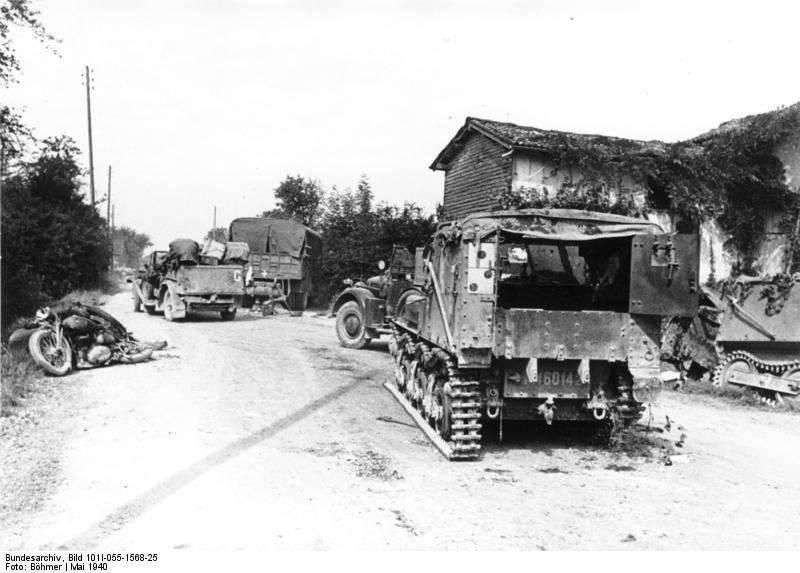
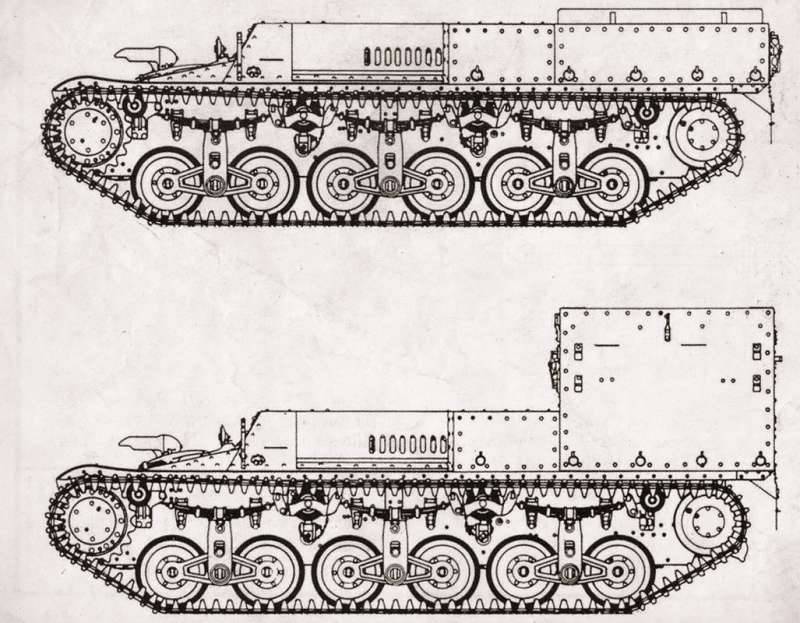
French armored personnel carriers Lorraine 37L and 38L
The crushing defeat of France in 1940 left the indelible seal of “defeatists” and “losers” on the armed forces of this country of that period. And if we talk about French military equipment, then it should be noted that there are widespread opinions about “complexity of construction”, “single towers”, “short-barreled guns”, “dispersion” tanks" etc. All this really was, but with a careful examination, you can see that in the mid-1930s in France, nevertheless, it was possible to create several advanced models of military equipment. And Lorraine 37L / 38L armored personnel carriers could be attributed to the best in their class precisely in the initial period of World War II, when the German armored personnel carriers Ganomag were not yet so massive.
The decision to create an armored tracked vehicle for the transport of infantry and cargo was taken by the French army command at the end of 1936. He was called to replace the Renault UE armored personnel carrier. In accordance with the issued tactical and technical tasks, the combat vehicle should not have been heavier than 2600 kg and able to transport at least 500 kg of cargo in the cargo hold and to 1000 kg - in the trailer. Own projects for the issued requirements in 1936-1937 developed 5 French companies. First coped with the task in the company Lorraine de Dietrich, which previously specialized in the production of locomotives. Already 23 on April 1937, the specialists of this company presented to the military a prototype of the Lorraine 37 armored personnel carrier (which in the future was called the “short version”). Already on 16 on April 1937, the military announced a new competition for the development of an armored tracked carrier designed for the carriage of goods in tank units.

