Sd.Kfz.250 / 11 combat reconnaissance vehicle (Germany)
It is known that the actual reason for the creation of combat reconnaissance vehicles based on Sd.Kfz.250 was the insufficient characteristics of the Sd.Kfz.222 armored car. This wheeled vehicle could not operate effectively in the off-road conditions characteristic of the autumn and winter on the Eastern Front, and required replacement. According to the results of the operation of such equipment, it was decided to develop similar machines based on the existing semi-tracked chassis. Soon there were projects leichter Schützenpanzerwagen 2 cm (Sd.Kfz.250 with a turret and 20-mm automatic cannon, borrowed from Sd.Kfz.222) and leichter Schützenpanzerwagen 3,7 cm (armored personnel carrier with 37-a-chomtrupanzerwagen 36 cm (an armored personnel carrier with XNUMX-a-chomtrupanzerwagen XNUMX cm - armored vehicle with XNUMX-ch-chf. Panzerwagen XNUMX cm).
Using two new types of equipment, it was decided to re-equip the army reconnaissance units. In this case, machines with more powerful guns were to be used as commanders and, using a large caliber of the main gun, to increase the firepower of the units. In addition, at the beginning of 1942, it was proposed to create another version of the BRM on the existing chassis, which differs from its predecessors in armament. This time again it was supposed to use another weapon with enhanced fire performance.
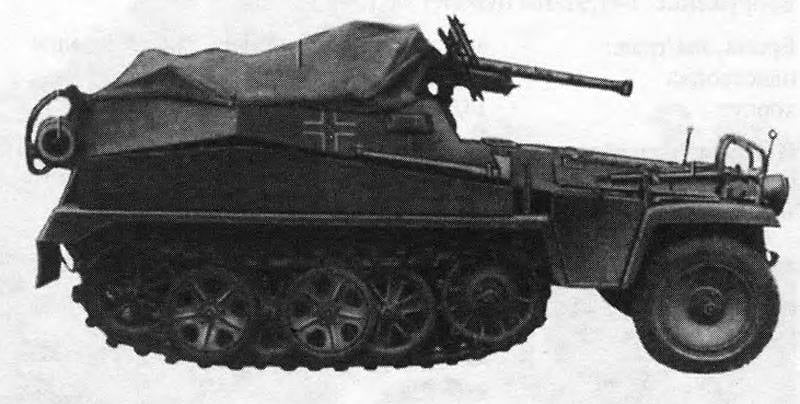

General view of the BRM Sd.Kfz.250 / 11. Photo by Chamberlain P., Doyle H. "Complete German Reference tanks and self-propelled guns of World War II "
The heavy anti-tank gun 2,8 cm s.PzB.41 or schwere Panzerbüchse 41 was chosen as the main means of increasing firepower. He, along with a special gun carriage should be installed on the existing half-track machine. The new project, in accordance with the German views on the range of equipment, received several designations at once. The main was the leichter Schützenpanzerwagen (schwere Panzerbüchse 41) - “Light armored vehicle with a heavy anti-tank gun s.PzB.41. In addition, the project is known as Sd.Kfz.250 / 11 and Gerät 882. All these names are equivalent and can be used without the risk of confusion with other equipment.
As the basis for the new combat reconnaissance vehicle, the serial semi-tracked armored personnel carrier Sd.Kfz.250 was chosen. This machine was produced serially in fairly large quantities, and was also actively used by the troops. Thus, the revision of the existing technology with the installation of new equipment and weapons allowed to speed up the creation of BRM, as well as to simplify its further operation. In addition, the selected semi-tracked platform had acceptable mobility characteristics both on highways and on rough terrain.
The combat vehicle Sd.Kfz.250 was originally created as an armored personnel carrier for the transport of two crew and four paratroopers. In the course of serial production, the armored personnel carrier was repeatedly refined, however, only two main modifications were distinguished, with different design features. The differences were manifested in the hull design, the composition of the power plant and other features of the project. It is noteworthy that during the construction of specialized equipment, base machines of both versions were used at different times.
