Tanks D and DD (second part)
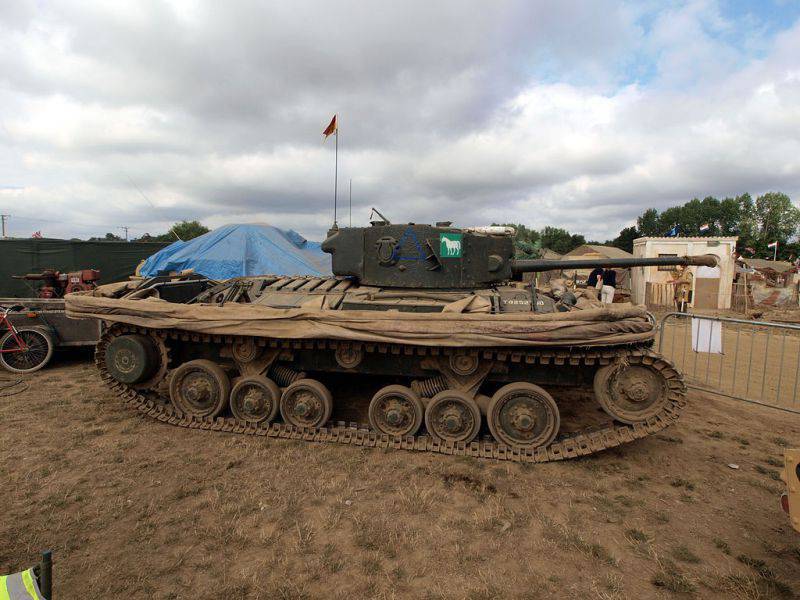
"Valentine" Mk IX DD.
Only the British had experience of creating them (Pig and Medium D tanks), but everyone understood that to go in their way would mean not to go anywhere. The fact is that it is not difficult to hang the pontoons to the tank. This can be done with almost any tank, the main thing - to attach the attachment. But the pontoons are ... great water resistance! Outboard motor afloat is not enough, the usual course can be demolished. Of course, the pontoons are simple and, moreover, unsinkable, since it suffices to fill them with ping-pong balls or balsa, and they are not afraid of any bullet shooting. But this is how much balsa you need? And then - pontoons need to carry for tanks. To install them, you need a crane! All this should be carried out in a band subject to enemy fire. And if the tank is landed from the ship? Then the dimensions of the pontoons will require an unthinkable width of the ramp, and how to deal with it?
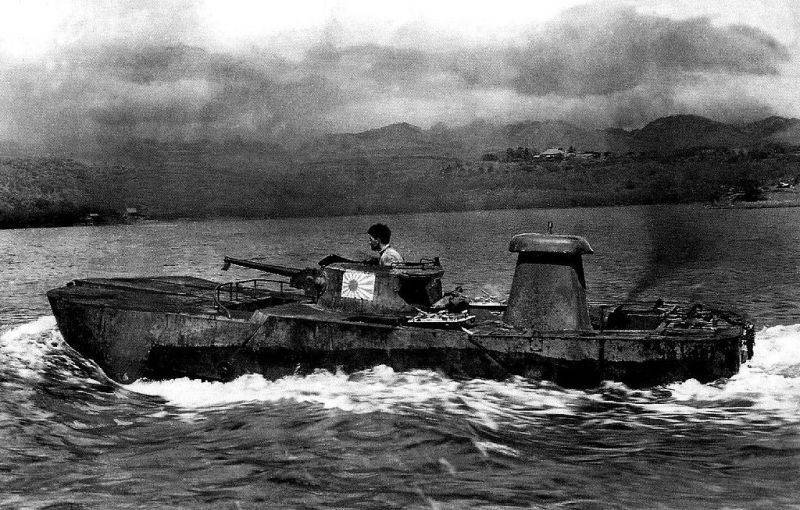
Tank "Ka-Mi" in the sea.
So - or something like that, both the military and the designers of those years reasoned. The obvious solution was to give the pontoons "ship form." That is, for each tank to prepare a set of four pontoons: a bow, a stern and two "sides". In a number of countries of the world they tried it, for example, in Czechoslovakia, and then in Japan, where already later, during the Second World War, a very good amphibious assault tank Ka-Mi appeared.
