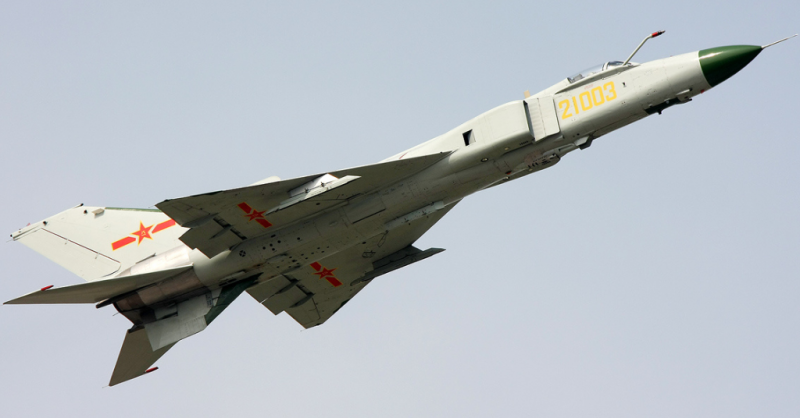
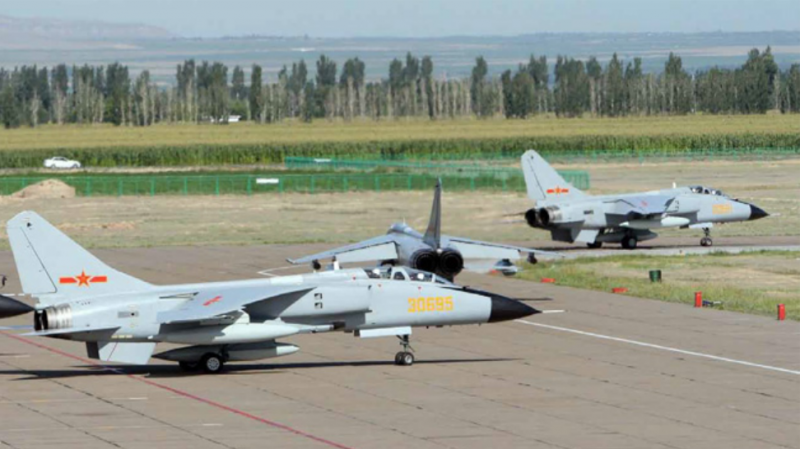
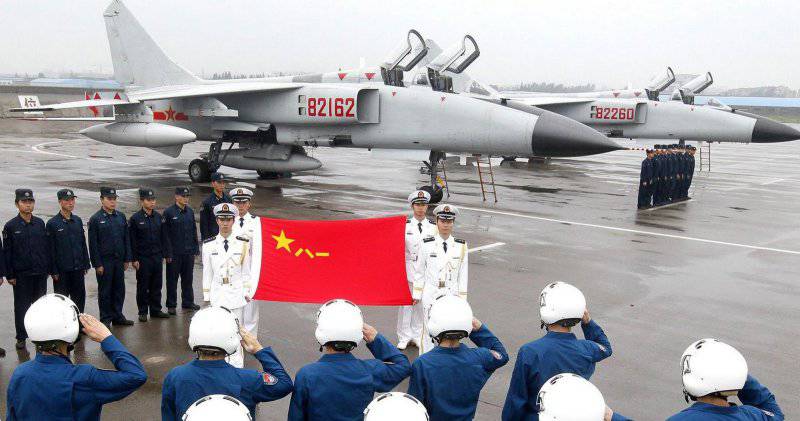
Chinese fighter-bomber JH-7 "Flying Leopard"
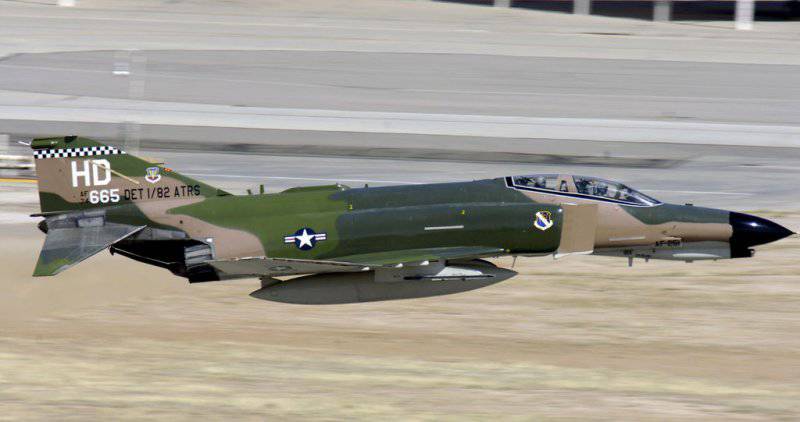
The formation of the image of the Chinese military aircraft, the development of which began more than 30 years ago, was greatly influenced by the Vietnam War. The “main hero” of this war by the US Air Force was the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II fighter of various modifications. As part of the concept of a universal multi-purpose heavy fighter, this aircraft delivered rocket-bombing strikes against ground targets and, if necessary, fought an air battle. And although in close combat, the Phantom often lost to lighter and more maneuverable MiGs, its range, acceleration characteristics, complex of electronic equipment, radar capabilities and weapons inspired respect. "Phantom" was the first multi-role tactical level fighter that could use medium-range air combat missiles. Prior to that, only specialized anti-aircraft interceptors had such an opportunity. In addition, he could carry a wide range of missile and bomb weapons for operations against ground and surface targets, including adjustable bombs and tactical nuclear weapons.
