Fiery fist staffs
Multiple rocket launchers are a weapon known to even highly dilettantes and people not interested in military affairs. If only because it is precisely to them that the famous Katyusha guards mortars belong. After all, no matter what anyone says, but it is Katyusha - BM-13 - that became the first real MLRS, embodying all the main performance characteristics of this type of weapon: small size, simplicity, possibility of simultaneous destruction of targets on large areas, suddenness and high mobility.
After 1945, the Soviet Army received a whole series of rocket artillery samples, developed taking into account the experience of the past war, such as BM-24 (1951), BM-14, 200-mm four-barreled BMD-20 (1951) and 140-mm 16 -barrel MLRS BM-14-16 (1958), as well as its towed 17-barrel version of the RPU-14 (on the gun carriage D-44). At the beginning of the 50-x was developed and tested fairly powerful and long-range MLRS "Kite", but the series did not go. However, all these installations were, in fact, only variations of the BM-13 - that is, in fact, the machines of the battlefield.
Combat vehicle rocket artillery BM-24
Reactive salvo fire system BM-14-16
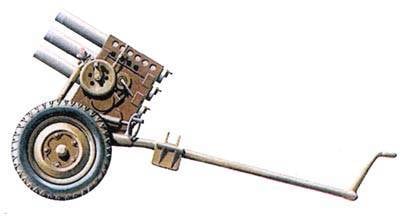
Jet salvo fire system RPU-14
“HOW I’m Glad When“ Grad! ”Falls
Finally, in 1963, the world's first second-generation MRL system was put into service.
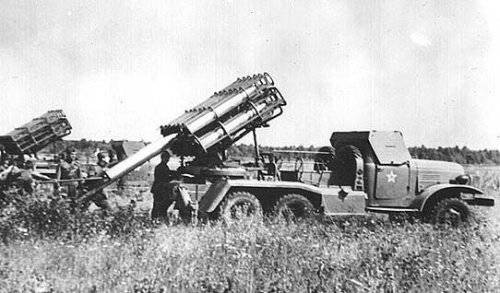
It was the world-famous (without exaggeration) BM-21 - “Grad” caliber 122 mm, which in terms of manufacturability and today has no equal in the world. Technical solutions that have arisen during the development of the “Grad” are repeated in one way or another in all the systems existing in the world - for example, the “folding” tail, ensuring the compactness of the guide block.
BM-21 Grad
And most importantly, perhaps, the dignity of the machine, which favorably distinguishes it from what must be confessed, of many types of domestic weapons, is a large modernization reserve. For example, over the past 40 years, the range of the “Grad” was increased from 20 to 40 km. System modifications were created for the Airborne Forces and the Navy. In 1965, for three months, a light portable, Grad-P MLRS with a range of 11 km was put into mass production. Soon she went through "combat tests" in Vietnam, as a result of which the Vietminh partisans put down the saying: "How glad I am when Grad is falling!"
And today "Grad" is the most effective system of volley fire in the world by the combination of technical, tactical, economic and military-logistic characteristics. It is not by chance that it was copied - legally and illegally in many countries. For example, in 1995, it — through 32 of the year after its creation — decided to put Turkey on stream.
Back in 1964, when the production of Grad was just beginning to be mastered, its designer Ganichev began the development of a more powerful salvo fire system. Its development was completed in 1976-m - so the troops received a "Hurricane" with a range of 35 km and cluster munitions.
Without stopping at what was achieved, at the end of the 60-ies, Splav's specialists began designing the 300-mm MLRS with a firing range of up to 70 km. However, they were denied funding - the Minister of Defense, Marshal Grechko, personally indicated to the lobbyists of the MLRS from the Main Directorate of the Armed Forces of Ukraine that the Soviet budget was not bottomless. As a result, work on the creation of third-generation systems dragged on for almost 20 years.
Only in 1987, the 300-mm MLRS “Smerch” entered into service with the SA. The firing range has increased to 90 km, topography has been carried out automatically through satellite systems. A system for correcting the flight of a rotating rocket using a gas-dynamic rudder controlled by an individual electronic unit was applied. The Smerch also was equipped with a fully mechanized loading system using disposable transport and launch containers loaded at the factory.
MLRS "Smerch"
These weapons can be considered the most powerful non-nuclear weapons system in the world - a volley of six Smerches can stop the advance of an entire division or destroy a small city.
The weapon turned out so perfect that many military experts talk about redundancy "Smerch". And by the way, according to experts, the new MLRS, which has the code name Typhoon, is being developed at NPO Splav. Everything rests only on money - which is now much less in the budget than at the time of Marshal Grechko.
AMERICAN UNIVERSAL
After World War II, the United States paid little attention to the development of the MLRS.
