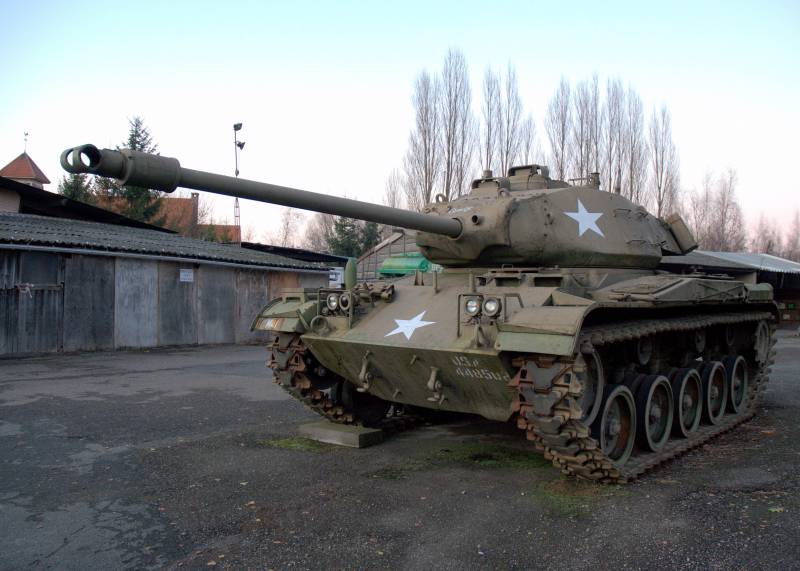
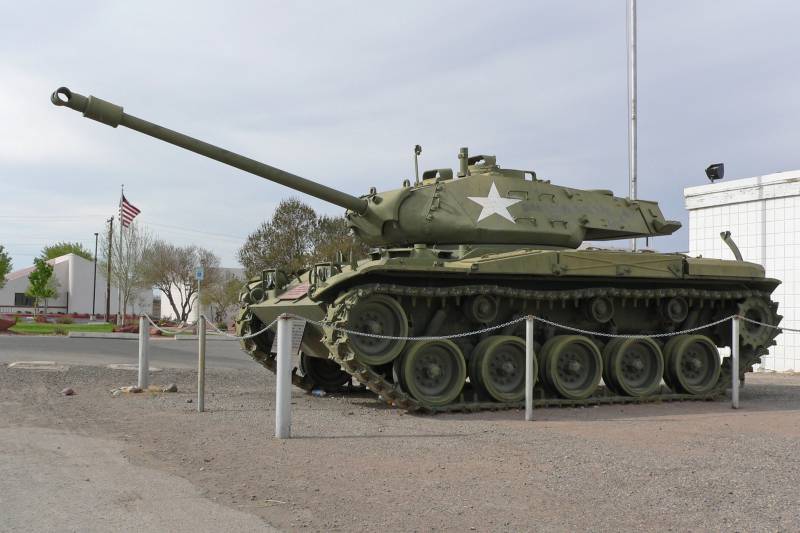
Light tank M41 Walker Bulldog
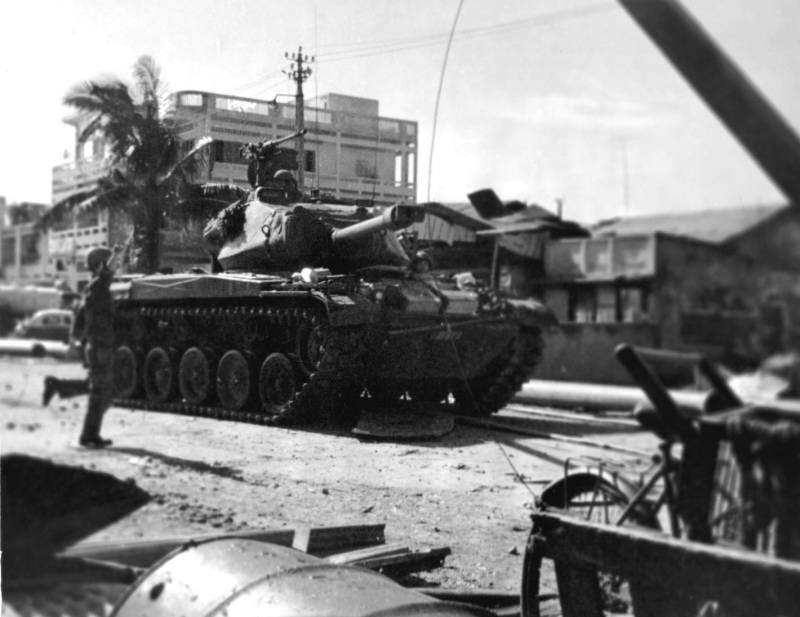
The main difference from its predecessor was that the tank received a more powerful 76-mm gun. It was a long-barreled (60 caliber), but, as practice has shown, such a replacement was already insufficient, especially in the 1960-s. For example, during the Vietnam War, M41, which acted as the main tank of South Vietnam, turned out to be almost completely useless against the main battle tank of North Vietnam - T-54. Approximately with the same "success" the tank M41 Walker Bulldog was used in other local conflicts of the second half of the XX century. In the US Army, this tank was finally removed from service in 1969. He was replaced by the light tank M551 "Sheridan", which was created in the framework of the new concept - a light combat vehicle with the most powerful weaponry.
