Four-engine turboprop deck aircraft (Patent RF № 2402459) TANTK them. Beriev, 2009
The present invention relates to aeronautical engineering, in particular to naval aviation, and is intended for use with a heavy aircraft carrier cruiser (TAKR) for solving various tasks on the maritime theater of military operations (MTVD). Decker aircraft can be performed for the tasks of long-range radar patrol and guidance (ASDF), anti-submarine defense (ASR) and for other tasks.
To ensure the take-off of aircraft from the deck, all aircraft carriers of the United States and other countries of the world [1] are equipped with launching catapults. Domestic carrier-based aviation (PA) is based on the Admiral Kuznetsov [2] type TAKR, which do not have launching catapults, therefore only heavy-thrust aircraft, such as fighters and attack aircraft, can take off from the deck equipped with springboard. The maximum available runway on the TAKR deck is no more than 200 meters, from which it is necessary to ensure both normal take-off and take-off with engine failure during the takeoff run. Therefore, the TAKR does not have airplanes of other assignments other than the above and helicopters that partially perform various tasks.
For the analogue adopted deck fighter Su-33 [3], based on the deck and in the hangar TAKR "Admiral Kuznetsova". The aircraft contains a fuselage, swept wing, twin-engine jet propulsion system, two-tail fin, chassis and landing gear. Having a high thrust, he takes off from a short deck TAKR without accelerating catapult and even with the failure of one engine can continue to take off.
The disadvantages of this aircraft are the significant fuel consumption of the power plant and the inability of the aircraft to be in flight for a long time, performing the functions of patrolling or performing anti-submarine operations, since its fuel reserves are limited and allow only one or two visits to the target to destroy it. The increase in fuel capacity is impossible due to the limited size of the fuel tanks and restrictions on the take-off weight of the aircraft.
Thus, there is no aircraft on the deck of the TACR that could be in flight for a long time, performing the functions of the RLDN or PLO.
The closest technical solution chosen as the prototype is the USA HUKAY E-2D [4] carrier-based carrier aircraft containing the fuselage, the wing folded down on the deck, 4's keel tail assembly, two-engine powerplant, movable antenna radome with pylon, landing gear and landing gear. The wing of the aircraft and its mechanization are partially located in the area of blowing screws. The plane takes off from the deck, equipped with a starting catapult, at the start the plane is hooked on the front landing gear support to the catapult, and when the engines start to take-off mode, the catapult accelerates the plane to take-off speed at which even if one engine fails, the aircraft can continue flying on one engine.
The marked prototype without launching catapults cannot take off from the deck of an aircraft carrier.
Starting catapults are bulky, expensive and complex devices that require constant performance. Even a single failure case during the take-off phase leads to a plane crash. Moreover, the existing TAKR in Russia is not equipped with such catapults, and there are not even prospects for equipping such catapults.
The task of the invention is to reduce the take-off distance of the aircraft to 200 m, ensuring the safety and reliability of the aircraft, replenishing the PA fleet with an airplane with economical fuel consumption, capable of performing the tasks of XRDNS or PLO for a long time and taking off from the deck, equipped with a springboard without a starting catapult, only by thrust propulsion engines.
The technical result is achieved by the fact that the deck aircraft is equipped with four fuel-efficient TVD-type engines located along the wing span in such a way that the wing and its mechanization, as well as the ailerons, are located in the zone of propellers blowing.
The essence of the invention is illustrated by a brief description and the accompanying drawings, where:
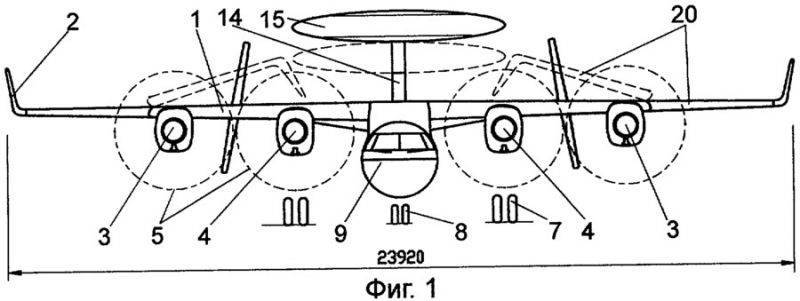
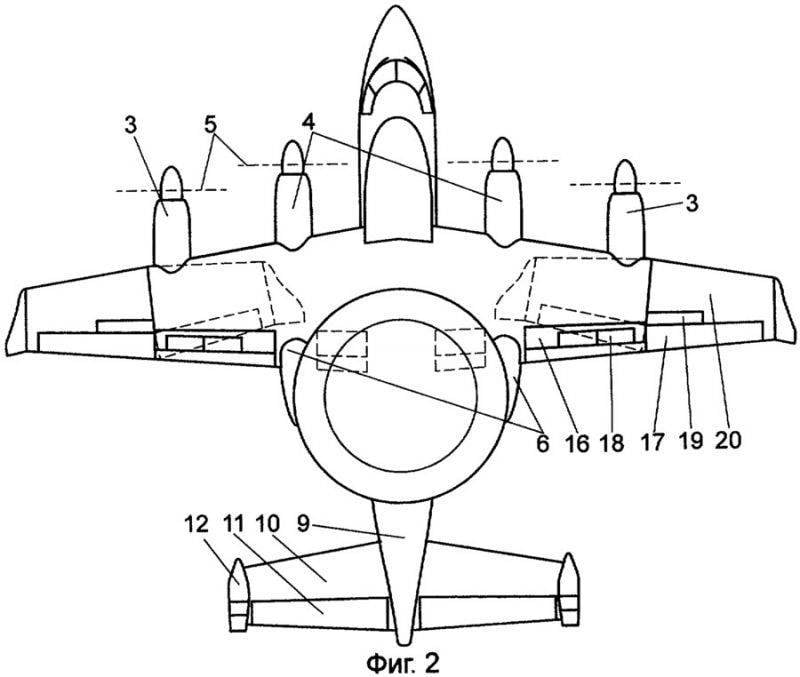
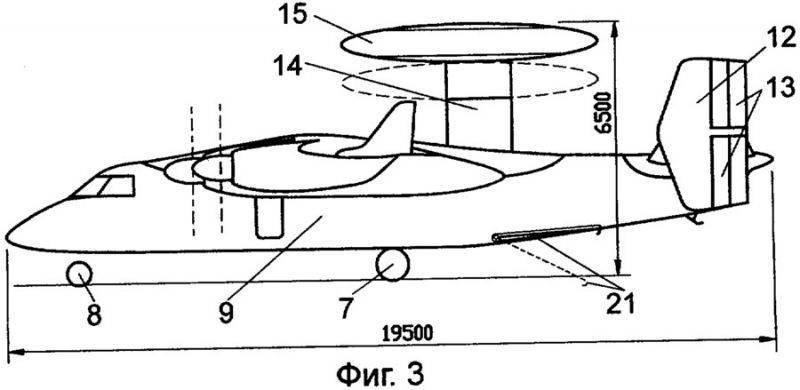