According to Western military theorists, this type of weapon could not play a significant role in the future Third World War. Almost until the beginning of the 80s, the American MLRS were inferior to the Soviet ones. They were considered as weapons almost exclusively in the battlefield and infantry support and were rather a development of the direction represented by the German "Nevelwelfer". Such, for example, was the 127 mm Zuni. Curiously, the main technical requirement was the universal nature of multiple launch rocket systems equipped with conventional aviation rockets.
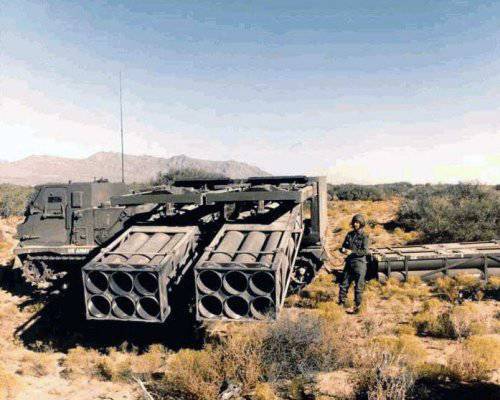
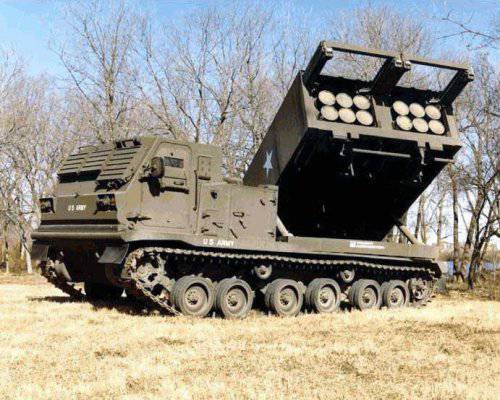
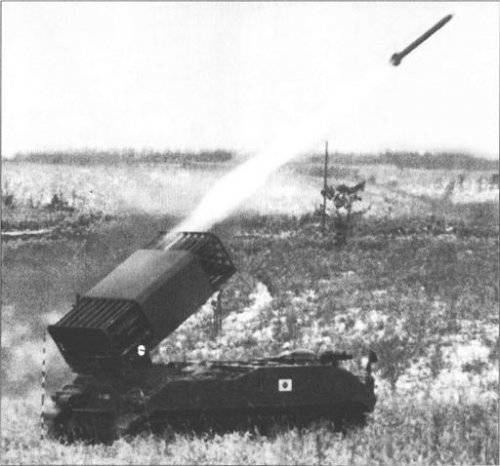
Only in 1976, by order of the military department, has the development of a new MLRS begun, designed to eliminate the backlog from the “potential adversary”. So there was the MLRS, developed by Lockheed Martin Missiles and Fire Control and adopted by the 1983 year. We must pay tribute - the car turned out to be quite good and convenient, in terms of automation and autonomy of the superior Soviet “Hurricanes”. The MLRS launcher does not have the traditional permanent guides that the armored box truss replaces - the “swinging part” of the launcher, where disposable launch canisters are placed, so that the MLRS can easily use two-caliber projectiles - 227 and 236 mm. All control systems are concentrated in one machine, which also facilitates combat use, and the use of the Bradley МNNXX infantry fighting vehicle as a chassis has increased the safety of calculations. It was the American MLRS that became the main countries for NATO allies.
MLRS developed by Lockheed Martin Missiles and Fire Control
In 1990 – 2000, a number of other MRL systems — not so powerful — were developed for the US Army. For example, MLRS RADIRS, using aviation 70-mm NURS type HYDRA. What is curious is the most multi-barreled MLRS in the world - the number of guides can reach 114 (!). Or the ARBS salvo assault landing system, which includes two six-container launchers of 227 caliber mm.
HOT DRAGON BREATH
Perhaps it will sound unexpectedly, but at the moment, the PRC in terms of development of the MLRS takes the second place after Russia.
The “patriotic legend” is widely known that the creation of its system of volley fire began in the PRC only after the Soviet-Chinese armed conflict on Damansky Island, when the military use of Grad made a strong impression on the PLA command.
In fact, the development of its own MLRS in China began much earlier. The first was the 107-mm towed rocket launcher type 63, adopted by the People’s Liberation Army of China in the 1963 year. Export deliveries of this cheap and relatively efficient system were carried out to Syria, Albania, Vietnam, Cambodia, Zaire, Pakistan and a number of other countries. Licensed production was organized in Iran, the DPRK and South Africa.
107 mm towed multiple launch rocket system "Type 63"
The current basic model of the Chinese MLRS 122-mm 40-barreled "Type 81" really is in many ways a copy of the Soviet BM-21. In 1983, this system was put into mass production, and its deliveries to the PLA rocket artillery divisions began.