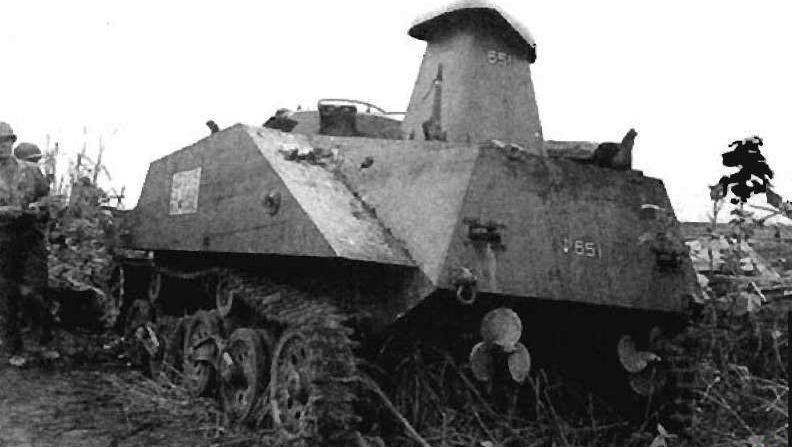

The screws of the tank "Ka-Mi"
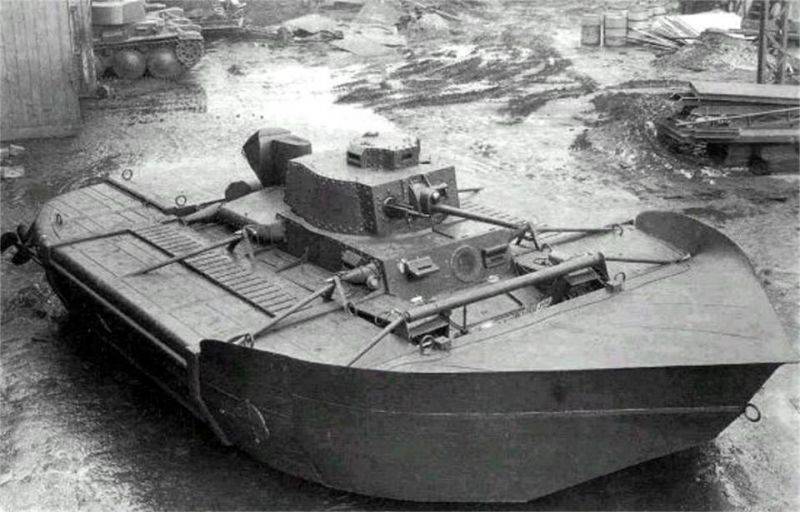
The tank had the original pontoon device: the front pontoon with a volume of 6,2 m³, which gave the structure a streamlined seaworthy shape, was solid on the machines of the first series, but then it was made into two parts, which when dropped were divided into two halves, which facilitated the passage of the tank. The volume of the rear pontoon was 2,9 m³, but both of them were dumped from inside the tank. To leave it for this was not necessary!
Tank "Ka-Mi". Side view.
The tank had a hull of considerable volume, which, together with the pontoons, gave it excellent seaworthiness. And two screws he had on the case, but the steering wheels with a drive - on the pontoon, behind the screws! The pontoons were stuffed with balsa powder, so that the tank itself could also have been drowned, except with a direct hit. But ... for all its virtues, "Ka-Mi" was still too specific. His main goal was landing on the islands of the Pacific Ocean. And again, the pontoons needed to be assembled, stored somewhere, hung on a tank.
PzKpfw38t in the version of a floating tank.
The Germans did something similar, preparing for the landing on the British islands: the Pz.II tank was equipped with a pontoon in the shape of a boat and with a rectangular cutout in the middle. Below the "boat" had a folding support. When they were leaning back, the corps was leaning on them, rising (leaning on the stern) and the tank was going out from under this structure. Either called in to him when it was necessary to use it. These tanks even fought, however, not against England, but against the USSR - forced the Southern Bug. However, after all these technical tricks still decided to give up.
The floating tanks with a displacement hull, which also appeared at that time, solved the problem of pontoons. But because of the presence of such a hull it was impossible to put on them neither thick armor nor solid armament. In addition, they plunged into the water so deep that they could only swim in the quietest weather. So all these two solutions had serious flaws that prevented the use of "amphibious tanks" in combat conditions.
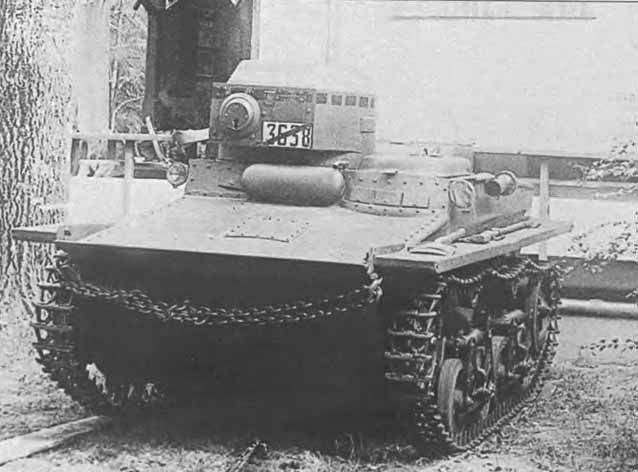

Soviet amphibious tank T-37.
