Protection of military facilities
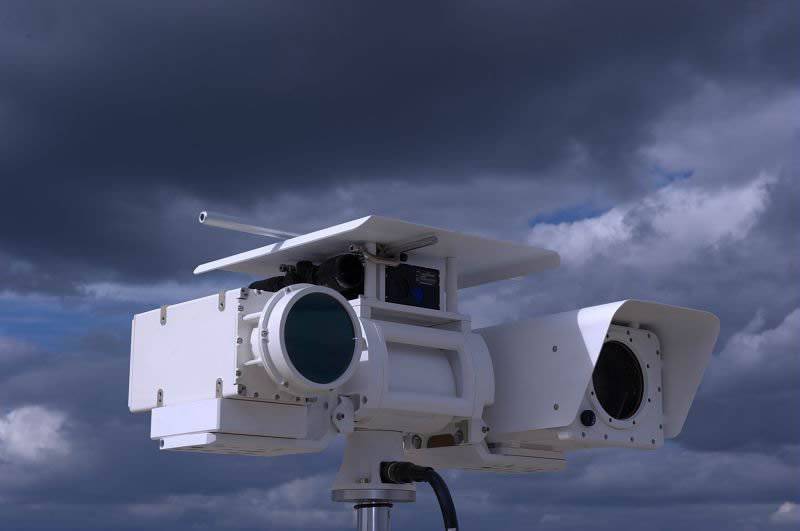

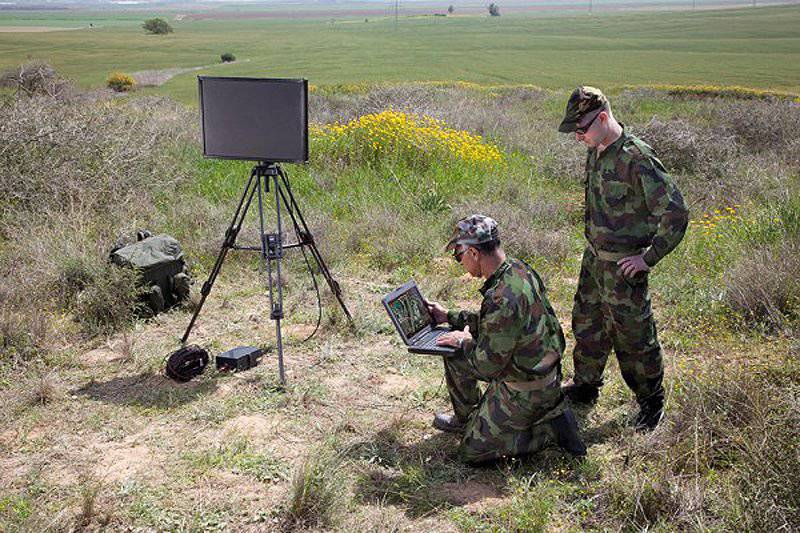
Sagem Teos identifies targets day and night and provides control and command systems with their coordinate grids.
Protection of military bases and camps was a problem during the Roman era. In the 70's, the Vietnam War showed how many military camps were subjected to various threats, especially in the jungle. In addition to direct infantry attacks, military targets were subjected to mortar attacks daily (the threat remained unchanged to this day), to which direct sniper fire was added. Long-range observation, physical protection and executive elements capable of neutralizing the threat remain the main components necessary to protect the camps.
Physical protection of military facilities is the last barrier to the attacks of opponents, but identifying and neutralizing the threat as far as possible from the camp is still the best way to reduce the risks to its inhabitants. To ensure optimal sensor coverage and, therefore, reduce the required amount, as well as enable the entire working range of this equipment, height is the main parameter. When installing radar and opto-electronic sensors (various types of video devices) on the walls of the protected object, their field of view will be limited to dead angles and obstacles.
This led to two types of solutions that, following their first deployment in Iraq, are now widely used in Afghanistan: towers and balloons. Desert terrain is obviously the ideal place to deploy such systems; Although sandstorms can reduce visibility to zero, this is unlikely to affect ground sensors.
