Outside the Alliance. Forms of NATO cooperation with third countries
NATO is currently actively cooperating with third countries outside of the organization. Such interaction is carried out within the framework of a number of organizations and formats, uniting several dozen countries from several regions. These measures allow the Alliance to expand its presence outside the Euro-Atlantic region and solve other problems.
Evolution of the Soviets
The foundations of the modern system of NATO cooperation with third countries were laid after the end of the Cold War. In the early nineties, taking into account recent events, the Alliance updated its Strategic Concept. One of the main foreign policy goals was now interaction with third countries that are not part of any blocs and alliances. Later, these plans were implemented through the creation of new organizations.
Already in 1991, the North Atlantic Cooperation Council (NACC) was founded. All NATO countries, as well as a number of European states, have joined this multilateral forum. Neutral countries and former Soviet republics were invited to cooperate. In its original form, the NACC existed until 1997, when it was reorganized into the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC).

Currently, the EAPC includes 50 members - NATO countries in full force, 6 European countries adhering to neutrality, 3 states on the territory of the former Yugoslavia, as well as 12 states of the post-Soviet space. Almost all member countries of the Council have their diplomatic missions at NATO headquarters in Brussels. EAPC meetings are regularly held with the participation of officials of different levels.
Within the framework of the EAPC, cooperation is carried out in a number of main areas. These are peacekeeping and conflict resolution, the fight against international terrorism, joint defense planning, arms control, etc. Every two years, a plan of the Council's activities is developed, which defines the main goals and objectives for the near future.
NATO's cooperation with Russia, Georgia and Ukraine is considered to be of particular importance and priority within the EAPC. In this regard, in the past, the Russia-NATO Council was established, as well as its own commissions for interaction with other priority partners.
In the Name of the World
In 1994, NATO initiated the Partnership for Peace (PfP) program. A number of countries that were not members of the Alliance were invited to participate in it, including former Soviet republics. At the time of its start, the program united 24 countries. Subsequently, the number and composition of participants changed several times.
At the moment, the PfP includes 20 countries in Europe, Transcaucasia and Central Asia. 14 states previously participated in the program, but have now become members of NATO and dropped out of it. Russia once joined the "Partnership", but at the moment does not participate in it due to the termination of cooperation on the main NATO programs.
The mission of the PfP program is NATO's assistance in the building and development of national armed forces. As a result of this development, the participating countries get the opportunity to full-fledged military cooperation with the Alliance, and in the future - to join it. Every two years, PfP participants provide information on the state of their armies, on the basis of which plans for further development are drawn up. In addition, NATO provides training for the personnel of partner states in its educational institutions.
Regional initiatives
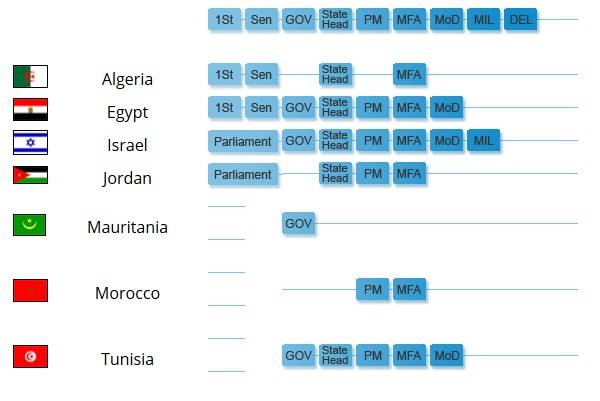
In 1994, NATO launched the Mediterranean Dialogue (MD) project, which aims to unite the efforts of the Alliance and the countries of North Africa and the Middle East. In 1995-2000. only seven countries have joined this format - Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Jordan, Mauritania, Morocco and Tunisia. Expansion of the project is not planned yet.

Cooperation on SD is mainly carried out in a bilateral format according to individual plans for each country. At the same time, joint events are regularly held. As in the case of the PfP, under the SD, the Alliance countries help partners with training, planning and developing armies.
In 2004, the Istanbul Cooperation Initiative (ICI) was launched to complement the Mediterranean Dialogue by attracting new Middle East partners. The ICU includes Bahrain, Kuwait, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates. There are plans to include new countries such as Saudi Arabia and Oman in the ICU.
According to the principles of interaction with NATO, the ICU program is similar to the PfP and SD. At the same time, partner countries can provide the Alliance with their military infrastructure facilities and participate in its international exercises. In 2016, several ICU countries received permission to open permanent missions at NATO headquarters.
Global partnership
NATO's interests extend beyond the Euro-Atlantic region, and there are countries willing to cooperate with the Alliance. For this purpose, a format of “global partners” (formerly “contact countries”) has been created, within which interaction is carried out according to individual plans, taking into account the needs of the country and NATO's plans in relation to it.
Global partners include Afghanistan, Australia, Colombia, Iraq, Japan, South Korea, Mongolia, New Zealand and Pakistan. Cooperation is carried out through legislative structures and ministries of defense. At the same time, the methods of interaction with different countries differ.
New approaches
The described cooperation formats provide for the unification of third countries on a geographic basis, and also propose plans for cooperation outside the main regions. In 2011, the so-called. Berlin package - new principles of interaction with third countries. The main idea of this package is to move away from geographical principles and to more harmonize approaches.
Since 2012, uniform lists of events held in the framework of partnership with NATO have been compiled annually. In 2014, we adopted the Partnership Interoperability Initiative, aimed at reducing the disparity between the armies of different countries. Depending on the current state of the armed forces and the political course of the partner country, the Initiative provides for several levels of interaction.
In 2014, the initiative “Assistance to non-aligned states” was launched. NATO offers advice on building national military forces. Georgia, Jordan, Iraq, Moldova and Tunisia have already joined the program and have been offered individual development plans. It is curious that when launching such cooperation, NATO gives preference to partners that are most interesting from a military-political point of view.
Own interests
There are currently 30 countries in NATO, and several more wish to join this organization. In addition, the Alliance actively cooperates with 40 foreign countries that are not part of it or adhere to neutrality. There are obvious reasons for this NATO interest in foreign cooperation.
Through a variety of programs, the Alliance interacts with almost all European and North African countries, gaining more convenient access to the Middle East and Central Asia, and expanding its presence in the Asia-Pacific region. Some partner countries become full members of NATO as they implement relevant programs. Military modernization programs almost always provide for the supply of products manufactured by the Alliance countries.
Thus, with the help of all programs and formats of cooperation, NATO gets the opportunity to go beyond its original Euro-Atlantic region and tries to establish relations with the maximum number of countries. In the future, their military and political potential is used to some extent in the interests of NATO. At the same time, measures are being taken to attract new potential partners - and obtain new opportunities. On the whole, such approaches justify themselves, making it possible to set and solve new military-political tasks.

Information