In the burning hut entered ...
The Great Patriotic War of 1941-1945 took the lives of millions of citizens of the Soviet Union: men, women, old people and children. She changed the way of everyday life, demanded the mobilization of human and material resources of the country. Not only men stood up to protect their family and honor, but also women, on whose fragile shoulders lay the burden of hardship, loss and adversity.
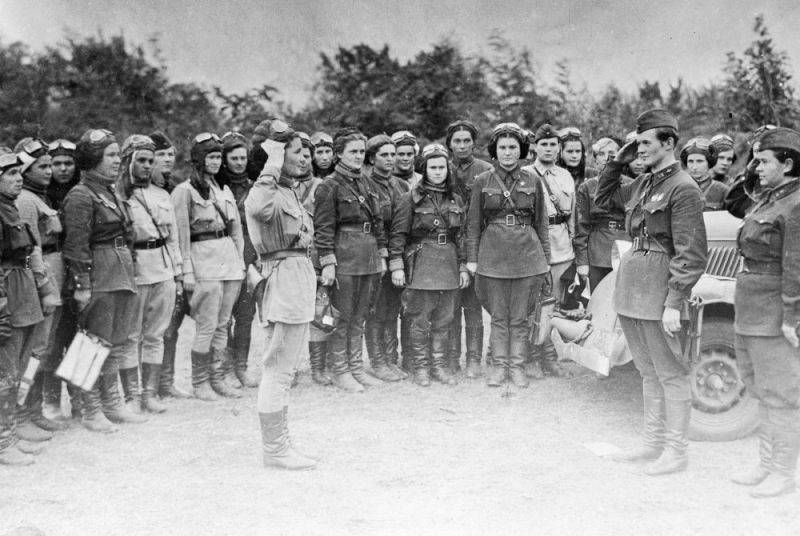
It so happened that the Soviet Union was the only country during the Second World War, where women were directly involved in hostilities. Of course, on the one hand, this is connected with the colossal loss of life during the war yearsNUMX, and on the other hand, with the incredible spiritual impulse of the women of the USSR who voluntarily went to the army, they insistently sought to be sent to the front. Women replenished the people's militia and partisan detachments, replaced men for service in the air defense forces, on military roads, in the Navy and Air Forces, in the communications troops. Working in enterprises, they mastered the hardest male professions in the rear, engaged in evacuated children, fought for the lives of soldiers in military hospitals and on the battlefield.
It was during the Great Patriotic War that women's military formations first appeared in the Armed Forces of our country2. On the basis of decrees of the State Defense Committee (GKO), formed on June 30, 1941, in 1942 alone, three mass mobilizations of women were carried out. The first mobilization, according to the decree of the State Defense Committee of the USSR of March 25, 1942, sent 100 Komsomol girls to the country's air defense to replace Red Army telephone operators, radio operators, reconnaissance air observers of anti-aircraft artillery and other male military positions (doc. 000). The second mobilization on April 1, 15 sent 1942 women to the front to serve in the signal troops. Women replaced male morzists, field post workers, forwarding agents, telegraph technicians, clerks, draftsmen, clerks, orderlies (doc. N 30). However, less than a week later, by a decree of the State Defense Committee of the USSR of April 000, 2, the third mobilization of women for the defense of the country and the replacement of male military personnel in the country's Air Force was announced18. This time, 1942 women were sent to the posts of specialists in the administrative and economic service (warehouse managers, drivers, tractor drivers, cooks, storekeepers, bookkeepers), as well as to the signal troops, complementing the previous call. Some of the mobilized women were subject to training and sent to the front after 3-40 months, the other part, distributed to service units, was sent immediately after the call. The liberated men, first of all, replaced the losses of the front: they were transferred to staffing rifle divisions and rifle brigades withdrawn from the front (document No. 000), ground and aviation units of the active army4, replaced the dead with living ones.
