A.M. Isaev. Taming the fire

In the seventies on the screens of our country came the famous film "The Taming of Fire." He was seen by many, but very few people knew that the prototype of the main character of the film, rocket designer Andrei Bashkirtsev, served not only S.P. Korolev (the name of the Queen came to mind in the first place), but also another outstanding designer - Alexey Mikhailovich Isaev.
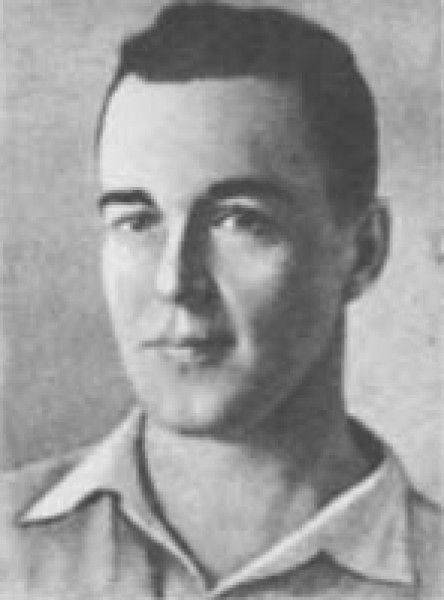
Alexey Mikhailovich Isaev is an outstanding engineer, the creator of rocket and space technology and at the same time the brightest person, endowed in some amazing harmony with truly bright human qualities that made him a true leader in business and earned him deep respect and love of employees, as well as many who was lucky to communicate with him.
Small homeland Alexei Mikhailovich - St. Petersburg. There he was born on October 24 1908, in the family privat-associate professor of jurisprudence of the university. The Isayev family lived in St. Petersburg until 1918. The head of the family was a specialist in criminal law and, apparently, could predict the development of events. The family took the decision to leave Petrograd and go to the village as the only correct one. We moved to the village of Mstera, Vladimir province - the native place of the children's nanny. There Isaev organized school. They had a vegetable garden, a cow. Life went on as usual.
Gradually, the situation in the country became calmer, and the family moved to Moscow after their father, who was invited to Moscow State University. Alexey Isaev received his engineering degree at the Mining Academy, from which he graduated in 1931. Apparently, the choice was influenced by the opinion of the father and the fact that the specialty of a mining engineer has traditionally been considered one of the most prestigious since the times of Peter I.
"Hit" Isaev in Aviation It wasn’t easy, he constantly ran into failures of personnel officers. Finally, after a direct appeal to the director of the 293rd Aviation Plant in Khimki, the issue was resolved - Isaev was accepted. There, fate brought him to the aircraft designer V.F. Bolkhovitinov. Viktor Fedorovich was a bright personality, versed in all the intricacies of aerodynamics and structural mechanics of aircraft, had a keen sense of the new. Perhaps this attracted talented young engineers to him. Bolkhovitinov Design Bureau became an excellent school, from which prominent Soviet scientists and designers of rocket and space technology came out: V. Mishin, B. Chertok and K. Bushuev, subsequently the closest associates of S. Korolev.
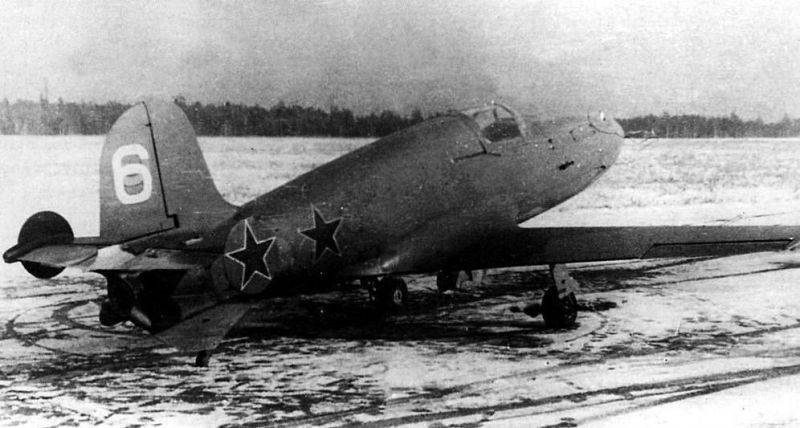
His extraordinary abilities quickly identified Isaev as one of the best workers in the design bureau, and he was appointed the lead designer of an experienced fighter who could reach speeds in excess of 700 km / h. Alexey Mikhailovich began to engage in rocket technology later - with an initiative project of a fighter-interceptor with a liquid rocket engine (LRE), carried out jointly with A. Berezniak and called “BI” (from the initial letters of the creators' last names). Subsequently, already after the war, A. Bereznyak became the chief designer of a number of combat cruise missiles, which were in service with the Air Force and Navy, and the engines for them were developed under the guidance of the chief designer A. Isaev.

