Heavy Flame Tank Flammwagen auf Pz.Kpfw. B2 (f), Germany
Insufficient characteristics of the existing flamethrower tank became clear even before the start of the fighting on the Eastern Front. The basic light tank Pz.Kpfw.II was not distinguished by high performance, and the alteration of its design associated with the installation of new weapons had a negative effect on some parameters. Thus, instead of a cannon, a flamethrower tank received one rifle caliber machine gun. In addition, it was equipped with two flamethrower hoses, however such weapon could be used at ranges of no more than 25-30 m. As a result, the survivability of the tank on the battlefield was questionable. Later, such doubts were confirmed by practice.
In March, 1941, the decision was made to create a new flamethrower tank with enhanced protection and firepower. As a base for such a machine, we chose the captured French heavy tank B1bis. The armored hull of this vehicle allowed the crew and the flamethrower elements to be protected from the enemy’s artillery, and the existing weapon system ensured the preservation of high firepower regardless of the use of the flamethrower.
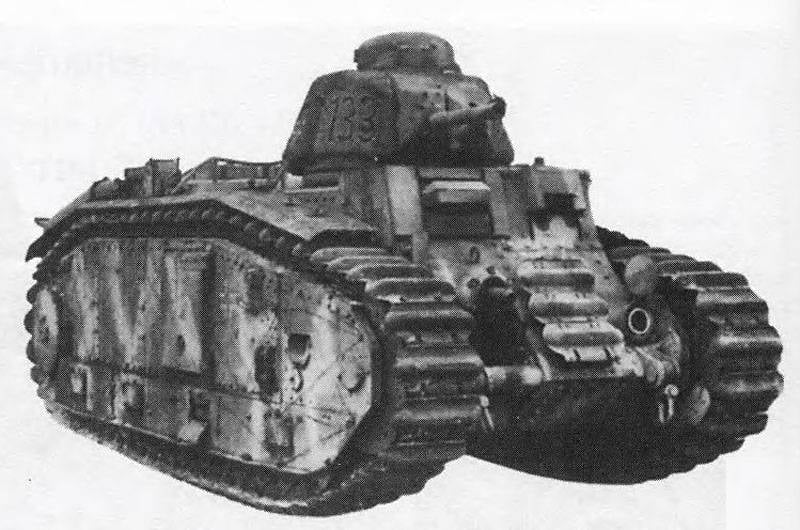

Flamethrower tank Flammwagen auf Pz.Kpfw.B2 (f). Photo of Chamberlain P., Doyle H. "Complete reference book of German tanks and self-propelled guns of the Second World War"
An order for the development of a project to upgrade the captured technology was placed in March 1941. Over the next few months, the industry had to create a project and assemble a prototype of an updated armored vehicle. In November, it was supposed to begin serial assembly. Until January, 42 was planned to be made up to 20-25 of a new type of flamethrower tanks. The development of the project involved several organizations. The overall coordination of the work and the modernization of the basic machine were entrusted to the Daimler-Benz specialists. The development of the flamethrower and all its components was entrusted to “Koebe”, and the assembly of equipment was to be carried out at the “Wegmann” plant.
In accordance with the existing designation system at that time, the new project was called Flammwagen auf Panzerkampfwagen B2 (f). Also in different sources there may be other designations reflecting the type of base armored vehicle and the presence of a new flamethrower weaponry.
The trophy tank had rather high characteristics that allowed it to be used as a carrier of flame-throwing weapons. The main reasons for choosing B1bis as a base for flamethrowing tanks were booking up to 60 mm thick and having two artillery pieces, one of which could be replaced with a flamethrower. In addition, the need to install new equipment led to some modifications of the hull structure with the addition of a set of non-standard units.