Despite this, the Bulldogs did not go to landfill after they were removed from service. stories. In the US, they have become donors of chassis for various self-propelled guns, armored personnel carriers and other tracked vehicles. M41 also became a fairly common export tank, which was in service with almost 30 states of the world. Some of them continue to exploit this tank in the 21st century. For example, in the Brazilian army in 2010, the 152 of the M41 Walker Bulldog was still listed as XNUMX.
History of the tank M41 Walker Bulldog
At the request of the US military, the new light tank, which would have replaced the M24, would have to combine higher firepower and mobility. That is why the tank decided to arm a long-barreled 76-mm gun that was able to pierce 127 mm of armor (5 inches) mounted at an angle of 30 degrees at a distance of 914 meters (1000 yards). The weight of the tank should not exceed 25 tons.
The very concept of a light tank, the M41 Walker Bulldog, was born back in 1942, after work began on creating a new medium tank under the designation T20 in the USA. The US military believed that from it it would be easy to get a light tank, which has the same internal dimensions of the hull, but weaker weapons and a smaller thickness of armor. A similar project was developed, but it never came to the stage of production of a prototype. As a result, this idea was again returned after the end of the Second World War in 1946, when developing the first post-war program of tank building in the USA. Light and medium (T37 and T42 tanks, respectively) should have the same hull design, which would differ only in the thickness of armor plates, engines identical to each other, and similar running gears. Tanks were different only towers - the tower of a light tank was designed for the installation of 76-mm guns, and the average - for the placement of 90-mm guns.
This unification ultimately played a cruel joke with both tanks. The T42 medium tank was never adopted by the American army, since the military considered its corps too small and its powerplant low-powered. Only the tower of this tank was then used to develop a new medium tank T47. A light tank projected in the end came out too heavy and large, but initially no one paid attention to it.
The best fate awaited the project T37. The development of this project began in the Detroit Arsenal in July 1946. 27 September of the same year, he officially received the designation T37. The US Army Directorate initially recommended the production of a tank prototype 3 (in May 1947, this order was reduced to two cars). The design work was fully completed at the beginning of 1949, at the same time the wooden layout of the tank was ready. The first T37 tank was sent to the Aberdeen Proving Ground in May 1949, where it was tested until August 1950, after which the car was returned to Detroit.