And here a completely unusual idea came to the Hungarian engineer Nicholas Straussler, in 1933, he moved to England, where he clearly had more opportunities to work. He thought that it was easiest to surround any tank with a displacement screen and thus make even the most “non-floating” tank float! The first sample of its device, which had the form of a canvas screen on metal batten struts, was tested on the Tetrarch tank in June 1941. Alan Brook, commander of the metropolis, liked the idea, and he ordered that work be continued.
Already in September of the same year, the Straussler system, called the DD - “Duplex Drive” or “Double Drive”, because besides the crawler drive, his tank also had a drive from the propeller, we decided to put it on the “Valentine” tank. Bribed in the design that neither the screw nor the screen did not interfere with the tank to perform its "work" on land, and most importantly - did not have much weight. The height of the screen was increased, the thickness of the tarpaulin also increased, and the thickness of the rubber tubes into which the air was pumped and thereby straightened the screen.
The tests of the new model began in May 1942 of the year, and the tank was specifically sank with machine-gun fire, figuring out how dangerous it was for him. Finally, the DD system was recognized as fully compliant with the task and began to equip it with tanks. Already in December, the British army had 1944 tanks “Valentine” DD, modifications V, IX and XI.
We tried to make the same screens for the Cromwell and Churchill tanks, but both of them (and especially the last one!) Turned out to be too heavy for that. Along with the adoption of new tanks, the means of rescuing them were also worked out, in the event that the tank was flooded during the landing. In this case, the tank crews had to put on special breathing devices, wait until the tank was completely filled with water and then leave it through the hatches.
Meanwhile, while the Valentine’s crews were preparing to land in France, it became obvious that they could be said to be outdated right before our eyes, and they had to be urgently replaced. Therefore, it was decided to equip the United States Sherman tanks with the DD system. The weight of the tank 30 tons again demanded improvements. Now the screen has become three-layer at the bottom, then two-layer, and only at the very top - single-layer. Another problem was the drive. After all, the transmission on it was located in front. But even here they found a way out: they put additional gears on the sloths, and from them they made gears on the screws. In addition, an electric pump for pumping water was installed in the housing. As a result, the speed of the new “DD tanks” increased to 10 km / h. However, handling was still very bad.
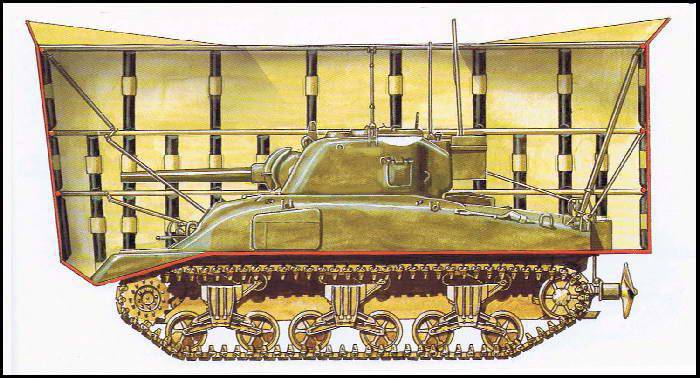
The device of the tank "Sherman DD".
To participate in the landing in Normandy, the British attracted amphibious ships LCT (3), which took aboard five tanks "Sherman DD" instead of the usual nine, and the Americans - LCT (5), carrying four tanks.
The "finest hour" tanks with the Straussler system came 6 June 1944 of the year. The landing of tanks under enemy fire began on 6: 30 in the morning on the Utah sector. The vehicles were landed in 900 m from the coast, however, the waves and current carried them aside for two kilometers, and it turned out that the tanks were in one place, and the infantry, which they had to maintain, was in the other!
Beach area "Utah". Tanks "Sherman DD" out of the water.
On the Gold section, part of the tanks managed to land directly on the beach, and it was very good, but the rest of the vehicles landed in the water in 4500 meters from the shore! Strong waves flooded many tanks, as a result of the 29 machines reached the coast only ... two! But it’s good that only five tankers were killed.
English tanks in this sector were launched in the 600 m from the coast, but eight vehicles sank. Here, part of the tanks landed directly on the shore, without raising screens. But ... the sand was saturated with water, so many cars were stuck, and when the tide began, water filled them.
