The first ship of the series of rocket launchers

2. LTH:
Modification Lun
Wingspan, m 44.00
Length, m 73.80
Height, m 19.20
Wing area, m2 550.00
Weight, kg
empty 243000 aircraft
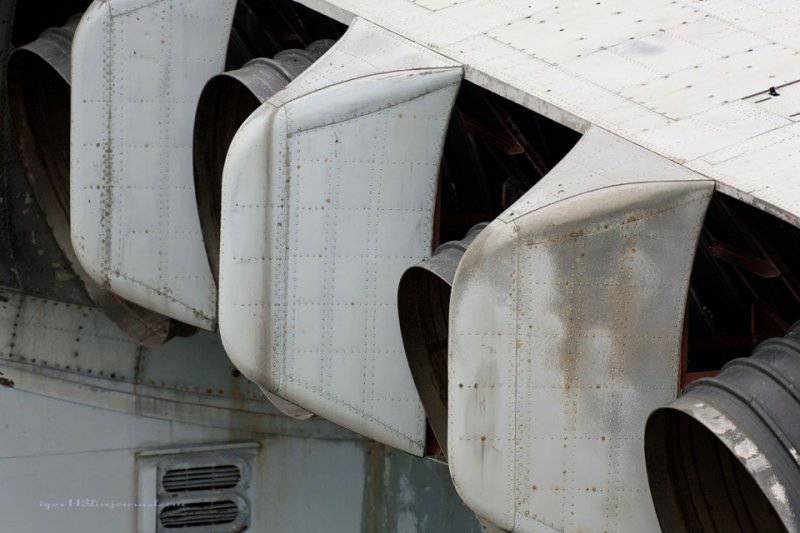
maximum take-off 380000
Engine type 8 TRD NK-87
Thrust, kgf 8 x 13000
The maximum speed, km / h 500
Practical range, km 2000
Flight height on the screen, m 1-5
Seaworthiness, points 5-6
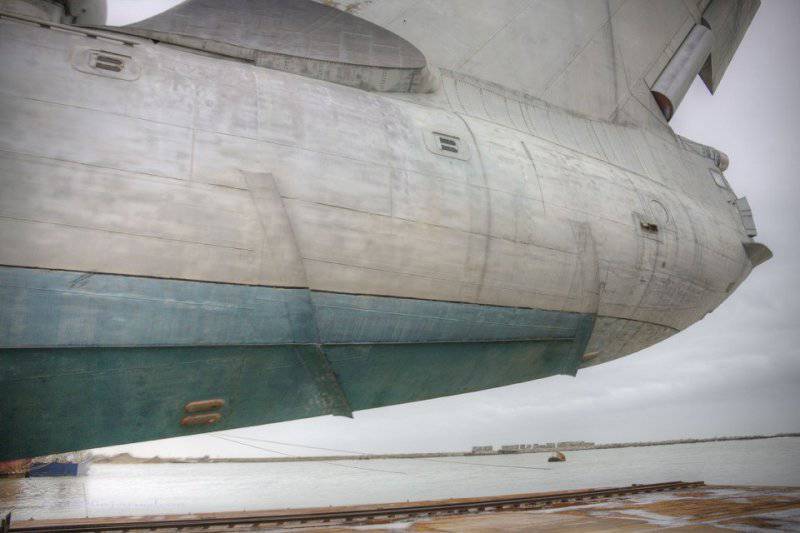
Crew 10
Armament: 6 PU PKR ZM-80 Mosquito
The weather was disgusting, so the photos are faded, but what is - that is.
There will again be many photos, and many of the same type.