Women's mobilization was not "blind." If in respect of men, “they cast nets” and called for almost everyone, then there were restrictions for women. Taking into account the age of girls (from 18 to 25 years), their education (not lower than 5-7 classes, but with the obligatory condition of having complete secondary education in 40% of the total number mobilized) and how happened in the last female mobilization, absence of children and family.
1943 and 1944 war years are not marked by such a significant number of mobilized women, as it was in 1942: after all, the battle for Moscow and Stalingrad are behind. The next mobilization took place in October 1943 in the Udmurt, Kabardino-Balkarian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics and in eight more regions of the Soviet Union. 4200 women aged from 18 to 45 years (doc. N 3) were called up to work at the central artillery bases and warehouses of the USSR. Nevertheless, the need to recruit posts for cooks, laundresses, signalers and paramedics of the Air Defense Forces and the Main Administrations of the USSR People’s Commissariat of Defense demanded that the last one be mobilized by the female population of the country. The local city and regional committees of the CPSU (b) and the executive committees of the Soviets of Workers' Deputies voluntarily called 25 000 women aged from 20 to 35 years without children and not burdened with family. This decision is reflected in the memorandum of the USSR People's Commissariat of Defense I.V. Stalin and the resolution of the GKO USSR on May 16 1944 of the year (dc. N 4,5)
There is no exact number of women participating in the fight against fascism during World War II. As N.K. Petrova, at the front in different periods, fought from 600 thousand to 1 million women 5. Of course, not all of them were directly involved in hostilities, but, as published documents show, the scope of the activities of mobilized women was infinitely diverse.
For feats during the Great Patriotic War, around 100 women were awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union, but, unfortunately, most of them posthumously ... However, we should not forget about women partisans and underground fighters, about women-doctors, pilots, snipers and about those who did not accomplish the feat and did not receive a great reward, but passed this war and contributed to the victory of the Soviet people.
Published documents and photographs are stored in RGASPI in the fund of the USSR State Defense Committee (F. 644. Op. 2), in the fund of the Central Headquarters of the Partisan Movement at the Headquarters of the Supreme High Command (F. 69. Op. 1). Documents are reproduced while preserving the stylistic features of the sources, in compliance with generally accepted rules of spelling and punctuation. Identified typos corrected and not specified.
The publication was prepared by leading expert RGASPI Zoya Vishnyakova.

N 1. Draft Resolution of the State Defense Committee of the USSR N 1488 "On the Mobilization of Young Komsomol Girls in the Air Defense Part" dated March 25 from 1942
* ind. N 1 * 6
RESOLUTION * N 1488 ss * 7
STATE COMMITTEE OF DEFENSE * UNION SSR * 8
"25" March 1942 year of the mountains. Moscow
On the mobilization of female Komsomol in air defense
In order to make the most appropriate use of trained contingents and to strengthen the existing army, the State Defense Committee
DECIDES:
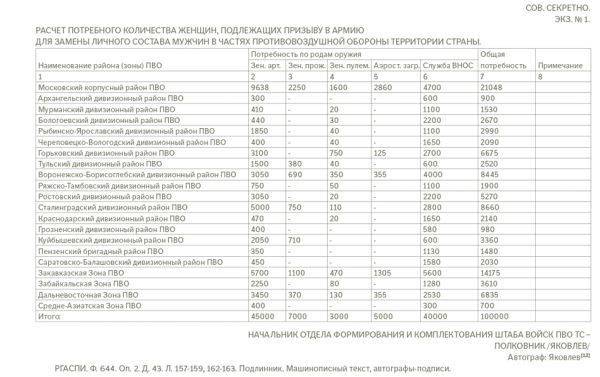
1. Replace the troops of air defense of the country 100.000 Red women to fill positions: telephone operators, radio operators, instrument operators anti-aircraft artillery, reconnaissance observer for air flak and fasts air warning service, some rooms searchlight stations, anti-aircraft guns, and barrage balloons, and various specialists departments service.