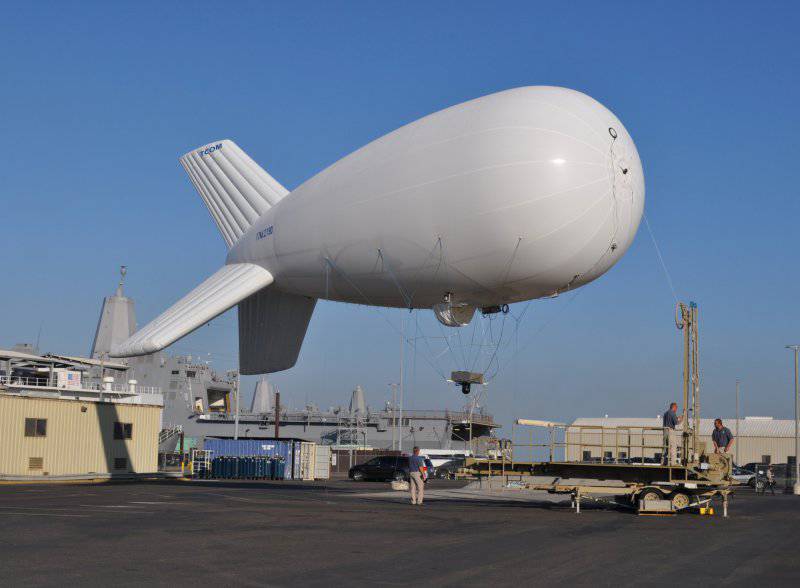
Within the framework of the American global system of continuous observation and transmission of information aimed at improving the protection of advanced bases, we see the use of the Raid system (Rapid Aerostat Initial Deployment - rapid initial deployment of balloons), consisting of towers and aerostats. The first balloon within the Raid system was the Tcom 17M, capable of flying at altitudes up to 300 meters with a load of 90 kg. Deployed by two or three people in less than an hour, it can stay airborne for a week. A well-known limitation of a balloon is its sensitivity to strong winds; but Tcom 17M can operate at wind speeds of 40 nodes and can even withstand gusts of up to 55 nodes.
To meet the need for larger balloons with higher payloads and greater working heights, Tcom launches a series of balloons ranging from an 22M model capable of flying 300 meters of 10 days at a height with a working limit of 50 nodes (part of the American Army PGSS (Persistent Ground Surveillance System) program - a system of continuous monitoring of the surface of the earth), and up to the 38M model, which, with a load capacity of 400, remains airborne for up to 14 days at an altitude of 900 meters (or from 225 kg at an altitude of 1500 meters), while 71M1 can reach the ceiling above 5000 meters and stay in place for more than a month, although in this case more work is needed to equip the landing pad.More than 300 Raid towers were installed at one time by the US Army in Iraq and Afghanistan.
With a payload capacity of 90 kg, the Tcom 17M balloon is the main carrier of the touchscreen equipment of the American Army’s Raid
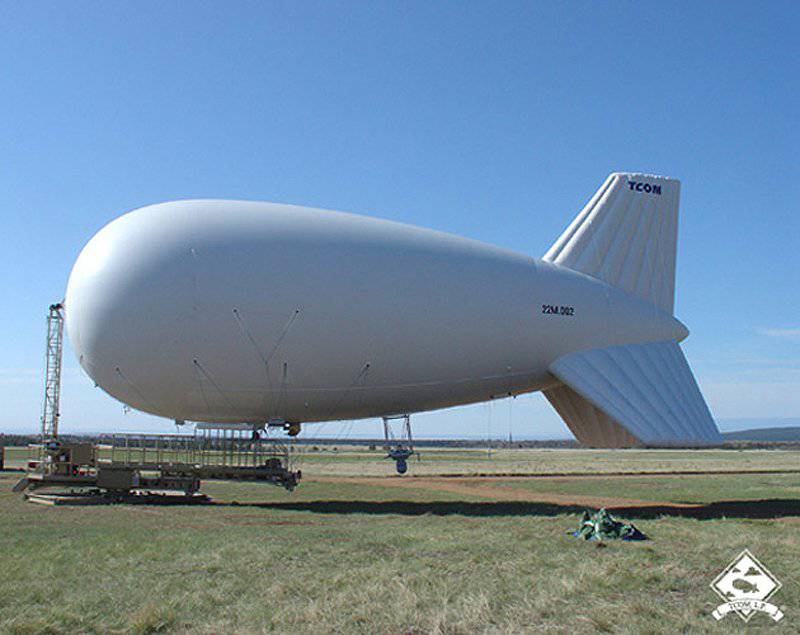

Tcom has developed a family of balloons - in the photo 22M with a load capacity of 400 kg
Another US manufacturer is Lighter Than Air Systems (Ltas), whose systems are based on Kingfisher tied balloons, developed by Aerial Products in collaboration with Embry Riddle Aeronautics and Aeronautics University. The airbag of the Kingfisher Balloon can be enlarged in order to obtain a greater carrying capacity. Ltas offers its advanced systems such as the Ltas 200 and 300 (the number shows the load capacity in pounds) with a two-touch gyro-stabilized camera for military applications, since the protection of troops is one of the main tasks of these systems.
