Tactical nuclear weapons in Europe
At the end of September, a number of publications appeared on the Military Review website devoted to the planned deployment of the American nuclear bombs B20-61 in Büchel 12 air base in Germany. This news, picked up by other world media, has published a German television channel ZDF.
It got to the point that this unconfirmed report by journalists of the ZDF channel was commented on by the press secretary of the President of the Russian Federation Dmitry Peskov. He stated literally the following: "This will require Russia to take appropriate counter-steps, countermeasures to restore this strategic balance and parity."
Let's try to figure out what kind of “imbalance” is being discussed, and what our country can oppose to this.
Since the attainment of the US nuclear monopoly, the atomic bomb has been viewed as a strategic “super-weapon” for the destruction of large administrative-political and industrial centers and it was not discussed at first on the battlefield. This is due to several reasons. The carriers of the first American nuclear bombs, which weighed about 5 tons, were strategic bombers Boeing B-29 Superfortress, dropping their deadly cargo from a height of 10-11 km. It is clear that the accuracy of the bombing in this case was not too high, and there was a risk of attacking their troops. In addition, at first the nuclear charges were “piece goods”, in other words they were not enough even for “strategic goals”.
Simultaneously with the development of nuclear bombs and high-powered warheads for strategic bombers and ballistic missiles in the United States, work was underway to miniaturize nuclear weapons.
At the beginning of the 50, the US military began to consider nuclear weapon as a means of destruction on the battlefield. This was due to various reasons.
On the one hand, the use of a nuclear charge with a power of even a few kilotons made it possible to create a gap in the enemy’s defense or to destroy a concentration of troops in one concentration area with one sudden blow. On the other hand, after the loss of the “nuclear monopoly” in 1949, the Americans were well aware that the use of “strategic nuclear warheads” on the territory of the USSR would immediately trigger a retaliatory strike against the United States.
In this regard, the doctrine of "limited nuclear war" arose in the heads of American generals and politicians. According to this doctrine, the use of nuclear weapons was to be limited to a local territory outside the United States. Western Europe, Korea, Indochina and Cuba were considered as theaters for the use of tactical nuclear weapons (TNW).
The main carriers of tactical nuclear bombs were fighter-bombers. However, on navy The first carrier-based nuclear bomb carrier was the relatively low-speed P2V-3C with piston engines. This aircraft was created on the basis of the Lockheed P-2 Neptune base patrol aircraft.
On the plane instead of partially dismantled weapons in order to increase the radius of the installed additional fuel tanks. In the tail section to reduce the takeoff at takeoff, powder accelerators were attached. All atomic X-NUMX units "atomic carrier bombers" were equipped with a AN / ASB-16 radar bomber.
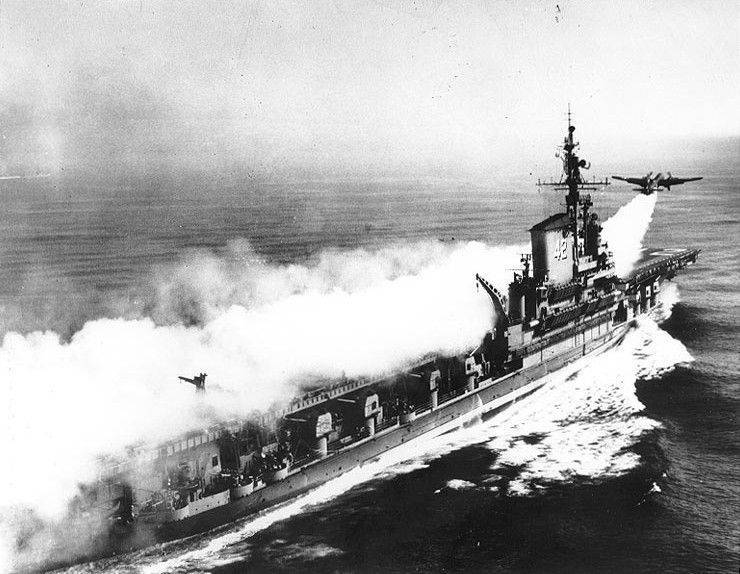
For the first time, the take-off from the aircraft carrier Coral Sea with an onboard weight of 4500 kg took place on 7 March 1949 of the year. The take-off weight of the P2V-3C is over 33 tons. At that time it was the heaviest aircraft taking off from an aircraft carrier.