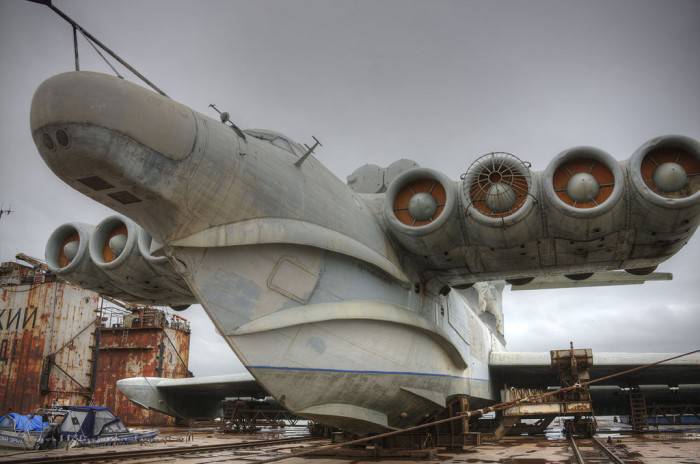
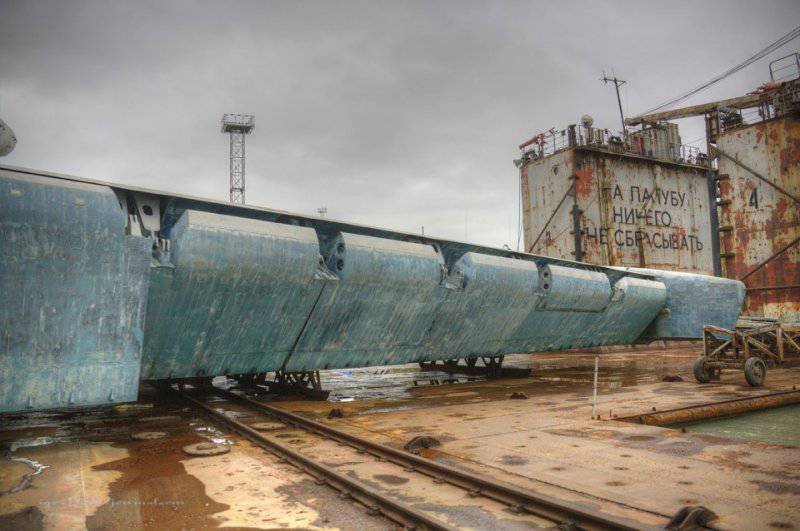
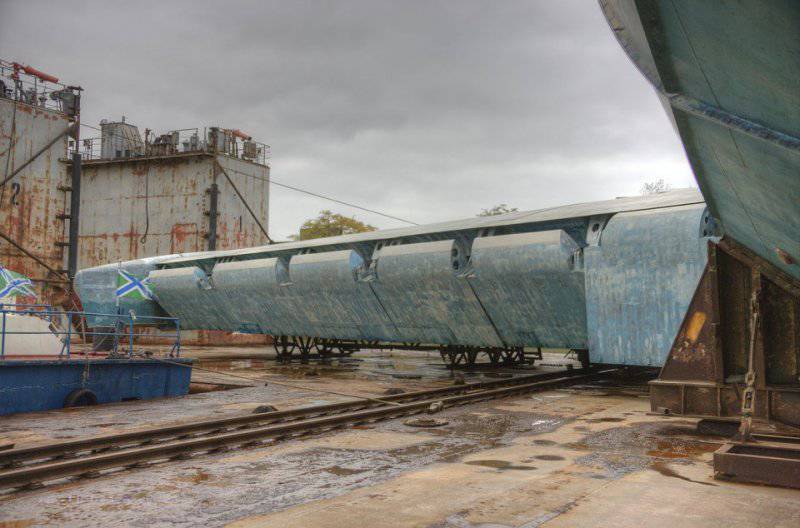
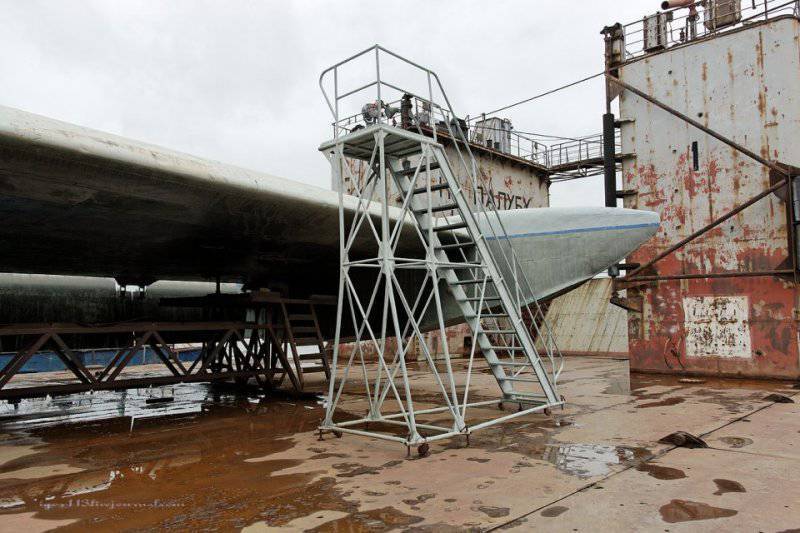
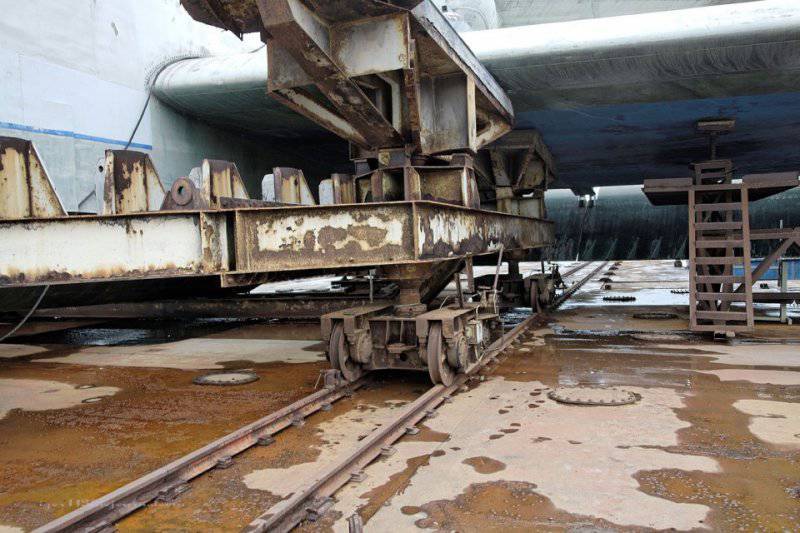
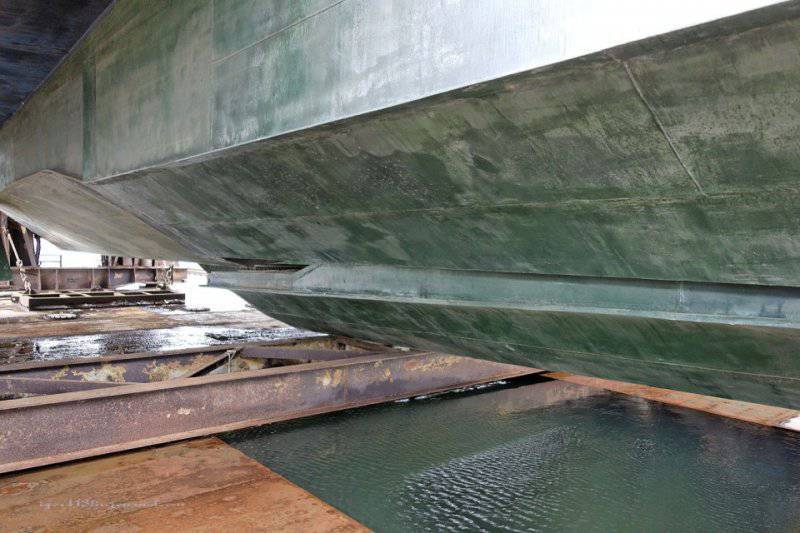
Lun is located on the dock, specially designed for it, with a load capacity of 500 tons.
3. Unlike the "Eaglet", "Lun" does not have a landing gear, only a hydro-ski, so it cannot climb ashore on its own. Therefore, he needs a dry floating dock.