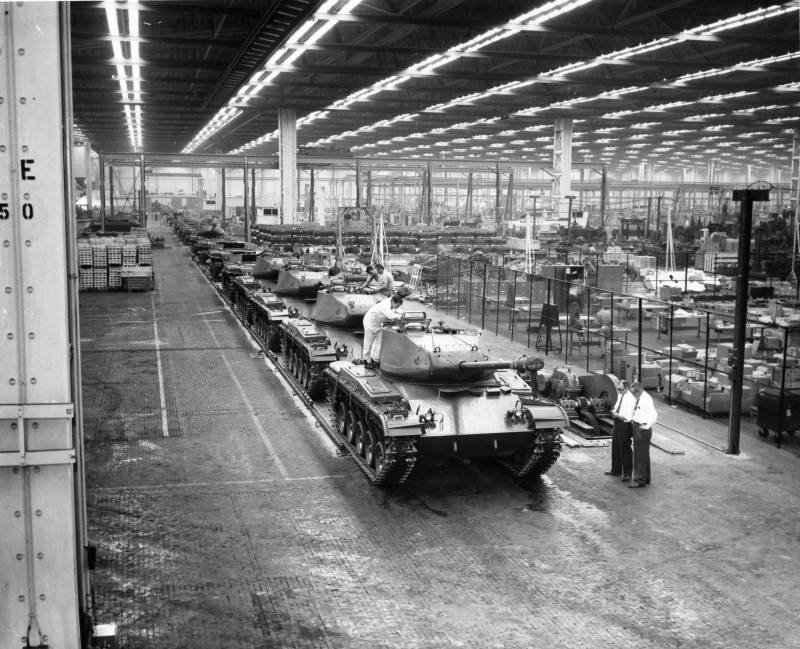
Along with T37, tests of the T37 of the second phase of development (under the new designation T41, prototype 3) were tested here at the Aberdeen Proving Ground. This model was armed with 76-mm high-power gun Т91, which was installed in a modified turret. The following modification of the T41 tank underwent a number of changes, in particular, the internal layout of the turret was changed, the size of its shoulder strap was increased, and the machine-gun installations located on the sides of the turret were also abandoned. This modernized version of the light tank of the Detroit arsenal was renamed to Т41E1, and it was she who later became, through some modifications, the massive lightweight tank M41 Walker Bulldog, which began to be mass-produced in 1953 year.
The layout and design of the tank M41 Walker Bulldog
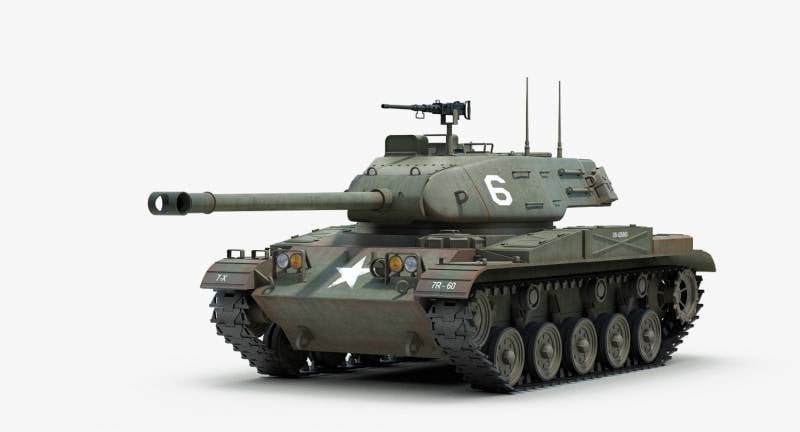
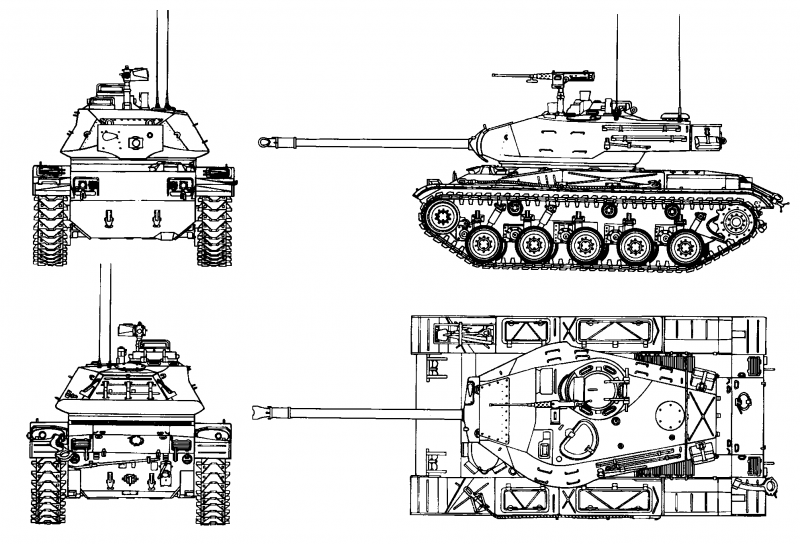
The light tank M41 has a classic layout. In front of the hull of the tank there is a control compartment, then a fighting compartment with a turret, and the engine compartment is located in the stern of the hull. Combat and engine compartment of the tank were separated by a special fire-resistant partition. The fighting compartment of the tank was equipped with a rotating polycom. Part of the ammunition was located in the forward part of the body on the right side of the mechanical drive point.