The immediate impetus for the development of a fighter-bomber of the new generation in the PRC were unfavorable conclusions on the basis of the operation to capture the Paracel Islands in 1974 year. These islands in the South China Sea, which were controlled by South Vietnam at that time, were captured by the landing of the Chinese amphibious assault forces. Saigon troops did not render much resistance, and the islands in a short time completely came under the control of the PRC. Americans, who had already left Vietnam, chose not to interfere.
The range of the Chinese Q-5 attack aircraft and the J-6 fighter (MiG-19) did not allow for air support to the landing. And the use of N-5 (Il-28) bombers was ruled out because of the fear of large losses that the South Vietnamese Air Force, which had F-5E supersonic fighters, could inflict. Difficult to use Chinese aviation and the imperfection of navigation and sighting systems, communication and control systems, as well as the lack of modern electronic intelligence and electronic warfare equipment. As a result, the PRC fleet was forced to operate without air support, and the first PLA Navy aircraft appeared over the islands only a few hours after they were completely captured.

The events around the Paracel Islands gave a powerful impetus to the work on creating a modern strike aircraft. The military leadership of the PRC came to the conclusion that the state of the economy and the aviation industry of the country would not allow two independent programs to create strike aircraft systems to be carried out simultaneously. As a result, it was decided to develop a single aircraft in two extremely unified versions - for the Air Force and Navy. The armament of the projected strike aircraft was supposed to include both conventional and guided weapons. The possibility of using tactical nuclear weapons was also envisaged. During preliminary studies and consultations between representatives of various military branches, it was concluded that the fleet and the PLA air force needs a supersonic all-weather attack aircraft to replace the N-5 bombers and the Q-5 attack aircraft, capable of operating not only in tactical, but also operational depth. At the same time, representatives of the Navy insisted on a twin-engine power plant and a crew of two people (following the example of the Panavia Tornado fighter-bomber).
At the first stage of the program, it was supposed to create a new combat aircraft based on the J-8II interceptor. This ensured the unification of the aircraft fleet and significantly reduced the cost of production of "fighter" and attack aircraft complexes.
However, the Chinese military had reasonable doubts about the possible effectiveness of this aircraft with a delta wing, “sharpened” to perform air defense tasks, when operating in the range of speeds and altitudes characteristic of a fighter-bomber.
The next contender for this role was the shock Q-6. It was assumed that the Q-6 fighter-bomber will become the Chinese version of the Soviet MiG-23BN fighter-bomber (previously, China received several vehicles of this type from Egypt).
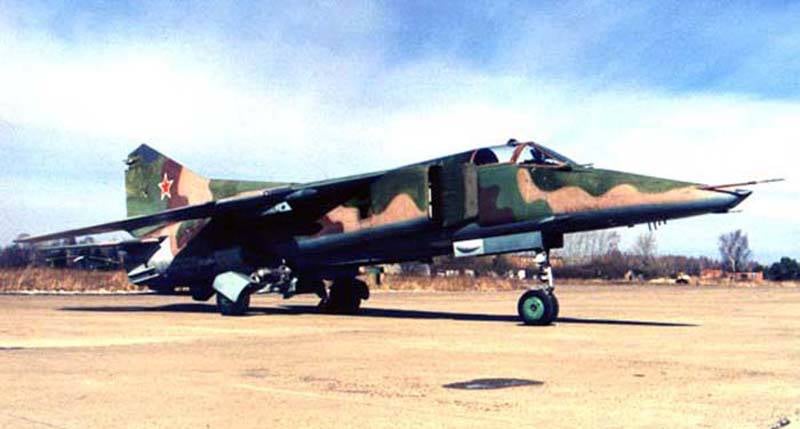

It seemed that the use of Soviet technology and design approaches familiar to and understood by Chinese specialists would make it possible to create a new fighter-bomber in a relatively short period of time and at moderate cost.
