Way out of chaos
Apparently, historical the choice has already taken place: the Russian leadership’s policy of restoring sovereignty and Eurasian integration has led the US ruling circles to aggression against the Russian Federation by seizing control of Ukraine and turning it into a bridgehead to launch the world hybrid war being fought by Washington in order to maintain world leadership in growing competition with China. Russia was chosen by American geopolitics as the direction of the main blow due to a combination of objective and subjective circumstances.
Objectively, the escalation of international military-political tensions is caused by a change in technological patterns and secular accumulation cycles, during which a profound structural reorganization of the economy takes place on the basis of fundamentally new technologies and mechanisms for the reproduction of capital. In such periods, as shown by 500 years of experience in the development of capitalism, the system of international relations is sharply destabilized, the old and the formation of a new world order are taking place, which is accompanied by world wars between the old and new leaders for dominating the market.
Illustrative examples of such periods in the past can be: the Netherlands’s war for independence from Spain, which resulted in the shifting center of capitalism from Italy (Genoa) to Holland; Napoleonic wars, after which domination passed to Great Britain; The First and Second World Wars, as a result of which domination in the capitalist world passed to the USA, and the cold war between the United States and the USSR, after which they seized global leadership due to the superiority in the development of a new microelectronics-based information and communication technological structure and monopoly on the issuance of world money.
In the current period, in the wake of the growth of a new technological order, China is breaking out ahead, and the accumulation of capital in Japan creates opportunities for moving its center of world reproduction to Southeast Asia. Faced with the re-accumulation of capital in financial pyramids and outdated industries, as well as the loss of markets for their products and the fall in the share of the dollar in international transactions, the United States seeks to retain leadership by deploying world war to weaken both competitors and partners. Trying to establish control over Russia, Central Asia and the Middle East, the United States is seeking a strategic advantage in managing the supply of hydrocarbons and other critical natural resources. Control over Europe, Japan and Korea ensures dominance in the creation of new knowledge and the development of advanced technologies.
 Subjectively, the anti-Russian aggression is explained by the irritation of American geopolitics by the independent foreign policy of the Russian president to broad Eurasian integration: from the creation of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) to initiatives to form a harmonious zone of trade and humanitarian cooperation between Europe and Asia (common economic space from Lisbon to Vladivostok). The United States fears the formation of global contours of expanded reproduction independent of them, first of all, by the BRICS countries.
Subjectively, the anti-Russian aggression is explained by the irritation of American geopolitics by the independent foreign policy of the Russian president to broad Eurasian integration: from the creation of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) to initiatives to form a harmonious zone of trade and humanitarian cooperation between Europe and Asia (common economic space from Lisbon to Vladivostok). The United States fears the formation of global contours of expanded reproduction independent of them, first of all, by the BRICS countries.Russia's historical experience in organizing global integration projects induces a surge of American Russophobia. It is characterized by the demonization of President Vladimir Putin, who Washington regards as the main culprit for the loss of control over Russia and Central Asia, and considers the independent foreign policy pursued by him as a key threat. In the inflamed imagination of American geopolitics, traditional Anglo-Saxon schemes of global dominance were revived due to the weakening and collapse of large independent states, as well as the establishment of control over transcontinental communications. And in the worst traditions of the British geopolitics of the past and the last century, Russia is again chosen as the key object of aggression because of its size and geographical position, and Ukraine as the first strike direction, which has been considered a necessary condition for the latter’s defeat for two hundred years. To this “geopolitical intoxication”, which has not been settled over two centuries, are added the ghosts of the previous Cold War, which frighten the American establishment with the revival of the Soviet Union.
Despite the seeming absurdity of psychosis occurring in Washington, this aggravation of paranoid Anglo-Saxon mania towards world domination has objective reasons.
Warfare
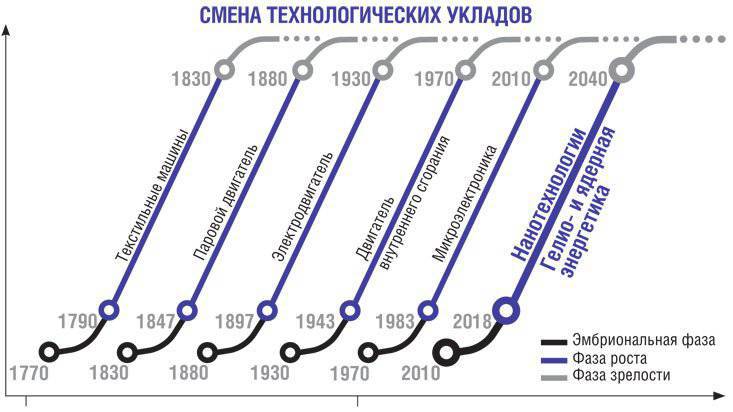
The current global crisis, which replaced the long economic recovery of the developed countries, is a natural manifestation of long cycles of economic activity, known as Kondratieff waves. Each of them is based on the life cycle of the corresponding technological structure - a complex of technologically related industries, which together with the corresponding institutions constitute self-replicating integrity.
 To date, in the world technical and economic development (starting with the industrial revolution in England), it is possible to distinguish the life cycles of five successively changing technological structures, including the information system that dominates the structure of the modern economy. The key directions of the development of a new technological structure are already visible, the growth of which will ensure the growth of the economies of the advanced countries on a new long wave: biotechnologies based on the achievements of molecular biology and genetic engineering, nanotechnologies, artificial intelligence systems, global information networks and integrated high-speed transportation systems. Their implementation provides a multiple increase in production efficiency, reducing its energy and capital intensity.
To date, in the world technical and economic development (starting with the industrial revolution in England), it is possible to distinguish the life cycles of five successively changing technological structures, including the information system that dominates the structure of the modern economy. The key directions of the development of a new technological structure are already visible, the growth of which will ensure the growth of the economies of the advanced countries on a new long wave: biotechnologies based on the achievements of molecular biology and genetic engineering, nanotechnologies, artificial intelligence systems, global information networks and integrated high-speed transportation systems. Their implementation provides a multiple increase in production efficiency, reducing its energy and capital intensity.Currently, a new technological mode is emerging from embryonic development in the growth phase. Its expansion is constrained both by the insignificant scale and lack of development of relevant technologies, and by the unreadiness of the socio-economic environment to their widespread use. However, despite the crisis, the costs of mastering the latest technologies and the scale of their use are growing at a rate of about 20 – 35 percent per year.
The further development of the crisis will be determined by a combination of two processes - the destruction (replacement) of the structures of the former technological order and the formation of the structures of the new. The totality of work on the product life cycle chain (from basic research to the market) requires a certain amount of time. The market is conquered by those who know how to go this way faster and produce a product in a larger volume and of better quality. The faster financial, economic and political institutions are restructured in accordance with the needs of new technology growth, the earlier the rise of a new long wave will begin. This will change not only the technological structure of the economy, but also its institutional system, as well as the composition of the leading firms, countries and regions. Those of them who will be able to more quickly reach the growth trajectory of a new technological structure and invest in its production components in the early stages will succeed. And vice versa - the entrance for those who are late will become more and more expensive with each passing year and will close with the achievement of the maturity phase.
Studies show that during periods of global technological change in the wake of the growth of a new technological order, a “window of opportunity” opens up for developing countries that have succeeded in preparing the prerequisites for its development. Unlike advanced countries that are faced with a crisis of capital accumulation in obsolete industries, they have the opportunity to avoid a massive depreciation of capital and concentrate it on breakthrough growth directions. To retain leadership, advanced countries have to resort to power techniques in foreign and foreign economic policy. During these periods, military-political tensions and the risks of international conflicts sharply increase. This is evidenced by the tragic experience of the two previous structural crises of the world economy.
Thus, the Great Depression of 30-s, due to the achievement of the growth limits of the “coal and steel” technology that dominated at the beginning of the century, was overcome by the militarization of the economy, which resulted in the catastrophe of the Second World War. The latter not only stimulated economic restructuring with extensive use of the internal combustion engine and organic chemistry, but also caused a radical change in the entire world order: the destruction of the core of the world economy (European colonial empires) and the formation of two opposing global political and economic systems. The leadership of American capitalism in entering a new long wave of economic growth was ensured by an extraordinary increase in defense orders for the development of new technologies and the influx of world capital in the United States with the destruction of the production potential and the depreciation of capital of its main competitors.
Depression of the middle of 70-x - the beginning of 80-s, due to the exhaustion of the growth possibilities of this technological structure, led to an arms race in space with a wide use of information and communication technologies that formed the core of the new technological structure. The collapse of the world socialist system that followed, which failed to move to a new technological order in a timely manner, allowed the leading capitalist countries to use its resources for a “soft transfer” to a new long wave of economic growth. The export of capital and the brain drain from the former socialist countries, the colonization of their economies facilitated the restructuring of the core of the world capitalist system. On the same wave of growth, new industrialized countries have risen, having managed in advance to create key industries and lay the prerequisites for their rapid development on a global scale. The political result of these structural transformations was liberal globalization with the US dominance as the issuer of the main reserve currency.