The country that has relied on lighter air to ensure its safety is undoubtedly Israel, which operates a surveillance system based on the Skystar 300 balloon from Aeronautics. It is able to hold 30-kg load at 300 meters height for 72 hours; It takes only 10 minutes to refill with helium before restarting for another three days. A typical load consists of a round-the-clock set of sensor equipment stabilized in three axes.
As noted above, continuous observation from above can also be provided by fixed towers that optimize the position of the sensors around the perimeter of the camp. Tower Solutions offers three options for self-retractable towers, respectively 6, 12 and 24 height meters and a load capacity from 63 kg to more than 900 kg. Two smaller towers can be installed respectively on a category Humvee or pick-up truck. The towers withstand strong gusts of wind with minimal swing; in the stationary mode, the maintenance of sensors and equipment installed on them is greatly simplified.
Sensors
Sensors mounted on aerostats and towers are for the most part day / night optoelectronic systems or radars, which are often integrated with laser range finders, which, together with geolocation, provides information about the target. One of the main suppliers of such systems is Flir Systems, whose products are installed on many systems of protection of American forces.
The analogue Star Safire III system includes a 640x512 cooled sensor with a wavelength range of 3-5 microns with a field of view from 0,35 ° to 25 °, a color CCD camera with a field of view of 2,7 ° -28 °, a telescope (for observing pinpoint targets) with a field of view of 0,29 ° -5,4 ° and a camera with enhanced image brightness with a field of view of 0,7 ° -5,4 ° (the last two coincide with the infrared field of view), a laser rangefinder with a range of 25 km, a laser illuminator and a laser pointer. This kit is installed in the ground operational surveillance system of the US Marine Corps, as well as the Raid, Raid-Eagle Eye, Cerberus systems and the Base Expeditionary Targeting & Surveillance Sensors-Combined system of the US Army.
Star Safire HD is a fully digital high definition system that includes an 1280xXNNMX X-ray sensor with 720 ° field of view -0,25 °, a 30x1280 CCD camera with 720 ° -0,25 °, a telescope with 29 ° field of view, PTZ infrared PTZ, PTN infrared PTZX-0,25 °. low illumination with 1,5 ° -55 ° plus the same laser systems as in Star Safire III.

The expanded tower of Cerberus. Flir Systems Star Safire III is installed on these retractable platforms, among other sensors.
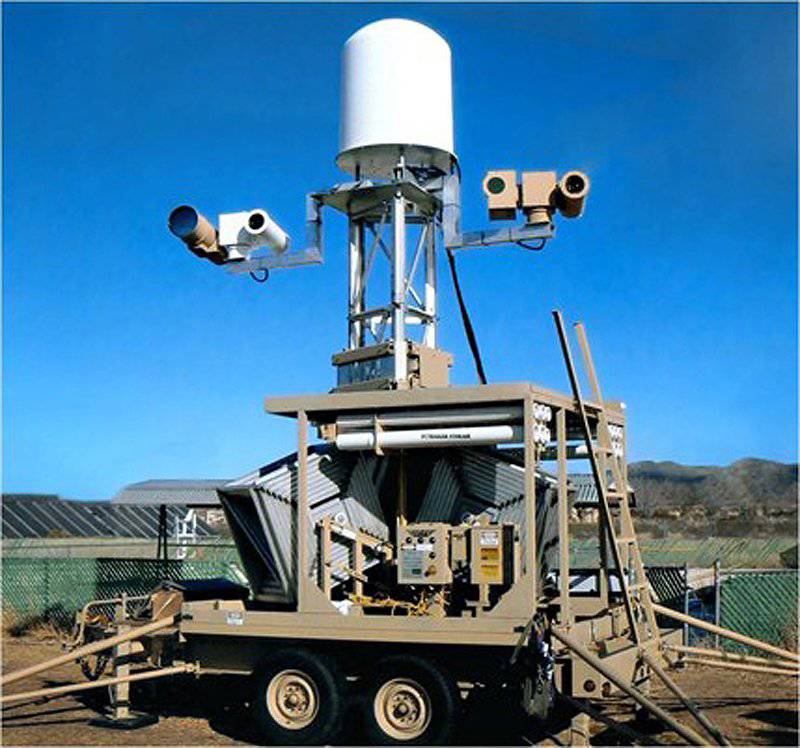

The system from Tower Solutions with all installed sensors, including optical-electronic and radar
In addition to the Flir systems (Forward Looking Infra-Red - a long-range thermal imaging system), American forces protection systems as well as similar systems from other countries use Flir sensors of medium and short range, such as Thermovision 3000 and Sentry.