The first serial modification of Sd.Kfz.250 under the symbol Alte (“Old”) had a characteristic multifaceted armored body, consisting of 19 main sheets of different shapes and sizes. The recognizable features of the car were the roof of an elongated engine hood, consisting of three elements, as well as sides, made in the form of a structure from the lower parts collapsed to the outside and the upper parts tilted inward. The frontal projection of such a body had armor protection with a thickness of up to 14,5 mm, and the sides and sterns had a thickness of 8 mm. This made it possible to protect the crew and units of the machine from small arms and debris.
The Alte designation appeared in the fall of 1943, when the BTR version of the Neu (“New”) went into the series. It was distinguished by a simplified armored hull, which included a total of nine sheets from 8 (feed and side) to 15 (roof) mm. The shape of the new building was significantly simplified. In particular, the boards of complex shape disappeared, instead of which box-shaped aggregates were used now. Significant changes were made to the front of the hull, covering the power plant.
In the front part of the body of the armored personnel carrier of the first modification, a Maybach HL 42TRKM carburetor engine was placed, hp power 99. Subsequently, in the course of modernization, it was replaced with an HL 42TUKRM product with similar power ratings. The engine was connected to a mechanical transmission on the basis of the gearbox, which provided seven forward speeds and three reverse. All transmission units were located in the central part of the hull and were intended to transmit torque to the front drive wheels of the tracks.
The Sd.Kfz.250 armored personnel carrier had a semi-tracked undercarriage. In front of the hull there was a wheel axle with a control system and suspension on leaf springs. The central and aft parts of the hull were equipped with a tracked propulsion unit. There were four large diameter skating rinks with an individual torsion bar on each side. Due to the relatively small body length, the rollers were placed in a staggered pattern. In front of the caterpillars were driving wheels, in the stern of the hull - guides.
In the original configuration in the habitable compartment of the armored corps fit up to six people. Own crew of an armored personnel carrier consisted of two people and was on the ground in front of the general compartment. The landing of four fighters located on the benches along the sides. The crew could monitor the situation with the help of viewing instruments in the front and side sheets. A door in the stern sheet of the hull was used for landing. For assault fire support and for self-defense, the Sd.Kfz.250 armored personnel carrier could carry one or two MG 34 machineguns.
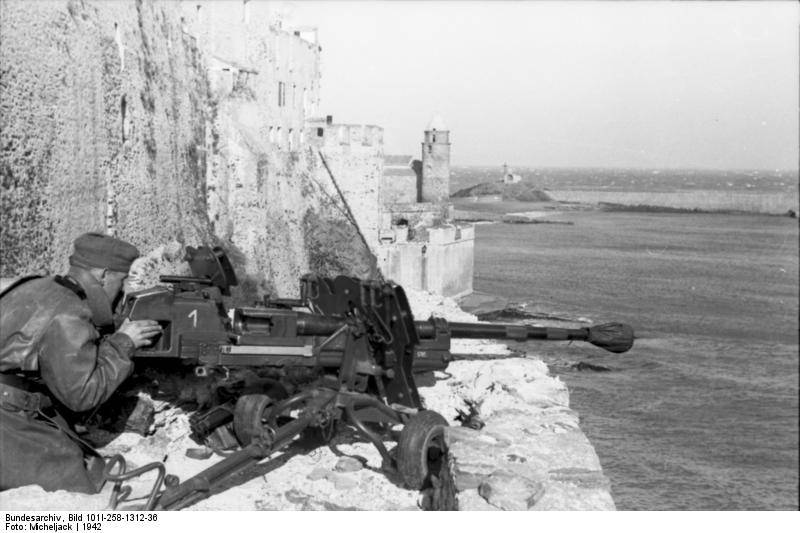

Anti-tank shotgun on lightweight carriage. Photo of Wikimedia Commons