According to their geopolitical and geo-economic consequences, the structural crisis of 70 – 80-s of the last century and the associated arms race in space had no less consequences than the Second World War. The United States and NATO won, which was brought by a combination of informational and psychological weapons. The Soviet security system was not ready for its reflection. Although this war was of a “cold character”, it did without bloody battles and the victims were formed mainly as a result of the colonial policy of the genocide of the population of the former Soviet republics, in its historical, geopolitical and geo-economic significance it was equal to the third world war. Accordingly, the current aggravation of military-political tensions that occurs according to the same logic of long cycles should be regarded as the appearance of signs of a fourth world war.
“Modern exacerbation of military-political tensions should be regarded as the appearance of signs of a fourth world war”
The exhaustion of the growth potential of the dominant technological structure has become the cause of the global crisis and depression that has engulfed the leading countries of the world in recent years. Replacing the old technological structure with a new one is a period of crisis, during which there is a depreciation and capital flight from the outdated technological chains that have lost their profitability and countries burdened with overproduction of customary goods. The way out of the crisis, as before, will be accompanied by large-scale geopolitical and economic changes. As in previous cases, leading countries demonstrate the inability to joint fundamental institutional innovations that could channel the released capital into economic restructuring based on a new technological order and continue to reproduce the existing institutional system and serve the interests embodied in it.
The US and its G7 allies have so far exhausted the possibilities of drawing out resources from post-socialist countries, which have their own corporate structures that have privatized the remnants of their productive potential. The financial war that Washington is waging with unprotected national monetary systems has also exhausted itself, tying them to the dollar through monetarist macroeconomic policies with the help of the IMF dependent on it, rating agencies, agents of influence. The capital that is being dragged out from all over the world is no longer enough to service the growing US obligations.
At the same time, catching-up countries with a not very large technological lag get the opportunity to “cut the circle” during this period - to save on fundamental and exploratory research by imitating the achievements of advanced countries. Since the latter are burdened with significant capital investments in the production of the dominant technological order, which give considerable inertia to the production and technological structure, those who are catching up with the opportunity to “take the lead” by concentrating investments in promising growth directions. In this way today, China, India and Brazil are trying to make a technological breakthrough. In an effort to protect themselves from speculative attacks and preserve economic sovereignty, they do not open their financial systems to the expansion of American capital, demonstrating strong growth in a crisis. Their example is followed by the largest countries in Latin America and Southeast Asia, resisting the absorption of assets by speculative capital. Through currency swaps, China quickly creates its own international payment system. The room for maneuvers of the US Federal Reserve is inexorably shrinking - the US economy has to take the brunt of the depreciation of capital.
Between crisis and collapse
Based on this, we can talk about one of three scenarios for the further development of the crisis, programmed by the internal logic of the development of the current global economic system.
1. Scenario of a quick exit to a new long wave of economic growth (optimistic). It provides for the transfer of the crisis into a managed mode, which allows leading countries to channel the decline in obsolete sectors and peripheral regions of the world economy and direct the remaining resources to boost innovation activity and accelerate the growth of the new technological order. At the same time, the architecture of the global financial system, which will become a multi-currency, as well as the composition and relative weight of leading countries, will change dramatically. There will be a significant strengthening of state institutions for strategic planning and regulation of financial flows, including at the global level. Globalization will become more manageable and balanced. A sustainable development strategy will replace the doctrine of liberal globalization. Among the goals uniting the leading countries of the world will be the fight against terrorism, global warming, mass starvation, disease and other threats to humanity.
2. A catastrophic scenario accompanied by the collapse of the existing American-centric financial system, the formation of relatively self-sufficient regional monetary and financial systems, the destruction of a large part of international capital, a sharp drop in the standard of living in the “golden billion” countries, the deepening recession and the erection of protectionist barriers between regions.
3. The inertial scenario, accompanied by the growth of chaos and the destruction of many institutions both in the core and on the periphery of the world economy. While preserving some of the institutions of the existing global financial system, new centers of economic growth will appear in countries that have managed to outrun others in the formation of a new technological order and “ride” a long wave of economic growth.
The inertial scenario is a combination of elements of a catastrophic and controlled recovery from the crisis. However, it can be catastrophic for some countries and regions and optimistic for others. It should be understood that the core institutions of the global financial system will survive at the expense of tightening resources from peripheral countries by establishing control over their assets. This is achieved by exchanging the issue of their currencies on the property of the countries receiving these currencies in favor of banks and core corporations.
For the time being, the development of events proceeds according to the inertial scenario, which is accompanied by the stratification of leading countries of the world according to the depth of the crisis. The greatest damage is borne by open economies, in which the fall in industrial production and investment amounted to 15 – 30 percent in the initial phase of the crisis. Countries with autonomous financial systems and a capacious domestic market, protected from attacks by speculators, continue to grow, increasing their economic weight.
To reach an optimistic scenario, it is necessary to form global regulatory institutions capable of curbing turbulence in global financial markets and authorized to adopt universal global rules for financial institutions. Including managers providing for responsibility, transparency of stock options, elimination of internal conflicts of interest in institutions that assess risks, limiting leverage, standardizing financial products, and conducting cross-border bankruptcies.
In any of the scenarios, economic growth arises on a new technological basis with new production capabilities and qualitatively new consumer preferences. The crisis will end with the flow of the dollar pyramid remaining after the collapse and other financial bubbles of capital in the production of a new technological order.
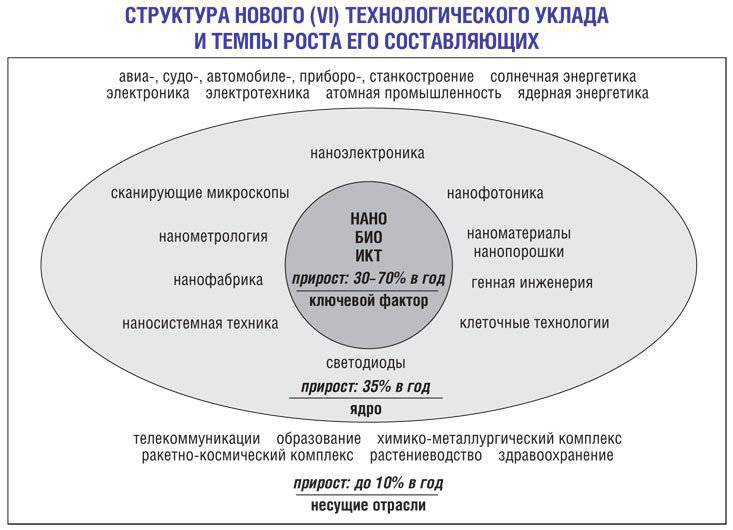
The basis of the new (sixth) technological structure is a complex of nano-, information-communication and biotechnologies. And although the main sphere of their application is health care, education and science, and is only indirectly related to the production of military equipment, the arms race and the increase in defense spending in the usual way become the leading way of state stimulation of the new technological order.
Unfortunately, Russia missed a historic chance to propose at the G20 leaders meeting in St. Petersburg in September 2013 a plan for broad international cooperation in jointly developing and mastering key areas for the development of a new technological structure that would become an alternative to the arms race as a stimulating mechanism for innovative activity. The initiative proposed by the Scientific Council of the Russian Academy of Sciences on complex problems of Eurasian economic integration, modernization, competitiveness and sustainable development to launch an international program to protect the Earth from space threats was not accepted by the officials who prepared the G20 meeting. They preferred to follow the US proposed rate of churning out the key problems of the global crisis with the focus of attention of the leading countries on the secondary issues of improving the sustainability of the global monetary and financial system working in their interests. Meanwhile, the US itself was preparing the ground in Ukraine for launching a world war on new technologies.
The fact is that the liberal ideology that dominates the ruling circles of the United States and its NATO allies leaves no other reason for expanding direct state support to the economy, except for defense needs. Therefore, when faced with the need to use government demand to stimulate the growth of a new technological order, leading business circles have resorted to the escalation of military-political tensions as the main way to increase public procurement of advanced technology. It is from this perspective that the reasons for Washington’s promotion of the flywheel of the war in Ukraine, which is not a goal, but an instrument for realizing the global task of preserving US dominant influence in the world, should be considered.
Along with the structural crisis of the economy, due to the change of the dominant technological order, a transition to a new secular cycle of capital accumulation is currently taking place, which further aggravates the risks of a world war. The previous transition from the colonial empires of European countries to American global corporations as the leading form of organization of the global economy took place through the unleashing of three world wars, the outcome of which was accompanied by fundamental changes in the world political order. As a result of the First World War, the monarchist system collapsed in three empires, restraining the expansion of national capital. As a result of the Second the colonial empires collapsed, limiting its international movement. With the collapse of the USSR due to the third - cold - world war, free movement of capital swept the whole world, and transnational corporations got the entire economy at their disposal.
But the story does not end there. The development of mankind requires new forms of organizing the global economy, which would ensure the sustainable development and reflection of planetary threats, including environmental and space ones. In the context of liberal globalization, built under the interests of transnational, mainly Anglo-American corporations, these challenges to the existence of mankind remain unanswered.