The crew of the tank consisted of 4-x people: the driver was located in the control compartment, the commander of the combat vehicle, the gunner and loader in the tank turret, the first two sat on the right side of the gun, the last on the left side, which allowed him to charge the gun by hand. In the non-rotating commander's turret 5 glass blocks were placed, intended for a circular view. In addition, the gunner and tank commander had a periscopic device M20А1, which turned to 360 degrees.
The hull of the tank is welded, it is made of rolled steel armor. Bronelists in the frontal part of the body are located at rational angles of inclination. The tank tower is welded from cast and rolled armored parts. The thickness of the tower armor was from 12,7 mm (roof) to 38 mm (gun mask). The nose parts of the hull had a thickness of 50 mm, the hull sides of the hull were 12-15 mm, the front part of the tank bottom was 32 mm, the rear part was 9,25 mm. Special means of protecting the crew of the tank from the use of the enemy weapons mass destruction it was not. A fire-fighting equipment system was located in the MTO, which could be activated from the mechanical drive point.
The main armament of the light tank was the 76-mm M32 rifle gun (T91E3), during the modernization it was replaced with the M32-1. The gun was equipped with a muzzle brake to reduce recoil. The ammunition of this tank gun included shots with cumulative, armor-piercing tracer and high-explosive fragmentation projectiles, as well as projectiles with ready slaughter elements, smoke and others. Already in 1982, an armor-piercing feathered sub-caliber projectile was created specifically for this gun. Initially, the tank ammunition consisted of 57 unitary shots, after upgrading, starting with the modification М41А1, the ammunition was expanded to 65 shots. 24 shots were located in the fighting compartment, they were ready for immediate use. The remaining 33 shots were in the hull of the tank, and their overload in the fighting compartment was possible only in the case when the tower was deployed strictly in the stern.
Auxiliary armament light tank was represented by two machine guns. Directly with the gun was paired 7,62-mm machine gun with ammunition 5000 cartridges. A large-caliber 12,7-mm anti-aircraft machine gun (2175 rounds of ammunition) was mounted on the roof of the turret at the hatch of the tank commander. The weapon was controlled by the gunner and the tank commander with the help of electro-hydraulic guidance drives available at their disposal. The first version of the weapon stabilizer tank and range finder did not have. Later, already on the M41А1 modification, the weapons installation was stabilized in two planes.
The commander and the gunner could use for their own purposes the periscopic observation devices M20A1, which had two optical channels: one-time, for orientation in the terrain, and 6-multiple, intended for firing. In addition, the gunner could use the M97 telescopic sight, which had a threefold increase. No night vision devices were installed on the base model of the light tank; in the course of further modernization, these instruments and the IR illuminator were introduced into the equipment on the M41А3 tank. The communication means of the M41 tank consisted of two radio stations, a TPU and a telephone intended for communication between infantry / troops and crew members.
Initially, the 41-cylinder gasoline engine Continental AOS 6-895 air-cooled was installed on the light tank M3. In 1956, it began to be changed to an AOS 895-5 gasoline engine with a direct fuel injection system, which was more economical, having the same horsepower 500. In all cases, the tank was used hydromechanical transmission type "Cross-drive" CD-500-3 production company "Allison". The transmission had a complex cylindrical input gearbox with an automatically locked friction clutch, a planetary gearbox, a torque converter, a differential double-flow brake turning mechanism with metal-ceramic discs that worked in oil.
Additionally, the tank was mounted an auxiliary engine GMC model A41-1 with a charging unit, designed to warm up the main power plant in the winter season. The equipment for overcoming the deep ford, a flare heater for the crew and an electric bilge pump were included in the standard equipment of the light tank. With the help of special equipment, the tank could easily overcome the ford to a depth of 2,5 meters.