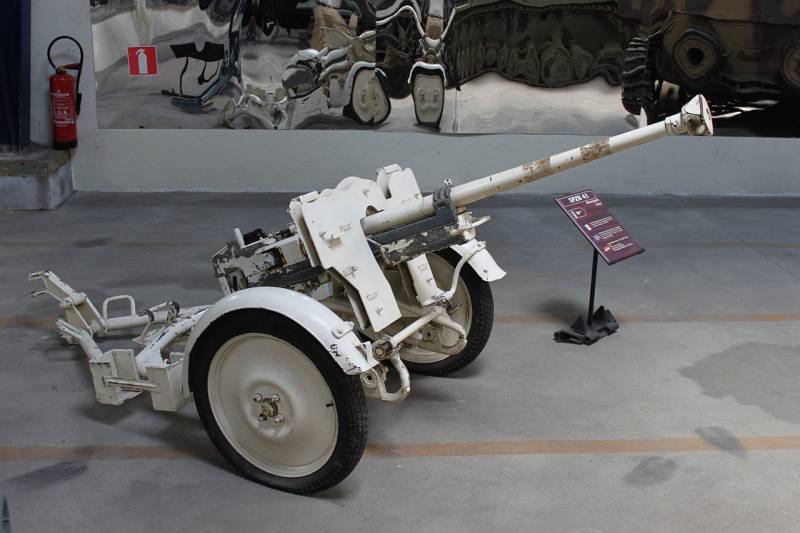
For a significant increase in the firepower of a combat reconnaissance vehicle in comparison with the base armored personnel carrier, it was decided to use new weapons. For the "main caliber" for the BRM Sd.Kfz.250 / 11 a heavy anti-tank rifle (according to the German classification) or a small-caliber s.PzB.41 gun was chosen. These systems were produced from the beginning of the forties and were rather actively used by the Wehrmacht to fight the enemy’s armored vehicles. In the course of the new project leichter Schützenpanzerwagen (schwere Panzerbüchse 41), it was proposed to adapt an anti-tank rifle for installation on a half-track chassis.
The main feature of the s.PzB.41 product was the design of the trunk. Gun got rifled barrel with a conical channel. The breech of the trunk had a caliber 28 mm, and on the muzzle section it was 20 mm. For such weapons were created several versions of special-purpose ammunition, suitable for use with a conical bore. When using an armor-piercing projectile, the muzzle velocity at the level of 1400 m / s was provided. A sabot weight of 130 g at such a speed could penetrate up to 66 mm of homogeneous armor from a distance of 500 m. Thus, in terms of armor penetration, a heavy anti-tank gun exceeded some other systems, including significantly larger calibers.
Initially, the s.PzB.41 rifle / cannon was mounted on a wheeled carriage with an armored shield. Subsequently, a modification appeared for the landing parts, in which a three-legged carriage was used with the possibility of mounting wheels. For mounting on the semi-tracked chassis, the design of the second version of the mast was slightly modified. The original carriage was divided into two parts, which allowed to use the gun in two configurations: on a self-propelled chassis or as a portable / towed system. In the first case, the elements of the gun carriage with a weapon and a shield were mounted on the corresponding mounts in the front part of the habitable compartment of the armored vehicle hull. If necessary, the weapon could be removed and mounted on a tripod, using the original quality.
Directly on the armored mounts there was a simple guidance system in the form of hinges, without the possibility of mechanical adjustment. With it, the gun could be aimed within the horizontal sector width 70 ° at elevation angles from -5 ° to + 30 °. The moving mechanisms had attachments for mounting the barrel with a length of 1730 mm. Provided hydraulic recoil device and muzzle brake. To protect the gunners used armor shield, consisting of two parts. There is information about the modernization of the guards forces combat units. In some divisions, additional armor plates were independently installed on the available parts, with the help of which the overall width of protection was increased.