There was no means for landing on the aircraft carrier. In the case of a combat departure, the bomber was disposable, it had to land on a land airfield, or the pilots were thrown out on parachutes.
What was the probability of surviving in the event of a meeting with jet MiGs from this rather large aircraft, which developed a speed of just over 500 km / h, one can only guess. Most likely, the American admirals also thought about it. After the appearance of sufficiently compact nuclear bombs that could carry carrier-based jet attack aircraft and cruise missiles, all P2V-3B were excluded from the list of carrier-mounted nuclear weapons.
With all the many advantages of jet fighter-bombers as carriers of tactical nuclear bombs, they also had drawbacks. For example, the accuracy of bombing allowed to strike only in the depths of the enemy’s defense, the effectiveness of combat aviation It is directly dependent on the weather and time of day, in addition, combat aircraft are vulnerable to air defense.
For “nuclear weapons of the battlefield”, sufficiently accurate, all-weather, invulnerable to air defense systems and, if possible, mobile and compact delivery systems were required.
These carriers were tactical (TR) and operational-tactical (OTR) missiles. The 50-70-ies in the United States created a series of rockets with engines operating on both solid and liquid fuels.
Rockets “Honest John”, “Little John”, “Sergeant”, “Corporal”, “Lacrosse”, “Lance” had rather high mobility, their accuracy allowed to strike blows at objects located near the line of military contact of troops.
Some of these missiles were handed over to American allies. For example, the Lance missiles (the launch range with YABCh-120 km) were delivered to the UK, Germany, the Netherlands, Italy, and Belgium.
Following the agreements concluded by the United States with these countries, nuclear warheads stored at American bases in Europe were transferred to the missile units of satellite countries in the event of a threat of war. Including it was supposed to transfer and "neutron charges", the production of which was established at the beginning of 80-x. A total of 380 neutron warheads for Lance missiles were manufactured.
The successes achieved in the field of miniaturization of nuclear warheads made it possible to create "atomic shells" for artillery guns.
At the beginning of the 50-x for strengthening the army corps of the US Army in Europe received 280 mm "atomic weapon" M-65 with a T-124 projectile (with nuclear power 15 CT).
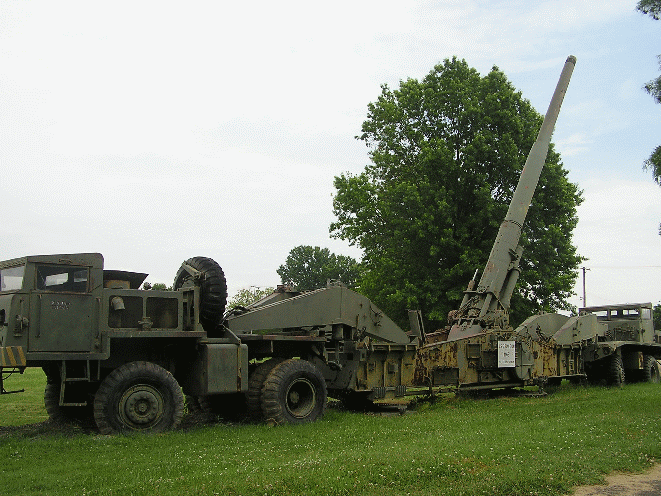
This gun could fire at a distance of 24 km, with half of the shells falling into a circle with a diameter of 130 meters. The weight of the artillery system in the stowed position was 75 tons.
