Front lines in the Syrian conflict as contours of the future world order
In the Syrian crisis, which has long gone beyond the scope of a regional conflict, the interests of the largest centers of power have crossed. Under the pretext of fighting international terrorism, each of the coalitions operating in Syria pursues its own goals. In many ways, the end of the Syrian crisis will depend on who will attract more global centers of power to his side and whose coalition will last longer.
After the disruption of the second since the beginning of this year truce in Syria, charges of war crimes and mutual vetoing in the UN Security Council, it became obvious that there would be no compromise between Moscow and Washington in this conflict. There is nowhere else to retreat, because the American global leadership is at stake. The parties are forced to go for broke and prepare for a protracted confrontation, in which the external factor will be decisive.
To be precise, the first attempt to resolve the Syrian crisis can be considered the initiative of Moscow to destroy the chemical weapons in Damascus. On September 14, 2013, following the results of the first talks between the Russian and US foreign ministers on Syria, the parties spoke in favor of a political settlement and military non-intervention, subject to the transfer of international control to the Syrian chemical weapons. It is believed that the efforts of Russian diplomacy then saved Syria from a large-scale military invasion of the United States and its allies.
For the first time, there appeared a chance to resolve the conflict, which has lasted for more than three years. It would seem that this is a good time to jointly strike at international terrorism in Syria and launch the political process of national reconciliation. But the United States had a different opinion on this. Washington refused to recognize Russia's diplomatic victory, deciding to prove that Moscow’s efforts to support the Bashar Assad regime are worthless.
In February 2014, world attention shifted to events in Ukraine. The violent seizure of power and the subsequent events in the south-east and in the Crimea demanded that Moscow concentrate its full attention, forcing it to forget about the conflict in Syria for a while. While the Americans continued to actively train and arm the Syrian opposition, which they were trying to use as a ram against the current regime supported by Moscow.
8 August 2014 began the military operation of the United States and its allies against ISIS * "Unshakable determination." The actions of the Americans then caused a lot of criticism, since the strikes on the territory of Syria were carried out without the permission of the Syrian authorities and bypassing the UN Security Council. Literally a month later, on September 10 of 2014, Barack Obama announced the creation of an international antiterrorist coalition under the auspices of the USA, which was then supported by more than 60 countries of the world. This move was supposed to give legitimacy to the actions of Americans in Syria, who continued to ignore international law.
At the same time, the struggle of the American coalition against terrorist groups on the territory of Syria was conducted very mediocre: the terrorists continued to actively seize more and more new settlements, confidently moving inland. Thus, the main goal of Americans in Syria was not the destruction of the “Islamic state” *, but the change of the regime of Bashar al-Assad. For these reasons, Russia did not consider for itself the opportunity to join the international coalition under the auspices of the United States. However, no one there and did not call.
Looking ahead, we can say that this is not the only attempt to create an international antiterrorist coalition. In December, 2015, Saudi Arabia, which itself is formally an ally of the United States, announced the creation of an antiterrorist coalition of Islamic states, which immediately included 34 countries, including Turkey and Pakistan. It is believed that the Saudis task was to demonstrate the solidarity of the Islamic world with the actions of the United States in Syria. Finally, in August, 2016 announced the creation of its own coalition with the participation of Pakistan, Afghanistan and Tajikistan (which is a member of the CSTO), and China. However, the matter did not go further than the statements - neither the Chinese nor the Saudi projects showed themselves.
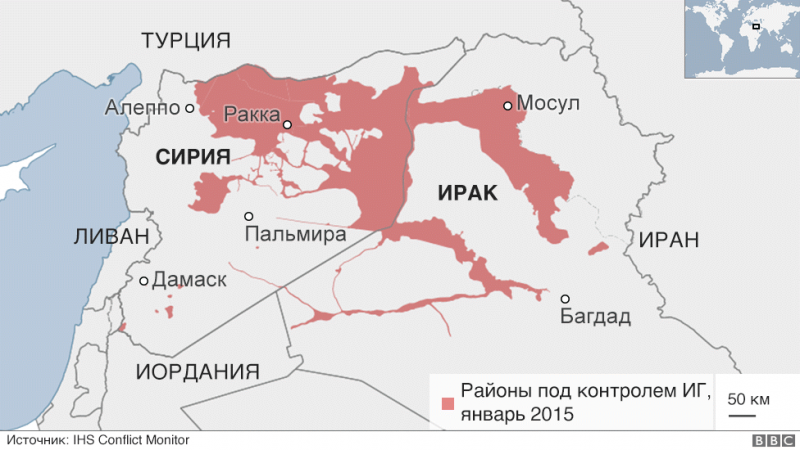
As a result, at the start of the Russian military operation in Syria 30 September 2015, the terrorists already controlled up to 70% of the territory of this country. Quickly seizing the initiative from the Americans, the Russian military actively destroyed terrorist facilities, equipment and manpower of terrorist groups throughout Syria.
