Russian cyber threats are growing
Approximately two years after the initiative of the American President to begin the formation of a global information infrastructure under the Russian Security Council, an interdepartmental working group was formed to analyze this issue and develop proposals on the position of Russia, which was planned to be brought to the American side within the framework of the Gore - Chernomyrdin Commission. The working group included representatives of the SVR, the FSB, the FAPSI, the Ministry of Internal Affairs, the Roscominform, the Security Council apparatus, the leading specialized organizations of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the military-industrial complex. The author of these lines, who was represented by the Ministry of Defense and had by that time some experience in exploring the possibilities of using GII for solving a number of tasks in the profile of his research institute, was assigned to lead this group.
Within a few months, the corresponding document was developed. It took almost 20 years. What has changed during this time?
New reality
Firstly, in this historically short period, the GII did not just become a reality, but turned into a global infosphere, the dynamics of development of which it is appropriate to estimate by the number of recipients of its technical basis - the global Internet metanet. The development of the Internet communication infrastructure (personal communication networks and telecommunication super highways, primarily satellite and fiber optic), combined with an exponential growth in the number of devices using the Internet, in the near future will lead to the emergence of the so-called concept of the Internet of things (Internet of things) order 100 billion units.

Secondly, the number of technosphere objects that use the Internet as a unified communication environment for the operation of distributed technical systems that form the so-called critical infrastructures (CI), whose state depends on the livelihoods of entire states and regions of the world - energy, fuel, transport, defense, industrial, banking and financial, housing and communal services, state administrations and others.
Thirdly, the influence of the infosphere on individual, group and mass consciousness has increased many times. Back in the year 2006, in the USA, advertiser spending on Internet advertising exceeded similar advertising costs on television. In fact, this meant that the Internet had become the number one tool for influencing consciousness. With the development of social networks, the possibilities of using the Internet for diverse non-directive management of groups and masses of people have increased many times over.
As a result, a new reality was created in which the objects of the global technosphere and anthroposphere were exposed to a whole spectrum of previously non-existent threats, the source of which is the full-connectivity of the GII: each of its addressees has the physical ability to exchange information with each. At the same time, the presence in terminal devices (smartphones, tablets, personal computers, various sensors) and network facilities (servers, routers) of both unintentional and sabotage defects (i.e. exploits or pre-implanted software and circuit operating mines) makes the infosphere not only a source total control and leakage of confidential information towards the centers of the organization of this activity, but also large-scale man-made disasters.
This is, in its most general form, a system background against which it makes sense to consider in more detail the complex of problems that are to be solved under current conditions in order to ensure the information security of Russia and its Armed Forces.
Information security is usually divided into information technology and information technology.
The informational and psychological security of any society is its protection from the threats realized by means of informational influence on the consciousness of the individuals forming it.
Let us consider in detail the information technology (called for short also cybernetic) security of the material and information objects of the technosphere, that is, their protection from threats realized through the use of special information technologies for destruction or for the unacceptable use of these objects. If the mentioned technologies are applied in relation to information objects, they speak about cybernetic influence on them, if in relation to material objects - about cybernetic influence (Fig. 1). An example of a cyber-attack might be a covert change by an attacker of the content of a public site (so-called defacer). An example of cyberkinetic effects is withdrawal from the standard trajectory of an unmanned aerial vehicle of the enemy and the disconnection of traction power grids that ensure the movement of electrically dependent ground vehicles, which causes them to immediately stop.