The M-65 gun was in service for a short time, because of excessive mass, its maneuverability and mobility were unsatisfactory.
Equipment firing position took several hours.
In 1957, the 203 mm M-422 artillery projectile with ABT was adopted; its power, depending on the modification, was 5-40 CT. 203 mm nuclear shells can fire 203 mm self-propelled artillery systems M55 and M 110.
Especially for howitzer type M 110 at the end of 70-x created an active-projectile M753 projectile with a power up to 1,1 CT. The nuclear warhead was manufactured in two versions: with a “normal” nuclear charge and with a nuclear charge, which has an increased neutron yield in an explosion.
In 1963, the 155-mm projectile M-454, equipped with the nuclear warhead W-48 with 0,1 CT power, entered service. In 1989, the 155-mm M-785 projectile with the nuclear warhead W-82 1,5 CT power was adopted.

These 155-mm projectiles can be included in the ammunition of the most common in NATO self-propelled howitzers М109 and FH70, as well as towed howitzers М114А1 and М198.
The American "nuclear bezkotkatki" system "Devi Crocket": 120-mm М28 and 155-mm М29 became the easiest and most unusual. In 1962, they entered service with US infantry divisions in Europe.
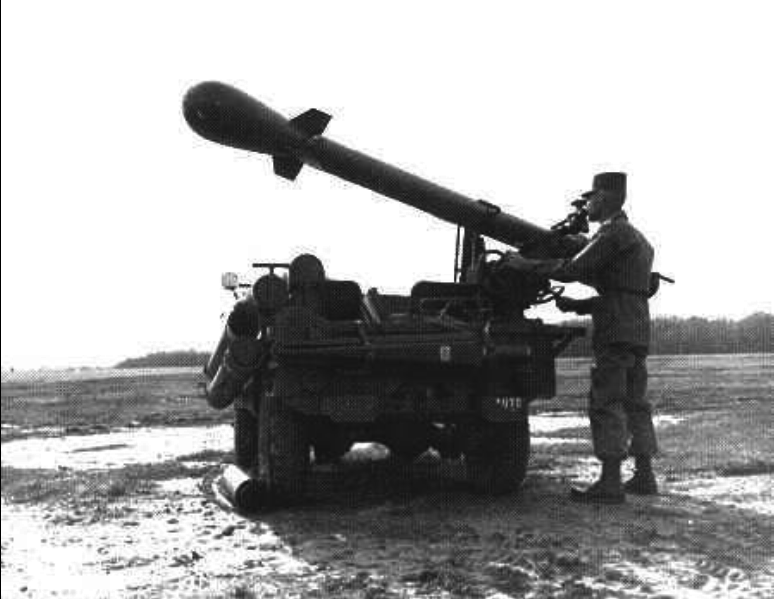

Both guns, firing the same M-388 nad-caliber projectile with a nuclear power up to 1 kt, were “melee” systems with a firing range of up to 2 km at M28 and up to 4 km at M29.
In the 60s, tactical nuclear weapons entered all branches of the American armed forces. In addition to offensive weapons, purely defensive systems were also equipped with nuclear warheads.
So more than half of the American anti-aircraft missiles of the Nike Ajax and Nike Hercules anti-aircraft missiles carried nuclear warheads. Placed in the United States and Canada, the ultra-long Bomark air defense system was armed only with them.
Things reached the point that non-guided missiles, which were supposed to be used on Soviet long-range bombers, were supplied with nuclear warheads.
In West Germany, a network of wells was established along the highways for laying American nuclear bombs. Thus, the command of the military forces of NATO proposed to fight against the Soviet wedges that are torn to the Channel. True, no one was interested in the opinion of the Germans living in the Federal Republic of Germany.