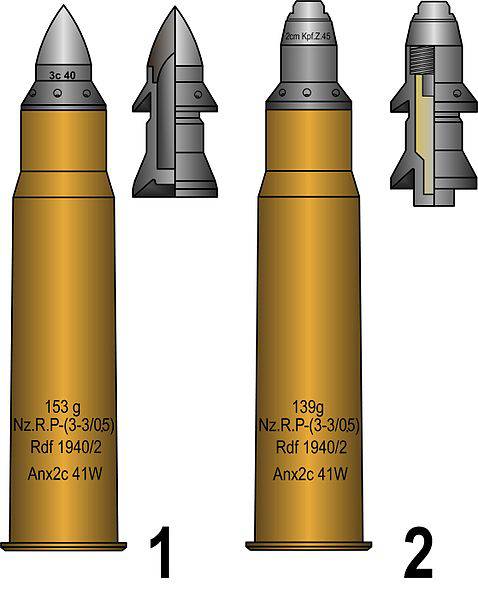
Ammunition for a gun. S.PzB.41: 1 - armor-piercing sabot projectile, 2 - fragmentation. Figure Wikimedia Commons
Inside the former troop compartment of an armored personnel carrier, it was possible to place several shelves for storing ammunition. The main weapon’s ammunition consisted of 168 unitary projectiles. Removing ammunition from the stowage and feeding the gun into the chamber must be carried out manually, one by one.
As an additional weapon, it was proposed to use one MG 34 machine gun of 7,92 caliber mm. This weapon should be mounted on the aft installation of the hull, standard for the Sd.Kfz.250 BTR. Machine gun ammunition reached 1100 cartridges.
The crew of a combat reconnaissance vehicle consisted of five people. On the ground in front of the hull were located the driver and commander. Three more crew members were placed in the rear of the manned volume and had to engage in maintenance tools. Observation of the situation and search for targets should be carried out both with the help of standard viewing devices and “through the board.” The method of landing in the car with the aft door remained unchanged.
According to various sources, the serial production of Sd.Kfz.250 / 11 combat reconnaissance vehicles or leichter Schützenpanzerwagen (schwere Panzerbüchse 41) began in the last months of 1942. Serial equipment of the new type was planned to be sent to reconnaissance units, where they were to be used in parallel with other state-of-the-art equipment based on a semi-tracked armored personnel carrier. In this case, the equipment with a heavy anti-tank gun was considered as an alternative to the BRM Sd.Kfz.250 / 10 with 37-mm guns.
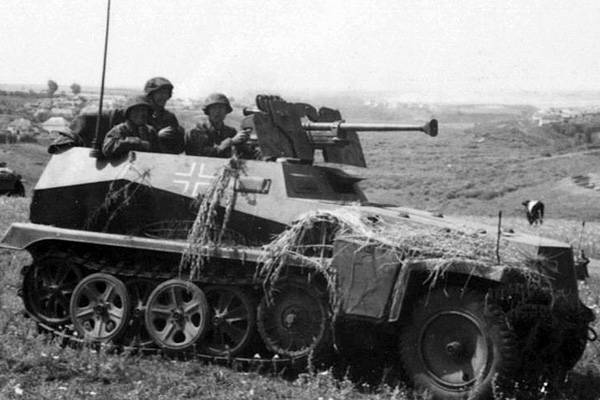

Sd.Kfz.250 / 11 reconnaissance vehicle at the front. Photo Kfzderwehrmacht.de
During the parallel operation of several types of reconnaissance vehicles in the army, the German military was able to compare the latest industry developments. It turned out that Sd.Kfz.250 / 11 with a gun equipped with a tapered barrel has noticeable advantages over both the BRM of previous models. For example, from the 200 distance m, the crew of such a machine could hit a target with protection in the form of 86 mm. The 3,7 cm PaK 36 cannon under similar conditions could penetrate only 56 mm of armor. Thus, in the fight with enemy armored vehicles, newer reconnaissance vehicles had some advantages.
However, the s.PzB.41 system had some problems. For example, its fragmentation projectile was equipped with a charge of a mass of just 5 g, which was not enough to reliably defeat manpower and unprotected equipment. According to similar characteristics, the heavy anti-tank rifle lost to all the BRM armaments based on Sd.Kfz.250. In addition, the situation on the battlefield was not always possible to realize the benefits associated with a high initial velocity of the projectile. To ensure the defeat of Soviet armored vehicles, German crews had to approach targets at a distance of hundreds of meters and go deep into their zone of guaranteed destruction. Thus, the enemy’s own weak booking and powerful armament in most cases made it impossible to show the main differences between 37- and 20 / 28-mm guns.
