Possibilities for improving the air defense of corvettes
In a previous article "What are we building - corvettes or flag demonstrators?" it was about the construction of a new series of 6 corvettes of project 20380 at the Amur shipyard. The article emphasized that the air defense of the 20380 corvette is so ineffective that it can only play the role of a flag demonstrator. Corvette 20386 is much more efficient, but some authors on VO argue that 20386 is too expensive, and 20380 needs to be built, which they consider to be more efficient. The purpose of this article is to substantiate some measures that simultaneously reduce the cost of the air defense complex of light ships and increase its efficiency.
1. Problems of existing radar systems (RLC)
One of the troubles of the Russian Navy is the lack of equipment unification. In particular, there are many types of radars, but most of them lag behind the current level of radar. Mechanical scanning antennas are already an exception. The most effective are active phased antenna arrays (AFAR). AFAR is being introduced into the Navy very slowly. The first on the corvette 20385 should be the Zaslon radar. However, its price is unacceptably high, apparently, it will exceed $ 100 million. Given that the Redut 9M100 and 9M96 air defense systems are complex and expensive, it seems that the main task of the corvette is to defend itself from raids.
The high cost of Russian radars is explained by their low serial production, caused by the lack of unification and the use of outdated design approaches. The newest Zaslon radar contains two radars - a surveillance radar operating in the meteorological-resistant 10 cm wavelength range, and a missile guidance radar operating in a less stable but providing more accurate guidance range of 3-4 cm. ship, it will be able to provide the range and accuracy required for the air defense system in adverse weather conditions. Its main drawback is its high cost.
With smaller ships, the situation is much worse. On MRK 21631, a surveillance radar with a short detection range is installed, which does not allow to prepare in advance for an attack. On the MRK 22800 Odintsovo, the Pantsir-M air defense system was installed, the guidance radar of which operates in the mm-wavelength range, which is completely unacceptable for a shipborne radar, which should operate in rain and fog conditions.
2. Ways to reduce the cost of radar
The key condition for reducing the cost of radar is the obligatory unification of the radar of all ships of the 1st and 2nd classes and MRK. The number of radars on the ship should be reduced to one. Instead of surveillance radar and guidance radar, it is necessary to develop a multifunctional (MF) radar. One exception is allowed - the radar of destroyers must solve not only air defense missions, but also missile defense missions. That is, in addition to the MF ZLS, missile defense requires a separate radar with four very large AFAR with an area of 50-100 square meters. m each.
2.1 Choosing a method to reduce the cost of MF radar
It is known that the detection range of targets of a surveillance radar in the first approximation is determined by the product of the radiated power by the area of the radar antenna.
However, the MF radar must not only detect the target at maximum ranges, but also accompany them with high accuracy. The error in measuring the coordinates of the target is mainly determined by the width of the radar beam, which can be calculated by the formula:
α = λ / L
where:
α is the antenna beamwidth (either horizontal or vertical), expressed in radians;
λ is the radar wavelength;
L is the length of the antenna (either horizontally or vertically).
For example, to get a beam with a width of 1 ° * 2 °, the antenna must have dimensions 58λ * 29λ.
It is impossible to arbitrarily reduce the wavelength, since the meteorological resistance can significantly deteriorate and the AFAR area, that is, the detection range, can also decrease. On the contrary, the parameters of the ship's superstructure usually allow increasing the size of the AFAR. However, it is also difficult to make an AFAR in the form of a rectangle, similar to the Zaslon RLK, due to the increased cost of the AFAR.
AFAR consists of transceiver modules (TPM), the cost of which is very high - $ 1000-2000 for PPM. We will take into account that they must fill the area of the AFAR with a step of λ / 2. Then 14000 PPMs will be required, that is, the cost of a PPM kit for the manufacture of one square APAR with a beam width of 1 ° * 1 ° will be equal to $ 14-28 million, which is unacceptable for a corvette.
The way out can be found in the fact that instead of a square AFAR, use an AFAR in the form of a cross of two intersecting rectangles, for example, 58λ * 8λ in size. One rectangle is positioned horizontally and serves to measure the horizontal angles of targets, the other - vertically and measures vertical angles. Then the cost of the PPM set will be reduced by 4 times, and the accuracy of measuring the angles will not deteriorate. It is best if the AFAR will have the form of a "+" sign, but if there is no way to place a "+" on the superstructure, then you can use a construction in the form of the letter "T" or even "G".
When choosing a radar operating wavelength, conflicting factors have to be taken into account. On the one hand, it is necessary to ensure weather resistance even at the far detection limit, which will require an increase in λ. On the other hand, obtaining a narrow beam with limited space on the superstructure requires decreasing λ. In addition, in the future, UAVs with radar will definitely be present on ships. It will not be possible to place a large antenna on the UAV. As a result, we choose λ = 5,5 cm.