The M41 Walker Bulldog tank suspension was an individual torsion bar. On the first, second and fifth suspension nodes were placed telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers. In this case, the torsion bars of the first and fifth nodes of the tank suspension were of a larger diameter than all the others. Basic skating rinks - the duo-pitch rubberized (on 5 on board). There was also an 3 supporting roller on each side. Tracks with rubber-metal hinges of the sequential type were used on the tank, they could be equipped with removable rubber pads. In the undercarriage of the tank, a lever compensating device was used, which ensured the constant tension of the tracks.
At the design stage, it was also planned to equip the M41 tank with an automatic loader system, but this series did not appear on serial combat vehicles. Also in the framework of the experiment on the "Bulldog" 90-mm gun was installed (this tank was designated as T49), but this experiment did not progress further than the creation of a prototype.
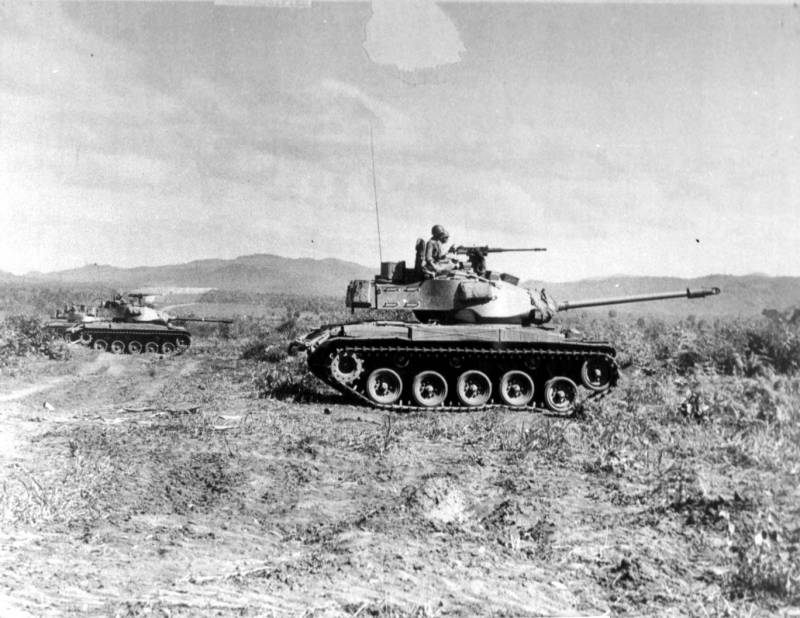
The peculiarity of the Walker Bulldog МХNUMX light tanks was that they were very widely exported. These combat vehicles were in service with the 41 order of the countries - members of NATO, Asia, Africa and Latin America. This combat vehicle was actively used in the fighting by the South Vietnamese troops, starting with the 30 year and up to the end of the Vietnam war in the 1965 year. At the same time, a certain number of combat vehicles of this type were subsequently used by the Vietnamese People’s Army (VNA). Apparently, the last combat episode, in which M1975 took part, happened during the Falkland conflict between Argentina and Great Britain. However, several Argentine M41s transferred to the islands were quickly destroyed by British soldiers.
Performance characteristics of the M41 Walker Bulldog:
Overall dimensions: body length - 5819 mm, with a forward gun - 8092 mm, body width - 3198 mm, height - 2726 mm.
Combat weight - 23,2 tons.
The power plant - 6-cylinder carburetor engine Continental AOS 895-3 turbocharged, power - 500 hp
Maximum speed - 72 km / h (on the highway).
Power reserve - 160 km (on the highway).
Armament - 76-mm gun M32, 7,62-mm machine gun Browning M1919A4E1 and 12,7-mm anti-aircraft gun Browning M2HB.
Ammunition guns - 57 shells.
Crew - 4 person.
Information sources:
http://techno-story.ru/articles/tanks/152-bronirovanyj-buldog-amerikanskij-ljogkij-tank-m-41-walker-buldog
http://www.militaryparitet.com/perevodnie/data/ic_perevodnie/6242
http://warspot.ru/4190-bezzubyy-buldog
http://www.dogswar.ru/bronetehnika/tanki/3499-legkii-tank-m41-walk.html
http://pro-tank.ru/brone-america/brone-usa/352-tank-m41-walker-bulldog






Information