Overconcentration of capital and influence in the hands of several hundred families in the absence of mechanisms of democratic control creates the threat of the formation of a global dictatorship in the interests of ensuring the dominance of the world oligarchy by oppressing all of humanity. The risks of abuse of such power are increasing, fraught with the destruction of entire nations and catastrophes of a global scale. Objectively arising the need to curb the world oligarchy and streamline the movement of capital is achieved in the East Asian model of the organization of the modern economy. With the rise of China, India, and Vietnam, following Japan and Korea, the contours of the transition from the Anglo-American to the Asian secular cycle of capital accumulation are becoming more and more obvious.
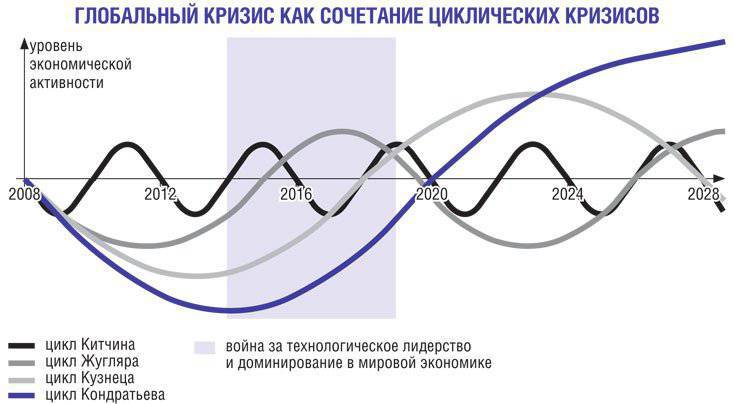
The superposition of Kondratieff's long waves, Kuznets' accumulation cycles and business cycles suggests that the world is passing the moment of coincidence of the lower turning points, which creates an extremely dangerous resonance. Mathematical modeling indicates an extreme decline in economic activity in 2014 – 2016. For the same period, the maximum risk of exacerbation of political tensions and the struggle for leadership is accounted for. With all the conventions of mathematical modeling of such processes, the historical fact is the emergence of deep military-political and social conflicts during periods of coincidence of downward waves of Kondratieff cycles and secular cycles of accumulation.
“The actions of the Bank of Russia killed high-tech industries and at the same time brought unprecedented profits to foreign capital”
The struggle for world leadership in the economy is unfolding between the United States and China, and America, to maintain its dominance, plays the usual scenario of unleashing a world war in Europe, trying once again to strengthen its position at the expense of the Old World. For this, the tested English geopolitical principle of “divide and rule” is taken, the subconscious Russophobia of the political elites of European countries is resurrected and the emphasis is placed on the traditional for them Drang nach Osten. Following the precepts of Bismarck and the advice of Brzezinski, the United States uses Ukraine as the main line of split, counting, on the one hand, on weakening and aggressive reaction of Russia, and on the other, on consolidating European states in their traditional desire to colonize Ukrainian lands. Keeping control of the Old World can give the United States a geopolitical and geo-economic safety margin necessary to maintain global dominance in competition with China.
Conflict pyramid
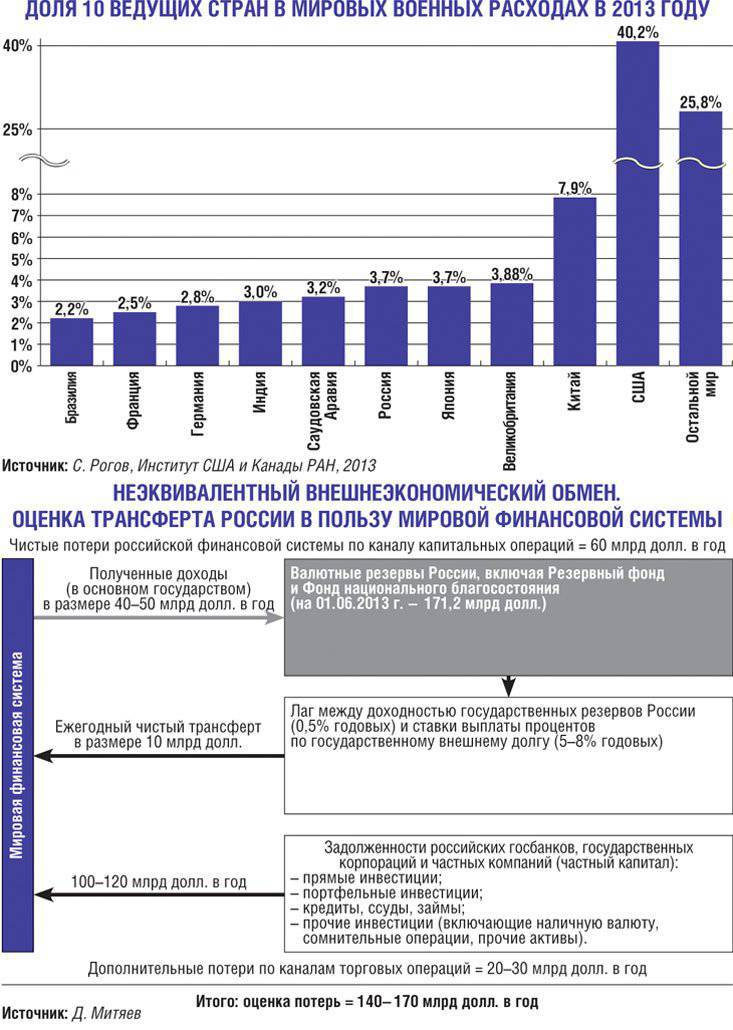
The global domination of the United States is based on a combination of technological, economic, financial, military, and political superiority. Technological leadership allows US corporations to assign intellectual rent, financing through its research and development to outrun competitors on the widest possible front of the NTP. By holding a monopoly on the use of advanced know-how, American companies have an advantage in world markets both in production efficiency and in offering new products. Economic superiority creates the basis for the dominant position of the US currency, which is protected by military-political methods. In turn, by appropriating the global seignorage (income from the issue of world currency), the United States finances its state budget deficit, which develops as a result of bloated military spending, including the cost of promising R & D. The latter today are more Russian by an order of magnitude and exceed the aggregate volume of the ten countries following the United States combined.
In the period of changing technological structures, all these components of American domination are subjected to endurance tests. Having sufficient scientific and educational potential for copying the technical achievements of advanced countries and training personnel to the best design and engineering practices, the BRIC countries are able to get ahead on the change of technological structures and in time “ride” the new long wave of economic growth. It is projected that by 2020, the aggregate GDP of Brazil, Russia, India and China may exceed one third of the world total. China has already reached the first place in the world in the export of high-tech products. Together, the BRIC countries provide a quarter of the global production of such products with the prospect of increasing their share to 1 / 3 by 2020. Their spending on research and development is growing, cumulatively approaching 30 percent of the world total. Our countries already have sufficient scientific and industrial-technological base for the technological breakthrough.
And the share of the USA in the world market is constantly decreasing, which undermines the economic basis of their dominance. The latter today rests mainly on the monopoly position of the dollar in the global monetary and financial system. It accounts for about 2 / 3 global cash flow. America is trying to compensate for the erosion of the economic foundation of global domination by increasing military and political pressure on competitors. The US share in global defense spending is 37 percent. With the help of a global network of military bases, information monitoring, electronic intelligence, they are trying to keep control of the whole world, stopping attempts by individual countries to break out of dollar dependence. However, it is becoming more and more difficult to do this - the implementation of structural changes necessary for retaining the leadership is hampered by the inertia of investments in obsolete fixed assets, as well as giant financial pyramids of private and state obligations. To shed their rapidly growing burdens and maintain a monopoly position in the global monetary and financial system, the United States is objectively interested in a world war. The impossibility of holding it in the usual way due to the risks of the use of weapons of mass destruction, the United States is trying to compensate by unleashing a series of regional wars and political conflicts. Together, they add up to a global hybrid war on the principle of “whoever is not with us is against us” and should be destroyed, dismembered, destabilized, sanctioned “whipping”.
Creating “controlled chaos” by organizing armed conflicts in the zone of natural interests of leading countries, the United States first provoke them to respond, and then carry out campaigns to put together coalitions against them in order to consolidate their leadership. At the same time, they receive unfair competitive advantages, cut off “outsiders” from promising markets, create an opportunity to ease the burden of public debt by freezing dollar assets of other countries and justify the many-fold increase in their spending on developing and promoting new technologies necessary for their economic growth.
From the point of view of the cycles of world economic and political development, as V. Pantin argues, the period 2014 – 2018 corresponds to the period 1939 – 1945, when World War II broke out. Events in North Africa, Iraq, Syria and Ukraine are only the beginning of a series of interrelated conflicts initiated by the United States and its allies. Using the strategy of “controlled chaos,” they seek to solve their economic and socio-political problems, just as they did during World War II, which in America is called a “good war.”
The United States became a superpower due to the First and Second World Wars, which caused a huge outflow of capital and minds from the European countries fighting against each other to America. The third world, remaining cold, ended with the collapse of the world socialist system, which gave the United States an inflow of over a trillion dollars, hundreds of thousands of specialists, 500 tons of highly enriched (weapons-grade) uranium and other valuable materials, a variety of unique technologies.