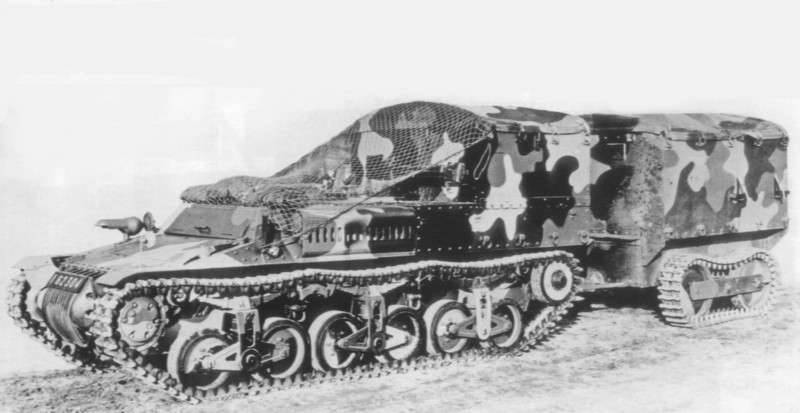
Since the Lorraine 37 conveyor initially laid a significant reserve for further modernization, its designers were able to quickly develop a new model, the Lorraine 37L (it became known as the “long version”). The undercarriage of the “short” model of an armored personnel carrier consisted of two trucks with two rollers on each side, and the undercarriage of the “long” model consisted of three trucks with two rollers on each side. So the specialists of Lorraine presented two prototypes to the competition at once, which were unified among themselves, such a move was also an indisputable competitive advantage.
Despite the somewhat angular appearance, the design of the armored personnel carrier was quite successful. The riveted body was made of armor plates with a thickness from 9 to 12 mm. In front of the vehicle there was a control compartment, and the cargo landing compartment, which most resembled a box-shaped cabin without a roof, was located in the rear of the hull. The open cargo compartment provided a load capacity at the level of 800 kg, but when used together with the conveyor of a specially designed trailer, the load capacity increased to 1900 kg.
On the armored personnel carrier, the carburetor 6 X-cylinder engine Dela Naye 103 TT was installed with a displacement of 2130 cubic centimeters, which developed the power of the 70 hp. at 2700 rpm. The engine was located almost exactly in the middle of the conveyor housing. The transmission used was mechanical and consisted of a five-speed gearbox and a lockable Cletrac differential. The conveyor's running gear (applied to one side) consisted of 6 track rollers, which were pairwise interlocked into three carriages with shock absorption from leaf springs and a vertical block with a spring on each of the carriages, three supporting rollers and a driving wheel located in front. The fuel tank capacity in 144 liters was enough for 140 km of travel on the highway. At the same time, armored personnel carriers were distinguished by good tactical and technical characteristics: strong undercarriage, sufficient maneuverability, and effective anti-bullet protection. Armament was not installed on them, but later the French were going to put on them 7,5-mm machine gun. The lack of a lack of armament on the transporters was "corrected" in the future by the Germans.

The first stage of testing a new combat vehicle started on 28 on April 1937 of the year and lasted until 10 June. After testing, the armored personnel carrier was returned to the factory, where the identified deficiencies of the vehicle were eliminated. Although the mass of the resulting conveyor was almost twice as high as originally set by the military, the army commission in Vincennes came to terms with this, realizing that it is impossible to create a conveyor of the required carrying capacity without increasing its own weight. The second stage of testing, which lasted from 8 to 23 in August, was actually already an acceptance test. 25 August prototype Lorraine 37L handed over to the infantry commission in Mormelon to evaluate the tactical qualities of the new machine. At the end of 1937, both submitted to the military version were finally adopted.
From this point on, the service of the Lorraine family of armored personnel carriers began, first in the French army and then in the Wehrmacht. It should be noted that only armored personnel carriers of the “long” version carried the service. The French military quickly realized that it was better to abandon the use of two unified transporters in favor of a single machine. In this case, the order for the release of 100 armored personnel carriers in the "short" version was canceled. Despite the limited period of mass production (1938-1940), the armored personnel carrier had time to release in four major versions.
The first Lorraine 37L armored personnel carriers began to enter the French tank units only at the end of the 1939 year. Although they originally planned to replace the Renault UE, the actual all Lorains were used with them, adding to the existing fleet. For example, the 12 armored personnel carriers 37L relied on a separate tank battalion according to the state, on the battalion of heavy tanks B1 - 18 of such vehicles, and on the squadron of cavalry tanks S-35 or H-3, three transporters. Before the start of the Nazi invasion, it was not possible to complete the acquisition of French tank units. However, during the active phase of the fighting in May-June, the 1940 of the Lorraine was used by three French armored divisions (1, 2, and 3-DCR), most light mechanized divisions (DLM), as well as individual tank battalions.