2. * To ask the Central Committee of the CPSU (b) * 9 * to oblige * the 10 Central Committee of the VLKSM to mobilize 10.4 X-NUMX-1942 female XMNUMX X-age girls with full secondary education and the rest no lower than 100.000-19 classes.
Mobilization to be done on a regional basis in accordance with the application of the Commander of the Air Defense Forces of the territory of the country.
3. Mobilized female Komsomol to send to replace the Red Army in the air defense forces of the country:
a / in anti-aircraft artillery- 45.000;
b / in anti-aircraft machine gun parts- 3.000;
In / in anti-aircraft searchlight parts- 7.000;
g / in parts of balloons
air barrage- 5.000;
d / in the part of the service VNOS-40.000.
4. Replacing the mobilized Komsomol girls of the Red Army men in the air defense forces of the country's territory in the following terms:
A / in service units - immediately after being called up;
b) specialists in anti-aircraft artillery units no later than six weeks after the conscription;
c / anti-aircraft parts — two months after the call;
d / balloon barrage specialists - one and a half months after the draft;
e / machine gunners - one and a half months after the call;
e / telephone observers of VNOS service posts - two months after the call.
5. The liberated Red Army soldiers, after replacing them with Komsomol girls, should be used to recruit infantry divisions and infantry brigades according to the plan of the Red Army Main Command.
6. Mobilized female Komsomol girls appointed to the positions of Red Army men who are part of the line-up units / gunners, machine-gunners, projectors, aerostats, communications men, contributors, scouts /, provide all kinds of allowance on an equal basis with the military and extend to them the effect of the decree of the Presidium of the USSR Supreme Council 26.6-1941 of the year and the resolution of the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR from 16.7-1940 of the year N 1269; appointed to the administrative and economic positions / clerk, clerk, storekeepers, cooks, paramedics, orderlies, San. instructor, tailors / contain as freelancers.
7. For the period of training in the air defense units of the mobilized female Komsomol members, highlight the 100.000 NGOs for one and a half months rations.
8. Oblige Comrade DRACHEVA in a month's time to make 90.000 uniforms for mobilized girls Komsomol.
DEFENSE COMMITTEE (I. STALIN)
Autograph: I. Stalin11
Edit I. V. Stalin

N 2. Resolution of the State Defense Committee of the USSR N 1595 "On the replacement in front-line, army and spare parts of communications and rear communications centers of the Red Army women by women" from April 13 1942 g.
copy N___
STATE DEFENSE COMMITTEE
RESOLUTION OF N GOKO - N 1595
From "13" April 1942.
Moscow, the Kremlin.
On the replacement of frontline, army, and spare parts of communications and rear communications centers of the Red Army women
In order to make the most appropriate use of trained contingents to strengthen the combat units of the existing Army, the State Defense Committee DECIDES:
1. Replace in front-line, army and spare parts of communications and rear communications centers 30.000 man of the Red Army women for the posts:
a) bodiste, estista, morzist, telephonists, radio operators, telegraph technicians, telephone and telegraph masters, radio masters, film radio mechanics, field mail workers and freight forwarders;
b) draftsmen, clerks, clerks, paramedics, sanitary instructors, medical assistants, administrative staff and various specialists of the service departments.
2. * Require t.t. SCHEVERNIKA and MOSKATOVA mobilize between 15 April and 1 May 1942 of the year 30.000 communications women between 19 and 25 years, including: * [13]
a) 24.144 women with education not lower than 7 classes of secondary schools for the training of specialists indicated in paragraph 1- "a" of this resolution;
b) 5.856 women to fill the positions specified in paragraph 1- "b" of this resolution.
The mobilization should be done on a regional basis, in terms of the application of the Chief of the Main Communications Directorate of the Spacecraft.