2.2 Features of the air defense system of the corvette
The air defense missile system should prevent the enemy fighter-bombers (IS) from approaching the corvette at dangerous distances. It is impossible to give IS the opportunity to approach a distance of 50-60 km and accurately measure the coordinates of the corvette, its speed and course.
You can’t allow IB to start up weapon medium-range, such as GBU-39 gliding bombs with a launch range of 110 km, the number of which on one IS can be 9 or more, etc. To do this, on the corvette it is necessary to have not the planned 9M96 medium-range missiles, but 9M96E2 long-range missiles (DB) with a launch range of 130-150 km. The costs of both missiles are close, since they differ only in the mass and length of the engine.
SAM DB is justified to use only for firing at IS, so their number may be small - 8 pieces. To combat anti-ship missiles, MD missiles are used, the number of which, by the standards of a corvette, should be large - for example, 48. Then the MD 9M100 missile defense system is hardly suitable due to the high cost and low average speed, which will make it difficult to intercept supersonic maneuvering anti-ship missiles.
The question of which MD SAMs should be used - Pantsir-M air defense missile system with an inclined launch or Tor with a vertical launch, should be decided by the ship designers. Both missiles are "headless", but Thor is more expensive and heavier due to the vertical launch. MF radar will provide all-weather guidance of both missiles with errors 1,5-2 times less than the standard radars of these air defense systems.
2.3 Design of AFAR MF radar
The AFAR scheme is shown in Fig. one.
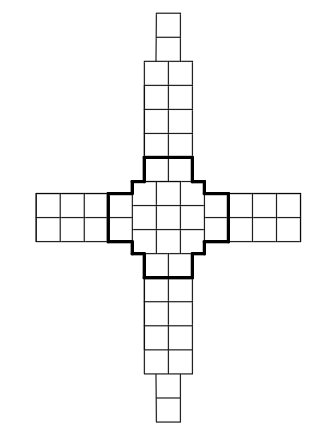
AFAR is divided into 49 square independent modules - clusters measuring 0,22 * 0,22 m each. The central 17 clusters (highlighted by the bold line) are receiving and transmitting and contain 64 PPMs. The remaining 32 clusters are purely receiving and are used to obtain narrow radar beams. At the same time, they also increase the detection range.
The total size of the AFAR cross is 2,42 * 3,74 m. The AFAR contains 1088 PPM and 2048 receiving modules. Pulse power PPM 15 W. Power consumption of one AFAR 11 kW.
The cost price of AFAR can be estimated only approximately, since the price of one PPM significantly depends on the volume of the order. If we assume that the MF radars become unified for all ships and the total number of APMs and receiving modules reaches 100 thousand pieces, then the price of one APM will be $ 1000, and the receiving module - $ 700. Then the cost of all 4 AFAR will be $ 11 million, and the entire serial MF radar will be $ 16 million.
The radar beam width for radiation is 3 ° * 3 °. At the reception, the horizontal and vertical crossbeams of the cross form rays independently of each other, only the central part of the 3 * 3 cluster is common. Then the beam of the horizontal crossbeam of the cross has a width of 1,3 ° * 5 °, and of the vertical one - 5 ° * 0,85 °. During the detection process, the target can be at any point in the emitting beam. However, during reception, both the horizontal and vertical reception beams must be directed at the target simultaneously. This means that the horizontal bar must simultaneously form a "fan" of three beams that cover the entire emitted beam. The vertical bar should form 4 beams. Then the entire area of both rungs will be used both to detect the target signal and to measure its angles.
Additional tasks of the MF radar are to provide covert communication with other KUG ships at a distance of up to 30 km in radio silence and communication with the UAV.
2.4 Comparative assessment of the costs of the MF radar and radar Zaslon
Almost nothing is known about the Zaslon radar station. There are not even photos of corvette 20386, there is only a drawing. Some experts call the detection range of the Zaslon 75 km, while others - 300 km. Therefore, further we will consider only a comparative estimate of the costs of the proposed MF radar and radar Zaslon. We will assume that the Zaslon guidance radar operates at a typical wavelength λ = 3,2 cm, and the radar MF - λ = 5,5 cm.
Let's compare the costs of both radars, provided that they provide the same detection range. The detection range of radars with the same radiated power, as indicated in clause 2.1, is determined only by the AFAR areas, which, therefore, must also be the same. Considering that PPMs in AFAR should be spaced with a step λ / 2, we get that the number of PPMs in one AFAR Zaslon should be equal to 9400.
Accordingly, the total cost of a serial sample of the Zaslon guidance radar will be $ 43 million. Since the AFAR Zaslon shape is close to a square, with such a number of PPMs, the angle measurement accuracy will be close to the accuracy of the MF radar, but still 10% worse.