Fig. 1
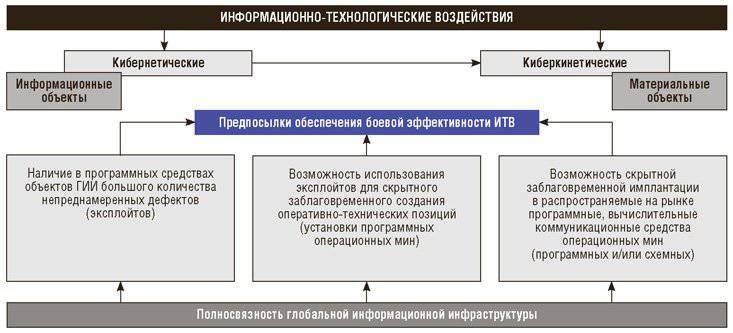
It is clear that the countries with the most developed and therefore vulnerable for cybernetic impacts of the technosphere, primarily the United States, implement a set of measures aimed, on the one hand, at minimizing the capabilities of their opponents on the destructive, system-destroying impact on their critical infrastructures, and on the other - on the early hidden preparation of global systems of operational and technical positions (cyber-agent networks) for the above-mentioned monitoring and implementation, if necessary, of similar impacts on key you critical infrastructures abroad (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2
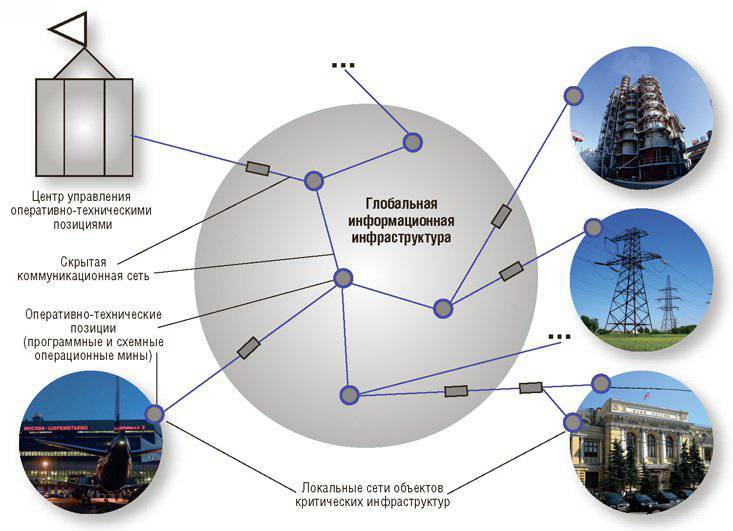
In the United States, the need for systematic organization of cybersecurity activities and the protection of CI at the state level was realized in the second half of the 90s. In May, two directives signed by President Clinton appeared on 1998 — PDD 62 and 63 “On Countering Terrorism” and “On Protecting Critical Infrastructure”. As part of the implementation of these directives, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) was created with a staff of 170 of thousands of people who are entrusted with solving a set of tasks to ensure the stability of critical US infrastructures to possible system-destroying impacts and to prevent them. After the September 11 terrorist attacks, 2001 of the year was issued the so-called PATRIOT ACT, which significantly expanded and deepened activities in this area.
USA and China in the global infosphere
In general, the activities of the US federal leadership to ensure the safety and sustainability of their critical infrastructures leaves the impression of sufficient competence and rationality, although, of course, it has weak points.
As part of the total control over the management, intelligence agencies, the armed forces and the population of foreign countries, the United States proceed from the concept of "Big Brother". Relying on the dominant position of American cyber economics, the US political and military leadership has been implementing cyber intelligence programs since 90, which combine passive, active, and combined methods of access to confidential information resources and traffic of global computer networks and their national segments. The central role in this work belongs to the National Security Agency and the Cyber Command of the US Armed Forces created in May 2010, although recent events have shown that the United States suffered more damage from their activities than gained. However, to exaggerate this damage is certainly not worth it. Its sources are tectonic tensions and contradictions between various special services belonging to the American intelligence community, combined with a certain loss of control by the legitimate political leadership of the United States. If you take into account the huge money, the basis of which is Afghan opioids and which over the past 12 years have been at the disposal of individual intelligence services from the community, as well as a spasmodic increase in the number of cryptocratic controlled, equipped and funded private military companies (their number in the world is estimated in 400 – 500, and the volume of orders - in 150 – 200 billion dollars), we get a fundamentally new array of security threats of all countries. Russia here, of course, is no exception.