The global hybrid war being developed by the USA is being waged with the widespread use of weapons of the new technological order, being at the same time a catalyst for its development in the American economy. These are primarily information and communication technologies and high-precision weapons based on their use, ensuring the Pentagon’s systemic superiority in managing combat operations and minimizing casualties. They are complemented by the widespread use of cognitive technologies, which turn the media into highly efficient psychotropic weapons of mass destruction of people's minds, and diplomacy into information weapons that paralyze the political will of the leaders of the enemy.
As all the US-organized wars of the last two decades, starting with Iraq and Yugoslavia and ending with Ukraine, show, the types of technologies used are complex, where the military component itself plays the role of the “last argument” in the final phase (which is why they are called hybrid). Prior to this, the focus is on the internal destabilization of the region targeted for aggression, for which information weapons are used, aimed at deforming the mass consciousness and discrediting traditional morality. In other words - to the shaking of the foundations of society, which inspires aggressive and even misanthropic landmarks. At the same time, bribery and the establishment of control over the ruling elite occur. Influential families and promising youth are drawn into special relations with the US and its NATO allies through foreign accounts and savings, training, grants, invitations to prestigious events, citizenship, and property purchases.
In this case, the Americans themselves choose opponents and then control the fighting, as well as determine the winners and pretend the loser. So it was with Iraq, which provoked an attack on Kuwait, after which it was indicatively punished. With Serbia, whose leader was promised security in exchange for refraining from causing unacceptable damage to NATO countries, and then defeated and condemned. With the countries of North Africa, the rulers of which were misled by signs of attention, and then given to the mercy of a crowd distraught of permissiveness. With Yanukovych, who has been courted by American consultants for a long time, and in the decisive phase - officials and politicians of the US and the EU, with the sole purpose of persuading not to use force against militants of the pro-Western opposition, then to sacrifice their agents and seize power.
The wars started by the United States seem to be senseless chaos. In fact, they are organized and coordinated by all interested departments in conjunction with the actions of big capital, the media and an extensive intelligence network. And the results achieved by the United States are quite planned: American corporations gain control over the natural resources and infrastructure of the defeated countries, banks freeze their assets, specially trained vandals ruin historical museums, the financial system is tied to the dollar. All the conflicts organized by the United States have repeatedly paid off, including the war in Afghanistan, as a result of which the “uncontrolled” American intelligence services increased the flow of drugs to Russia and Europe by an order of magnitude.
Such wars are also called chaotic, because the leadership of the victim country until the last moment does not feel threatened by the enemy, political will is constrained by endless negotiations and consultations, immunity is suppressed by demagogic propaganda, while the enemy is actively working to destroy the structures of its internal and external security. . At the crucial moment, they are undermined by the military suppression of the emerging centers of resistance. It was in this way that the US achieved success in the phase of “defusing tension” of the Cold War against the USSR, and is currently creating craters of expanding chaos in strategically important regions of the Middle East, trying to regain control of the post-Soviet space.
By organizing a coup d'état and establishing full control over the structures of Ukrainian state power, Washington is banking on turning this part of the Russian world into a springboard for armed, informational, humanitarian and political intervention in Russia in order to transfer the chaotic war to our territory, organize the revolution and the subsequent dismemberment. At the same time, the anti-Russian economic sanctions of the United States are seeking to weaken the EU and consolidate control over Brussels. The organization of an armed conflict involving NATO on the territory of Ukraine is the most desirable scenario for the United States. The unleashing of such a war under the slogans of protection against "Russian aggression" is the main goal of the Russophobic regime established by the Americans in Kiev. As long as it exists, the provocation of war will continue, including through terror against the Russian population of the southeast.
Even if we succeed in stopping the American aggression and stopping the Ukrainian crisis, there is no doubt the inevitability of a prolonged and significant deterioration in trade and economic relations between Russia and NATO members, as well as other US allies (Japan, South Korea, Canada, Australia). Given the high external dependence of the domestic economy, this creates serious threats to national security. The most acute of them concern the risks of freezing foreign exchange assets, disconnecting banks from international payment and information systems, prohibiting the supply of high-tech products, and the deterioration of export conditions.
In whose hands the paper money
Economic policy is conducted in the interests of the dominant groups of influence, which are far from always corresponding to the national ones. For example, the IMF imposes the Washington Consensus on countries contrary to the needs of their development. We observed the consequences of such a policy in Russia in the 90s, when the actions of the Central Bank at the same time killed high-tech industries and brought unprecedented profits to foreign, mainly American, financial capital. A similar picture is taking shape today.

With the escalation of sanctions pressure and disconnection of Russian borrowers from world capital markets, an increase in interest rates increases the cost of credit and increases the risk of defaults of borrowing companies. Instead of creating a mechanism for replacing external sources of credit with internal sources to cover the emerging deficit, the Bank of Russia is aggravating it. At the same time, while maintaining a free regime for capital transactions, it contributes to the export of money, approaching this year to 100 billions of dollars.
It is curious that the amount of leakage (illegal export) of capital, which amounted to more than 80 billion dollars in the first half of the year, coincides with the amount of reduction of foreign loans to Russian structures as a result of sanctions. Thus, their negative effect could be completely neutralized by stopping the leakage, for which the Central Bank and the government have great opportunities. However, stating the acceleration of capital flight, the Central Bank refuses to apply the norms of currency regulation and control necessary for its termination.
Raising interest rates in the current environment of increased external economic risks cannot serve as a sufficient incentive to curb the outflow and stimulate capital inflows. It only aggravates the lack of competitiveness of the domestic banking system in comparison with OECD countries, which have cheap and long-term credit resources, which are provided to them almost free of charge by their state monetary institutions. The predominant position of foreign lenders is fixed by the regulatory policy of the Central Bank, which assesses the obligations of foreign, including offshore jurisdictions with a lower discount than Russian issuers, on the grounds that the latter have lower ratings of the Big Three of US rating agencies.
The monetary policy pursued in Russia objectively entails the colonization of the domestic economy by foreign capital. It gains an advantage by being associated with the emission centers of world currencies of fiduciary (fiat) nature. They are created without any real security, the substitute for which is the debt obligations of the respective states and corporations. Therefore, they can be printed without restrictions and released at any interest in the interests of the issuer.
This is the most profitable type of economic activity. At the same time, seignorage may actually be transferred by the Central Bank (with interest-free, in real terms, lending) to the government or financial institutions. In the US, these are commercial banks related to the Fed. In the EU - the state - the issuers of bonds taken under collateral ECB loans. In Japan and China, there are government lending institutions, primarily development institutions. It is the share premium generated by the creation of fiduciary money - the main economic instrument of the state in Western countries at the present time. Seignorage advances the creation of added value by generating economic energy.
Modern fiduciary money and capital created on their basis are the most effective tool for expansion, which allows them to seize the resources of other countries and exploit their peoples with minimal cost. The fact that the victims of such a policy, including Russia, do not hinder their penetration into their economic space and even make efforts to attract them, is due to the low level of financial literacy. So, our monetary authorities thoughtlessly in the wake of the IMF and experts of the American Treasury, who inspired dogma that would be beneficial to them. The essence of the latter is to conduct the issue of money for the purchase of foreign exchange (mainly dollar) reserves and its restriction to the volume of their growth. In this case, the national currency becomes a substitute for the dollar, and the country's economy is subject to the interests of American capital, whose investments turn out to be the main source of domestic credit. The industries to which foreign investors show no interest remain without money and are declining. The economy is evolving under the decisive influence of external demand, acquiring commodity specialization.
This is exactly the situation today. The American authorities are cutting off the Russian economy from external financial sources, and their own monetary authorities, instead of replacing them with their own, are pursuing an increase in their domestic credit. Until now, despite the sad experience of the outflow of foreign speculative capital in 1998 and 2008, the Central Bank continues the policy of full openness of the financial market, not taking proper measures both to counteract the outflow of capital and to create domestic sources of credit. As a result of such a policy, the money supply in the Russian economy is mainly formed under foreign obligations and remains clearly insufficient to finance even simple reproduction. The result was a deep dependence on the external market, commodity specialization, the decline of the manufacturing industry, the degradation of the investment sector, the subordination of the financial system to the interests of foreign capital, in favor of which annual transfers in the amount of 120 – 150 billions of dollars (6 – 8% of GDP) are made.
The experience of the 2008 crisis of the year revealed the high vulnerability of the Russian economy. Regulation of the global financial market is carried out by means that are discriminatory for the country, including lowering credit ratings, presenting uneven requirements for openness and complying with financial constraints, imposing mechanisms for unequal foreign exchange, in which Russia annually loses more than 100 billions of dollars. Including the order of 60 billions of dollars leaving the country in the form of a balance of income from foreign loans and investments, about 50 billions are leaked capital. The accumulated volume of the latter reached 0,5 trillion dollars, which in total with foreign direct investment (FDI) of Russian residents amounts to about a trillion dollars of exported capital. Income losses of the budget system due to capital flight amounted to 2012 839 billion rubles (1,3% of GDP) in 2012 year. The total amount of losses from the offshore economy, capital flight and tax evasion is estimated at X5NUMX at five trillion rubles.
The policy of the Central Bank (CB) to overstate interest rates and limit the amount of credit against the background of freezing its external sources leads to a contraction of the money supply, falling production and investment, as well as a chain of bankruptcies of enterprises with negative social consequences.