In its first military company outside the post-Soviet space, Russia for the first time used the latest high-precision weapons, cruise missiles, homing bombs, as well as strategic Aviation and warships of the Caspian flotilla and the Black Sea Fleet. In addition, with the participation of Moscow, the Information Center for the Exchange of Intelligence between Russia, Syria, Iraq and Iran was created.
The decisive actions of Moscow allowed preserving constitutional power in Syria and creating conditions for the government forces, who had suffered one defeat after another, to take the counteroffensive. At the same time, unlike the American coalition, Moscow operates in Syria at the official request of the Syrian leadership.
The success of the Russian military operation gave an impetus to the resumption of the Russian-American negotiations on Syria, which resulted in the harmonization of the cease-fire, which came into force on February 27 of the year 2016. At the same time, the truce did not extend to the “Islamic State” * and “Dzhebhat al-Nusra” ** (branch of Al-Qaeda). Shortly thereafter, 14 March 2016, Russia withdrew most of its air group from Syria, demonstrating a commitment to the political process.
Thanks to the military and diplomatic efforts of Russia, the Syrian people once again had the fragile hope of a peaceful life. However, the so-called “moderate opposition” clearly had other plans. Acting under the banner of the “Syrian Free Army” created by the Americans, militant groups continued fierce battles, effectively disrupting the cease-fire.
According to the Russian Defense Ministry, only for the period from February 27 to 1 September 2016, the Russian military managed to destroy at least 35 thousands of terrorists, including 2700, who came from Russia and the CIS countries. At the same time, 586 settlements and 12360 square kilometers of the country's territory were freed from terrorist groups.
Following the 13-hour talks between the heads of the Russian and US foreign affairs agencies in Geneva, 12 of September of 2016 was declared another truce attempt. The next cease-fire by the Syrian army, as six months ago, was used by militants to regroup and strengthen positions.
The third chance of peace in Syria was buried on September 17, when fighters from Australia and Denmark as part of the American coalition attacked the positions of the Syrian forces in the Deir ez-Zor region, resulting in 62 deaths and 100 more injuries. The mistake of the American command allowed the terrorists to go on a large-scale attack using artillery, tanks and multiple launch rocket systems. Under these conditions, a unilateral ceasefire by government forces has become simply meaningless.
After just 2 of the day after the tragedy, 19 of September 2016, in the area controlled by Dzhebhat Fatah al-Sham ** (the former Dzhebhat an Nusra), the UN and Red Crescent humanitarian convoy were attacked. The Americans immediately rushed to accuse Russia of air strikes. Moscow replied that there were no Russian planes at the time of the shelling in the specified area, and an unidentified vehicle with a large-caliber mortar was moving under the guise of a gkkonvoya. The Russian Foreign Ministry described the “attack” on the cargo convoy with humanitarian aid as a dramatization in order to divert attention from the American coalition’s attack on the Syrian army. At the same time accusing the Americans of the inability to control the "moderate opposition" that disrupted the cease-fire.
After the failure of three attempts at a peaceful settlement, the parties to the conflict and their external "curators" began to prepare for a protracted war without any hope of peace in the foreseeable future. The new stage will be expressed in new deliveries of weapons and ammunition, as well as an increase in financial assistance to the parties to the conflict, which will allow them to replenish their ranks with foreign mercenaries.
As is known, the backbone of the terrorist group formed in 2006 on the territory of Iraq is made up of former soldiers of the Iraqi army who went underground after the US invaded Iraq in 2003. But the truly powerful “Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant” became already after the events of the “Arab spring” in the Middle East and, in particular, the civil war in Syria. Taking advantage of the resulting vacuum of power, the terrorists invaded Syrian land from neighboring Iraq and quickly took control of the oil fields, setting up black gold smuggling.