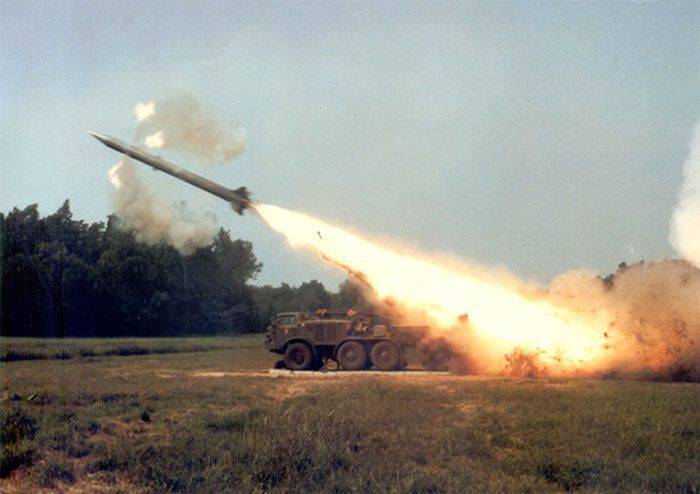

Prior to the start of the 70, the USSR was significantly inferior to the United States in terms of the saturation of troops with tactical nuclear weapons. The Soviet response to the mass deployment of US tactical nuclear weapons in Europe was solid-fuel missiles of the Mars, Filin and Luna mobile complexes, as well as liquid missiles with a large firing range of the P-11 and P-17. The FKR-1 (КС-7) and ФКР-2 (С-5) cruise missiles occupied their niche.
The Soviet tactical "special ammunition" carriers were the Il-28 and Yak-28B bombers, the Su-7B fighter-bombers and the specially-tuned MiG-25СН and MiG-21СМ fighter for the use of the nuclear bomb RN-21.
Nuclear charges were equipped with anti-ship missiles, sea and air-based, torpedoes and depth charges.
In order to defeat group targets in the conditions of a complicated jamming situation, anti-aircraft missiles with “special ammunition” were introduced into the ammunition of the ZRK: C-25, C-75, C-200 and C-125. Moreover, C-125 could apply them to the sea and terrestrial radio contrast purposes.
Apparently, the first domestic "atomic" artillery systems were 240 mm self-propelled mortar Tulip and 203 mm howitzer B-4M. Soon, shells with YABCH received 152 mm self-propelled "Acacia" and towed D-20.
In 80, the Soviet Union overtook the number of deployed US tactical nuclear weapons. According to some data, as of the end of 80, there were about 22000 units of tactical nuclear weapons in the Soviet armed forces.
In the 1990-2000 years, the number of American and Russian tactical nuclear weapons decreased significantly. Since this type of nuclear weapon does not fall under any international agreement, the United States and Russia do not publish official statistics related to this area.
According to expert estimates, there are about 500 units of tactical nuclear weapons in the US military. This number includes approximately 100 YABCh for cruise missiles (in warehouses) and 400 nuclear free-fall bombs of V61 of various modifications. About 200 such bombs are located in the repositories of American air bases in Europe.
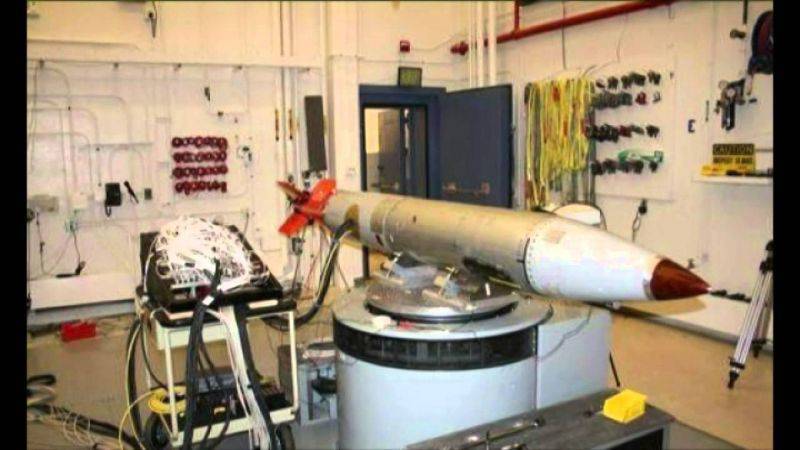
It is worthwhile to dwell in more detail on the B61 family of American nuclear free-fall bombs. This type of medium-sized nuclear weapon was developed by the Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory specifically as an ammunition that could be delivered by front-line aircraft on an external sling.