The unjustifiably tough policy of the Central Bank has already led this year to a reduction in real money by more than 700 billion rubles and an increase in the cost of credit resources by an average of 2 – 2,5 percent, which has led to the economy being drawn into stagflation. According to the experts of Delovaya Rossiya, if a year ago the level of profitability of the national economy was in 1,5 – 2 times lower than the average cost of credit resources, then since last spring the return on invested capital was less than even the key interest rate of the Central Bank (6% against 8% ). With the average profitability of today's sales of industrial products of about 10 percent, the cost of a loan in the amount of 10,3 – 12,2 percent offered by banks allows financing only the working capital of enterprises for a short period. Attracting a loan for investment purposes makes no sense. Along with a decrease in the volume of profits of industrial enterprises and a reduction in budget investments, this causes a decline in investment activity, preserves scientific and technical backwardness. Increased depreciation of fixed assets. From 45,2 percent in 2005, it has already grown to 48 percent, and this year due to the decline in capital investment by 2,5 percent will reach 48,5 percent.
Prior to the introduction of Western sanctions, corporations and banks compensated for a restrictive monetary policy with external loans, the total amount of which exceeded 650 billions of dollars (74% are denominated in dollars and euros). This represents more than half of the money supply circulating in the national economy. Of these, over the next three months, you need to pay over 61,4 billion, which is equivalent to 2,45 trillion rubles or 3,5 percent of Russia's GDP. In 2015, you will have to pay off more than 112 billions of dollars. Total for 15 months, Russian borrowers are obliged to return over 173 billions of dollars. Including 60 – 65 billions are payable by private companies and banks that do not have access to an alternative source of refinancing under similar conditions. Additional losses of the Russian financial system in the amount of more than 50 billions of dollars arise from the illegal export of capital. Another 60 billion will leave the country in the form of a balance of income from cross-border investments.
Proposed by the Central Bank The main directions of the unified state monetary policy for 2015 – 2017 years ignore this problem. If the outflow of capital to the end of 2015 is estimated at more than 11 trillion rubles, it is planned to increase the loan to banks for the next year by 700 billion rubles, and in the future to 2018-th - by 2,1 trillion. Taking into account that part of the debt will be repaid due to foreign currency savings, as well as loans provided by the Central Bank to the banking sector this year, a squeeze against the current level that is clearly insufficient even for simple reproduction will be at least five trillion rubles. Taking into account the import substitution announced in response to the sanctions, as well as the demand for loans from small and medium-sized businesses, the shortage of money supply will reach 6,5 trillion rubles. If we also take into account the need for crediting the growth of production in existing facilities and investments in their modernization and development, the artificially created shortage of money in the economy reaches 8 – 9 trillion, which is about 12 percent of GDP. If the current trends continue, the fall in GDP may reach four percent next year. By squeezing the money supply and raising the interest rate, the Central Bank artificially worsens the conditions for lending to enterprises, which forces them to reduce production and investments, and also to compensate for the additional costs by raising prices. At the same time, declaring “targeting inflation”, the Central Bank cannot at all achieve the declared goals, because with its policy it spins the flywheel of costs and strengthens inflation expectations by switching to a floating exchange rate of the ruble. In contrast to the scholastic models of market equilibrium in real Russian conditions, an increase in interest rates gives not an inflow of capital, but its outflow from the real sector to foreign currency accounts, and the floating exchange rate turns into a free fall. The chain of defaults of enterprises facing the impossibility of refinancing their obligations is inevitable.
Dangerous maneuvers
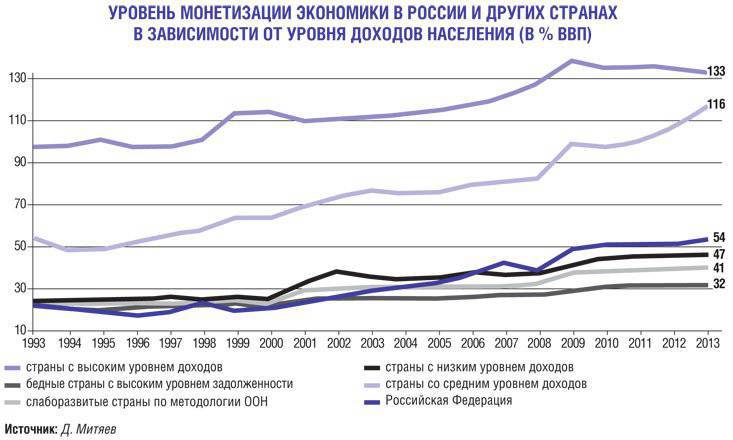
One can argue endlessly about how an increase in money supply affects inflation, but it is clear that its reduction is automatically associated with a decline in production, business, investment and innovation activity. This year’s decline in monetization from 47 to 44 percent of GDP coincides with a three percent drop in GDP growth rates relative to the previously expected figure, as well as a two percent reduction in investment. Over the past 16, similar compression of real money supply has been noted only twice: shortly before the collapse of the GKO-OFZ pyramid and the default on government debt in 1998 in August, and then at the height of the 2008 – 2009 winter financial crisis.
The economic recession also contributes to the withdrawal of about seven trillion rubles from the government, frozen on the accounts of the Central Bank. This is more than his credit to commercial banks and, through them, to the economy as a whole. In other words, its real creditor is not the Central Bank, but taxpayers. Their funds are withdrawn from circulation and partially replaced by loans from the Central Bank. Thereby, the final demand for goods and services is artificially reduced and the money supply in the financial market increases accordingly. At the same time, the government and the Central Bank work as "communicating vessels." When the cabinet withdraws money from the economy to the accounts of the Central Bank, the latter increases the loan and vice versa - when the government increases spending, the Central Bank turns off the proposal. In general, the monetary authorities are idling, creating annual cyclical fluctuations of the financial market without its development and without any reference to the goals of economic growth.
In addition, by withdrawing money and thereby reducing demand and production, the government simultaneously provokes inflation not only by raising regulated tariffs, but also by a strange “tax maneuver” to replace part of export duties with a mineral extraction tax. NDPI is essentially a tax on oil and other natural resources. Adding to the "closing" cost of production at the worst for the profitability of the field, it is automatically included in the price of goods. Even with the planned reduction in excise taxes on petroleum products, this maneuver takes the economy to a new level of costs, representing a redistribution of natural rent in favor of oil exporters at the expense of its domestic consumers. It pushes the economy even further into the stagflational trap created by the policies of the Central Bank.
A simple extrapolation of a clearly observed statistical relationship between the growth rates of GDP and the money supply shows that with such a policy one should expect a fall in GDP of four percent in 2015 and two percent in 2016.
It is not the first time that such an oppression of the economy has occurred in our recent history. In 90, the policy of quantifying the growth of the money supply resulted in a two-fold reduction in industrial production and a four-fold reduction in investment. It did not help to overcome inflation, but led to the bankruptcy of the state in 1998. In 2000-ies, the sterilization of oil and gas revenues and the restriction of the issue of money to buy currency deprived the economy of investments that are crucial for its modernization and development of a new technological order.
The combination of Western sanctions, unjustifiably tight monetary administration and sterilization fiscal policy leads to an economic catastrophe, to prevent which it is necessary to replace external sources of credit with domestic ones. It requires a transition from a speculative model of the financial market to one that is aimed at ensuring sustainable growth and modernization. However, repeated proposals to solve this problem, consistently expressed by Russian scientists and specialists for two decades, categorically rejected by the leadership of the Central Bank, which continues to follow the recipes of the IMF, focused on serving the interests of foreign capital. The result was a deep dependence of our economy on the external market, its specialization in raw materials, the degradation of the investment sector and the decline of the manufacturing industry, the subordination of the financial system to foreign capital, in favor of which annual transfers to 120 – 150 billions of dollars are made (6 – 8% of GDP). Despite the sad experience of 1998 and 2008, the Central Bank does not take adequate measures either to counteract capital outflows and to offshore the economy, or to create domestic sources of credit. The money supply is formed mainly under foreign obligations and remains clearly insufficient to finance even simple reproduction. With the closure of external sources and the deterioration of the balance of payments due to falling oil prices, the risk of an avalanche-like contraction of the monetary supply and a collapse of investments increases.
To ensure expanded reproduction, the Russian economy needs a substantial increase in the capacity of the banking system. In contrast to the countries issuing reserve currencies, our main problems are caused not by an excess of money supply and related financial bubbles. The Russian economy has been working “for wear” for a long time due to an acute shortage of loans and investments.
For two decades, the monetary authorities of the country are guided by ideas about the linear relationship between money growth and inflation that do not correspond to reality, ignoring both scientific knowledge about the dynamics of economic processes and world and domestic practical experience. The Central Bank makes mistakes that are naive and extremely harmful in their consequences. In particular, it proceeds from the incorrect hypothesis of the exhaustion of traditional sources of economic growth, while the observed recession occurs against the background of 30 – 40-percent underloading of production capacities, 15-percent over-employment in industry and services, highly inefficient use of natural resources and human potential.
To realize the opening up of opportunities on the wave of growth of the new technological order, a powerful initiating impetus to the renewal of fixed capital is required. However, the required level of investment and innovation activity is twice as high as the Russian financial system currently has.