Let us also compare the meteorological stability of the radar. The shorter the wavelength, the more it attenuates during propagation. For example, if the target is at a distance of 200 km, and there are clouds of medium saturation on the entire route, then the signal strength of the target received by the Zaslon radar will decrease by 8 times, and the MF radar will only be 2 times lower. If there is rain, the difference will increase even more. Some justification for the Zaslon guidance radar is that overcast clouds are rare, and IS radars operate at the same wavelength, that is, the signal from the ship to the radar will also decrease by 8 times. The Zaslon radar also has a meteorological surveillance radar of 10 cm range, but it lacks guidance accuracy. However, the MF radar will provide launches of anti-aircraft missiles with greater reliability.
It is difficult to estimate the cost of the Zaslon surveillance radar. The size of its AFAR is unknown, but it is clear that the number of PPMs in it is less than 2000. With such a small serial production, the price of one PPM can rise to $ 2000. Taking into account the mechanical drive, the cost of the surveillance radar will exceed $ 8 million. As a result, the cost of the Zaslon radar section alone will exceed $ 50 million, which is 3 times higher than the cost of the MF radar.
2.5 TTX MF radar
Detection range
for IS type F-16 with EPR 2 sq. m - 300 km,
for IS type F-35 with EPR 0,1 sq. m - 130 km.
For anti-ballistic missiles with EPR 0,03 sq. m, flying at a height of 3 m, and at a superstructure height above sea level of 20 m - 20 km.
Errors of a single measurement of IB angles
at a range equal to 80% of the detection range:
in azimuth - 0,2 °
in elevation - 0,15 °.
at a range equal to 50% of the detection range:
in azimuth - 0,1 °
in elevation - 0,08 °.
Note. In the process of tracking, the angular error decreases by a factor of 2–3 in comparison with the given values.
Errors of a single measurement of RCC angles:
at a distance of 20 km in azimuth - 0,03 °.
The measurement of the elevation angle of a target flying at an altitude of less than 25 m does not occur due to signal re-reflections from the sea surface. Instead of measuring the altitude, only the "low-flying target" (NLC) sign is formed, which means that the target has a height of less than 25 m. At a distance of 10 km, the NLT sign is generated for targets flying at an altitude of less than 10 m, and at a distance of 5 km, the NLT sign appears unnecessary, and the error in the measurement of the elevation angle is 0,04 °.
3. The tactics of aiming missiles on anti-ship missiles
The difficulty of hitting subsonic anti-ship missiles is that they fly at extremely low altitudes of 2–5 m. The echo signal reflected from the anti-ship missile system enters the radar antenna in two ways - directly and specularly, re-reflected from the sea surface. Then the radar will see two targets at once, one - true and directly below it - a mirror, as if at the same height under the surface of the sea. The radar elevation angle measurement unit, while receiving two signals, cannot understand this confusion and gives an incorrect estimate of the target height, which can be either lower or higher than the true value. The main means of dealing with altitude distortions is the vertical narrowing of the radar beam, that is, our AFAR requires an increase in the size of the vertical crossbeam of the cross. Then, if you direct the receiving beam to the true target, then the signal of the mirror image will be either outside the beam, that is, it will not be received, or will be received significantly weakened.
The second means of dealing with mirror reflections is to increase the height of the AFAR placement, but even here the real height of the superstructure does not allow us to count on much. Next, we will consider the AFAR with the above dimensions and evaluate what missile guidance capabilities are achieved in this case.
At ranges of no more than 5-6 km, the radar provides precise guidance both in azimuth and in altitude. At a distance of 10 km, the altitude measurement becomes unreliable, and the missile defense system must fly up to the target using the altimeter data, which will have to be included in the missile defense equipment. The flight altitude of the missile defense system is chosen fixed and equal to 4 m to defeat subsonic anti-ship missiles and 8 m - for supersonic anti-ship missiles. If the height of the anti-ship missile system exceeds 10 m, then the radar will note this fact, and the guidance will continue with the usual methods. At ranges of 10-15 km, the target height uncertainty reaches 20 m, and guidance at a fixed height becomes ineffective. Then it is necessary to switch to the differential guidance method, when it is believed that at approximately the same ranges to anti-ship missiles and missiles, the distortions of their heights become the same, and guidance in the last 0,5-1 km section is carried out so that the difference in the height estimates is equal to 0.
The likelihood of defeat with such guidance will be slightly reduced compared to the usual one.
As a result, we come to the conclusion that with a sufficient supply of missiles, the first shelling of a subsonic anti-ship missile system can be carried out at a distance of 10-15 km, evaluate the result of the firing and conduct a second shelling at a distance of 5 km.
Since the supersonic anti-ship missile flies at an altitude of 10 m, shelling at a distance of 10 km will already be effective with conventional guidance.