4. This dock is towed into the bay by tugboats, then it sinks a few meters (it is possible to dive up to 10 meters), and then the ekranoplan that has surfaced goes on its own.
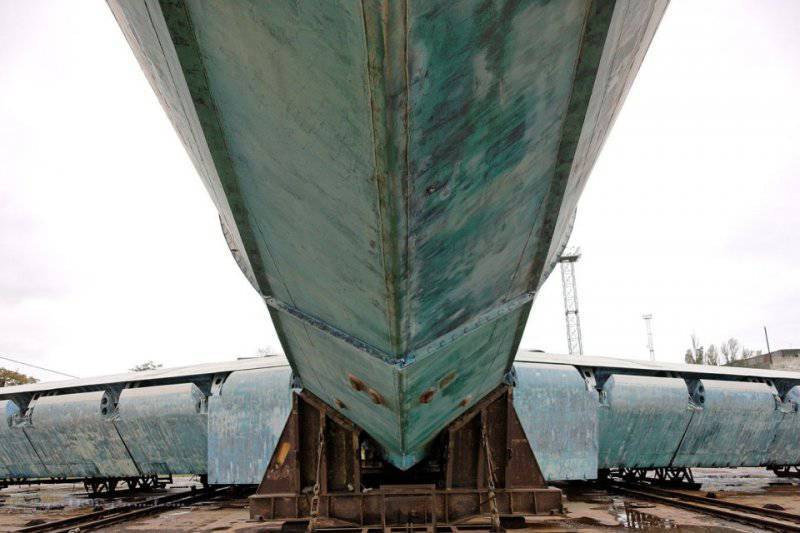