The Israeli company Controp has developed Speed-A, special stabilized equipment for balloons, which includes a continuous-magnification thermal imager, a color day camera, an eye-safe laser range finder and a laser pointer. The Israeli company sought to create Speed-A as easy as possible due to the installation of this equipment aboard the Aeronautics Skystar 300.
Israeli company Rada announced in June 2011 of the development of a new system RHS-40, optimized for the defense of advanced bases. Pulsed Doppler radar with active scanning is offered as a universal hemispherical surveillance radar MHSR (Multimission Hemisphere Surveillance Radar). He is able to identify a rocket, artillery and mortar shells, a shooting point and a meeting point, as well as direct-fire weapons, such as anti-tank missiles and rocket-propelled grenades, and, in addition, typical field targets, such as infantry and vehicles (respectively, the detection distance is 8 and 20 km).
To ensure circular detection, four flat panel antennas are installed on it, which can be installed as a single assembly or deployed as a group of elements, each of which covers 90 ° in azimuth and elevation in 80 °. The system is deployed by the Israeli army to protect its particularly important facilities.
The Elta division of Israel-based Israel Aerospace Industries has developed the EL / M-2083 radar specifically for balloons. The sensor is a further development of the EL / M-2080 Green Pine sensor, designed for the Arrow system (protection against ballistic missiles). He is able to detect low- and high-flying targets using his 3D radar with a phased array, the sensor's range is about 500 km. The radar has been in service with Israel since the middle of the 2009 of the year, in the same year it was acquired by India, and the third unnamed buyer purchased at least two systems in the 2010 of the year.
As for ground-based sensors, Sagem recently introduced its Teos (Territory Electro-Optic Surveillance - Territory Electro-Optic Surveillance Territory) system, which is available in various configurations (depending on the stated distance). Teos - Teos XM system options for long-distance monitoring up to 20 km, Teos LR (Long Range - long range) up to 15 km, and Teos MR (Medium Range - medium action) up to 10 km. These systems are equipped with high-resolution infrared sensors Sagem Matis 3 or 4 generation.
Sagem Teos can be easily installed on a car or on an observation tower, it is distinguished by such operating modes as autoscanning, motion detection and tracking. Sagem Jim LR multi-function long-range binoculars have day and night channels (3-5 micron), a telemetry sensor, a laser pointer, GPS and a magnetic compass. Binoculars are used to protect military camps, including in Afghanistan.
DRS offers its Watchmaster Pro system, a turret with a Quickset QPT-LT positioning device installed on both sides, in which you can install one or more cameras for round-the-clock surveillance. The quick-change system allows cameras to be switched on the “plug and play” principle. The standard DRS system includes an uncooled thermal imager and daytime color camera.
Thales' Teoss was at one time only a night sensor for marine applications, but now it is also used in a non-stabilized version in terrestrial applications. The elevation range is -25 ° to + 45 °, the azimuth range is ± 170 °, although continuous circular rotation is available as an option. Sensors are used in the cooled Albatross thermal imager. The entire system weighs less than 11 kg.
Argon ST has developed a towerscout hardened detection and surveillance system designed to work on poles and towers in extreme conditions. It is equipped with a cooled thermal imaging camera with three fields of view (1,2 °, 5 ° and 22 °) and a color CCD camera with x27 magnification. A laser range finder can be added, and a standard thermal imager can replace an uncooled camera. The system interface unit provides network connectivity and image stabilization.