During the years of the Syrian conflict, the ranks of dozens of different sort of terrorist groups were replenished by immigrants from 86 countries of the world. Therefore, for the authorities in Syria, this is no longer just a civil conflict and the fight against international terrorism, but a national liberation war against foreign intervention. Unlike the “Islamic State” *, the basis of “Dzhebhat Fatah al-Sham” ** (branch of Al-Qaeda) and numerous Salafi groups are people from the Syrian opposition who divided Syria into zones of influence.
So, ISIL controls mainly the east and northeast of the country, including the Syrian-Iraqi border. To the west of the “capital” of the “Islamic State” - the city of Raqqa, through the eastern part of Aleppo and further north-west of the country to the Syrian-Turkish border, the “zone of responsibility” “Dzhebhat Fatah ash-Sham” ** (“Front n-Nusra” ). The smaller groups prefer to dig in the cities of the central and southern provinces of Syria.
The question arises: why are the numerous armed opposition, LIH * and the last rebranding of “al-Nusra” ** not fighting among themselves? After all, it would be much more logical for the Syrian authorities and the opposition to unite in the fight against the common terrorist threat coming from ISIS *. Firstly, because they are allies in the war against the legitimate authority in the person of Bashar al-Assad. Secondly, because the Syrian opposition in the north of the country actually covers the exit of ISIS to the Syrian-Turkish border. Thirdly, because the terrorist groups operating in Syria have a unique “personnel rotation” among themselves.
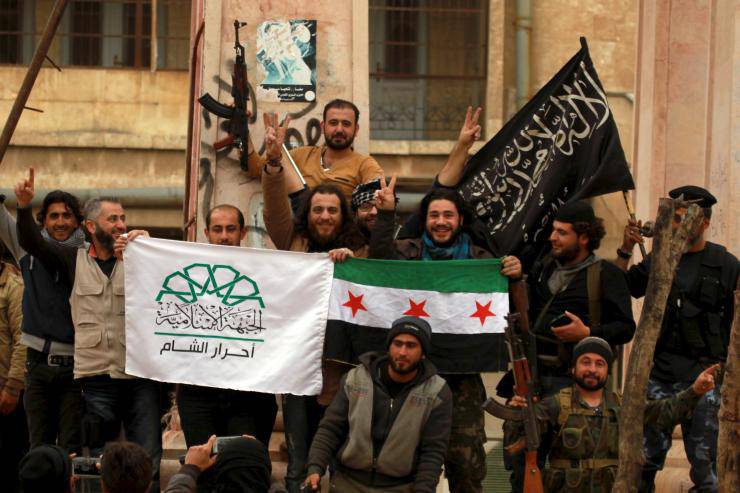

In particular, shortly before the beginning of the Russian military operation in Syria, the Americans had to curtail the special Pentagon program approved by Congress and the US President to train four brigades of Syrian opposition fighters, totaling 15 thousand, worth 500 million. The program failed due to mass desertion and the transition of Sunni Arabs, trained and armed by Americans, to the side of terrorist groups.
Despite this, the United States does not refuse to support the "moderate" Syrian Free Army (FSA), which is a kind of "personnel reserve" for ISIL * and "al-Nusra" **. In this regard, the difference between "rebels" and "terrorists" depends, rather, on the foreign policy situation, than on the actual situation on the fronts. However, after freezing Russian-American contacts in Syria, hotheads in the United States openly declared the need to resume the supply of American weapons to the Syrian opposition, if not directly, then through the US Middle East allies.
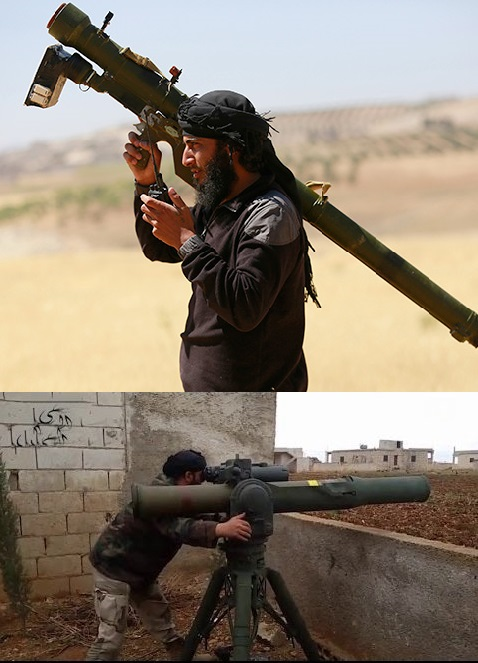 We are talking about American anti-tank missile systems (ATGM) and man-portable air defense systems (MANPADS) used against air targets. At the same time, it is not customary in the United States to recall that during the years of the Syrian conflict from 60 to 80% of American weapons fell into the hands of terrorist groups. Another proof of this is the firing of ISIL from MANPADS of a Russian Mi-8 helicopter in the province of Hama 8 in October 2016.