Speaking about the activities of foreign countries in cyberspace, it is impossible not to mention China. In 2012, a special commission of the US Congress announced the results of its work on the analysis of the use of counterfeit element base in armaments and American-made military equipment. These results puzzled the American establishment. 2008 – 2011 revealed about 1500 cases of the use of counterfeit foreign-made microcircuits in such critical for US defense systems as the THAAD missile systems, Los Angeles-class attack submarines, F-15E fighter jets and so on. At the same time, about 30 percent of these chips were of Chinese origin. Chinese cyber economics lags significantly behind the US in terms of information services and software, but it is almost the same as in hardware and hardware: the number of Internet production tools in the Internet produced by Huawei Technologies in China is comparable to the number of similar American CISCO and Juniper products. The world's most powerful Tianhe-2 supercomputer with peak performance of 55 petaflops and Kylin's own operating system currently operates in the People's Republic of China, while the next American supercomputer Titan Cray XK7 has twice the performance.
These are in general terms the capabilities of the two largest powers of the global infosphere.
Russia minimizes the risks
As for the Russian Federation, at the state level information security activities are organized in accordance with the Information Security Doctrine approved by the President of the Russian Federation 9 September 2009 of the year and the Federal Law 149-FZ on Information, Information Technologies and Protection of Information from 2006. . This activity is carried out in the following main areas:
the creation and organization of the effective functioning of departmental and corporate information protection systems against leakage through computer networks and other technical channels;
minimizing the risks of revenues to the objects of the technosphere and the Armed Forces of Russia of software and hardware containing sabotage defects that allow the creation of cyber-agent networks and cyber actions on these objects in our automated systems;
organization of research and training in the provision of the first two directions.
In the framework of the first direction, in accordance with the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of 15 in January 2013, under the leadership of the Federal Security Service of Russia, work has begun to create a nationwide system for detecting and preventing computer attacks (SOPKA). The current segment of this system only in 2013-m ensured the identification of three cyber-agent networks of foreign countries, which prevented the theft of two million pages of secret information. It is extremely important that the President of the Russian Federation in December 2012 developed the Federal Security Service’s Guidelines for the State Policy in the Field of Ensuring the Security of Automated Systems for Managing Production and Technological Processes of Critical Infrastructure Facilities of the Russian Federation, which can be considered a breakthrough regulatory document for the systemic organization of work to protect Russian critical infrastructures. In 2014, the adoption of the federal law “On the critical information infrastructure of the Russian Federation” is expected, which will become the basis for the subsequent organization of work in this area.
As for the second direction, only lazy does not speak about our dependence on the import element base and import software, which is critical for the security of the country, which really is the source of the threats being discussed. In this area, there are two main approaches to minimizing existing risks:
the organization of an effective certification system for imported software and components that are planned for use at facilities that are critical for the country's defense and security;
increasing import substitution in order to move in the foreseeable future to a fully domestic element base.
In the framework of the first approach, a number of testing laboratories are operating, licensed by the FSB, FSTEC and the Ministry of Defense and performing work to identify sabotage defects in certified products. Only one of such laboratories in the period from 2008 to 2013 revealed 38 of similar defects in software and hardware of American, Chinese, Israeli production. It should be understood that this approach has limitations both economic and fundamental.
As for the import substitution of the element base, it should be noted: in Russia, under the leadership of the Military-Industrial Commission under the government since the time when it was headed by Sergey Ivanov, complex and purposeful work is underway to develop our radio-electronic industry and master production technologies achieved by leading global manufacturers. The systematic contribution to the deployment and conduct of this work at all its stages was made by Yuri Borisov, currently holding the position of Deputy Minister of Defense of Russia. The result is that Russia is among the eight countries that have the technological capabilities for the production of microelectronics products with design standards 90 nanometers and less. 2013 has mastered the production of 65 nanometer microcircuits. By 2020, about 95 percent of the element base for the needs of our military-industrial complex will be produced in Russia.