The Lorraine 37L armored personnel carriers from armored divisions and mechanized units were actively used in the spring of 1940 during the battle for France to provide and supply armored units. In the first place, they were intended to supply tank units in the breakthroughs. Driving along the highway at speeds up to 37 km / h and towing fuel tanks, the Lorraine 37L had to supply the tanks and fuel that had gone into the offensive and ammunition. Almost half of all vehicles of this modification was lost by the French during the May-June 1940 fighting.
Almost immediately after the adoption of the Lorine armored personnel carrier, they began to produce a modification intended for the transport of motorized infantry - Lorraine 38L. The body of this machine has been significantly redone. It has increased in height for a more comfortable accommodation for the crew and the landing troops. In addition, the trailer, which was specially adapted for the transport of soldiers, was modified. Such machines were assembled 100 pieces.
The next modification was an armored personnel carrier Lorraine 38L VBCP (Voiture Blindee de chasseurs Portes), which could carry up to 6 soldiers or 1000 kg of cargo in the cargo-landing compartment, 4 soldiers could be additionally placed in the trailer. The weight of this machine has grown to 5460 kg. This modification was mainly used for towing an 25-mm anti-tank gun and 81-mm mortar and transporting them. In total, 130 armored personnel carriers of this modification were assembled, and from March 1940 began to enter service with the 5 and 17 battalions of motorized infantry from the 1 and 2 armored divisions (48 vehicles in each battalion). In May of the same year, the 20 battalion of the 16 Armored Infantry received the 3 battalion of such armored personnel carriers.
Lorraine 38L RS became the last serial modification of the car, which they managed to produce in France before its occupation by the Germans. It was the commander version of the armored personnel carrier, which was intended for commanders of tank companies, battalions and divisions. The car was released in a very limited edition - only 10 units. Depending on the control level, the transporters were equipped with an ER-55 radio station (company / battalion) or ER-51 and a TM32 phone (division). Thus, all in France before its occupation by the Germans, the 618 Lorraine armored personnel carriers were launched: 378 vehicles in the 37L version, 100 in the 38L version, 130 - 38L VBCP and 10 - 38L PC.
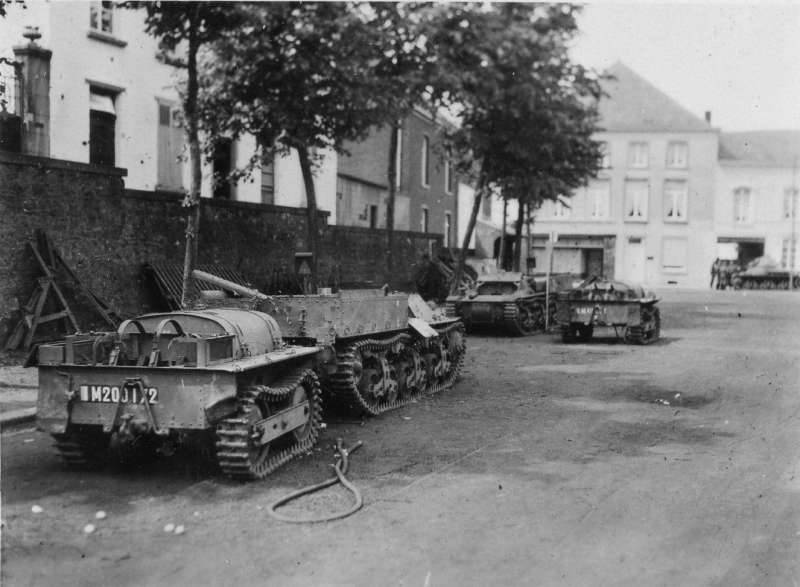
The defeat of France was a real catastrophe, especially for its army, which suffered heavy material and human losses, which could not be compensated for. Most of the remaining conveyors on the move Lorraine as trophies went to the Germans, who first used these machines for their intended purpose. However, after the start of the war against the Soviet Union, the Germans began to feel an acute shortage of mobile anti-tank weapons and mobile artillery. From July to August 1942, all on-the-go Lorraine 37L and Lorraine 38L armored personnel carriers that were in the possession of the Wehrmacht were converted into self-propelled units using the original chassis and hull booking elements. Alterations were carried out at the Alfred Becker plant in Krefeld. So in stories French armored personnel carriers opened a completely new page.
Of the 330 trophy "Loreins" that were in the Wehrmacht, 179 was converted into PT-ACS with 75-mm gun (Sd.Kfz.135 or "Marder I"), 94 in SAU with 150-mm leFH13 (DFX) helmet (SdUMX) .135 / 1) and 12 in ACS with XFUMX mm howitzer leFH105. In addition, 18 transporters became the machines of artillery observers, and several were converted into conveyors ammunition and equipment Munitionstransportkraftwagen auf Lorraine Schlepper. Although as part of the modernization, the mass of cars increased almost twice, the main characteristics of the self-propelled guns remained at the level of the original models, which once again proved the reliability and the safety factor of the French cars.