The small number of design bureaus L. Dushkina worked in the country during these years and was engaged in the development of liquid-propellant rocket engines, but only aircraft. This team became the head of the engine for BI. Isaev was responsible for tanks and fuel valves. The plane had to be built quickly - the situation for the country was difficult. The government gave only one month. The car was rolled out of the workshop on time, but the engine was not ready for it. He was not ready even a year later, despite the best efforts of the Dushkin team. Only in 1942, the combat pilot G. Bakhchivandzhi raised this plane from the Koltsovo airfield near Sverdlovsk. He took off six more times. The last flight, where the highest speed was reached - over 800 km / h, ended tragically: the plane suddenly entered its peak and crashed into the ground. The pilot died.
The reason, as it became clear later, was the discrepancy between the aerodynamic shape of the wing and the flight speeds, at which the so-called local sound speeds had already occurred, not only reducing the lift force of the wing, but also leading to a diving moment. At the same time, they sinned on the engine and transferred the development of the LRE and the propulsion system as a whole to Isaev.
In the spring of 1943, the Bolkhovitinov design bureau collective returned from the Urals to Moscow. Isaeva was appointed head and chief designer of the newly created department of LPRE. As a “living space,” the department received three walls of an unfinished hangar. Work premises and test benches had to be built by ourselves. In less than a year, the RD-1 propulsion system for the aircraft was to be built up multiple-stage with adjustable thrust from 1100 to 400 kg with a specific impulse of at least 200 with and a service life of at least 30 minutes. Everything was done on time and met the specified requirements. It is important to note that to complete the entire work program, including two flight tests, it took only four engine instances. Such an economical approach to the expenditure of the material part in working out has since become characteristic of Isaev's work style.
The creation of the RD-1 engine and the propulsion system for the BI plane provided Alexei Mikhailovich with recognition and put him among the leading specialists and leaders in the field of rocket engine building in the country.
The next step in the life of Isaev and the team he led was the U-1250 engine, created in 1945 year and determined, in essence, the basic principles of modern-level LRE, which became the alphabet of engine building. These are flat heads of combustion chambers with a multitude of centrifugal nozzles providing high quality mixing of liquid oxidizer and fuel; creation of a colder surface layer due to enrichment of the peripheral zone with fuel; thin, rigidly interconnected welding shells, forming the design of the combustion chamber and the nozzle, and a fully welded engine design. Such innovations allowed the developers not only to drastically reduce the weight of the LRE, but also to switch to high pressures and the widespread use of turbopump feed systems for this, and technologists to create new technological processes and methods of communication of the shells.
Armed with this knowledge and experience, Isaev in the 1946 year, leading one of the groups of Soviet specialists in the study of captured samples of rocket technology, was able to appreciate the achievements of German designers. He realized that the time had come to apply the LRE precisely on rockets. However, after returning from Germany, Isaev supervised the creation of the engine and propulsion system of a four-meter supersonic model aircraft for research in the field of supersonic aerodynamics (they, by the way, clarified the cause of the BI crash), as well as the SU-1500 launch accelerator for heavy bombers. These works ended by 1948.
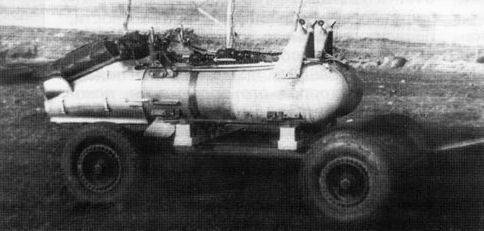
At that time, the country was in dire need of such a promising weapons defense like anti-aircraft guided missiles (SAM). It was here that, in spite of the efforts made, there were no successes: neither in the rocket itself, nor in the control system, nor in the engine. The situation had to be urgently corrected.
Apparently, therefore, even before I.V. Stalin in June 1950 of the year decided to build an air defense system in Moscow, D.F. Ustinov, in those years, the Minister of Armaments, invited Isaev to the institute of his department - NII-88 (now TsNIImash) as the head of the 9 department and the chief designer of the missile system. There he was already working as the head of the 3 department and the chief designer S. Korolev.
The invitation was accepted, and Isaev with the backbone of his design bureau moved from Khimki to Kaliningrad, Moscow Region. The move was followed by the construction of a test base, the organization of an experimental workshop, the arrangement of premises for designers. The Isaev people had at their disposal a two-storey dilapidated building, which remained from pre-war times from the P.O. Dry. Nearby is a young pine woods, where intensive construction of test benches unfolded. The work was carried out so quickly that by the time of the receipt of the task to develop the engine for missiles, whose chief designer was S.A. Lavochkin, test benches were ready.
The rocket required an engine with a pitch adjustable from 8 to 2,5 t. The solution to the problem began with an attempt to create an engine in a single-chamber version that promised the highest parameters for the rocket. However, here for the first time we encountered a completely unknown phenomenon at that time — the destruction of the combustion chambers in the first seconds of work. Initially, no design changes led to a positive result. Then it became clear that the cause of the explosions was high-frequency instability inherent in relatively large chambers with high mixing characteristics. At that time, the task was accomplished by moving to a four-chamber engine with a load of each 2 r. The rocket with it underwent extensive testing and was put into service at the end of 1952. Since then, for many years, the sky of Moscow has been guarded by the missile of the Berkut C-25 complex, the engines for which were developed by A.M. Isaev.
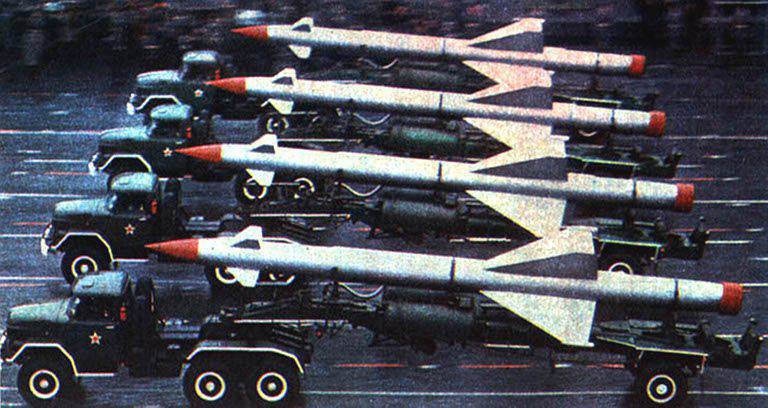