3. The liberated Red Army signalmen of the front army signal units after replacing them with women should be used primarily for staffing and replenishment of signalmen of rifle divisions and rifle brigades, artillery, tank and mortar units at the front. The communications specialists who remained in surplus should be used to staff the communications units withdrawn from the front of rifle divisions and rifle brigades according to the plan of the Glavupraform.
4. Mobilized women appointed by the Red Army in the units and establishments of communications and field mail located in the current Army, as well as communications specialists who are part of the crew calculations of communications units and universities, provide all types of allowances on an equal basis with military personnel and extend to them the Decree of the Presidium Supreme Council of the USSR of 26.6.41, and the Resolution of the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR from 16.7.40, N N 1269.
5. To oblige the Chief of the Main Communications Directorate of Comrade. PERESYPKINA in the period from April 25 to September 1, replace:
a) to 1-th of May this year. in the communications troops at the front and in the rear, serving the composition of men in the number of 5.856 people;
b) to the 1 of June this year. - 2042 telephonist, 920 forwarders of telegraph stations, 1000 seniors and 500 junior receivers of field postal stations and bases - all 4.462 people;
c) to July 1, c / g - 6.595 Morse telegraph operators and 1.050 junior receivers of field post stations and bases, in total - 7.645 people;
d) to 1 August august - 3.000 telegraphist-estists, 250 chiefs and assistants of branches and 1.200 senior receivers of field post stations and bases, in total - 4.450 people;
e) to September 1, c / g - 5.315 radio operators, 500 radio masters, 872 bodiste and 1.100 technicians, film and radio mechanics, and telegraph, in total - 7.587 people.
Total for this period of time replace 30.000 people.
6. For the period of study in the communications units of mobilized women, highlight the NK0 24.000 monthly rations, of which: for the month of May - 11.910, for June - 7.250, for July - 3.820 and for August - 1.020.
7. To instruct the chief quartermaster of the Red Army (comrade Drachev) to "15" in May of this year to manufacture 30.000 outfit kits for women to be mobilized.
DEFENSE COMMITTEE I. STALIN
Autographs: I. Stalin 14, E. Schadenko,
I. Peresypkin15
Mailing address: Schadenko, Peresypkin, Shaposhnikov, Shvernik, Mosk [t] ov, Mikoyan, Pavlov, Drachev.
RGASPI. F. 644. Op. 2. D. 51. L. 105-107. Script. Typewritten text, autograph-signature.
N 3. Order of the State Defense Committee of the USSR N 4239 on the mobilization of women and persons liable for military service who are not suitable for service in the Red Army to work in the central artillery bases and warehouses from 5 in October 1943.
STATE DEFENSE COMMITTEE
DISPOSAL N 4239
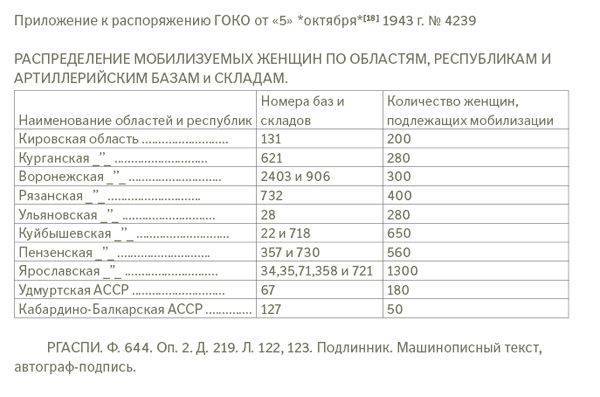
1. To oblige the Committee for Accounting and Distribution of Labor at the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR, Kirov, Kurgan, Voronezh, Ryazan, Ulyanovsk, Kuibyshev, Penza, Yaroslavl Regional Executive Committees, Council of People's Commissars of the Udmurt and Kabardino-Balkarian ASSR to mobilize in the period from 15, in order to participate in the program for the Udmurt and Kabardino-Balkar ASSR urban unemployed and rural population of 15 women aged from 1943 to 4200 years to work in central artillery bases and warehouses, according to the annex.