It was a fairly advanced design, over the years, the technical and technological part of the bombs has changed little. Major changes in the design touched to increase the level of reliability and safety. At present, the free-fall nuclear air bombs В61 have practically supplanted all other samples from the USAF.
The first modification of the B61-0 entered service in the distant 1967 year. Since then, 9 serial modifications have appeared and, in total, more than 3000 nuclear bombs of this type have been assembled, which have come into service with tactical and strategic aircraft.
A special feature of B61 is the ability to change the power level of the charge before combat use, depending on the type of target and the tactical situation. The maximum power of this family of bombs is within 340 CT.
The bomb has a welded metal housing, 3580 mm long and 330 mm wide. The weight of most B61 is within 330 kg, but may vary depending on the specific modification. According to some data, the mass of the promising B61-12 being developed will exceed 500 kg.
Most bombs from the B61 family are equipped with a braking nylon-Kevlar parachute. It is necessary in order to give time to the aircraft carrier to safely leave the affected area, which greatly facilitates combat use.
In 50-60-years, the main method of using free-fall nuclear bombs by fighter-bombers was bombing from a cabrio (the so-called suicide loop). To perform this maneuver required very good training and flight training of pilots, but the risk was very substantial.
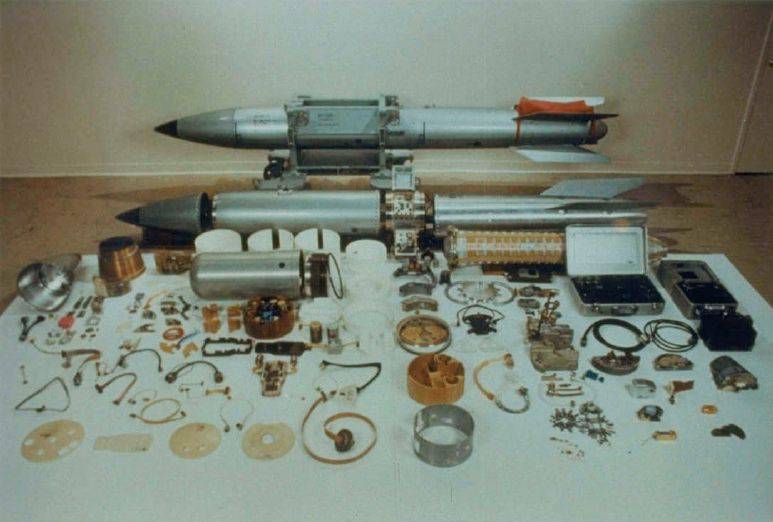

Currently, the 9 B61 and 5 modifications remain in service. These are bomb models: B61-3, B61-4, B61-7, B61-10 (in reserve), B61-11. The latest 11-I most modern version weighing about 540 kg was adopted in 1997 year. A total of about 50 B61-11 bombs were collected.
The greater weight of the 11 th modification as compared to the earlier ones is explained by the more durable and thicker body of the bomb, specially created for the destruction of well-reinforced bunkers. This bomb is designed to explode with a delay after digging into solid ground to a depth of several meters.
In terms of its effectiveness in underground shelters, the B61-11 explosion is equivalent to the 9 megaton charge eroded on the surface without penetration. But depending on the task, the bomb detonator can be set to ground or air explosions.
After the end of the Cold War, the United States and Russia substantially reduced their nuclear potentials; this also affected tactical nuclear weapons deployed in Europe.