5. The general impression of the ekranoplan: an aircraft made at a shipyard according to the technologies that they had. The more unique his abilities.
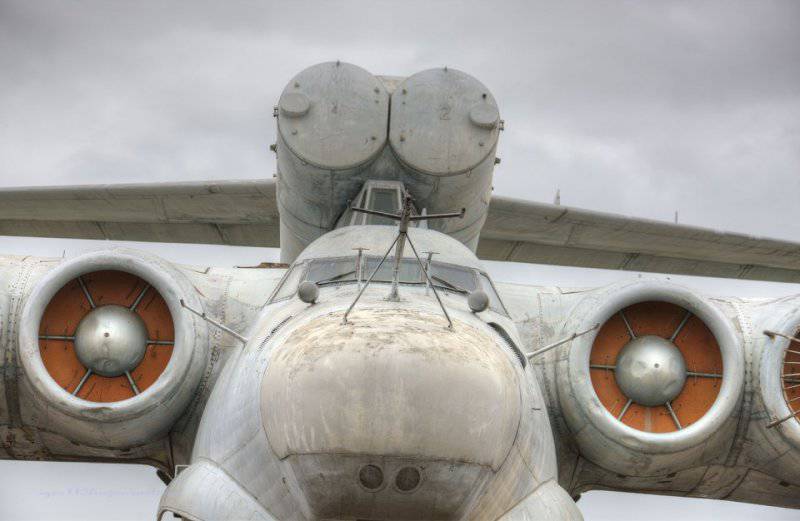