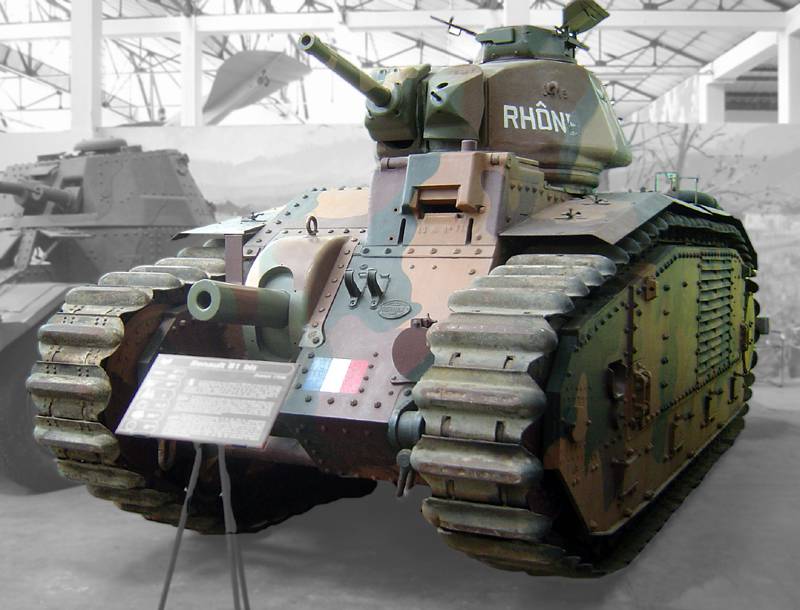

Trophy tank B1bis, which became the basis for a flamethrower machine. Photo of Wikimedia Commons
The base tank had a riveted body, consisting of sheets of thickness up to 60 mm. The most powerful booking was used in the manufacture of the forehead and sides of the hull. The stern leaf was slightly thinner, 55 mm. The case was protected from above and below by details of 20-25 mm thickness. On the roof was mounted tower with protection to 56 mm. A classic corps layout was used with the placement of artillery weapons in the corps. The front of the machine was given under the jobs of the driver and the gunners who served the frontal gun. The fighting compartment continued in the central part of the hull, and the feed was allocated for the placement of the power plant and transmission.
The French tank was equipped with a Renault six-cylinder engine rated at 307 hp. With the help of a Naeder transmission that includes a five-speed gearbox, the engine torque was transmitted to the drive wheels. Tank B1bis had a characteristic chassis. In its composition there were 14 track rollers assembled in several blocks with a spring suspension. To increase the mobility characteristics, the caterpillar was large and covered the side of the hull.
In the original configuration, the French heavy tank carried a 75-mm semi-automatic cannon in the front hull plate and an 47-mm cannon in the turret. Also near the guns were mounted two machine guns caliber 7,5 mm. Initially it was assumed that a smaller-caliber turret cannon would be used to destroy enemy armored vehicles, and the task of the frontal weapon would be to attack manpower and fortifications.
During the modernization of the new project, the base tank was to receive a number of new components for a particular purpose. In addition, some parts were removed. All these changes in the design of the hull and other units were aimed at solving the main task, which consisted in the installation of a flame thrower.
In accordance with the new project, the equipment of the flamethrower was to be divided into several units, distributed in different parts of the base tank. Thus, the hose was to be placed in the front of the machine, the compressed air cylinders were placed inside the case, and a special external tank was developed for carrying the fire mixture.
The flamethrower hose should have been mounted in a frontal sheet installation. To do this, the 75-mm cannon should be removed from the tank and part of the front sheet should be dismantled. Instead of the curved mask of the gun and the upper part of the inclined frontal sheet, new parts had to be mounted. The upper part of the forehead now contained a cabin, similar to the one installed at the driver’s workplace. Instead of the gun mask, a sheet was mounted with a cylindrical protrusion, in which the installation of the fire engine was mounted. Due to such improvements in the front of the case it was possible to place not only the flamethrower, but also the workplace of the gunman controlling them.
The shooter had the possibility of targeting a flamethrower within small sectors. Horizontal guidance was provided within 10 ° to the right and left of the neutral position and elevation from -2 ° to + 10 °.