The s.PzB.41 product differed from other weapons by a relatively small resource. A conical barrel could withstand no more than 500 shots, after which it needed to be replaced. It is known about the development of a tool with a chrome-plated bore and a doubled resource, but it has not left the stage of pre-production and testing. For comparison, other small-caliber anti-tank weapons of the time could have made up to several thousand shots.
If necessary, the crew had the opportunity to remove the heavy anti-tank gun from the armored vehicle and mount it on a tripod carriage. In this case, it was possible to equip a firing position and use weapons as a field artillery system. However, no significant increase in combat qualities was expected.
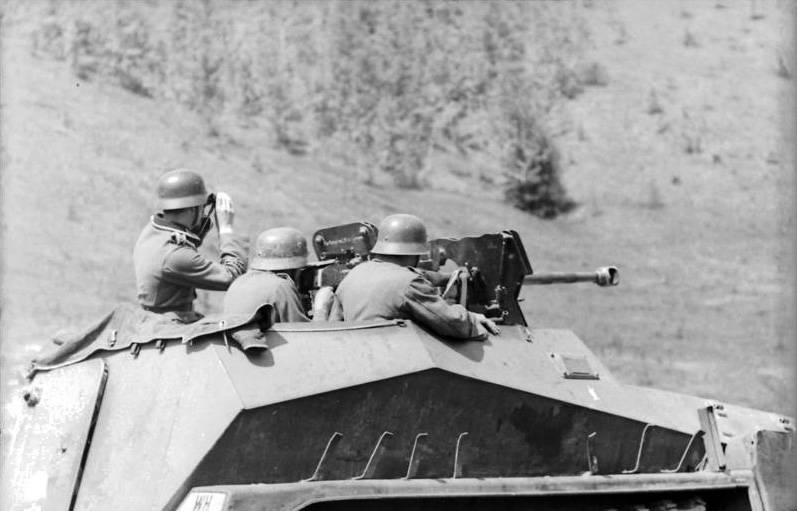

Shooting from the main weapon BRM. Photo of Wikimedia Commons
By the beginning of 1943, the fat is clear that the schwere Panzerbüchse 41 heavy anti-tank rifle has no prospects. It was distinguished by high price and low manufacturability. In addition, for the release of shells required scarce tungsten. All these factors, as well as fallen combat effectiveness led to the emergence of an order to stop the production of such weapons. In 1943, the largest number of anti-tank guns was produced during the entire production period, after which the assembly of such products ceased. Since 1940, German companies have supplied the customer with a little less than 2,8 thousand guns and more than 2,1 million shells of two types.
The termination of the release of weapons led to a halt in the assembly of combat reconnaissance vehicles equipped with them. As far as we know, the last BRM Sd.Kfz.250 / 11 went to the front until the autumn of 1943. Thus, all such vehicles were based on the Alte version armored personnel carrier. In total, no more than a few hundred reconnaissance vehicles were built.
The specific and ambiguous characteristics of the BRM leichter Schützenpanzerwagen (schwere Panzerbüchse 41) did not allow to solve a wide range of tasks. In some cases, such equipment could conduct reconnaissance and participate in other operations, but a direct collision with the enemy’s armored vehicles was associated with significant risks. Artillery or Red Army tanks could destroy Sd.Kfz.250 / 11 from a safe distance without any problems.
Part of the reconnaissance vehicles was destroyed during the fighting, mainly on the Eastern Front. Part of the equipment survived until the end of the war, but later went for recycling due to the lack of prospects and the need for such machines. As a result, over time, all the BRM Sd.Kfz.250 / 11 eventually ceased to exist. Nowadays, in many museums of the world, a significant number of surviving armored vehicles of the Sonderkraftfahrzeug 250 type are stored in various modifications, but among them there is not a single model of equipment with the s.PzB.41 heavy anti-tank gun.
Based on:
http://pro-tank.ru/
http://achtungpanzer.com/
http://kfzderwehrmacht.de/
Chamberlain P., Doyle H. Complete reference book of German tanks and self-propelled guns of the Second World War. - M .: AST: Astrel, 2008.
Information