We are talking about American anti-tank missile systems (ATGM) and man-portable air defense systems (MANPADS) used against air targets. At the same time, it is not customary in the United States to recall that during the years of the Syrian conflict from 60 to 80% of American weapons fell into the hands of terrorist groups. Another proof of this is the firing of ISIL from MANPADS of a Russian Mi-8 helicopter in the province of Hama 8 in October 2016.Since 2014, the international terrorist groups in Syria and Iraq have unsuccessfully opposed an alliance from the United States, Australia, the Netherlands, Britain, Canada, France, Belgium, Denmark, Jordan, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. Far from the last role in the Syrian crisis are other Middle Eastern allies of the United States - Turkey and Qatar.
The resulting “Syrian impasse” can be considered the natural outcome of the demands for the resignation of legitimate authority and at the same time the support of the so-called Syrian “moderate” opposition from the United States and its allies. At the same time, no one is able to answer the question of where the fine line between terrorists and “oppositionists” lies in the context of endless battles “against all”.
Meanwhile, according to the Syrian Center for Political Studies, 470 thousands of people have already fallen victim to the Syrian conflict, which is twice as much as the UN. The number of injured is estimated back at 1,9 a million people. In the five years of ongoing fighting, their homes were forced to leave more than 6,5 a million Syrians, which to some extent triggered a European migration crisis.
The Syrian army is also exhausted to the limit. The main striking force of government troops, in addition to the special forces division “Tigers”, which includes the brigades of the “Cheetahs” and “Sokolov Desert”, is the Syrian militia, almost entirely composed of foreign volunteers, and not at all the regular army, which constantly suffers a shortage of weapons and lively strength In other words, the Syrian Arab army has long been unable to independently win this war.
In addition to Russia, the main allies of Bashar Assad are the international brigades of the Arab Socialist Renaissance Party (BAAS), the Palestinian and Iraqi volunteers, as well as the Lebanese Shiite Hezbollah fighters. The latter is believed to “oversee” the Iranian Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), which specializes in secret operations throughout the Middle East. However, practically nothing is known about their exact number and location, since, unlike Russia, Iran prefers to act in secrecy. According to analysts, the strategic goal of Iran in the Syrian conflict is the formation of the Middle East "Shiite soul", the geopolitical union of Iran, Iraq, Syria and Lebanon, which could press the monopoly of American allies in the region, which at this stage coincides with the interests of Russia and China.
Despite repeated statements by Moscow that the Russian military will not take part in the ground operation, Russia's military presence in Syria, however, is by no means limited to the airborne forces and military advisers. According to official information, in addition to the Khmeimim airbase and the naval base (logistics point) in Tartus, the Russian Center for reconciliation of the warring parties also operates in Syria. It is also known about military sappers performing the tasks of demining the territories freed from terrorists. Russian military facilities in the SAR are guarded by the marines and cover the C-300 and C-400 anti-aircraft missile systems (SAM), which are in service with the Air Defense Forces.
But the actions of the VKS would not have been so effective without re-checking the Syrian intelligence data and adjusting the work of combat aircraft from the ground. And this is the profile of the General Directorate General Staff (former GRU). In addition, in the key battles for control over strategic areas, the Special Operations Forces (MTR), a unit of the Russian Armed Forces specially formed for foreign operations, comes to the aid of the Syrian army. They were the ones who helped the Syrian special forces repel the ancient city of Palmyra from the terrorists.