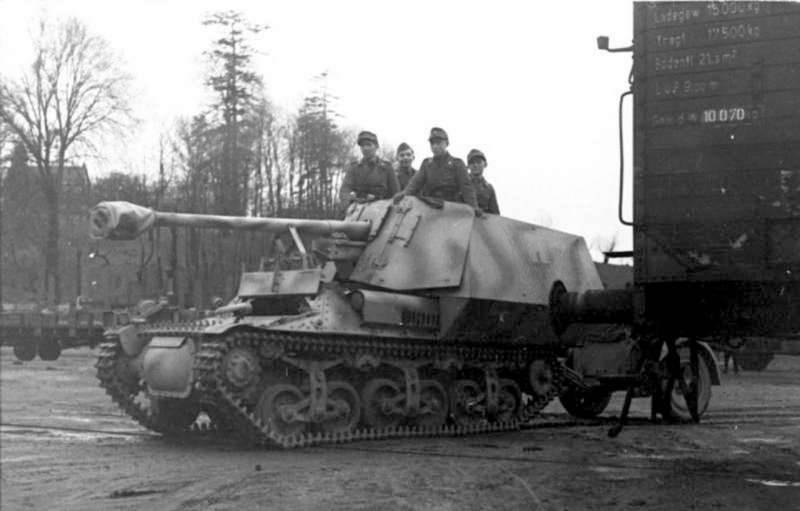
All self-propelled artillery mounts created by the Germans based on the French Lorraine armored personnel carriers were structurally similar to each other and differed by the type of artillery systems installed in the box-shaped armored hull which was located at the rear of the hull. So on the Marder I anti-tank self-propelled gun, armor plates with a thickness from 5 to 12 mm were located at small angles of inclination. The main weapon was selected 75-mm anti-tank gun 7,5 cm Pak40 / 1 L / 46, which was equipped with an optical sight ZF 3x8. Vertically, the gun was induced in the range from -5 to + 22 degrees, horizontally - 64 degrees. To protect against enemy infantry on self-propelled guns installed 7,92-mm MG34 machine gun. Full mobile ammunition consisted of 40 shots to the gun and 600 cartridges for machine guns.
Although the mass of such a PT-ACS has grown to 8 tons, it did not have a critical impact on the maneuverability of the vehicle. The self-propelled crew consisted of a 5 man (driver, commander, gunner, loader and radio operator). The presence of a radio operator in the crew, who served the FuG5 radio station, was a kind of visiting card of armored vehicles of Germany, while in the armies of the anti-Hitler coalition countries the functions of a radio operator in the crew were often performed by the commander. Mainly, Marder I anti-tank self-propelled guns were used by German anti-tank units on the Western Front. In France at the time of the Allied landings there in June 1944, there was 131 such PT-ACS. All of them took an active part in the battles in Normandy.
Self-propelled artillery mounts at the Lorain base repeated the anti-tank variant, with the exception that they were equipped with more powerful artillery weapons - 10,5 cm leFH 18 / 4 and 15 cm sFH 13 / 1. The need for the Wehrmacht to increase the mobility of its heavy field artillery units became the impetus for the appearance of these machines. In a single copy, the Germans also experienced a pilot modification of the 12.2cm Kanone (r) auf Geschutzwagen Lorraine (f). On this machine, they installed the captured Soviet howitzer M-30. Unfortunately, nothing is known about the testing of this combat vehicle, as well as its possible use in combat. However, there are references to the fact that in the summer of 1944, she was used at the front as an ACS support during the fighting in France, and in September of the same year she was captured in Burgundy on an armored train abandoned by the Germans.
At the same time, ACS based on Lorraine armored personnel carriers armed with 150-mm guns were actively used by the Germans in North Africa as part of the 21 Panzer Division, as well as for training purposes in France. After the start of the landing of the Allied troops in Normandy, these machines from training units began to be actively used in battles with them. One surviving self-propelled gun of this type is today on display at the museum of the Aberdeen testing ground of the American army.
Information sources:
http://www.aviarmor.net/tww2/tanks/france/lorraine_37.htm
http://alternathistory.com/osnovnoi-btr-frantsuzskogo-gosudarstva-lorraine-37l38l39l41l
http://bronetehnika.dljatebja.ru/Bronemashiny/Lorraine_37l.html
http://warspot.ru/1753-ot-frantsuzskogo-bronetransportera-do-nemetskoy-sau




Information