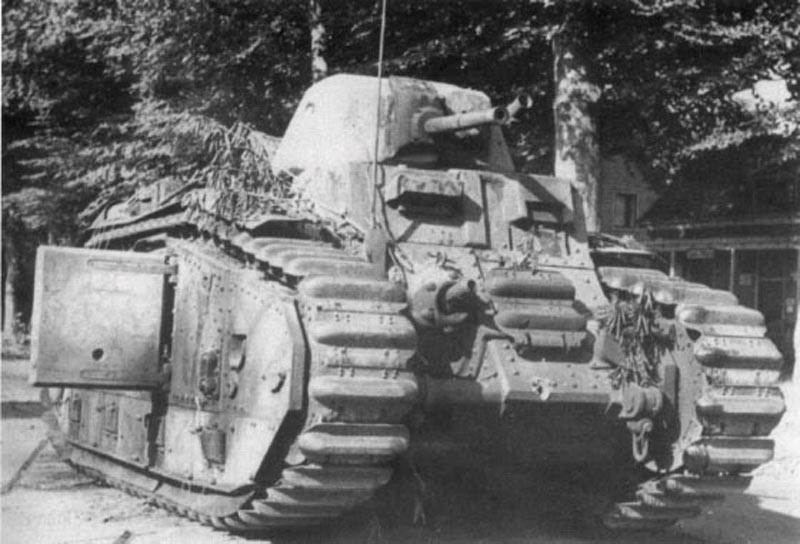

Flamethrower tank in the army. Photo Mg-tank.ru
Another noticeable improvement touched the aft hull. On the stern sheet it was proposed to mount a tank of complex shape, assembled from armor plates with a thickness of 30 mm. The tank for the fire mixture of sufficient capacity could not be placed inside the hull, which is why it was taken out to the stern of the car. This arrangement of the tank had some advantages. Thus, the tank hull could protect the container from firing from the front hemisphere, and with the defeat of the tank reduced the likelihood of fire of the machine itself.
The pneumatic system should ensure the supply of fire mixture from the tank to the fire engine and to the target. Inside the hull it was proposed to mount several compressed air cylinders used in firing. In addition, the tank received an additional two-stroke motorcycle engine associated with a compressor to supply air to the cylinders. According to others, the cylinders and the engine were used in various versions of the flamethrower. According to some sources, the early version of the flamethrower was supposed to emit a mixture of fires through compressed air, and the next modification was a compressor based on a gasoline engine.
The crew of the new flamethrower tank was to consist of four people. The driver and the radio operator, who controlled the flamethrower, were located in the building. Two more tankers were in the turret and could use an 47-mm cannon with a twin machine gun. All crew members had their own hatches and sets of viewing devices.

Shooting from a flamethrower. Photo Mg-tank.ru
Alterations of the base tank led to a slight change in its dimensions. Because of the feed tank, the length of the machine increased to 6,86 m. The width remained at the level of 2,5 m, height - 2,88 m. According to some reports, some of the serial flame thrower tanks were deprived of commander towers, which was done to reduce the overall height of the vehicle. The use of a large tank for transporting fire mixture and other new components led to an increase in the combat mass to 34 t.
Despite the increase in weight, the mobility characteristics should have remained the same. The maximum speed was limited to 28 km / h, the power reserve was 150 km. The parameters of obstacles to be overcome almost did not change.
By the autumn of 1941, the contracting companies completed the development of the entire project as a whole and its individual elements in particular. After the design was completed, the first batch of Flammwagen auf Pz.Kpfw flamethrower tanks was built. B2 (f) in the amount of five units. These machines with an updated composition of weapons came out of the assembly shop of the company Wegmann in November 41-th.
Tests revealed a fairly high potential of the new technology. Relatively powerful reservations allowed the flamethrower tank to be protected from various threats, and the 47-mm cannon in the turret ensured effective self-defense or attack of targets from a sufficiently long range. A flamethrower installed in the frontal sheet allowed to throw the fire mixture at a distance of up to 40-45 m. A full tank was enough for 200 shots. New development was approved, which allowed to continue upgrading the captured technology.