The disadvantage of the command method of targeting missiles is a significant reduction in the range of destruction when intercepting maneuvering anti-ship missiles. For example, at a distance of 5 km, the MF radar will take 0,5 seconds to detect an anti-ship missile maneuver with an overload of 2g, which will increase the miss by 2-3 m. Therefore, it is desirable to reduce the firing range at a maneuvering target to 3 km. The best way to increase the interception range is to install a simple IR seeker on missiles with an anti-ship missile capture range of 1,5–2 km. However, this will require a new ROC. Otherwise, you will have to reduce the beam width of the MF radar. It is desirable to increase the size of the AFAR cross to 3,74 * 6,18 m, but this requires coordination with the ship's designers and will increase the cost of the MF radar by $ 3 million.
4. The use of KREP for air defense
Suppose that while patrolling BMZ corvettes will operate singly or in pairs. Then, when an IS reconnaissance appears, the KREP of the corvette must turn on the interference of the IS radar. The on-board radar will necessarily track the direction to the interference, and in the presence of a second IS, it can approximately determine the distance to the corvette. Consequently, a single corvette, in principle, cannot hide its location with the help of KREP. A pair of corvettes can worsen the direction finding accuracy, but for this they must have a good location at the time of the start of reconnaissance - the distance between the corvettes relative to the direction to the IS should be from 1 to 4 km. Therefore, further we will consider the defense of only a single corvette.
Only an imposed jammer (PP) - a helicopter-type UAV - can significantly distort the results of reconnaissance. Consider two fundamentally different PP options - light and heavy.
A light PP flies off to the side of the ship by 1,5-2,5 km and suppresses the radar along the main beam of its antenna. The interference power is measured using the concept of "energy potential", which is equal to the product of the transmitter power of the transmitter and the gain of the antenna of the transmitter. The required energy potential (EP) is directly proportional to the RCS of the ship and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance the IS can fly to the corvette.
If there is a missile defense system on the corvette, this range will be 150 km. If we assume that the PP is required to suppress only the IS radar, then it is enough for it to have an antenna operating only in the wavelength range of 3-4 cm. Then, for example, if it is necessary to obtain an EF of 3000 W, then an APAR with a size of 0,15 * 0,15 is required m, containing 16 PPMs with a power of 2 watts. The mass of the PP equipment will be 5–7 kg. The required time of duty of the PP in the air is 1 hour.
The efficiency of a single PP is not very high - it can create an angular sector of interference on the radar indicator with a width of ± 1 °, and the PP itself will be tracked by the radar much more accurately. If the enemy uses two IS spaced 50-100 km apart, then he can accurately determine the coordinates of the PP. A pair of PPs will be much more effective. They will create an interference sector of ± 2 °, and none of them will be direction finding. The ship can be located anywhere in this sector.
Heavy PP is an AWACS UAV helicopter designed to detect ships at ranges up to 300 km and anti-ship missiles at ranges up to 50 km. Next, we will consider an approximate version of such an AWACS-PP.
If a rectangular AFAR with a length of 1,6 m and a height of 0,4 m, containing 96 PPMs with a power of 10 W each, operating in the range of 3-4 cm, is suspended under the UAV, then the UAV will be able to suppress the radar along the side lobes of the antenna. Equipment weight 50 kg. Such a UAV can fly off to the side of the ship by 10 km, and forward towards the IS - by 20 km. As a result, it becomes meaningless to determine the coordinates of the ship by measuring the coordinates of the PP. The best performance is obtained when light and heavy PP are used at the same time.
To combat the GOS RCC, it is best to use light PP. It should be borne in mind that one of three wavelength ranges can be used in the GOS: 3,2 cm; 1,8 cm and 8 mm. Even the option of a seeker with 3,2 cm and 8 mm at the same time is not excluded. It is possible to place all three ranges at once on one PP, and it is possible to use replaceable letters. The distance from the ship to the side will be 0,5-1 km and forward - 1-1,5 km.
One PP is capable of simultaneously suppressing two GOS.
5. findings
Corvette 20380 was created using technology 40 years ago and is so noticeable that it cannot be hidden by the interference of its KREP from the detection of IS even from a distance of 400 km.
The Redoubt air defense missile system at 20380 does not have a missile guidance radar and does not provide radio correction for missiles, that is, expensive missiles will miss the target during target maneuvers.
Corvette 20386 is made taking into account the Stealth technology, and if we eliminate obvious flaws such as signal bridges and protruding cylinders on the superstructure, then its visibility can be reduced by 10-30 times compared to 20380.
The cost of the Zaslon radar on the corvette 20386 can be reduced by three times by replacing them with a unified MF radar.
It is desirable to significantly simplify and reduce the cost of KREP Zaslon, but add light UAV jammers.
To detect over-the-horizon targets, it is necessary to develop an AWACS UAV that also performs the functions of a jammer.

Information