122 mm MLRS Type 83 (Chinese "clone")
Later versions of the 122-mm MLRS - with placement on the 89 Type armored tracked chassis and on the Type-2030 Tiema SC90 off-road truck chassis. These fairly high-quality machines have a modern, improved automated fire control system, which China is actively offering on the international arms market.
Tiema SC2030 "Type-90"
In recent years, the PLA has several types of new jet systems that are significantly superior to the previous ones - 40-barrel WS-1, 273-mm 8-barrel WM-80, 302-mm 8-barrel WS-1 and, finally, the largest caliber in Worldwide - 400-mm 6-WS-2.
 300-mm 10-barrel wheel MLRS A-100
300-mm 10-barrel wheel MLRS A-100From this number, it should be noted that even the domestic Smerch 300-mm 10-barrel A-100 with a firing range of up to 100 km is leading in a number of indicators.
In a word, the PRC has in the person of the MLRS a very efficient and powerful weapon.
EUROPEAN AND NOT ONLY
However, not only the major military powers produce the MLRS. The military of so many countries have wanted to get such a powerful means of warfare, to which, moreover, various international restrictions do not apply.
The first were the gunsmiths of the FRG, in the 1969 of the year they supplied the 110-mm 36-barreled MLRS LARS to the Bundeswehr, and are still in service in two versions (LARS-1 and LARS-2).

MLRS LARS
They were followed by the Japanese, in the 1973 year, following the usual national policy of doing everything alone, starting production of the 130-mm MLRS, two years later put into service under the name "Type 75".
Almost at the same time, the former Czechoslovakia developed the original RM-70 - 40 guides of the 122-mm caliber, equipped with the world's first automatic recharge device (in another version, two 40-charging packages, guides on one platform).
130 mm multiple rocket launcher system. Type 75 performs a single launch.
The 70-e in Italy created a series of MLRS 70-mm and 122-mm caliber FIROS, in Spain - Teruel caliber 140 mm, with anti-aircraft armament.
From the beginning of the 80, 127-mm 24-barrel MLRS Valkiri Mk 1.22 (“Valkyrie”) has been produced in South Africa, specially designed for the South African theater, as well as the MRL 1.5 RSZO.
Brazil’s technology, which is no different than the seemingly advanced engineering thought, created the Astros-1983 MLRS in 2, which has a number of very interesting technical solutions and is capable of firing five types of missiles of different caliber - from 127 to 300 mm. Brazil also produces the RSAT SBAT - a cheap launcher for firing NURS aviation.
In Israel in 1984 it was adopted by the LAR-160Y MLRS on the French light chassis tank AMX-13 with two packages of 18 guides.
The former Yugoslavia released a series of MLRS - heavy 262-mm M-87 Orkan, 128-mm M-77 Oganj with 32 guides and automatic reloading system (similar to PM-70), as well as light RSBO Plamen, a licensed copy of the Chinese "Type 63". Although their production was discontinued, they are in service and are actively used in the Yugoslav conflict of the 90's, having shown good results.
MLRS - Heavy 262-mm M-87 Orkan
The DPRK quickly copied (simplified) the Soviet Uragan complex, creating the 240-mm MLRS "Type 1985 / 89". And, as is customary in this country, I started selling it to anyone who can pay, and then sold the license to her long-time partner, Iran. There the complex was redone once again and received the name Fajr. (Incidentally, the MLRS in Iran is produced by a firm called Shahid Bagheri Industries - just like that, this is not a joke.) In addition, Iran produces the MLRS Arash with 30 or 40 mm 122 mm guides, very similar to the Grad system.
Even Egypt, with 1981, developed the MLRS Sakr ("Falcon"), an 30-barrel pirated copy of the same "Grad"
Of the most recent, the Indian 214-mm Pinaka multiple rocket launcher, the result of many years of efforts by the Indian military-industrial complex to create its own MLRS, stands out. The system is designed to perform combat missions in specific Indian conditions, with an emphasis on difficult terrain and mountainous terrain, as well as on the basis of the requirements of the fastest possible change of positions. Military trials began in February 1999 of the year, and in the summer of the same year combat use took place - during the Indo-Pakistani conflict in the state of Jammu and Kashmir.
Weapons of the past battles
It must be said that many modern military theorists consider the RSZO to be a kind of dead-end type of armament, whose heyday falls in an era when strategists were preparing for the Third World War. And in the current local conflicts, their power, as already mentioned, is highly redundant. Moreover, in their cost and complexity, modern MLRS approach operational tactical missiles and require sufficiently trained personnel to service. For example, in the course of the Arab-Israeli conflicts, even the Syrians, not to mention the Hezbollah militants, managed to overshoot when they fired at the MLRS not only at Israeli troops, but even at city blocks.
However, although the MLRS is not "gods of war", they are not going to resign either.














Information