The deck aircraft shown in the drawings (Fig.1-3), is a DRLO aircraft. The plane is made according to the “high-plane” scheme with a trapezoidal 1 wing in plan, at the ends of which 2 tips are installed, increasing the aerodynamic quality of the aircraft and contributing to an increase in the duration and range of the flight, rotated at a small angle from the vertical plane and increasing its effective elongation without a significant increase in span. At the front of the 1 wing are the external 3 engines and the internal 4 engines, such as theaters with 5 propellers. Engines of this type are very economical in terms of fuel consumption. Behind the internal 4 engines, 6 radomes are fitted into which the main legs of the 7 wheels retract; 8 nasal wheels retract into the 9 fuselage, round section. Such a cross section of the fuselage allows the design to favorably perceive the loads from overpressure inside the cabin when flying at high altitude, which is necessary to increase the target detection range. In the upper tail section of the 9 fuselage, there is a horizontal 10 empennage, equipped with 11 elevators, and at the ends of which there is a two-fin 12 vertical plumage with two-section 13 rudders.
At the top of the 9 fuselage on the 14 telescopic pylon is the 15 fairing, which serves to accommodate the target equipment. The 1 wing is mechanized and contains 16 twin-slot flaps, 17 ailerons hanging, 18 brake flaps and 19 interceptors. The 20 consoles of the 1 wing, together with the 2 tips, ailerons 17, are made with rotating-swiveling, in order to reduce the size of the aircraft when lowering it on the lift through the limited size hatch in the TAKR hangar, as well as to reduce the footprint while on the deck and in the hangar . In the lower part of the 9 fuselage, the 21 mobile-swiveling hook is installed, which ensures that the landing rope is grabbed at the landing of the aircraft on the deck.
The installation of fuel-efficient 4-type TVD 3,4 engines provides the aircraft with increased thrust-to-weight ratio, directly affecting the length of the takeoff run of the aircraft, as well as the possibility of a long flight. Wing mechanization - 16 flaps and hovering ailerons 17 are located in the blowing zone of 5 propellers, thereby further increasing the wing lift force (Su), which significantly reduces the takeoff run. With the failure of one engine, the plane loses only a quarter of thrust, but the symmetry in the wing blowing is broken, leading to the appearance of unbalanced forces and moments. To eliminate asymmetry in the wing lift and parry the moments that occur in the track and transverse channels on the plane, an automatic balancing system is used due to the speed of the ailerons, rudder and spoilers to disrupt the lift force on the wing section symmetrical to the failed engine. The remaining effect of the wing blowing, taking into account balancing losses, is approximately 50% of the effect of blowing the wing without engine failure. Placing the aileron 17 in the 5 propeller blowing zone allows for the take-off of an aircraft, if one engine fails, to maintain the aircraft’s lateral controllability.
These distinguishing features ensure the safety of the take-off of the aircraft from the deck of the TAKR equipped with a springboard, as well as increase the transverse and ground controllability of the aircraft.
Before the take-off of the aircraft at the place of its placement, all engines of the power plant are launched on the deck, and the aircraft is taxiing to the starting position with the consoles folded. Then the consoles and wing mechanization are set in the take-off position, and on the “Take-off” aircraft engine mode, the aircraft can take off.
Aerodynamic calculations were carried out with four TVD engines, or rather, with TV7-117CT. The maximum allowable take-off weight of the aircraft, taking into account the take-off with one failed engine during the takeoff run, is 28 tons. The patrol time at a height at a distance from the 400 TAKR kilometers is at least 7 hours. The operation of the engines in the takeoff mode allows for the failure of one engine to continue to take off the aircraft from the deck with the length of the runway in the 180-200 meter range.
Technical and economic efficiency is expressed in increasing the efficiency of use of an aircraft carrier group led by TAKR on MTVD, by illuminating air, surface and underwater conditions in a radius of about 1000 kilometers around the aircraft carrier group, as well as the ability to control and navigate the PA aircraft and cruise missiles on the target.
The proposed invention can be implemented on the existing technology of the materials used in aircraft, and the current level of development of antenna-feeder devices and the production of radio equipment.
Information