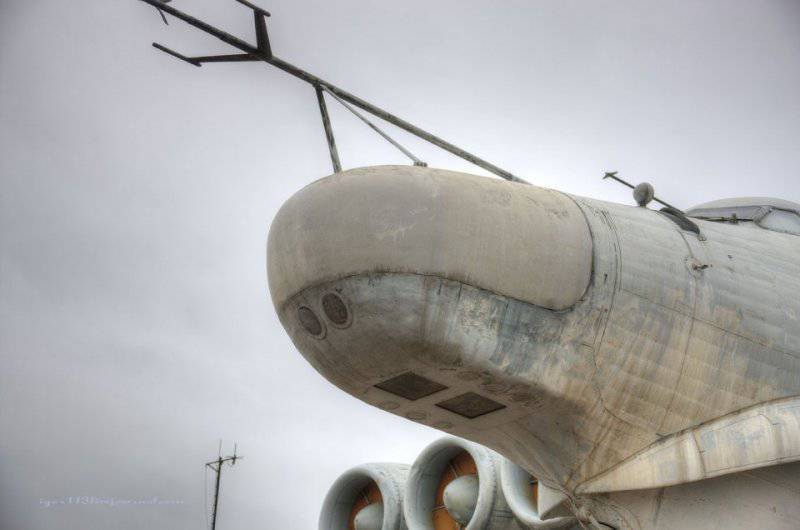
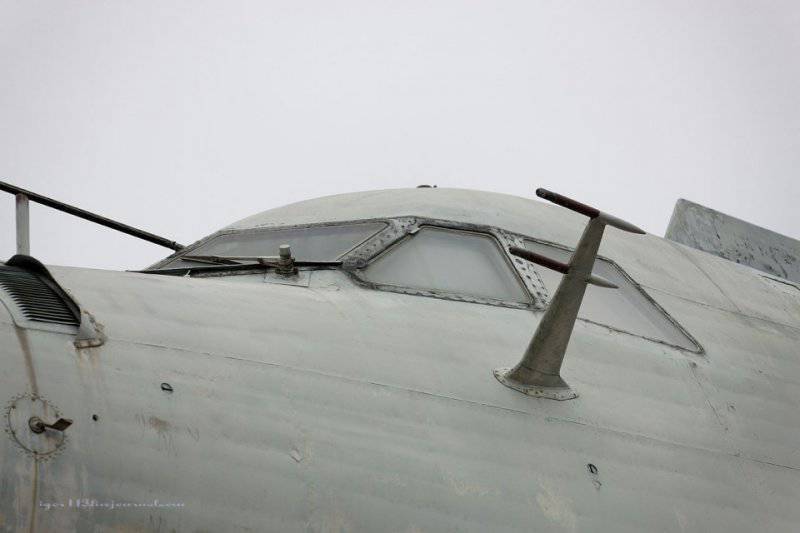
6. Under this fairing is a marine radar.
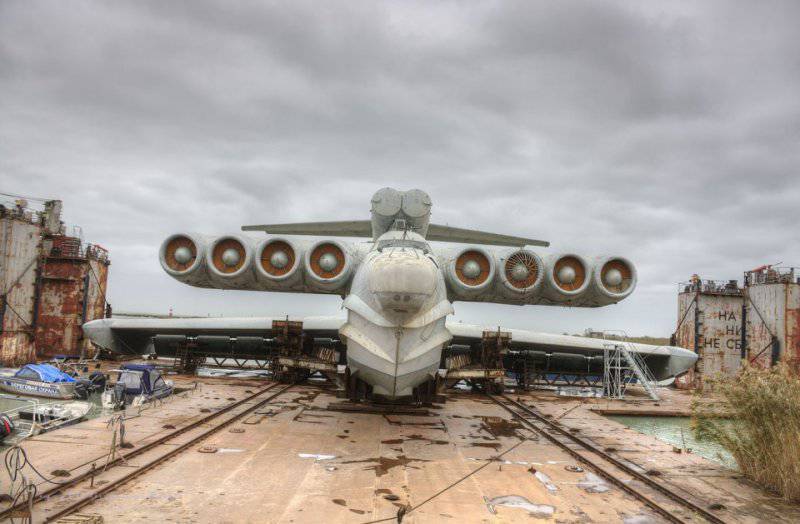
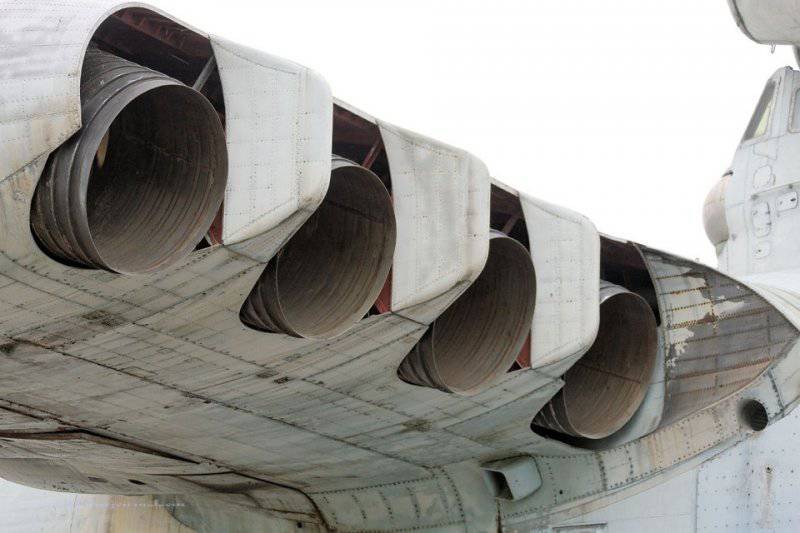
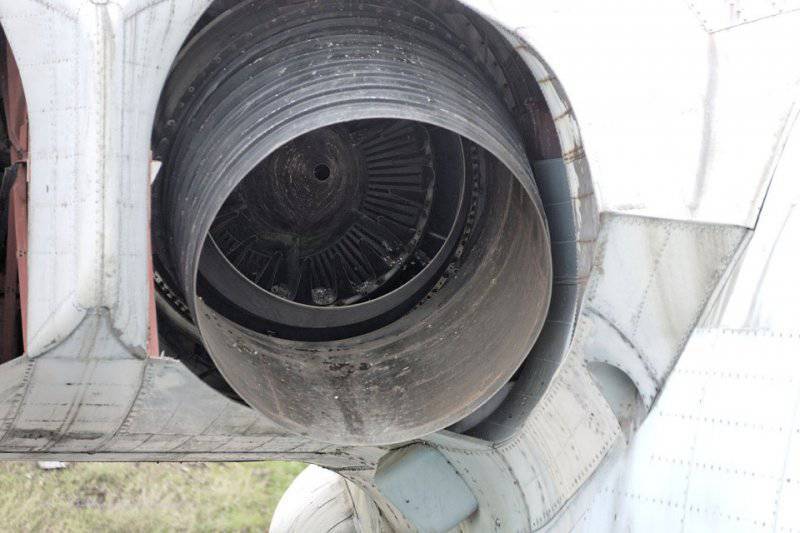