At the start of the 2000, the B61 nuclear bombs were removed from the largest American air base in Europe - Ramstein in Rhineland-Palatinate. Currently, this US Air Force air base in Germany is used only by military transport aircraft.
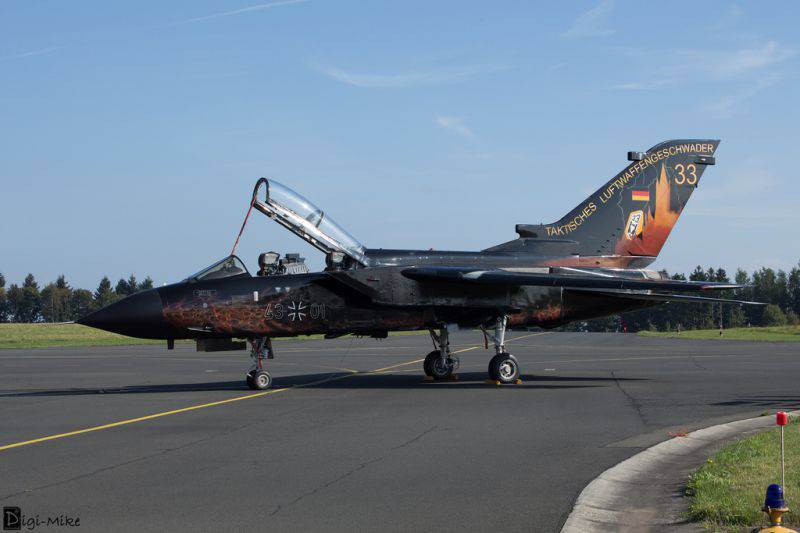
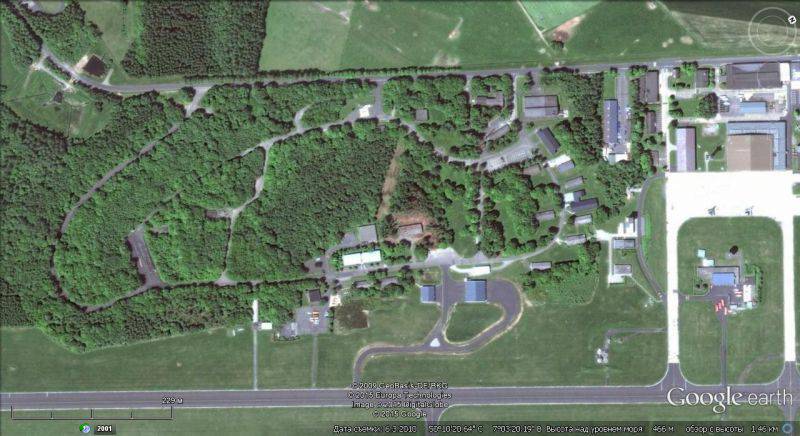
The B61 nuclear bombs in the amount of approximately 20 units remained in Germany in the repository of the German military air base in Büchel, where the 33-I squadron of the Luftwaffe, armed with Tornado fighter-bombers, is located.
Satellite image of Google earth: the proposed location for the storage of nuclear bombs at the Büchel airbase
However, not the largest number of American nuclear bombs are located in the Federal Republic of Germany. Approximately 90 B61 stored in Italy and Turkey. They are also available on the territory of Belgium and the Netherlands.
It may seem strange, but Russia is primarily interested in preserving tactical nuclear weapons in Europe. Currently, our "partners" in NATO have a significant advantage in the field of conventional weapons. Tactical nuclear weapons, which are much larger at the disposal of the Russian army than in the US, are the trump card with which this superiority can be reduced to zero.
Official information on Russian TNW has never been published and is classified information. According to most expert assessments, the current Russian tactical nuclear capability is estimated at about the 2000 warheads.