Eliminate chronic lag
According to expert community estimates, by 2020, the process of miniaturization of traditional semiconductor integrated circuits will approach its physical limit (around 6 nm), and the necessary scientific and technical prerequisites for refusing the semiconductor electronic component base will be created for 2030 and new physical principles and materials. In this situation, Russia has the opportunity, relying on the serious scientific and technical groundwork created by our academic science, not only to eliminate the existing backlog, but to take a leading position in some areas. This is primarily about quantum computing and quantum communication, the foundations of which were laid by the school of Academician Kamil Valiev in the 80-s. At the same time, quantum communication, along with the theoretically limit rate of transmission of one bit of information, is characterized by absolute intelligence protection. In principle, it is impossible to intercept the quantum information flow. Quantum calculators are a means unattainable by traditional computers for solving problems associated with a mass search of options. In particular, the problem of decomposing an integer into prime factors in the case of a number of 250 digits known in cryptanalysis can be solved by the mentioned American Titan supercomputer with a performance of about 20 petaflops in one year, whereas a quantum computer with a frequency of only one megahertz in four seconds. For numbers from 1000 digits, the corresponding values are hundreds of billions of years and 1,5 minutes, respectively.
Another promising direction, the development of which will allow us to reach a new level of weapon development and eliminate our chronic lag, is nanophotonics. The creation on its basis of radio frequency sensors and information processing tools of the next generation, along with the achievement of fundamentally new accuracy, mass-dimensional and energy-consuming characteristics, will ensure invulnerability for radio frequency weaponswhich in the prevailing military-technical situation poses a dangerous threat to almost all of the armed and promising systems of our army and fleet. It is important to note that the American developers of the appearance of the sixth generation aircraft directed energy weapons, including radio frequency, is considered as a standard.
It should be understood that cyber security is an important, but only the security segment of the entire critical infrastructure of the Russian Federation. In 2005, immediately after the accident at the Chaginskaya transformer substation, the author, being at that time the head of the information and analytical department of the Rosoboronzakaz, wrote a small monograph “Critical infrastructures as a sphere of confrontation”, in which he tried to give a systematic analysis of the new technological situation in which Russia, if not taking adequate measures can be extremely vulnerable to a new array of threats. In the 2012 year, taking up the duties of a member of the Military Industrial Commission, one of whose areas of work is the sustainability of the technosphere of the state and the Armed Forces, the author found that, in principle, the situation in this area is changing for the better much slower than the development of the geopolitical situation . The complex of problems of protecting and ensuring the stability of critical infrastructures of Russia is not being solved actively enough, and this is no less a danger to our country than all possible threats in the military sphere combined.
Speaking about the information-psychological security, we, as a rule, are localized on the means or technologies of implementing informational influences on the consciousness or subconsciousness of individuals. At the same time, most often we don’t even think about the models and technologies of informational impacts on societies, that is, we don’t see forests behind trees.
Management of society
Recently, the technologies of using social Internet networks to manage protest actions during the “Arab Spring”, “Orange Revolutions”, and recent events in Kiev have been actively discussed; technology of virtual characters used by the relevant special forces of the US armed forces, etc. These are certainly important, but private issues.
Comprehensive modeling of psychological operations for the system destruction of societies, their refragmentation and ultimately non-directive management of them can be carried out within the framework of a sociometric approach, the essence of which is as follows. The psychological state of a society consisting of n individuals (subjects) can be represented as a sociometric matrix S of dimension nxn, where the value Sij in the range from -1 to + 1 reflects the ratio of the i-th subject to the j-th. In a good, cohesive team, all Sijs are larger than 0. In the bad, disorganized - on the contrary. The goal of a psychological operation is to disintegrate the opposing society into uncontrolled by its leadership, hostile sub-societies. The means of carrying out such operations, as a rule, are evaluation frames: some judgment is conveyed to two subjects and their mutual exchange of assessments of this judgment is ensured (Stalin - hero: yes - no, etc.). At the same time, the value of Sij increases with the number of coincidences of assessments and decreases with the number of their inconsistencies (it is considered that for the system destruction of a society it is advisable to constantly keep in sight of its subjects precisely the destructive judgments). Another obvious way is to bring third parties to the subjects of their mutual evaluations (possibly distorted).
More subtle and effective ways and means of managing the state of societies exist and are applied. Anyone can remember how a megasocium like the Soviet Union was refragmented and disintegrated during 1988 – 1991. The global information infrastructure greatly simplifies and reduces the cost of such operations.