The theory of economic development and the practice of developed countries implies the need for an integrated approach to the formation of money supply in conjunction with the goals of economic development and with reliance on domestic emission sources. The most important of these is the refinancing mechanism, closed to lending to the non-primary high-tech sector. You can use the well-known and developed in the practice of developed countries indirect (refinancing on the security of the obligations of the state and solvent enterprises) and direct (co-financing of state programs, the provision of state guarantees, funding development institutions) emission methods.
For their money
For the formation of a modern credit and financial system, adequate to the tasks of raising investment activity in order to modernize and develop the Russian economy, the following set of measures is proposed.
1. Setting up the monetary system for development and expanding lending opportunities for the real sector.
1.1. Legislative inclusion in the list of objectives of the state monetary policy and the Bank of Russia activity creates conditions for economic growth, increased investment and employment.
1.2. The transition to the regulation of the money supply by setting the refinancing rate with the issue of money mainly for refinancing commercial banks on the security of credit requirements for manufacturing enterprises, government bonds and development institutions. At the same time, the refinancing rate cannot exceed the average profit rate in the investment complex minus the bank margin (2 – 3%), and the loan terms must correspond to the typical duration of the research and production cycle in the manufacturing industry (up to seven years). Access to the refinancing system should be open to all commercial banks on universal terms, as well as to development banks on special conditions that correspond to the profile and objectives of their activities (including taking into account the expected return on infrastructure investment - up to 20 – 30 years under 1– 2%).
1.3. The cardinal expansion of the Lombard List of the Central Bank, the inclusion in it of promissory notes and bonds of solvent enterprises operating in priority areas, development institutions, guarantees of the federal government, federal subjects and municipalities.
1.4. In order to avoid stimulating the export of capital and currency speculation, the acceptance of foreign securities and foreign assets of Russian banks as collateral for lombard and other loans of the Central Bank should be stopped.
1.5. A significant increase in the resource potential of development institutions by funding the Central Bank for investment projects approved by the government in accordance with the established priority areas. Development institutions should place such loans on the basis of targeted lending for specific projects that provide for the allocation of money exclusively for the costs they have established without transferring money to the borrower's account.
1.6. To prohibit commercial banks to revise the terms of credit agreements unilaterally.
1.7. Modify valuation standards for collateral, using weighted average market prices of the medium term, and limit the application of margin requirements. Provide for the rejection of margin requirements for borrowers by the Central Bank and banks with state participation.
2. Creating the necessary conditions for increasing the capacity of the monetary and financial system.
2.1. Gradually switch to the use of rubles in international payments for trade transactions of state corporations, to consistently replace their foreign currency loans with ruble loans of state commercial banks with the provision of appropriate funding by the Central Bank.
 2.2. To ensure the stability of the ruble exchange rate, expand the tools for regulating the demand and supply of foreign currency, providing for the possibility of collecting export duties in foreign currency with its accumulation in the government’s foreign currency accounts in case of over-supply of currency and introducing the rule of mandatory full or partial sale of exporters ’foreign exchange earnings in the domestic market. In case of insufficient supply.
2.2. To ensure the stability of the ruble exchange rate, expand the tools for regulating the demand and supply of foreign currency, providing for the possibility of collecting export duties in foreign currency with its accumulation in the government’s foreign currency accounts in case of over-supply of currency and introducing the rule of mandatory full or partial sale of exporters ’foreign exchange earnings in the domestic market. In case of insufficient supply.2.3. Fixing exchange rate quotes in relation to the ruble, and not to the dollar and the euro, as is currently the case. The establishment of pre-declared limits of fluctuations of the ruble exchange rate, supported by a long time. If there is a threat of going beyond the boundaries of the corridor, a one-time change in the rate with the establishment of new borders in order to avoid provoking an avalanche-like capital flight and currency speculation against the ruble, as well as ensuring an instant stabilization of its rate.
2.4. To prevent the flow of funds issued for refinancing production activities and investment of money to the financial and foreign exchange market, it is necessary to ensure the targeted use of such loans through banking supervision. To introduce restrictions on the change in the currency position of commercial banks that resort to refinancing securities. To limit financial speculation, expand the financial leverage regulatory system to include non-bank companies.
2.5. Creation of the EurAsEC payment and settlement system on the basis of the Interstate Bank of the CIS with its information exchange systems between banks, credit risk assessments, currency exchange rate quotes.
3. Stabilization of the banking system.
3.1. Providing commercial banks with the opportunity to immediately receive stabilization loans to meet the panic requirements of individuals in the amount of up to 25 percent of the volume of deposits of citizens.
3.2. The resumption of unsecured credit auctions of the Central Bank for creditworthy banks experiencing a liquidity deficit.
3.3. Take urgent measures to maintain the current liquidity of banks: reducing deductions to the Fund for Mandatory Reserves, increasing the lending capacity of banks against “non-market assets”, expanding the diversity of such assets. If necessary, set downward factors when calculating the value of assets weighted with regard to risks for enterprises having ratings of Russian rating agencies (RA). Ensure transparency and automatism of financial assistance mechanisms.
3.4. Develop a methodology for the formation and determine the list of strategic enterprises whose loans are refinanced on concessional terms.
3.5. It is hard to stop the attempts of commercial banks to provoke a panic in order to entice customers, to introduce criminal liability for such actions.
3.6. Postpone implementation of Basel-3 standards in Russia for two to three years, until the recovery of lending to the real sector at the pre-crisis level of the first half of 2008. Adjust these standards in order to eliminate artificial restrictions on investment activities. The calculation of credit risk (Basel-2) is based on internal ratings, not ratings of international agencies, the failure and unprofessionalism of which were manifested in the 2007 – 2008 financial crisis.
When forming the monetary policy, the Central Bank should evaluate the macroeconomic effects of the issue of rubles through various channels: for refinancing commercial banks under the obligations of industrial enterprises, for government bonds and development institutions, for replacing foreign currency loans, for purchasing foreign currency in the foreign exchange reserve, for external demand for rubles for lending foreign trade turnover, capital operations and the formation of ruble reserves of foreign countries and banks. Methodological support for this work, including the construction of imitational economic and mathematical models of monetary circulation, could be taken up by the RAS in collaboration with the research department of the Central Bank.
Change of values
Currently, the volume of foreign currency assets of the Russian Federation, located in the jurisdiction of NATO countries, is more than 1,2 trillion dollars, including short-term - about 0,8 trillion dollars. Their freezing can be partially compensated by countermeasures against the assets of NATO countries in Russia, the amount of which is 1,1 trillion dollars, including long-term - more than 0,4 trillion dollars. This threat would be neutralized if the monetary authorities organized the withdrawal of Russian short-term assets from the US and the EU in a timely manner, which would change the balance in their favor. However, despite the threat of sanctions, they continue to grow: in the second quarter of this year alone, the Ministry of Finance and the Central Bank placed more than 12 billions of dollars in US and European securities.
It is not too late, you need to sell off foreign currency assets placed in liabilities of the USA, Great Britain, France, Germany and other countries participating in the sanctions against Russia. They should be replaced by investments in gold and other precious metals, in the creation of stocks of highly liquid commodity values, including critical imports, in the securities of countries - members of the EAEU, SCO, BRICS, and also in the capital of international organizations with Russian participation (including the Eurasian Development Bank , Interstate Bank of the CIS, IIB, BRICS Development Bank, etc.), to expand the infrastructure to support Russian exports. Among the elements of the latter, the creation of international exchange sites for the sale of domestic commodities in the Russian jurisdiction and for rubles, as well as the creation of international distribution networks and the maintenance of our high value-added goods are of great importance.
The Central Bank has delayed the creation of a national payment system for servicing bank cards, as well as an international interbank information exchange system, which could protect the country from sanctions from Western-style settlement and payment systems VISA, Mastercard, SWIFT, which was discussed more than two years ago. Now the creation of such systems of international level must be put on the agenda of the next meeting of the BRICS countries in 2015.
The currently solved task of forming our own national payment system should be docked with established international payment systems. This can be done in cooperation with China, which will require the conclusion of an appropriate framework agreement. With the counter steps of other BRICS countries, it is possible to successfully promote in the global market a new international payment system with a card compatible with the national payment systems of the participants (with a total population of over three billion people). Russia can become a pioneer in issuing such a card.
It is necessary to develop international standards for determining the ratings and activities of the RA to reduce the systemic distortion of the risk assessment of assets listed on the market in favor of a country, as well as ensuring unified international regulation in this area. At the level of the BRICS countries, determine the relevant certification and licensing procedures of the Republic of Armenia, whose assessments should have international recognition. For this purpose, the BRICS Development Bank can be used. A similar approach should be applied to the activities of audit companies and legal advisers.
It is important to ensure the harmonization of the rules of action of national monetary authorities in protecting their monetary and financial systems from speculative attacks and suppression of associated turbulence. Contrary to the position of the United States and the IMF, it is advisable to agree on the need to create national systems of protection against global destabilization risks, including the institution of reserving foreign exchange capital movements; tax on income from the sale of assets by non-residents, the rate of which depends on the term of ownership of the asset; Tobin tax; enabling countries to impose restrictions on the cross-border movement of capital on transactions that pose a threat to national security.