In this connection, the MiG-23BN BRLS, which is necessary for searching land, sea and air targets, was absent, and there was only a laser range finder. It was decided to install a radar complex from the F-111A aircraft in Vietnam. It included the General Electric AN / APQ-113 radar and sighting radar, as well as two special radar following the terrain of the Texas Instruments AN / APQ-110 radar.
However, the Chinese radio-electronic industry was unable to reproduce the modern and complex American radio-electronic complex. The lack of the necessary element base required a partial return to the lamp circuits, which further increased the size and weight of the equipment. The need to place on board an aircraft a system of three radar stations with parabolic antennas, much larger than the RP-22 radar on the MiG-23C, caused an increase in the size of the fuselage, as well as a change in the entire layout of the fighter-bomber. The air intake of the projected Q-6 from the originally adopted side (made according to the MiG-23 type) became sub-body (as in the F-16), and the size and weight of the aircraft increased markedly, reaching the parameters of the Tornado fighter-bomber. The wing sweep change system created in China turned out to be 12% heavier than the similar Soviet system used on the MiG-23 aircraft. Ultimately, the growth of the weight and dimensions of the equipment was not managed to be kept under control, the situation was aggravated by the lack of suitable engines in the PRC, which further led to the loss of interest from the PLA leadership in this protracted program.
In the 1983 year, after several years of preliminary research, after analyzing previous work in this direction, the Xi'an Aviation Industrial Association began to develop a relatively heavy twin-engine, partially maneuverable, optimized for low-altitude applications. At the early stage of the project, a two-seater aircraft was considered, which in its layout resembled the F-111 and Su-24, having in-line accommodation for crew members. A variant of the lighter weight class, similar to the British fighter-bomber SEPECAT “Jaguar”, the Japanese Mitsubishi F-1 or the Yugoslav-Romanian JUROM IAR-93 “Orao”, was also considered. However, after weighing all the pros and cons, the Chinese experts came to the conclusion that the aircraft will be the most fully compliant with the requirements, in terms of dimension and mass, close to the American Phantom.
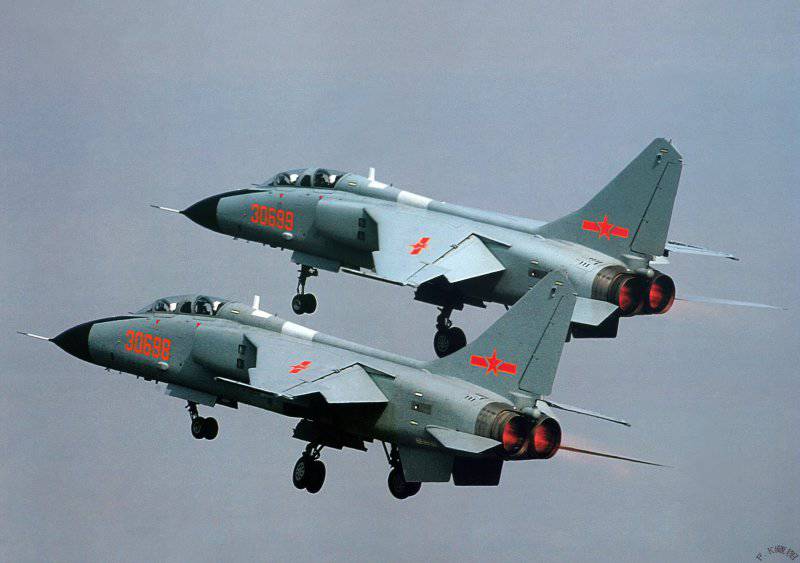
The original aircraft wore the designation H-7 (H - Hongzhaji, or bomber), and then was renamed JH-7 (Jianjiji-Hongzhaji - fighter-bomber). The aircraft has been designed for normal aerodynamic configuration with high wing having double sweep angle (55 deg. By 1 / 4 chord at the root and 45 deg. In the end portion), and a horizontal tail tselnopovorotnym odnokilevym vertical tail supplemented developed ventral ridge.