Thales's Wasp (Wide Area Surveillance Platform) global observation platform is designed to protect military bases. The system is mounted on a trailer, it can be deployed in less than 30 minutes, since the optical-electronic sensor kit is mounted on a telescopic mast. The kit includes a thermal imaging camera, a camera, a laser range finder and a laser pointer, as well as an integrated GPS and north orientation system. Such devices as radar, acoustic sensors can be built into the system; thus, electro-optical sensors are synchronized automatically or manually for the purpose detected by these devices.
Selex Galileo provides a simple solution in the form of an Observer 100 system; it is also mounted on a trailer, the mast lifts the sensory equipment to the height of 11 meters. The system consists of a third-generation thermal imager with 10,2 km human detection range and 3,4 km recognition range, a color camera with 9 km detection distance and 3 km recognition distance. Surveillance radar has a human detection range 2,7 km and 4,8 km for the car, a laser rangefinder with a range of up to 20 km is offered as an option.
Survey radar Cassidian Spexer 2000 is installed on the platform, from where it provides 120 ° coverage with tracking and scanning capabilities

An artistic representation of the use of the Cassidian Spexer 2000 radar, which is part of a critical infrastructure monitoring system.
As for ground-based surveillance radars, a variety of models and options are available on the market. Among the very new products, you can mention the Thales GO80 radar (Ground Observer 80), which can identify a heavy vehicle on 50 km, a light vehicle on 34 km and a person on 24 km. Operating in the I band (8 – 10 GHz), it can be divided into two portable components. Its rotating 1,6 meter-wide antenna covers 360 °, although the radar can be programmed to scan only certain areas.
Formerly known as TRGS-Sec, the Cassidian Spexer 2000 is a phased-array active radar spanning the 120 ° sector without mechanical scanning. Working in the X frequency band (5,2 – 11 GHz) with a dual beam provides simultaneous scanning and tracking; The radar can detect vehicles at a distance of 36 km, a human 18 km and a small UAV at 9 km. In marine mode, it can identify a swimmer on the 1 km and a small rubber boat on the 20 km.
The X-band radar under the designation Lyra 10 from Selex Sistemi Integrati has a typical detection range of 24 km and covers a sector ± 180 °, which can be reduced to ± 6 °. Portable antenna assembly weighs less than 25 kg; demonstrated its installation on a quad bike. Thus, the radar can be easily deployed to protect even small sites and bivouacs.
DRS Technologies, part of Finmeccanica, has in its arsenal a portable surveillance and targeting radar AN / PPS-5C Mstar (Manportable Surveillance and Target Acquisition Radar). The radar is tested in battles in Iraq, Afghanistan and the Balkans; 38,7 kg weighs, the heaviest element is the 13 kg main electronic unit, deployment takes less than 5 minutes. The radar operates in the Ku band (12 – 14 GHz), the observation range is from 100 meters to 42 km, differs in the zoom mode of the zone 1,5x1,5 km; can be used to adjust fire from closed positions to 15 km. The radar can detect a person on 11 km, a light car on 24 km, a heavy car on 36 km, accuracy is ± 10 meters in range and ± 5 thousandths in azimuth.
ICx Technologies, part of Flir's 2010, has developed a whole line of remote detection and tracking radars. The youngest member of this family is the STS-350 perimeter surveillance radar, which can detect a crawler on 125 meters, a man on all fours on 200 meters, and a walking or running person on 350 meters. Weight is 45 kg; when operating on two batteries, the duration of operation is from 12 to 20 hours. For the purpose of rapid deployment, STS-350 can be installed on cars or trailers, and up to 24, such radars can be combined into a single network. Also available is an option with increased range to 700 meters. Over 1200 radars STS-350 work in the areas of military and internal security.
The perimeter observation radar LSR-5000 was created to work in the desert, it has a detection range of machines up to 5000 meters, a crawling or swimming person can determine at a distance 500 meters, while a person walking 3000 meters. The radar operates in the Ka range (20 – 30 GHz), the 0,7 resolution in distance and 1 ° in azimuth; weight is 18 kg.
The STS-12000 long-range radar with improved fast scan performance is also a member of this family. He can identify a vehicle at a distance of 12 km, a person walking almost 10 km. The radar is offered by the Israeli company Aeronautics as a radar for its continuous monitoring system. The mass of the radar is about 300 kg, it is often installed on a trailer with a lifting platform to increase the coverage area.