It's not just economic sanctions. Studies show that the destabilization factors of the global financial system continue to operate. With continued turbulence in the global financial market, the United States plans to stabilize it by resetting its external obligations.
The risks associated with the large-scale emission of world currencies make it necessary to closely monitor the movement of capital not only from the country, but also, and no less important, into the country. At the same time, one should not be guided by the formal principles “any investments are good” and “the more, the better”. In modern conditions, especially with an excess of global liquidity, which is looking for areas for investment and can be destabilizing, it is important to pay attention to the quality of capital, terms, nature and directions of its use, conditions of repatriation, to ensure compliance of these parameters with economic priorities.
With monetary expansion and measures to reduce the cost of financial resources consistently conducted by issuers of world currencies, it is necessary to level the conditions for the activities of Russian enterprises in comparison with foreign competitors. This requires reducing the refinancing rate, which the central banks of many leading countries set below inflation for a long-term period in order to reduce the cost risks of borrowers, and lengthen loans. In developed economies, in the implementation of emissions, emphasis is placed on the formation of long and super-long target (in the United States, Japan and China - up to 30 – 40 years) resources under state obligations, including financing long-term investment projects that are complemented by medium-term refinancing tools.
Monetary policy conducted by the leading members of the WTO is linked to industrial priorities (sectoral, corporate, regional), which makes it possible to talk about the formation of a monetary policy toolkit (mondustrial policy).
If it is necessary to double investments in order to modernize the Russian economy, the Central Bank and the government of the Russian Federation need to link monetary policy with the solution of these tasks. In order to avoid negative influence of foreign factors, it is important to ensure the priority role of domestic sources of monetization, including expanding the long- and medium-term refinancing of commercial banks under the obligations of manufacturing enterprises and authorized government bodies. It is also advisable to conduct a consistent replacement of foreign borrowings of state-controlled banks and corporations with domestic sources of credit.
It is necessary to finally fulfill the instructions given by the country's president repeatedly about de-offshore the Russian economy, which creates a supercritical dependence of its reproductive contours on Anglo-Saxon legal and financial institutions and entails systematic losses of up to 60 billions of dollars a year only on the difference in profitability of the capital employed and allocated.
Along with de-offshorization, to ensure Russia's foreign economic security, it is important to achieve the fulfillment of repeated instructions by the Russian president to create a national financial market infrastructure, including a transition to using domestic rating agencies, auditing, legal and consulting companies. The hitch causes significant losses.
The increase in global instability requires in the shortest possible time to implement a set of measures to ensure the economic security of the country.
1. For de-offshoring and stopping the illegal export of capital
1.1. Legislatively introduce the concept of a “national company” that satisfies the requirements of registration, tax residency and core business in Russia, belonging to Russian residents not affiliated with foreign entities and jurisdictions. Only such companies and resident Russian citizens should be granted access to subsoil and other natural resources, government orders, state programs, subsidies, concessions, property and real estate management, housing and infrastructure construction, as well as other strategically important assets. for the state and socially sensitive activities.
1.2. To oblige the ultimate owners of shares of the backbone enterprises of the country to get out of the offshore shadow, to fix their property rights in the Russian registrars.
1.3. To conclude agreements on the exchange of tax information with offshore companies, to denounce agreements with them, including Cyprus and Luxembourg, to avoid double taxation.
1.4. It is legal to prohibit the transfer of assets to offshore jurisdictions with which no agreements on the exchange of tax information have been concluded - according to the transparency model developed by the OECD.
1.5. Introduce requirements for offshore companies owned by Russian residents to comply with national legislation to provide information on participants (shareholders, depositors, beneficiaries), as well as for tax purposes in Russia of all income received from Russian sources, under the threat of 30-interest tax for all operations with non-cooperative offshores.
1.6. To form a “black list” of foreign companies and banks participating in dubious financial schemes with Russian counterparties.
1.7. Introduce a permitting procedure for offshore operations for Russian companies with state participation.
1.8. Develop a presidential program for the de-offshorization of the economy.
1.9. Take a set of measures to reduce tax losses from capital flight: refund of VAT only after receipt of export earnings, charging advance payments on VAT by authorized banks when transferring advances to non-resident suppliers, imposing fines for overdue receivables under foreign contracts in the amount of illegal export.
1.10. To stop including bad debts of non-residents in non-operating expenses (reducing taxable income) to Russian enterprises, in case of such debts, to file claims for compensation for damage to managers.
1.11. To toughen administrative and criminal liability for the illegal export of capital from the territory of the Customs Union, including in the form of false trade and credit operations, payment of inflated interest on foreign loans.
1.12. Start active work of law enforcement agencies in extending the validity of Article 174 of the Criminal Code “Legalization (laundering) of money or other property acquired by other persons by criminal means” on income derived from tax fraud and illegal export of capital.
1.13. Introduce taxes on speculative financial transactions (Tobin’s planned EU tax) and net capital outflow.
2. To prevent further losses of the financial system and protect the money market from threats of destabilization
2.1. To curb illegal operations on the export of capital, accompanied by tax evasion, create a unified information system, including electronic declaration of transaction passports with their transfer to the databases of all currency control and tax control bodies, the introduction of standards for managers of enterprises that allow the accumulation of overdue export receivables import operations.
 2.2. Strengthen the supervision of the financial status of professional market participants, pricing and risk levels, create a national clearing center, adjust the activities of financial conglomerates.
2.2. Strengthen the supervision of the financial status of professional market participants, pricing and risk levels, create a national clearing center, adjust the activities of financial conglomerates.2.3. Stop discrimination of domestic borrowers and issuers before foreign ones. When calculating indicators of liquidity, capital adequacy, etc. The Central Bank should not consider the obligations of non-residents and foreign countries more reliable and liquid than similar obligations of residents and the Russian state. Introduce domestic standards for rating agencies and discard the use of foreign RA ratings in government regulation.
2.4. To impose restrictions on the volume of off-balance sheet foreign assets and liabilities to non-residents on derivatives of Russian organizations, to limit enterprises' investments in foreign securities, including government bonds of the United States and other countries with a high budget deficit or government debt.
2.5. Introduce advance advance notice of capital outflow operations, raise reserve requirements for Russian banks on foreign currency transactions, set limits on the values of long and short currency positions of commercial banks and backbone companies, as well as all state-controlled enterprises that receive state support and receive refinanced CBR loans.
2.6. Accelerate the creation of a central depository in which to organize the accounting of property rights for all shares of Russian enterprises.
2.7. Normatively secure the obligation of primary placements of Russian issuers on national trading floors.
3. To increase the potential and security of the Russian monetary system, to strengthen its position in the global economy, to give the ruble functions of an international reserve currency and to form the Moscow financial center
3.1. Stimulate the transition in mutual settlements in the CIS to rubles, in settlements with the EU - into rubles and euros, with China - into rubles and yuan. Recommend business entities to switch to settlements in rubles for exported and imported goods and services. At the same time, it is necessary to provide for the allocation of related ruble loans to states that import Russian non-primary products to maintain trade, to use swaps for this purpose.
3.2. To drastically expand the system of servicing settlements in national currencies between enterprises of the Commonwealth countries through the Interstate Bank of the CIS, with other states using the international financial organizations controlled by Russia (IBEC, IIB, EDB, etc.).
Table 1
3.3. Create a payment and settlement system in the national currencies of the EurAsEC member states. Develop and implement its own independent system of international payments, which could eliminate the critical dependence on the US controlled system SWIFT. Include the banks of Russia, members of the Customs Union and the CIS, as well as China, India, Iran, Syria. Venezuela and other traditional partners.
3.4. The Bank of Russia should recommend refinancing commercial banks for ruble crediting of export-import transactions, and also take into account additional demand for rubles in the main directions of monetary policy due to the expansion of foreign trade turnover in rubles and the formation of foreign ruble reserves.
3.5. To organize exchange trade in oil, oil products, timber, mineral fertilizers, metals, and other raw materials in rubles. To ensure market pricing and prevent the use of transfer prices, oblige manufacturers of commodities to sell at least half of their products, including those exported, through exchanges registered by the Russian government.
Table 2
3.6. To limit the borrowing of state-controlled corporations abroad, to gradually replace foreign currency loans with ruble loans of state-owned commercial banks at the expense of their targeted refinancing by the Central Bank at a corresponding percentage.
3.7. Exclude deposits in foreign currency from the deposit insurance system with a simultaneous increase in the required reserve ratios for them.
3.8. To establish, on the basis of the Export Insurance Agency, the Reinsurance Company with the provision of a dominant position in the risk management market for Russian residents.
3.9. Create a Moscow club of lenders and investors to coordinate the policies of Russian banks and funds abroad, work on the return of problem loans, holding a unified position with respect to the default borrowing countries.
From economic protection to development management
However, the measures listed are not enough. The results of measurements of indicators of the socio-economic situation of Russia in relation to the extremely critical values established as a result of scientific research indicate the emergence of a threat to the functioning of the national economy and the functioning of society.