The sociometric approach can be effectively applied in electoral situations. In this case, the sociometric matrix has the dimension m × n, where m is the number of voters or groups of voters with stable preferences, and n is the number of candidates for an elective office. The value of Sij is a measure of the attitude of the i-th voter to the j-th candidate. The goal of any election headquarters is to maximize the number of voters with the most positive attitude towards their candidate.
In general, within the framework of a sociometric approach, it is possible to achieve an adequate understanding of the actions of the enemy and on this basis to sufficiently effectively solve the tasks of countering the threats to information-psychological security and disintegration of society, as well as its various social segments, including the armed forces and individual military groups.
Three types of confrontation
Any confrontation includes elements from different spheres. In the view of English-speaking analysts reflecting the Anglo-Saxon approach to this integration, there are three types of confrontation: influence warfare, military warfare, and infrastructure warfare.

The highest form is the struggle of influence, the purpose of which is to lead the adversary to making decisions that are beneficial for themselves. This form is most well mastered by Western political makers, political technologists, special services and centers of power and is considered the most rational due to relatively low costs and high efficiency. In the event that the goal was not achieved within the framework of the “pure” struggle of influence, the transition to armed struggle remained until recently. As a result, the enemy was brought into a state by military force when his political leadership was forced to take the necessary decisions. The global computerization and network-centeredness of the technosphere with the concomitant emergence of cybernetic impact tools capable of disabling entire segments of critical infrastructures created a completely new reality. Within its framework, power support of the struggle of influence can be carried out without initiating warfare, but only through the struggle with infrastructures.
In the relationship between the struggle of influence and the fight against infrastructures, there are four segments: the subjects of the global economy that own the objects of critical infrastructures (including cross-border ones) - fuel, energy, transport, information, etc .; property relations (each owner has his own share of the profits from the functioning of these facilities, proportional to his degree of ownership of the profitable object); objects that make a profit and are in technological relations with each other, which causes the so-called cascade failures of these objects in the case of destructive effects on some of them; societies whose livelihoods are provided by these objects and in general, critical infrastructures. At the same time, the potential influence of the subject of the global economy (state, corporation, group of individuals or individual) is generally proportional to the size of its condition, the accumulation of which is carried out at the expense of income from the functioning of objects that it owns to some extent. Competition between subjects up to a certain point can be conducted by methods of fighting influence, but then it can go into a phase when, by means of private military companies or other structures and even individuals capable of executing destructive influences on competitor’s facilities, the latter will be put out of action, naturally , deprive him of planned profits and reduce the potential impact. It is just as natural that the damage from such impacts will also be borne by societies, whose vital activity depends on the targets affected.
Anglo-Saxon methods of struggle influence are used constantly. The relative success of the actions of the American troops in the conflicts of the last 22 years is due not only and not so much to the effectiveness of the newest means of warfare used by them then to its new forms and methods, but also to blocking the influence of comparable geopolitical forces, primarily Russia and China, on rendering military and military technical assistance to the enemies of the United States and NATO in these conflicts. However, the situation around Syria has already shown that the Russian leadership owns methods of influence warfare no worse than the American one. The warships of the Russian Navy in the Mediterranean, the active power work of Russian diplomacy, which imposed American counterparts, saying in an American, “telephone booth fight” when the enemy simply does not get the opportunity to swing for a knockout strike - and the second Libya did not happen.
It also makes sense to note that the “Big Brother” concept implemented by the United States, in which the entire world, all the objects that are critically important for the functioning of various societies, and these societies themselves are entangled by American cyber-agent networks, is fraught with dangers for the United States themselves no less than for their potential adversaries are subjects of their cyber activity. The identification of at least one cyber agent, as a rule, naturally leads to the identification of their entire grouping, and in a relatively short period of time (within one year). And this leads to at least two consequences. First, a competent adversary, having put the American cyber-agent networks under control, can totally exploit them and monitor all the subjects of the global information infrastructure, which are controlled by the United States. Secondly, the same competent adversary acquires the possibility of total disinformation of Americans and manipulating them in any situations, including conflict ones, without spending any efforts on creating the mentioned cyber-agent networks (naturally, having spent certain efforts on identifying the latter).