However, the problem, which then faced the KB, needed to be overcome. Isaev found a solution by introducing into the head zone a single-chamber eight-cross "cross" - partitions dividing its volume into four compartments. The reception was so effective that it was subsequently used in all Isaev designs.
Success in creating such an engine immediately aroused the interest of the Queen. He proposed to develop a ballistic missile operating on high-boiling components, stored and transported in the filled state, the future P-11. And then on its basis - the P-11FM - the first Soviet sea-based missile. Here, in addition to a single-chamber engine, to the nozzle of which gas rudders were directly attached, a lightweight component supply system was developed, based on the production of hot gases to displace the oxidizer and fuel from tanks neutral to the corresponding component. Such a system, in fact, completed all the work on pressure feed systems and provided invaluable experience for subsequent ones related to the creation of fully two-component engines with turbo pump feed systems.
The rapid development of the design and testing features of high-speed pumps and turbines allowed A. Isaev to declare 1954 a year - the year of turbopump units (TNA) and take to development new engines already from THA: for the second stage of a new anti-aircraft missile launch, and four-chamber - for the first (accelerator) stage of the intercontinental cruise missile "The Tempest".
The next year he declared the year of closed hydraulic control systems. Moreover, the success in creating control units made it possible to start developing new engines for cruise and ballistic missiles, which, while controlling thrust and various influences on the rocket during its flight, maintained the required ratios of the fuel components.
Alexei Mikhailovich has always formulated the fundamental provisions - such was his nature leader. Perhaps that is why he began to transfer the accumulated experience to others. He initiated the creation of the S. Kosberg design bureau, the emergence of topics on the LRE in the design bureau of S. Tumansky and S. Izotov, transferred design and construction documentation for new developments to the design bureau of V. Glushko. Such altruism and such generosity evoke respect.
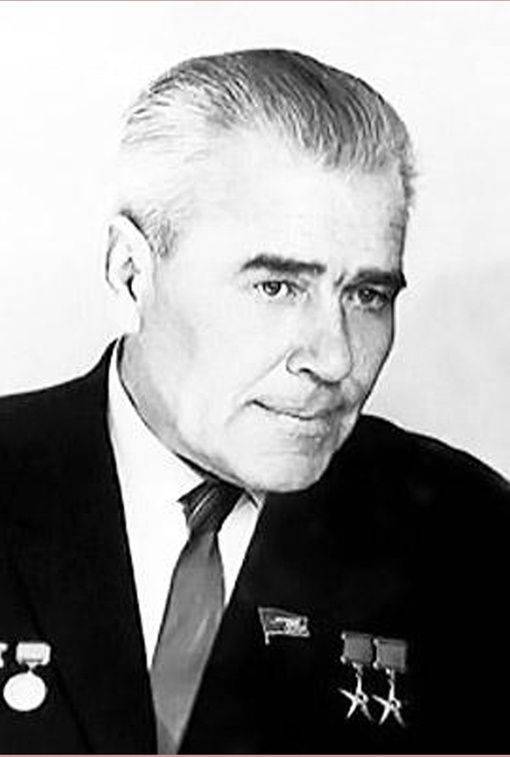