The avionics of the projected aircraft included a navigation and sighting system providing the use of weapons on small land and sea targets, as well as low-altitude flight. It was assumed that the fighter-bomber will have the ability to conduct defensive air combat using air-to-air missiles. When creating the Type 232H radar, technical solutions were borrowed from the American radar AN / APQ 120, several copies, which were dismantled in different degrees of safety from the F-4E fighters shot down in Vietnam. It was reported that the MiG-21 class fighter can be detected by this radar against the background of free space on a head-on course at a distance of up to 70-75 km, and a large surface target on 160-175 km. EW systems were installed: the active "Type 960-2" and the passive "Type 914-4", as well as the system for shooting heat traps.
The crew of the aircraft consisted of two people placed under the “tandem” scheme: a pilot and a navigator-operator. The crew members were located in the cockpit under a single lamp with a three-section canopy, which provided a good view in the forward-down direction. The complex of instrumentation equipment included traditional electromechanical devices, the BRLS indicator in the cockpit of the navigator-operator, and also the indicator on the windshield (HUD) of the pilot.
Using its status as the main fighter against "Soviet hegemonism" in the Far East, China managed to purchase Rolls-Royce "Spey" Mk.202 turbofan engines in the UK. Their British installed on their version of the deck "Phantom" FG.Mk.1 (F-4K). TRDDF Mk.202 had thrust 5450 / 9200 kg, weight 1856 kg, diameter 1092 mm and length 5205 mm. In terms of static, it slightly surpassed the General Electric J79 TRDF, used on American-made Phantom aircraft. However, due to the higher air consumption of the English engine, an increase in the air intake section was required, which affected the aerodynamics of the aircraft.
These engines, frankly, were not very successful - complex and capricious. During the testing and operation of the first JH-7 several aircraft were lost due to engine failure. As the further practice of using the Spey Mk.202 engines showed, these turbofans were not quite suitable for use on supersonic multi-purpose combat aircraft. But the Chinese didn’t have much choice, no one was in a hurry to sell more modern propulsion systems. It should be said that this was the first case in the post-war period when it was decided