Solution mega problems
Being engaged in ensuring the security of the Russian Federation in a new strategic and technological environment, we must create a system for neutralizing and countering the threats that actually exist. A low-cost and high-performance system, in which soft power plays a key role. The conceptual and operational-technical bases of special deterrence required to create the potential for fighting infrastructures in the Russian Armed Forces have been formed by a team for a number of years, whose leaders in 2013 awarded the Marshal of the Soviet Union Georgy Konstantinovich Zhukov Russian Federation Prize. The task is to develop the basics adequately, without opportunistic simplifications and profanations implemented. On the other hand, it is necessary in the shortest possible time to radically change the situation with the organization of work to ensure the safety and sustainability of critical infrastructures of the Russian Federation. Only by solving these two interconnected mega-problems, we will ensure the level of protection of our country, corresponding to the real spectrum of threats to its security in the historically visible part of life and development.
Speaking about the second of these megaproblems, it is necessary to understand that it has organizational and system-technical complexity, many times exceeding the complexity of nuclear and missile projects that are crucial for the survival of the Soviet Union. At the same time, the creation of an elastic, invulnerable for system-destroying effects, a fail-and-disaster-resistant tehnosphere based on the system for ensuring its safety and sustainability — a megaproject that needs to be implemented not in the conditions of comfort for such works of a self-sufficient state-owned infrastructure The USSR, and in a completely different way of life, in which the vast majority of such facilities are in the possession of private owners, in including foreign.
When deploying this megaproject, organizational decisions will be crucial for its successful implementation, in the course of which subsequent work will be carried out. Before proceeding to the consideration of possible options for these solutions, we note that in the emerging geopolitical and military-strategic situation, a scenario cannot be ruled out in advance prepared, hidden, anonymous, large-scale system-destroying effects on the objects of the Russian technosphere, the functioning of which most depend on the combat readiness and combat capability of the groups. our army and navy. After this, the methods of combating influence based on the threat of massive use of military force in the conditions achieved by the aforementioned impact of reducing the combat potential of the RF Armed Forces can be subject to increasing stressful pressure on the Russian leadership towards making decisions that are the goal of aggression.
Under these conditions, the system for ensuring the safety and sustainability of the technosphere of Russia should have at least four segments:
identifying and neutralizing, at the earliest possible stage, threats to the safety of the technosphere and their sources;
continuous monitoring of the state of the backbone objects of the technosphere and their surrounding natural environment;
ensuring the manageability of state institutions and the population against the background of the systemic destruction of critical infrastructure;
ensuring combat sustainability and combat effectiveness of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, primarily the strategic deterrent forces, against the background of the degradation of the technosphere objects, on the state of which their functioning and application depend.
Rational options
It is advisable to analyze the possible choices of the federal executive body to which it is necessary to transfer the leadership of the complex of works on creating a system for ensuring the safety and sustainability of the technosphere of Russia. At the same time, the option of creating a new supra-departmental structure like the US DHS, in our opinion, should be excluded from consideration. Any new managerial add-on is the years spent on its formation, equipment, debugging of the processes of functioning and interaction with external contractors, as well as a considerable number of “damaged phones” resulting from the overflow to the new structure, governing bodies and organizations. Plus an additional burden on the federal budget. No money, no time for this we have.
There seem to be only four rational options: the FSB, the FSTEC, the Ministry of Emergency Situations and the Ministry of Defense.
The Federal Security Service, relying on its operational, operational-technical and scientific-technical potential, as well as technology developed in the framework of the National Anti-Terrorism Committee to coordinate the activities of the federal executive body and the Federation's subjects in countering terrorism (the goal of which is, of course, the critical infrastructure of Russia) , in principle, could take on the necessary functions. The only question is in the already enormous overloads that this organism, which is most important for the viability of the country, is experiencing - essentially the state’s immune system.