All of the above radars as well as other members of the family, such as STS-700, 1400, 2800 and 4400, can work together in a network.
The Israeli company Elisra, a division of Elbit Systems, recently showed its new portable radar system Foxtrack. This lightweight, compact radar is carried by two operators and can work either on a tripod or on a vehicle. Foxtrack was created to conduct surveillance at medium and long distances, it identifies a soldier at 8 km and a small car at a distance of 15 km.

Foxtrack - the newest ground surveillance radar. The manufacturer-company Elisra does not disclose most of the characteristics of this device.
Acoustic Sensors
Raytheon BBN’s most recent success in the field of acoustic sensors includes a contract worth 54,3 million dollars, signed by the US Army for the supply of Boomerang III systems for defense of the perimeter and defining sniper fire for the parts involved in the Afghan campaign. To determine the location of snipers and other sources of fire from small weapons The Boomerang III system is based on a series of microphones and acoustic triangulation. It allows the Allied forces, after calculating the attacking fire and the relative position of the sniper, including vertical angles, to respond quickly with maximum accuracy.
Until recently, Pilar Mk IIw from 01dB-Metravib was based on two antennas connected to an electronic unit, which in turn was connected to a laptop computer, showing the location of the threat with an accuracy of ± 2 ° in elevation and ± 5 ° in elevation. Based on certain comparative tests with other systems, the Bundeswehr decided to purchase a French product, but requested the possibility of networking more antennas so that one operator could control the entire network.
The company began work on this order after a pause caused by a change of priorities and received a multi-million dollar contract in March 2011. The system is designed to protect large camps with an area of 1x1 km (possibly Urkuz), it will consist of 16 antennas, 4 side-by-side, connected to the electronic unit, which in turn will be connected via a fiber optic cable to the central control unit. Antennas are mounted on rotating viewing towers, equipped with thermal imagers, day cameras, and a laser rangefinder. The GPS system is supplied by the German company Aim.
Microflown offers its own border and perimeter guard system based on compact surround sound probes that measure the acoustic vector, instantly detecting a threat within a radius of 10 km. Multiple systems can be installed along a protected area at intervals of just under 10 km. For a few seconds, the system is able to establish a threat, as well as an approximate trajectory and time of arrival.
Artistic presentation of the program for the future interaction of the defense systems of military facilities Ficaps. The program is carried out by Germany and France under the leadership of Rheinmetall, from the French side the main partner is Thales

Typical sensor Boomerang III for the protection of stationary camps; Raytheon BBN system deployed in Afghanistan to locate enemy fire positions
Command and control
The above-mentioned sensors, along with modern infrared sensors, seismic and acoustic sensors, all need to be integrated into some type of control system that would allow the security personnel to identify any possible threat, immediately identify it and react in accordance with the rules of engagement .
For the first time deployed by the Dutch army in Afghanistan back in 2006, the Discus system (Deployable Integrated Sensors for CompoUnd Security - deployable integrated sensors for object protection) developed by Thales was also purchased by Canada in 2009 year. The system includes long-range radars Thales BOR-A550 / 560, portable Squire radars and optical-electronic sensors. Thales has also developed Specter, a demo designed for the French military.
Rheinmetall, Thales and Diehl Defense have also been selected for the Bundeswehr Seo (Schutz von Einrichtungen und Objekten) program to protect military installations. Thales Germany is responsible for Musec2 (MUlti-SEnsor Command & Control), an open system that is compatible with all sensor types, and for the MobUT (Mobile Uberwachungs-Technik) perimeter protection system. These three companies are also responsible for the Zosa (Zentrale Operative Schutzaufgaben) management system, which is the heart of Seo.
Cassidian (as part of Airbus Defense and Space) offers its Dome system (Defense of Mission critical Entities), which has a set of radars and sensors, as well as actuating elements for the timely definition of the target, its identification and proportional response. These are just a few examples of open-architecture command and control systems that allow optimal control of sensors and actuators that are currently available to protect military installations.
Materials used:
www.armada.ch
www.tcomlp.com
www.droneaviationcorp.com
www.lockheedmartin.com
www.flir.com
www.controp.com
www.iai.co.il
www.drs.com
www.elbitsystems.com
www.acoemgroup.com
www.defenceandsecurity-airbusds.com


Information