to equip the Chinese combat aircraft with a Western, not Soviet, engine with an engine. The first Spey 50 engines for testing and mastering production were obtained in 1975. In the same year, an agreement was signed with the British on the joint production of the Spey Municipal Unitary Enterprise MK.202, which received the Chinese designation WS-9. Up until 2003, China could not master the production of a copy of the Spy 202 engine. To continue the mass production of JH-7 and replace engines that have become exhausted, 2001 Spyew was additionally purchased in the 90 year from the presence of the British Air Force taken from the British F-4K.
The JH-7 became the first Chinese aircraft to receive “full-time” in-flight refueling equipment (an L-shaped fuel receiver placed the nose of the fuselage on the right side). The aircraft could carry up to three outboard fuel tanks with a capacity of 800 or 1400 l, which were suspended on two underwing and central underfuselazhnogo nodes external suspension.
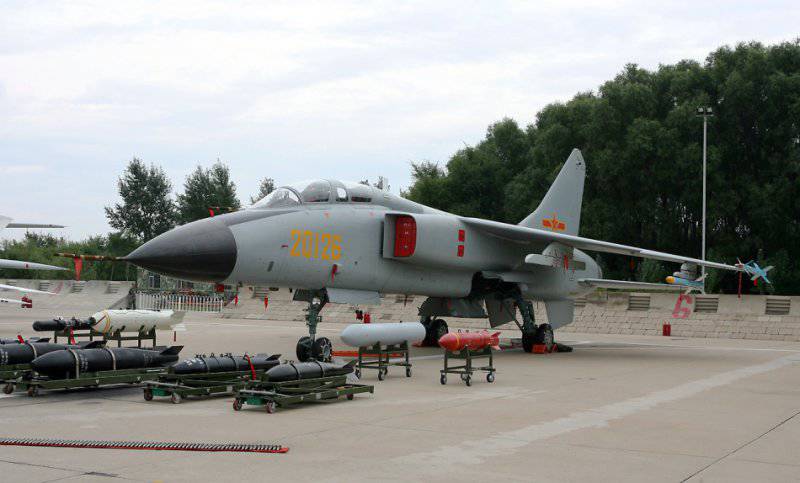
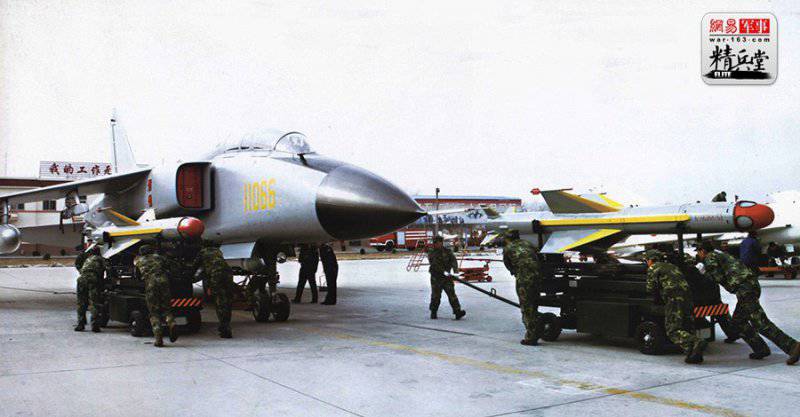
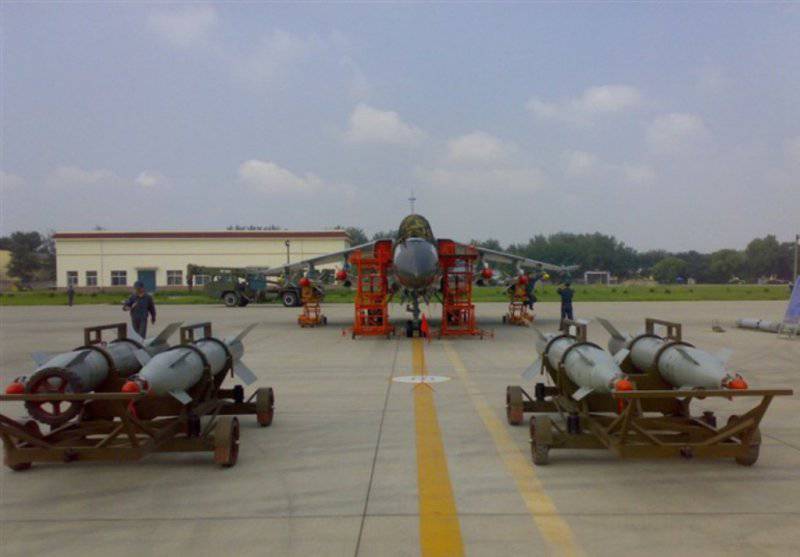
Strike weapons production aircraft, placed on six underwing and one central ventral nodes external suspension includes subsonic solid anti-ship missiles YJ-81 / C-801K with a range of start-up to 40-50 km, close to the French RCC "Exocet" (Two such missiles were suspended on root underwing nodes), as well as free-falling bombs in caliber up to 1500 kg and NAR. For self-defense, wing pylons were provided for air-to-air missiles with PL-5 type TGS. On the right fuselage "cheekbone" there was an 23-mm double-barreled gun "Type 23-III", which was an analogue of the Russian GSH-23L.
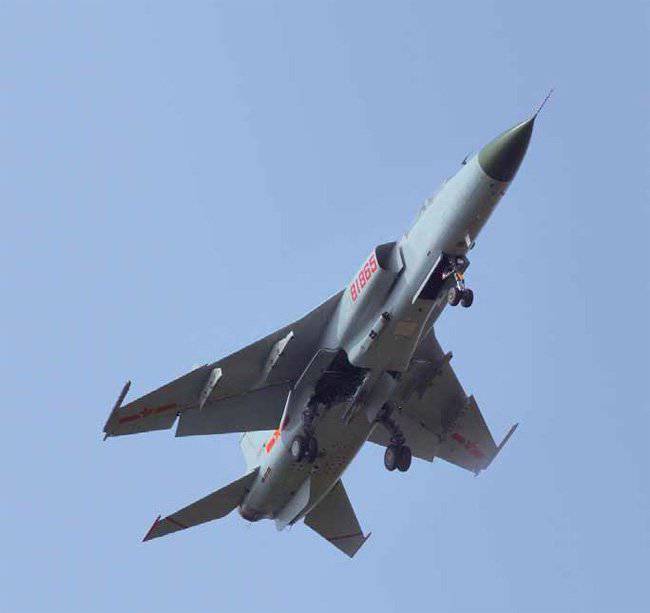

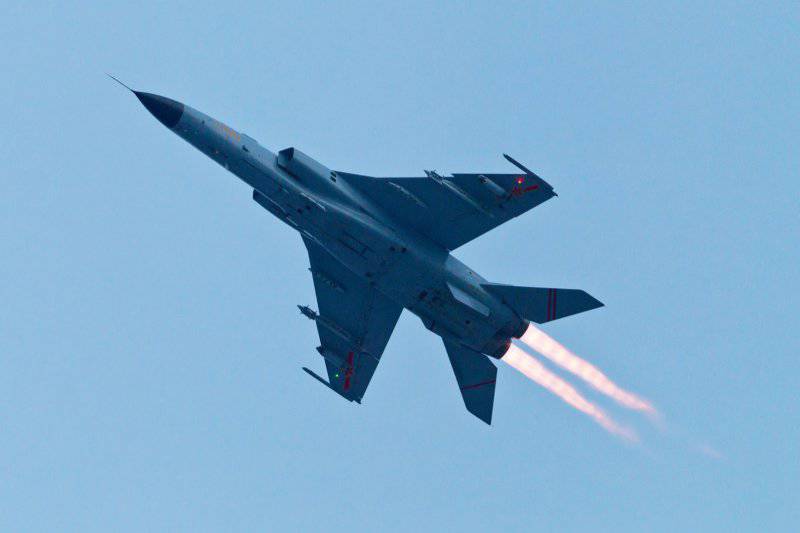
The first flight of the JH-7 prototype took place on 14 December 1988 of the year. Even before the aircraft began to be delivered to the line of command, a final split occurred in the views of representatives of the Chinese Air Force and Navy regarding the use of the aircraft and its characteristics. The Air Force wanted to get a plane to replace the Q-5 drums — live combat damage, capable of penetrating air defense at high speed and low altitude, resistant to EW and having modern on-board electronic equipment. For the fleet, the carrier of cruise missiles, optimized for searching enemy ships and operations at a considerable distance from the coast, was required.