Among the most obvious pressing issues that require immediate solutions, one should single out the depressing state of the investment sector, first of all machine tool and instrument making, of the electronics industry; degradation of scientific and technical potential due to repeated under-funding of R & D and the actual elimination of industry science and design institutes during the privatization campaign; disorganization of basic research due to an administrative clampdown as a result of the reform of the RAS; the growing technological gap in key areas of the formation of a new technological order; extreme dependence on foreign technology in critical areas (air transport, drugs, information and communication equipment).
Table 3
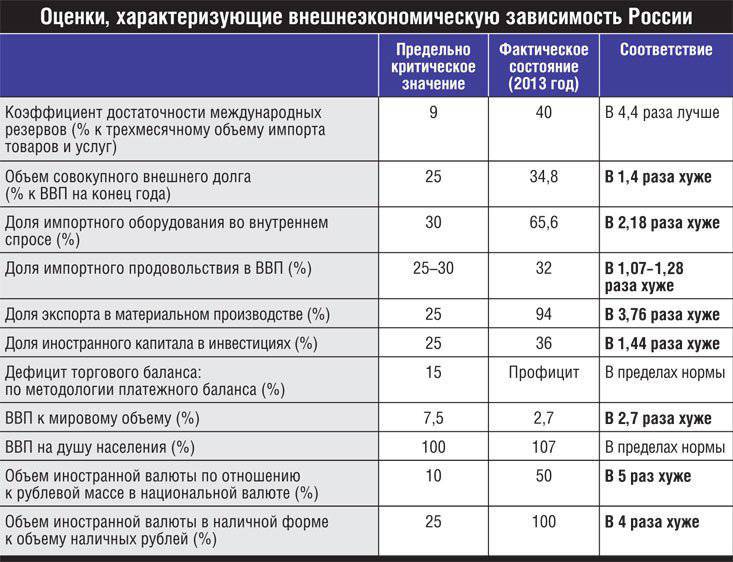
Large-scale import substitution programs are needed, balanced in material, financial and labor resources. This is impossible to do in the existing system of economic regulation, in which planning methods are lost, including the compilation of balances, target programming, scientific and technical forecasting, and system design. Import substitution should become part of the overall strategy of advanced development of the economy and begin with the deployment of a strategic planning system designed to ensure the systematic use of the resources available to the state to modernize and industrialize on the basis of a new technological order.
The strategic planning methodology provides for a system of long-, medium- and short-term forecasts and selection of priorities, tools and mechanisms for their implementation, including a system of concepts, programs and plans, institutions for organizing relevant activities, as well as methods of control and responsibility for achieving goals. The adopted draft law “On State Strategic Planning” provides for the creation of only some of the elements of this system, mainly the procedures for the preparation of relevant documents in the executive branch.
It is also advisable to establish control methods and mechanisms of responsibility of all participants in strategic planning on the basis of a private-public partnership. Of particular importance is the integration into this system of development institutions, leading corporations, companies and banks with state participation, large private financial-industrial groups. Their aggregate production, financial and management potential should be consolidated.
Strategic planning should be focused on the rapid growth of the new technological order. It is advisable to develop a five-year modernization program based on it with measures to create a favorable macroeconomic environment, the formation of relevant institutions and management contours.
Table 4
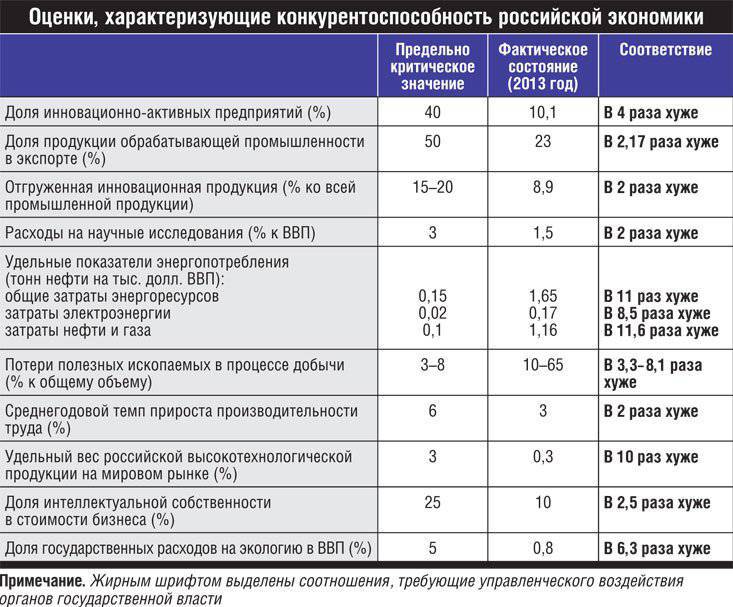
The conclusion of the economy on the trajectory of rapid and sustainable growth presupposes an innovative path of development, which requires a fundamental increase in the role of science both in economic activity and in the system of government.
Given the importance of the strategic planning system and the fact that the Russian government as a central executive body is loaded with current tasks and cannot formulate promising, much less control their achievement, it is proposed to establish the State Strategic Planning Committee under the President of the Russian Federation (GKSP RF) with the following powers:
-determination of internal and external conditions, trends, restrictions, imbalances, imbalances, opportunities for the socio-economic development of the country;
-establishment of ways and means of implementing the priorities of the socio-economic policies, goals and objectives of development;
- coordination of the work of subjects of strategic planning;
-the formation of a complex of measures ensuring the achievement of goals and the solution of tasks of socio-economic development;
- coordination of actions of participants of strategic planning;
-organization of monitoring and control of the implementation of strategic planning documents;
-scientific, technical, informational, resource and staffing.
The main threat of economic sanctions against Russia is isolation from access to new technologies. If it is not neutralized, in a few years our economy will irreversibly lag behind in the development of a new technological structure, the output of which on a long wave of growth will ensure re-equipment of both industry and the army at a qualitatively new level of efficiency. We need, on the one hand, to multiply allocations for R & D in key areas of growth, and on the other, to ensure a radical increase in the responsibility of heads of development institutions for the effective use of allocated funds.
The current situation is critical. The reasons lie in the chronic underfunding of science, the destruction of its cooperation with production, the aging of scientific personnel, and the brain drain. In many ways, these troubles were the result of privatization, which led to the destruction of the sector of applied science. The reformation of the RAS does not affect the main problems of the management of scientific and technical progress, does not provide for the improvement of institutional forms and methods of organizing applied research, is not focused on the development and implementation of high-performance technologies.
For a systematic approach to the management of NTP, it is advisable to create a supra-departmental federal body responsible for developing the state science and technology and innovation policy, coordinating the activities of sectoral ministries and departments in its implementation, the State Committee for Science and Technology Policy (GKNTP RF) under the President. The functions are as follows:
-evaluation, selection and implementation of the priority directions of the NTP;
-the formation and conduct of state policy in scientific, scientific, technical and innovation activities;
- coordination of federal and regional legislative and executive bodies involved in science and innovation;
-regulatory regulation of the development of science, scientific, technical and innovation activities, as well as intellectual property;
-analysis of the content, level and innovative prospects of research and development carried out in organizations with state participation, preparation of proposals for improving their effectiveness;
-evaluation of the level of development of scientific and technical potential, the processes of modernization of production, the implementation of research results;
-the introduction of a system of indicators of the effectiveness of the activities of state structures responsible for financing and organizing research and stimulating innovative activity;
development and implementation of the state comprehensive long-term program of economic modernization and NTP;
-development of a network of venture and other funds financing innovative projects and R & D, the creation of appropriate mechanisms through voluntary deductions from corporations with their inclusion in the cost of production;
c-action to the development of the system of training of scientific personnel and highly skilled engineering and technical personnel for knowledge-intensive industries;
-development and implementation of the state policy in the field of international scientific and technical cooperation;
-development of innovation infrastructure;
- assistance in attracting and using advanced high-performance foreign technologies;
-stimulation and support for the development of entrepreneurship associated with the commercialization and implementation of scientific and technological achievements;
- ensuring control over the targeted use of state budget funds allocated for scientific, scientific and technical, innovative activities;
- propaganda of scientific and technical achievements;
-organization of state scientific and technical expertise.
GKNTP RF should carry out joint activities with the Russian Academy of Sciences on the formation and implementation of basic research programs, the codification of knowledge about technologies, the implementation of innovative projects.
Proposals for strengthening the country's economic security in the context of the global hybrid war unfolding against Russia are focused mainly on improving the efficiency of state institutions. Along with this, a regime of favoring entrepreneurial initiative, private business activity is necessary. Along with the measures proposed above to form domestic sources of cheap long-term credit, a tax maneuver is needed to shift the burden from labor income to rent, from production to the consumption of luxury goods, as well as reducing the costs of infrastructure industries, primarily electricity, whose ill-conceived reform resulted in multiple tariff growth in the interests of monopolistic intermediaries.
The implementation of these measures should be carried out within the next two years at most. Otherwise, the escalation of economic sanctions will entail the destruction of reproduction circuits closed on the external market and a sharp drop in the level of enterprise income, the halt of many of them, the bankruptcy of companies dependent on external sources of credit. A noticeable drop in the standard of living of the population will give our opponents the opportunity to move to the next phase of the chaotic war against Russia.
Information