Shortly after the collapse of the Russian-American 5 agreements of October 2016, the Russian government approved the Ministry of Defense bill as part of a presidential decree on improving military service, according to which Russian military personnel will now be able to make short-term contacts to combat terrorism and “during emergencies abroad.” According to military experts, the purpose of the adopted amendments is to increase the mobility of troops and their accelerated recruitment by contract servicemen to participate in special operations in Syria. Following this, the State Duma and the Federation Council ratified the agreement between Russia and Syria on the indefinite and gratuitous deployment of the Russian military contingent at the Khmeimim airbase.
Both of these events directly indicate that Russia's military presence in Syria will not only continue, but also be expanded. Considering the titanic efforts spent on supporting the regime of Bashar al-Assad, Moscow simply has no choice but to hope for the remnants of the Syrian army.
Thus, after the collapse of the Russian-American agreements and the freezing of the political process, Russia can no longer retreat and is preparing for a wider use of military force in the Syrian conflict. However, it would be a mistake to believe that Moscow will confront numerous terrorist groups and their foreign "curators" alone. Russian diplomacy is actively seeking and finding new allies.
So, in August 2016, it became known about the desire to assist in the training of personnel of the Syrian army and send its military advisers from China to Syria. Of course, it’s premature to talk about China’s full-fledged participation in the conflict on the side of Syria, Russia and Iran, but the very fact of the intention of the country possessing one of the most powerful armies in the world to provide military assistance to the Syrian government forces deserves attention.
The world learned about the possibilities of the modern Chinese army as far back as 2011, during the conflict in Libya. Then, to evacuate Chinese citizens to the coast of Africa, accompanied by military transport aircraft arrived missile frigate of the PRC "Xuzhou", based off the coast of Somalia to fight pirates. As early as April 2015, the lightning-fast landing of Chinese special forces in Yemen to evacuate foreign citizens from the conflict zone showed that the Chinese army, if necessary, can send not only military advisers.
China’s interest in Syria can be explained for several reasons. First, since 2015, as part of Dzhebhat en-Nusra **, the group has been fighting the “Eastern Turkestan Islamic Movement” (Chinese Al-Qaeda), consisting of ethnic Uyghurs that pose a direct threat to the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China . Like Russia, China is interested in eliminating the terrorist threat on distant frontiers.
Secondly, until 2011, China was the main trade and economic partner of the CAP and the main importer of Syrian energy resources. In addition, China has sufficient financial resources to participate in the future recovery of the Syrian economy. So a presence in Syria for Beijing would be a good opportunity to strengthen its position in the energy-rich Middle East.
Finally, thirdly, the Syrian conflict could temporarily become a testing ground for the latest weapons and military equipment of the People’s Liberation Army of China (PLA) as a demonstration to the world of the combat capabilities of the modern Chinese army. And in this case, China has an infectious example of Russia, which has shown the high combat capability of the Russian army in Syria.
Thus, advanced mobile groups of Chinese "military advisers" from the composition of the secret special operations forces could, following Russia's example, secretly reinforce Syrian special forces, for example, in the battles for Aleppo, in the vicinity of which, according to intelligence data, Uighur militants were entrenched.
On the other hand, China, which traditionally shows restraint in its foreign policy, does not necessarily openly get involved in a protracted conflict, since it is possible to defend its interests in this war with the hands of others. For example, through Chinese private military companies operating around the world (PMCs) that can be used as mobilization points for foreign volunteers.
One way or another, the joint military exercises in the South China Sea, Sea Interaction-2016, held on September 12, 2016, indicate the convergence of the positions of the SCO of Russia and China. As is known, China is controlled by the energy-rich Spratly Archipelago, which is also claimed by Vietnam, Malaysia, the Philippines, Brunei, and American-backed Taiwan. In the context of the confrontation between China and the United States in the South China Sea, Russia's recognition of Chinese jurisdiction over the disputed islands gave impetus to Russian-Chinese cooperation in Syria.
However, the contours of the Russian-Chinese alliance appear in other countries. So, against the background of a noticeable cooling in Pakistan-US relations in recent years, Beijing is increasingly supporting Pakistan, in particular, in a territorial dispute with India. In turn, Russia, in the period from September 24 to October 7, 2016 for the first time conducted a joint military exercise “Friendship-2016” with Pakistan. The official goal of the Russian-Pakistani maneuvers is to strengthen and develop military cooperation between the armed forces of the two countries.