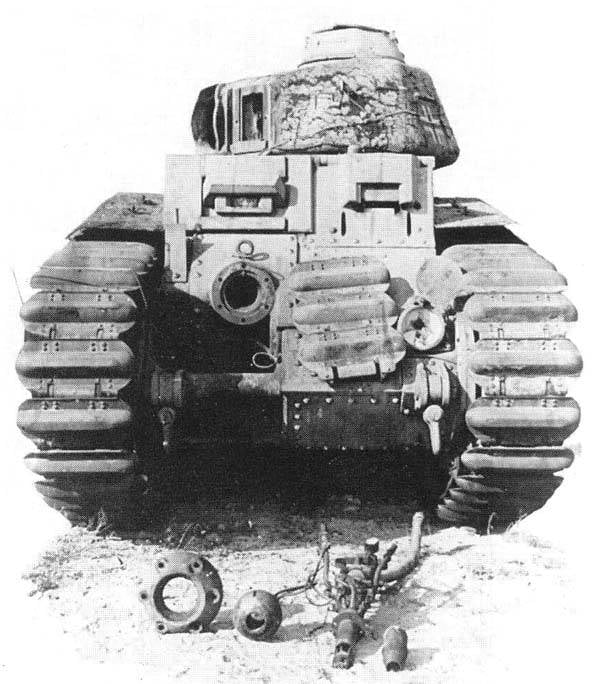
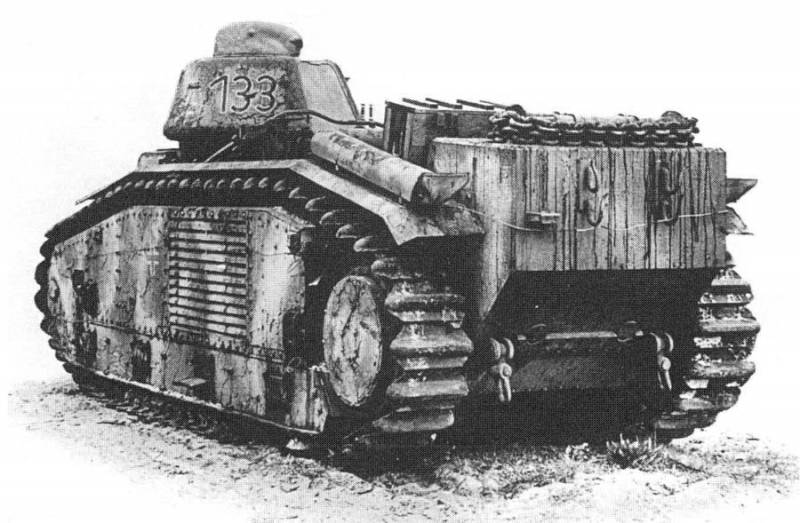
Tank with a flamethrower removed. Units last lie in front of the machine. Photo Aviarmor.net
The original plan involved building five flamethrower tanks in November 1941. In December and January, the industry had to deliver more 20 machines. At the same time, however, the order noted a possible decrease in production rates due to the lack of basic equipment. As practice has shown, the production of new tanks really could not immediately reach the required pace. In December, only three captured tanks managed to upgrade 41. Three more cars passed in March 1942 of the year. From April to March inclusively made nine more cars. In connection with the loading of Wegmann by other orders, the Flammwagen B2 (f) flamethrower tank assembly was transferred to French industry. The enterprises of occupied France transferred several dozen more heavy tanks with flame-throwing weapons to the customer. According to various sources, a total of flamethrowers received at least 60 tanks of French production.
Flame-retardant tanks of new type handed over to the troops were transferred to companies that were armed with basic B1bis with cannon armament. As part of such units flamethrower B2 (f) participated in various battles on different fronts. It is known about the participation of such technology in the assault of Sevastopol and in some other operations on the Eastern Front. In addition, about half of the flamethrower tanks managed to take part in the battles in Western Europe. Also, this technique participated in the battles on the territory of Yugoslavia.
By the time the assembly of new flamethrower tanks began, the base machine of the French design had become obsolete. As a consequence, the characteristics of the tanks Flammwagen auf Pz.Kpfw. B2 (f) over time, less and less met the requirements of time. However, the operation of such equipment lasted for a long time. Available information on the preservation of a certain number of such tanks in service at the end of the 1944 year suggests that several vehicles could even live to the end of the war in Europe.
However, a flamethrower modification of a heavy tank B1bis for objective reasons could not have a noticeable effect on the course of the war. During production, only 60 of such machines were built, which was extremely small for full-fledged combat use on all fronts. At the same time, within the framework of the project Flammwagen auf Pz.Kpfw. B2 (f) was able to successfully solve all the design problems posed, and also to find a worthy use of the obsolete trophy technique.
Based on:
http://armor.kiev.ua/
http://mg-tank.ru/
http://aviarmor.net/
Chamberlain P., Doyle H. Complete reference book of German tanks and self-propelled guns of the Second World War. - M .: AST: Astrel, 2008.
Ardashev A., Fedoseev S. Flamethrower tanks and hand-held flamethrowers in battle. - M .: Eksmo, Yauza, 2013.

Information