Canadians landed in the Juneau sector: two regiments with Sherman DD tanks. Because of the strong excitement, they suffered great losses and could not fully help the landing party, but it was still tanks, at least some!
On the "Svord" section, 40 vehicles reached the coast from 34 tanks "Sherman", and five more landed right on the coast. The tanks immediately folded the screens and rushed into battle. But then it was necessary to remove them, because the dried tarpaulin was flammable.
The experience of the operation in Normandy showed that the system needs to be further improved. On 30, see the height of the screen increased, the screen irrigation device was installed outside, in case of a fire afloat.
This was followed by Operation Dragoon, during which the Sherman DD tanks landed in the south of France. In all, 36 tanks were landed, of which one was flooded with waves, one hit something underwater, and five were blown up by German mines.
In May, 1945, these tanks forced the Rhine, and due to the strong flow of the tanks went into the water above the landing site, and for the sake of sailing floating conveyors LVT delivered special flooring there, making it easier for tanks to leave the water.
The last operation of these machines was the forcing of the Elbe. Moreover, so that a local German who sympathizes with the fascists did not make holes in the screens, all the inhabitants of the village, where they were prepared for landing, were evicted.
But in the Pacific, in Burma, the Americans preferred tanks with pontoons (T-6 system), which were navigated by water due to the rewinding of the tracks. It was more reliable, they thought, and besides, tanks could fire afloat.
Well, and then ... Then, as it always happens in such cases, a lot of suggestions for improvement appeared. For example, put rocket boosters on the tank in the lower part of the hull with an inclination of 30 degrees. Their simultaneous inclusion should have added speed to the tank. But ... the walls of the screen bent under the pressure of the water. And in general, this is a dangerous thing, like this, “flying” on rockets.
The tankers wanted to reinforce the armament of the DD tanks, because on the move they could not shoot. Well - want? So here you are: made a machine gun installation with two M1919 machine guns, put on top of the screen. Swim and shoot! But it showed low reliability, so things did not go further than the tests. Put on the screen and recoilless gun caliber 94-mm, but ... where are you getting away from it? And they also refused it, as well as from the periscope for the driver, so that he himself could see everything and where he should drive.
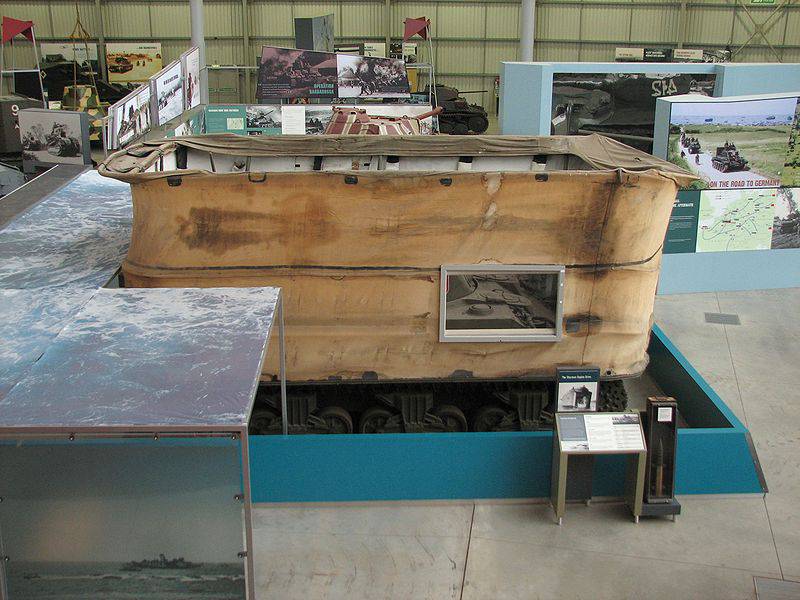

"Sherman DD" in the museum in Bovington.
They tried to make Churchill-crocodile a flame-thrower tank floating. But it all came down to placing the trailer with the fire mixture. Making it floating also turned out to be very difficult technically. Finally, in the 59s of the last century, they tried to make the new tank “Centurion” floating. But “Centurion DD” also “did not go” - the weight for the canvas screen turned out to be too big. Later, similar systems with folding screens were placed on Strv-103, М551 Sheridan, МХNUMX Бредли tanks and a number of other cars, but they all had little resemblance to the Shtraussler design. His contribution to the world tank building was not small, yes, because without his “DD tanks” the success of the landing force in Normandy was not that dubious, but not so impressive, and the losses would have been much greater, but not as great as the contribution same Christie and our Soviet designers.





Information