The first production aircraft were released in the 1994 year. A batch of XHUMX JH-20 fighters-bombers entered trial operation at the 7 Marine Attack Regiment of the 16 Division of the PLA Navy Aviation (East Fleet) located near Shanghai. These machines were used to develop weapons systems, conduct tests, as well as develop principles for the combat use of a fighter-bomber in the interests of the fleet. The program JH-6 developed in deep secrecy. For the first time, the plane could be seen in reports of Chinese state television from the PLA series of exercises in 7.
And although the JH-7 did not fully satisfy the military, therefore, attempts were made to acquire a more advanced radar and a more powerful and reliable engine in the USA, there was an urgent need to replace the outdated N-5 naval bombers. Therefore, the release and improvement of aircraft continued.
The upgraded version of the machine that received the updated avionics and armament, which first took off in the 1998 year, was called JH-7A, the FBC-1 Flying Leopard was approved for the export version of the aircraft. Glider aircraft was strengthened, the most vulnerable places covered with armor. The wing and stabilizer received changes, a second ventral carina was added, the number of suspension points under each wing console increased.
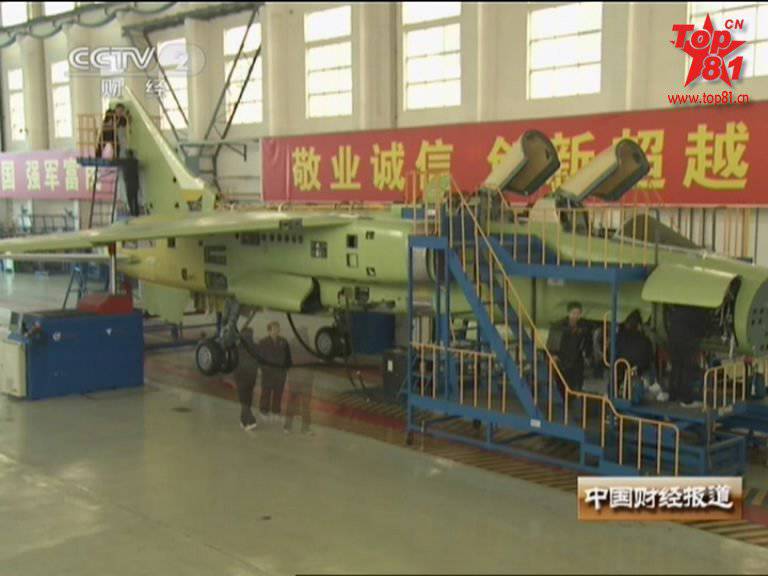

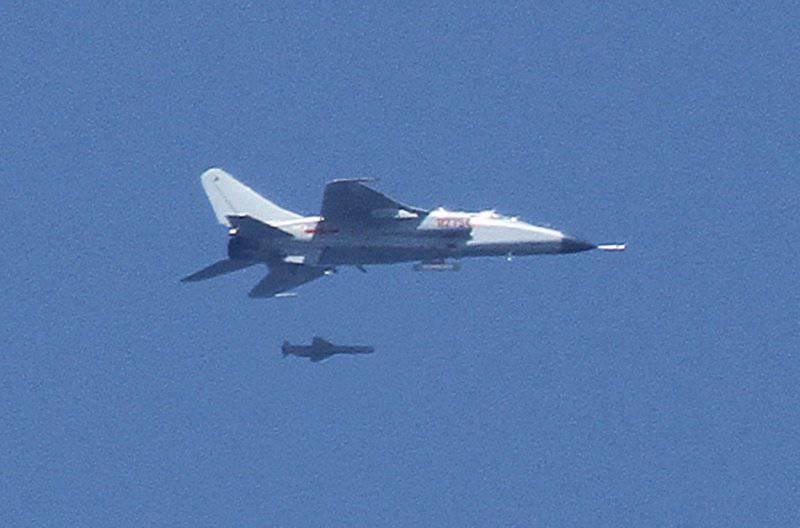
The aircraft gained the ability to use modern guided weapons. JH-7A received the equipment placed in the outboard containers, which determines the parameters of the irradiating radar and the targeting of the anti-radar missile YJ-91 (Russian X-31P), and for target illumination when using Chinese-made 500 calibrated bombs of laser-manufactured Chinese production. The number of suspension nodes has grown to 11.