2. Allow NGOs (comrades Smorodinov) to mobilize 1943 2000 in October from among those who are required to serve in the Red Army but are suitable for work in central artillery bases and warehouses.
Defense Committee (V. Molotov)
Autograph: V. Molotov17
Resolution: "No objection
28.9.43 Currants "

N 4. Draft decree of the GKO USSR N 5907 "On the recruitment of 25 000 women volunteers" from 16 May 1944.
Ex. N 2.
* PROJECT * 19
STATE DEFENSE COMMITTEE
RESOLUTION N GFCS - 5907
About the recruitment of 25.000 women volunteers
The State Defense Committee DECIDES:
1. Allow NGOs (Chief of the Glavupraforma Red Army SMORODINOVA) to voluntarily urge through the local city and regional committees of the CPSU (b) and the executive committees of the Soviets of Workers' Deputies 25.000 women aged from 20 to 35 years.
Called women to send in the part of the Red Army for the staffing of cooks, laundresses, signalers and nurses.
The call to hold in cities and large settlements of regions, territories and republics, according to the attached calculation, from among women who have no children and are not burdened with family.
2. Called women should be provided with all kinds of allowances on a par with military personnel, extending them to the effect of the Decree of the Presidium of the USSR Supreme Council of June 26 on June 1941 and the resolution of the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR on 16 of July 1940 of N 1269.
CHAIRMAN OF THE STATE
DEFENSE COMMITTEE - I. STALIN.
Autograph: I. Stalin20
RGASPI. F. 644. Op. 2. D. 335. L. 11. Script. Typewritten text, autograph-signature.

N 5. Report of the People's Commissariat of Defense to the People’s Commissar of Defense Marshal I.V. Stalin on the mobilization of women from 16 in May 1944.
Ex. N 1.
PEOPLE'S COMMISSAR DEFENSE
MARSHAL OF THE SOVIET UNION
comrade STALIN.
From the current front lines of the Air Defense Forces and the content of the Main Directorate of NPOs, petitions are received to send women to fill the positions of cooks, laundresses, signalers and paramedics.
At present, there are radio operators, telegraph operators, telephone operators and nurses - 176.000 women, aged from 18 to 35, trained in Vsevobuch, Osoaviakhim and Red Cross.
Thus, it is possible to appeal to women to meet the needs of the front and air defense.
In this regard, * we ask you to allow voluntarily to summon 25.000 women in the Red Army from 20 to 35 years who have no children and are not burdened with 21 family.
The number of women to be mobilized by regions was agreed with the secretaries of the respective regional committees.
Notes
1. In total, Soviet losses in World War II amounted to 26 600 000 people. (40% of all victims).
2. See: N. Petrova Women of World War II. M., 2014. C. 5.
3. From the draft resolution of the State Defense Committee of the USSR N 1618 "On the replacement in the rear units and establishments of the Air Force of the Spacecraft for men of military men by women" dated April 18 from 1942 // RGASPI F. 644. Op. 2. D. 53. L. 106-108.
4. Ibid. L. 107.
5. See: N. Petrova Decree. cit. C. 4.
6. The text is crossed out with a black pencil.
7. The text is crossed out with a black pencil.
8. The text is crossed out with a black pencil.
9. The text is crossed out in red pencil.
10. The word is corrected with a capital letter in red pencil.
11. Autograph red pencil.
12. Autographed in green pencil.
13. The paragraph is marked with a green pencil on the left.
14. Autograph in black pencil.
15. Autographs with a blue pen.
16. "September" corrected to "October" in black pencil.
17. Autograph blue pencil.
18. "September" corrected to "October" in black pencil.
19. The text is crossed out with a blue pencil.
20. Autograph red pencil.
21. The text is underlined in red pencil.
22. The date is indicated in blue pencil at the bottom of the text.
23. Autograph in black pencil.
24. Autograph blue pencil.
25. Autograph blue pen.

Information