Years passed, the staff qualifications grew, and the authority of the Isayev Design Bureau grew. He himself invariably took over the leadership of the main directions, put forward key ideas. So, he proposed to launch a sea-based rocket engine directly in the mine of a submarine; its layout solutions made it possible to use the volume of the mine space by almost 100 percent. This concerned the creation of autonomous propulsion systems for space objects.
For Isaev and his OKB, the “advent” into space technology occurred at the end of November 1958, when Korolev proposed developing a braking propulsion system (TDU) for the Vostok manned satellite. It was needed to return the astronaut to Earth by reducing the orbital velocity by about 150 m / s. The task was extremely responsible and contained many unknowns. But the proposal was accepted, and less than a year and a half later the TDU was ready for flight and tested at the 1KP facility (1st design "empty") in mid-May 1960. After that, the TDU worked in space more than 75 times, including historical flights of Yuri Gagarin, German Titov and our other astronauts. And there have never been any accidents because of her. Here it must be said that it was only practiced at twelve TDU. This embodied the ideas and methods of multifunctional tests, when the development of complexes is carried out in stages: components, assemblies, individual engine systems, engines, propulsion systems. Such an approach, already at the stage of the first tests of the complexes, provided a very high initial reliability - of the order of 0,99.

The second in time and significance of the Isaev’s “space work” was a corrective and braking propulsion system (KTDU) for landing an automatic lunar station. The lunar epic lasted for three years with great difficulties and ended only 3 with success February 1966 years after the death of the Queen.
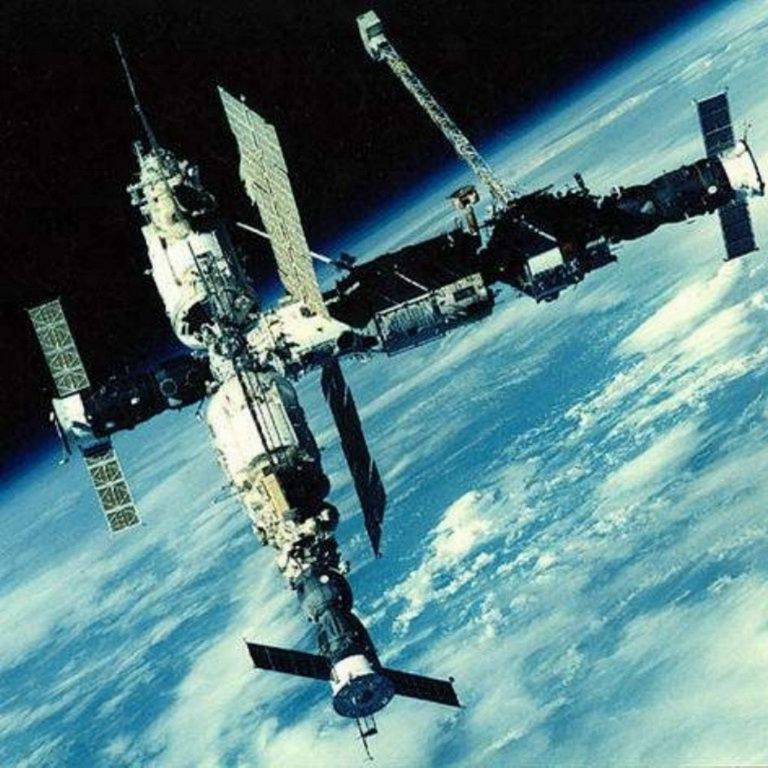
In the sixties, the Isaev Design Bureau created several generations of corrective propulsion systems (KDU) of spacecraft intended for flight to Mars and Venus, a new generation of corrective, approximating and braking propulsion systems (CS TDU) used at Soyuz, Progress, Salyutyakh "," World ", the ISS and the interplanetary spacecraft" Luna "," Mars "," Venus "," Probe ". He would have done more, but he died without having lived 63 for years.

Sources:
Velichko K. Alexey Mikhailovich Isaev // Earth and Universe. 1999. No.2. C.38-43.
Petrik V., Piunov V. TDU-1 A.M. Isaeva - the first in the world space propulsion system (on the fiftieth anniversary of the flight of Yu.A. Gagarin) // Engine. 2011. No.1. C. 34-38.
Tsetlin F. Creators of space technology // Aviation and Cosmonautics. 1993. No.9-10. C. 10-11.
Kuznetsov V. Severe Reality // Aviation and Cosmonautics. 2013. No.4. C.19-20.
Designer Isaev. Documentary. CSDF (RCSDF). 1979.

Information