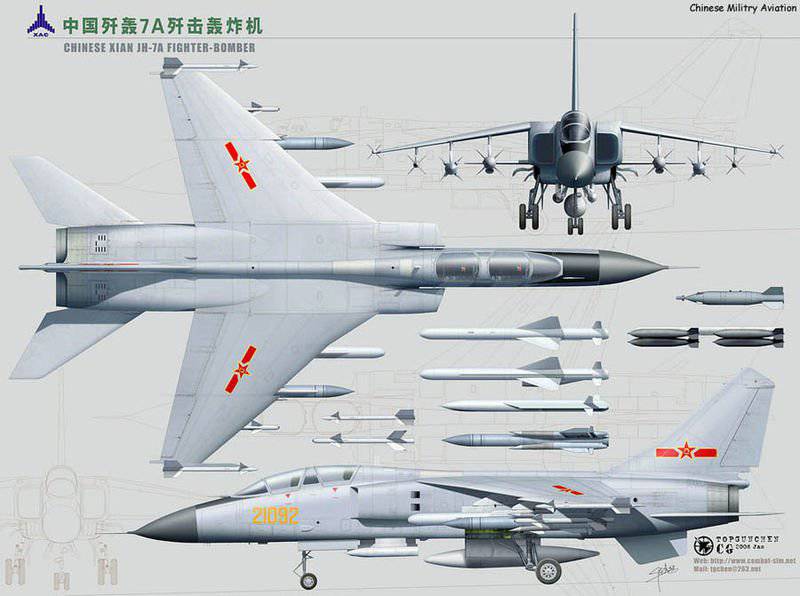

The armament also included Russian X-29L and X-29T air-to-surface missiles (in 2002, China purchased such URs from 2000 from Russia, and supplies were made not from industry, but from the Russian Air Force depots) bombs KAB-500kr, as well as their Chinese counterparts LT-2 (kg 500). Probably, the aircraft can also use KAB-500L, KAB-1500L-PR and KAB-1500L-F purchased in Russia with 1500 caliber kg.
In 2002, the new C-803K anti-ship missile, designed to equip JH-7A aircraft, entered service. It is equipped with a detachable solid-fuel booster and a sustainer jet engine. In the middle part of the trajectory, the CRC is guided by means of an inertial navigation system (with radio correction from the aircraft carrier), and the active radar homing head is activated at the end.
The main part of the flight of the anti-ship missiles takes place at an altitude of 10-20 m, and in front of the target, the rocket is reduced to an altitude of 3-5 m, which increases its invulnerability from near-missile defense assets. The maximum launch range is 250-260 km, and the cruise speed of the rocket corresponds to M = 0,9.
Improved EW facilities installed on the fighter-bomber include a radar warning system, an active jamming transmitter, as well as heat trap containers and dipole reflectors located at the base of the keel.
After the appearance of the new “Flying Leopard” modification with improved combat characteristics, the aircraft in 2004 were put into service with the PLA Air Force. In many ways, it was a necessary measure associated with aging and the urgent need to replace the main Chinese light tactical nuclear weapons carriers - the obsolete Q-5 attack aircraft, created on the basis of the MiG-19.
But even in spite of serious modernization, the JH-7A fighter-bomber is seriously inferior to the modern multipurpose Su-30MK2 multi-purpose attack aircraft, which were delivered to Chinese naval aviation in 2004. The Russian Su-30MK2 is superior to the JH-7A in all respects (including in solving shock tasks) and is inferior to the Chinese aircraft except in the “comfort” of a long flight at low altitude: this was due to the lower wing load on the Russian machine.
