the Allied losses in armored vehicles many times over. After the war, Erich Schneider, Lieutenant-General of the Wehrmacht, giving an assessment of this weapon, wrote: "cumulative charge ... in combination with a jet engine, like the RPG" Pantsershrek "(" Ofenror ") ... have become quite successful means of combating armored vehicles of the allies ... ".
Speaking of the German RPG period of the Second World War, it is necessary to mention the experiments in this area, conducted by designers at the end of the war. In August, 44, a number of weapon companies, attempted to develop new types of anti-tank weapons with greater efficiency, including the most powerful 105-mm cumulative over-caliber grenade with 6,1 kilogram mass for Panzerschreck. Developed a modernized 105-mm RPG RPzB.54 (Sonderversion) whose total length was 2,4 thousand mm. The armor penetration of a cumulative grenade at a distance of 300 meters was 180 millimeters. However, the specified armor penetration (equal to 240 millimeters) was not achieved in this model. Therefore, soon there appeared another sample of this grenade launcher with a mass of 13,6 kilogram and a length of 2 thousand mm. For this sample, an 6,3-kg grenade was designed with a new shaped charge design, which increased armor penetration to 220 millimeters. Since this grenade launcher had a great return, several types of special tripod machines were created for it. However, before the end of the war, work on the 105-millimeter RPG RPzB.54 (Sonderversion) was not completed. The original projects of grenade launchers, which are known under the name Stachelschwein ("Porcupine") and Igel ("Hedgehog"), were created by the firm Mauser-Werke at the end of the war. This weapon, structurally similar to the Panzerschreck, later developed under the indexes Gerat N26 and N28, also did not come out of the walls of Mauser. A feature of this weapon was the use of small-sized rockets and not grenades for firing. Thus, it became a transitional type from RPG to a fundamentally new type of weapon - anti-tank anti-tank anti-tank guided missiles.

Westfalisch - Anhaltische Sprengstoff AG designed to combat heavy tanks using RPzB.54 grenade launcher 105-mm anti-tank grenade launcher “Schuka” (Hecht) with 250-millimeter rocket-mounted grenade, with armor penetration rate of 92-gauge to HE / ZNMX. The grenade consisted of a warhead with a spherical cumulative burst of a bursting charge and a jet tail with a six-member ring plumage and a nozzle. The rocket chamber was a standard RPzB Gr.250 combustion chamber. The large mass of grenades (4322 kg) caused the firing range to drop to 6-30 meters, although the accuracy of the anti-tank grenade launcher was quite high. This was achieved using a new design of stabilizers. The new grenade was an attempt to expand the capabilities of this type of weapon. However, judging by the results, they reached their limit, which contradicted the requirements for a higher RPG firing range (up to 50 meters) while maintaining armor penetration like the RPzB.400 / 54, and the new design of the ammunition wiped out the previous ones Achievement in firing range. Hecht grenade launchers in combat were not used, since work on bringing this weapon to an industrial design was carried out until May 1. In parallel with these workings, in the 45-44 years, the Rheinmetall-Borsig concern resumed some research and development work in the field of developing anti-tank anti-tank infantry weapons.
In the winter of 1945, this company submitted to HWaA a new weapon complex with great prospects. The complex consisted of the Hammer 105-mm heavy machine gun grenade launcher (Hammer), also known under the designation Panzertod (Tank Death) and the 3,2-kilogram anti-tank cumulative grenade with an initial speed of 450 m / s. The absence of the combustion chamber was a feature of the new ammunition. The large weight of the weapon, equal to 40 kg, and rather large dimensions were the reason for the fact that the grenade launcher was installed on a tripod machine, which contributed to good stabilization during firing. The grenade launcher on experimental tests showed excellent results with minimal dispersion. For example, when firing from ranges to 500 meters, all hits hit the target having a size of 1x1 m, (this figure is still very high today). Designers Rheinmetall-Borsig managed to create the optimal combination of armor penetration, firing accuracy and effective range, maneuverability and rate of fire. However, the difficulties that were associated with the development of a new type of weapon (seizure in the barrel of a ring stabilizer, the melting of stabilizers, considerable pressure, etc.) did not allow to complete the work on a promising sample before May 1945, when it was too late. Moreover, many of the conceptual ideas embodied in it were implemented in easel anti-tank grenade launchers of the postwar period.

At the same time, German designers simultaneously with the modernization of anti-tank grenade launchers tried to use the ammunition from the Panzerschreck hand-held anti-tank grenade launcher as aviation ammunition. However, its low initial speed of 130 m / s did not satisfy aircraft designers. SS-Wafenakademie specialists created in 1944 aviation option - a cumulative rocket projectile, which was a combination of the warhead of an 88-mm cumulative RPzB Gr.4322 grenade and a rocket of an 80-mm WGr fragmentation rocket. Spreng. The initial velocity of the new projectile was 374 meters per second. The R-HL Panzerblitz 1 air-to-ground missile (“tank lightning”) was intended to destroy all types of enemy tanks with a direct hit. To launch the rocket, a special Schulder 75 launcher was designed. Testing of these weapons took place in October-December 1944 as part of the program "Destruction of tanks" conducted by the Luftwaffe command. The installation was mounted on Fokke-Wulf FW-190 F-8 fighter attack aircraft, which were armed with six launchers. R-HL Panzerblitz 1 was fired by volley fire. But these experiments did not give a positive result due to the high dispersion of the shells. Every sixth ammunition hit the target. At the same time, low flight stability significantly reduced the cumulative effect, the jet dispersed and poorly focused, which was affected by the shape of the projectile and the unsuccessful design of the tail unit. Soon, his improved options were created: the R4 / HL Panzerblitz 2, which is a 130-millimeter RPzB Gr.4322 warhead mounted on the rocket of the 55-millimeter R4 / M Hose rocket (initial speed 370 meters per second ), and a 75-mm rocket R4 / HL Panzerblitz 3 (initial velocity of 480 meters per second). The stabilization of the R4 / M shell was carried out using a six-feather stabilizer, which was opened in flight. This made it possible to launch them from launchers - a smooth-bore pipe. But the inevitable collapse of Hitler's Germany prevented the gunsmiths from completing these promising works.
In general, the Panzerschreck RPzB.54 (RPzB.54 / 1) and Ofenrohr RPzB hand grenade launchers, which appeared in the flames of the Second World War. 43 proved to be a weapon of great power, the competent use of which at the final stage of the war caused great damage in the battles of the Allied forces.
Based on: "Third Reich Infantry Weapons Part VI. Wehrmacht Jet Weapons" Special issue of the magazine "Weapon" for 11 / 12 2003 of the year.


Information