These include around 500 free-fall nuclear bombs and aircraft missiles for Tu-22М3 and Su-24М and М2 bombers. About 1000 units are combat units mounted on anti-ship, anti-aircraft and missile defense systems A-135, torpedoes, depth charges and long-range cruise missiles of multi-purpose submarines. The rest is nuclear mines and shells for barreled artillery, as well as warheads for operational tactical missile systems.
In peacetime, most tactical nuclear charges are stored at the facilities of the nuclear-technical units of the 12-GUMO, which are responsible for the maintenance and safety of Russian nuclear weapons. But the delivery and preparation of Russian tactical nuclear weapons for combat use is worked out by the troops annually.
The United States has repeatedly raised the issue of reducing Russian tactical nuclear weapons to an "acceptable level of international security", seeking to deprive the Russian army of this trump card.
The distinction between tactical and strategic nuclear weapons is fairly arbitrary. We can recall the events of the “Caribbean crisis”, when in Cuba, in addition to ballistic missiles, were deployed the FKR-1 cruise missiles and the Il-28 front-line bombers, which by virtue of being close to the United States became, in fact, strategic carriers.
The same applies to the deployment plans in the Kaliningrad region of OTR "Iskander". With their help, you can successfully solve strategic tasks to neutralize elements of the US missile defense system in Europe.
Thus, NATO bases in Europe are much more vulnerable for more numerous Russian tactical nuclear weapons than facilities on our territory.
As for the American nuclear bombs in Germany, because of which the hype began, they do not play a special role in the nuclear balance on the continent. In the end, the same France, which is an active member of the military structure of NATO, has a much more impressive tactical nuclear arsenal, but for some reason this fact does not cause any statements by the “press secretary”. Obviously, in this case we are talking about a new round of the “information war”.
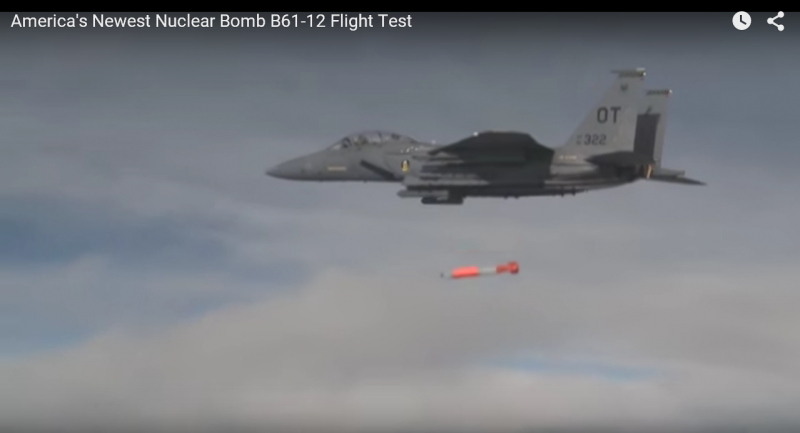
A new modification of the US nuclear bombs B61-12 is just undergoing a test cycle, the completion of which is planned in the 2018 year. The implementation of this project should reduce the cost of maintaining and maintaining tactical nuclear bombs.
The US military intends to gradually replace with the modification B61-12 all nuclear bombs of this family, with the exception of В61-11. In addition, it is planned to increase the reliability and safety of new bombs.
The 61-12 should also become the first adjustable nuclear bombs. Depending on the combat situation, it is supposed to use an inertial or guidance system similar to JDAM.
In general, this is not about strengthening the US tactical nuclear arsenal, but about trying to create a unified sample, more flexible in use, designed to replace most of the early versions of the 61.
But the German fighter-bombers "Tornado" is hardly destined to become the carriers of the new B61-12 nuclear bombs. By 2020, due to resource generation, it is planned to write off all aircraft of this type. Only the journalists of the ZDF channel, who published the next “sensation”, obviously did not know.
Based on:
http://atomas.ru/milit/mk61.htm
https://www.flightglobal.com
http://www.nationaldefense.ru/includes/periodics/geopolitics/2011/0310/10165834/detail.shtml






Information