Pakistan, as well as Afghanistan and Tajikistan included in the Chinese anti-terrorist coalition, are ideal countries in terms of recruiting volunteers to participate in the Syrian conflict on the side of Bashar al-Assad. These are not rich Muslim states with a secular regime and non-Arab population. The influence of neither the United States (with the exception of Afghanistan), nor Turkey, nor the Middle Eastern Arab monarchies, which to some extent support the Syrian opposition, is practically spread to them.
The problem is that international brigades are well suited to fight ISIS *, but they should not be used in battles for major cities against the local opposition, which immediately declares Assad a traitor to Syria and declares a national liberation war. That is why it is so important that the government army, with air support, take control of the north of the country, creating the conditions for the Assad allies to reach the positions of ISIL in eastern Syria.
Thus, the fighting capacity of the “Islamic state” in Syria is largely ensured by its strategic position, which is a chord from the border of Iraq, through Raqqu, to the border of Turkey. This allows ISIL * to simultaneously control oil deposits in the east of the country and smuggle it to northwest Syria. That is why Aleppo is so important for the Syrian army now - control over the city will allow government troops to advance in the northeast direction and take control of the border by cutting off the igilovskiye chord.
If, after the capture of Aleppo, the remnants of the Syrian army, with the participation of Russia, Iran, China, Pakistan and, possibly, other countries, will be able to jointly throw the terrorists to the Syrian-Iraqi border, from where they began their offensive against Syria, victory in the war. However, the fortifications of the so-called opposition, which in this case serve as a guarantor of the strategic position of ISIL * in Syria, lie in the way of the Syrian army. At the same time, attempts by government forces with the support of the Russian Aerospace Forces to liberate Aleppo are equated by Western leaders with war crimes.
Indeed, in the context of intense urban fighting, it is almost impossible to distinguish "moderate opposition" from terrorists. However, the true reasons for the breakdown of the truce lie much deeper. In the Syrian crisis, for the first time, the boundaries of non-regional blocs with opposing views on the future of the world were clearly manifested. The backs of the direct participants in the conflict are supporters of American hegemony, and those who oppose them, defending their own interests. At the same time, the rhetoric about democracy, human rights and the fight against terrorism, in fact, is nothing more than a screen, behind which everyone plays their own game.
In other words, the attitude of different countries to the Syrian crisis is a continuation of discussions about two opposing systems of international relations - a multipolar, polycentric world and global leadership (hegemony) of the United States.
A total of stories there are four systems of international relations. Based on the idea of a national state and the principle of state sovereignty, the Westphalian system formed after a large-scale Thirty Years War in Europe, which ended with the Peace of Westphalia. The Napoleonic wars that followed the French revolution ended with the Congress of Vienna and the transition to the Vienna system of international relations. The Washington Conference and the Versailles Peace Treaty at the end of the First World War defined the principles of the Versailles-Washington system, which existed during the interwar period. Finally, after World War II, the Allied negotiations on the anti-Hitler coalition in Yalta and Potsdam laid the foundations of the Yalta-Post-Ddam system of international relations.
It is obvious that since the end of World War II, the system of international relations has undergone significant changes. Strange as it may seem, but precisely because of nuclear weapons and the guarantee of mutual destruction, the Cold War between the USA and the USSR did not lead to a global conflict. However, the collapse of the Soviet Union gave the Americans reason to consider themselves winners and talk about a unipolar world in which they play the leading role. Allegedly, the decision taken by the leaders of Russia, Ukraine and Belarus to dissolve the USSR marked the transition to the “Belovezhskaya” system of international relations. Probably, this explains the already traditional for the USA neglect of the “remnants of the old system” - the UN and international law.
Indeed, the last 25 years of Russia and China have no choice but to silently observe how the United States and its allies in their own interests conducted military operations around the world, bypassing the UN Security Council. So it was with Yugoslavia, Afghanistan, Iraq and Libya. However, in Syria, the United States literally stumbled over the interests of the former "regional powers", who decisively contested American global leadership and declared a multipolar world order.
In this sense, the military victory supported by Russia and China's legitimate power in the Syrian conflict will mean for the United States the end of the “Belovezhskaya system” and the transition to a new international reality, where the West will be forced to reckon with other global centers of power. In a sense, the Syrian conflict is, if you will, a battle for the future of the world order. Is that why the West, led by the United States, so desperately defends Aleppo?
* Organizations are prohibited on the territory of the Russian Federation by the decision of the Supreme Court.






Information