The superiority of the Russian aircraft, in general, is natural. The multipurpose Su-30 family is a further development of the heavy 4 fighter of the Su-27 generation. And according to its characteristics and technical solutions used during the creation, the JH-7 aircraft is most correctly compared with the two-seat McDonnell Douglas F-4 “Phantom II” fighter.
The most revealing may be the comparison of the Chinese fighter-bomber with the multipurpose F-4K fighter - the English version of the Phantom. The F-4K had an empty mass of about 14000 kg (for JH-7 this indicator approaches 14500 kg) and a maximum take-off weight of 25450 kg (for JH-7 - 28480 kg). The mass of fuel in the internal tanks of the Anglo-American aircraft was 6080 kg compared to the 6350 kg of the Chinese car, and the mass of weapons located on seven external suspension nodes could reach 7300 kg (of the JH-7 - 6500 kg).
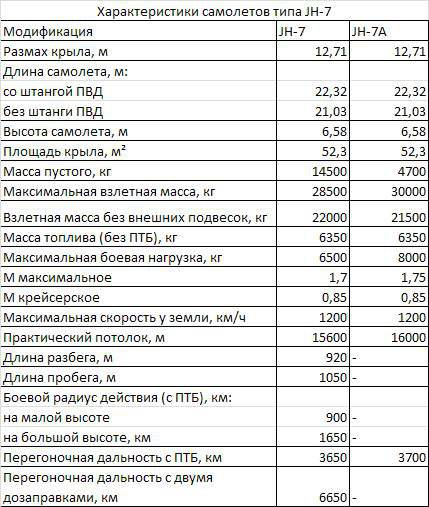
Having the same powerplant with the “Phantom”, very close weight characteristics and approximately equal wing load (wing area F-4K - 49,2 м2, and for JH-7 - 52,3 м2), the Chinese aircraft had significantly worse speed characteristics at high altitude ( the maximum speed corresponded to M = 1,7) than its Anglo-American counterpart (M = 2,07). At low altitude, the F-4K also had a speed advantage over the JH-7 (1450 km / h versus 1200 km / h). The characteristics of the range of both cars were approximately equal (without PTB - 2300-2600 km, distillation with PTB - 3650-3700 km).
Comparing the potentials of the on-board radio-electronic complexes of the American and Chinese aircraft, it must be remembered that the PRC actively copied the radio-electronic equipment of the aircraft shot down in Vietnam, the most massive of which was the “Phantom II”. It is safe to assume that JH-7 is equipped with avionavigation equipment, which largely follows the Phantom system and has similar technical characteristics.
If similar to the end of 7-s such as the F-1960K and F-4E can be considered analogs of the JH-4, then the JH-7A fighter-bomber can be compared with the “Phantoms” modernized in 1980-90-s (for example, Israeli) Phantom 2000 "or Japanese F-4EJKai).
JH-7A aircraft entered service with three naval aviation regiments of the PLA Navy and three regiments of the PLA Air Force. Each shelf equipped with JH-7A or JH-7 has 18-20 aircraft.
JH-7В, which is a deep modernization of the JH-7 fighter-bomber, is currently being tested. It was reported that especially for this aircraft, the development of LMDNXX turbofans with fairly high parameters (thrust 6 / 7300 kgf) was carried out. It can be installed on JH-12500В and Chinese engines of the new generation WS-7A, which develop traction comparable to the TRDDF AL-10F (i.e. on the order of 31-12000 kgf.). Currently, this engine is at the stage of refinement and launch into mass production. The design of the airframe is expected to widely apply the technology "stealth" (in particular, subtle air intakes and radio absorbing coatings deposited on the most "luminous" surface areas). The fighter-bomber should also receive a new complex of avionics, while using the radar with AFAR. Target equipment of Chinese-made radar should provide flight in a rounding mode of the terrain.
Further improvement of the "Flying Leopard", and the preservation of the entire program "afloat" is not due to the high performance of the aircraft. And in many ways due to the fact that the armament control system of the Su-30MKK and Su-30MK2 multifunctional aircraft purchased in Russia was technically incompatible with the missile systems developed and manufactured in China (the Chinese simply did not provide the Russian developers with information about their missiles). As a result, JH-7 remained the only carrier in its class of much cheaper and mass Chinese aircraft strike weapons. In addition, the creation, production and modernization of this aircraft stimulates the development of its own aviation design school, training of specialists and obtaining independent experience in creating modern combat aviation complexes, even if they do not correspond to the most advanced world achievements.
Based on:
http://www.aex.ru/docs/4/2011/8/29/1402/
http://www.livingwarbirds.com
http://www.flugzeuginfo.net















Information