The Federal Service for Technical and Export Control has a functionality that allows it to coordinate the activities of any subjects in the field of information protection and in this sense is the most preferred authority in terms of implementing the provisions of the aforementioned federal law "On the Protection of Critical Information Infrastructure of the Russian Federation ". However, the threats realized through the material space are beyond the competence of the FSTEC. In addition, being in principle a superordinate structure, the service is under the authority of the Ministry of Defense.
The Ministry of Emergency Situations, on the contrary, operates in the material space and is an efficient mechanism that has been debugged over 20 years of continuous hard work and ensures the sustainability of the technosphere and the survival of the population in conditions of man-made disasters and natural disasters. However, the potential of the Ministry of Emergency Situations is deployed mainly in the direction of eliminating the consequences of events that have already occurred.
Of all the possible options, it seems that only the Ministry of Defense has the capabilities sufficient to organize activities to create a system for ensuring the safety and sustainability of the technosphere of Russia. First, the objects of the Ministry of Defense occupy a special place in the critical infrastructure of the Russian Federation and the first thing that must be ensured is the stability of the segments that guarantee the functioning of these objects. (This situation is typical for armies of all countries. The Director of the NSA of the USA, General Keith Alexander, repeatedly said that the functionality of US military facilities by 95 percent depends on the capacity of the environment providing them, and demanded authority to protect the computer networks of this environment.) Next, by recursively expanding the composition of the protected objects, we get the so-called minimal value ( minimally essential) a segment of critical infrastructure, the protection of which is vital for repelling an armed attack on Russia (in the event that the aggressor changes from infrastructure warfare to military warfare). Secondly, the Ministry of Defense has in its jurisdiction the FSTEC, which allows you to directly link the activities to ensure the safety of critical objects in the material and information space. Thirdly, the Ministry of Defense incorporates a powerful and omnidirectional military science complex, which, despite all attempts to eliminate military research institutes under the slogan of integrating military education and science in 2009 – 2012, managed to be preserved (although it cost the pursuit of the - Scientific Committee of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, to the end opposing this disastrous line). Despite the losses suffered, the potential of this complex is still high and, with competent management of military science, it is able to provide formulation and military-scientific support of the entire vast amount of research on the implementation of the discussed megaproject with the involvement of specialists and organizations of the Russian defense industry, academic and university science. (In the US, the best research forces have been involved in similar research conducted on DHS orders from 1998 onwards. An open source “side effect” of these studies is an assessment of the sustainability of Russia's critical infrastructure. According to the Federation of American Scientists, which advises the political leadership of the United States, disabling only 10 objects of the technosphere of the Russian Federation, the list of which is made public, is sufficient for a complete paralysis of the Russian economy.) Fourth, transferring the management of the discussed megaproject to the Ministry of Defense can bring a systemic effect in the form of a number of means of "dual use", in particular aeronautic engineering. Tethered aerostat complexes and unmanned high-altitude aeronautic platforms (GDP) based on hybrid airships can carry sensors for monitoring the state of their critical infrastructure and their surrounding areas (water areas), as well as for detecting and controlling military facilities of foreign countries, as well as having on board means of counteracting the latter. Inhabited GDP, one of the main advantages of which is non-aerodrome-based, can be used as air control points and vehicles in the context of degradation of critical infrastructure (primarily energy and transport) over large spaces, as well as to effectively solve a number of economic tasks .
And finally, at last, but, apparently, the first in importance. The Russian Defense Minister has vast and unique experience in creating and managing the Emergencies Ministry, as a result of which he knows and understands the problems of ensuring the safety and sustainability of the Russian technosphere, and in this sense, the situation for making a breakthrough in the most important section under consideration is more than favorable. The deployed National Center for Defense Management of the Russian Federation has all the capabilities necessary for organizing a successful confrontation with any aggressor using complex infrastructure warfare and military warfare methods.
In connection with the above, it seems quite logical to organize the development of a federal target program for creating a system to ensure the safety and sustainability of the Russian technosphere under the leadership of the Ministry of Defense.
Of course, all proposals are no more than a basis for subsequent discussion and decision. However, in our opinion, it is necessary to do this without delay - too much time is lost and the threats mentioned above are too real and close.
Information