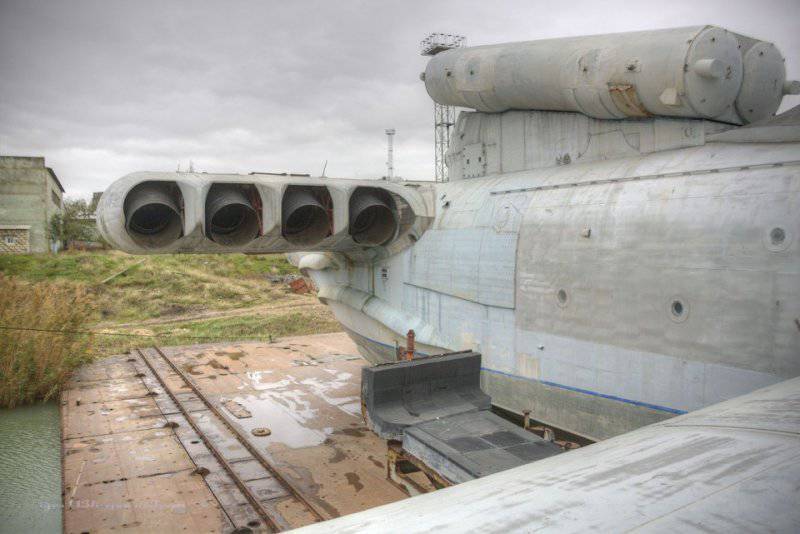
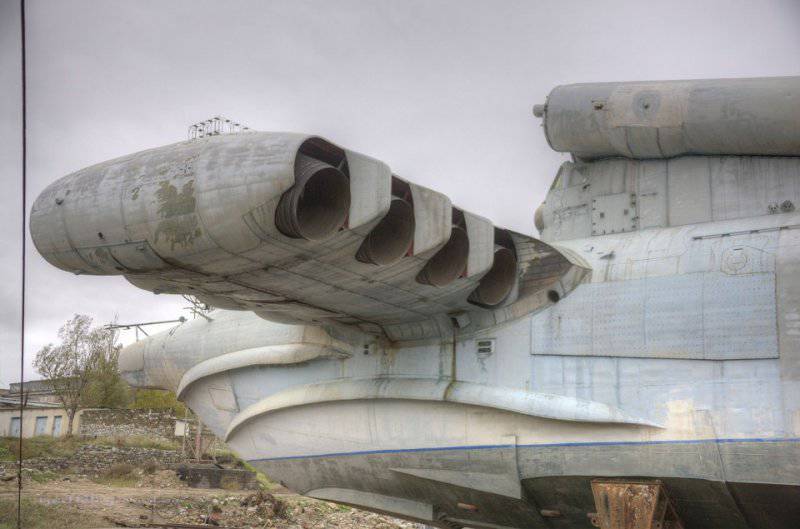
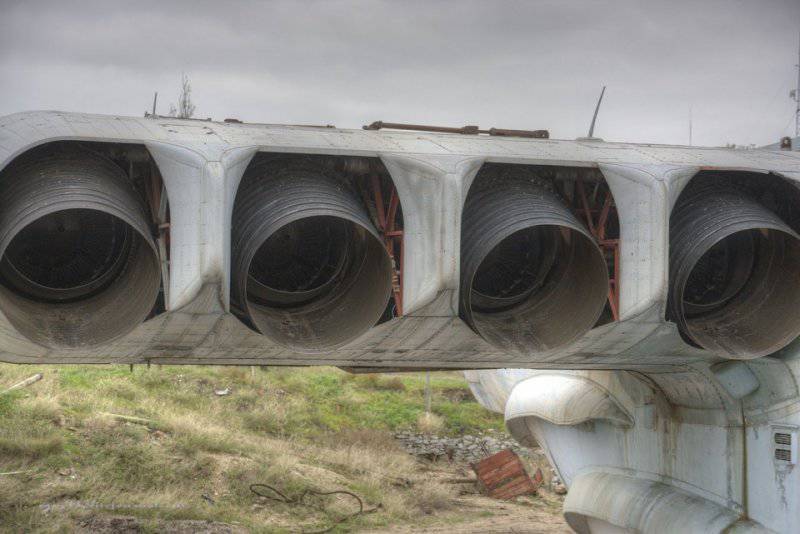
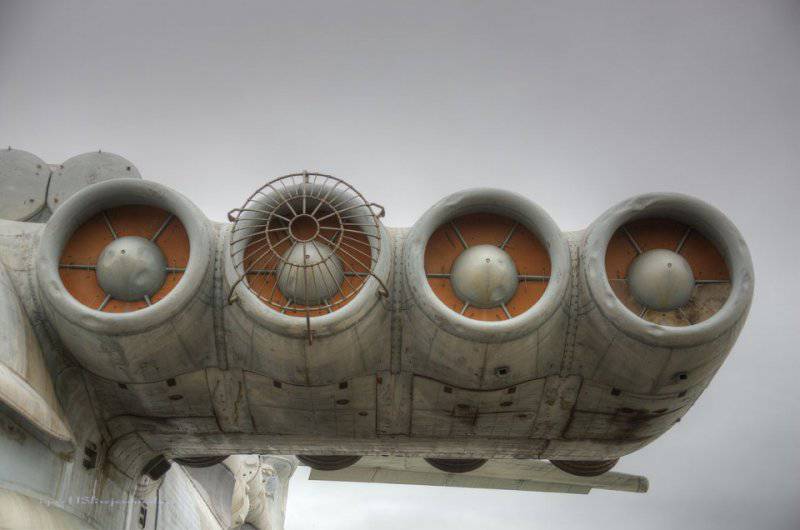
7. Lun is equipped with eight Kuznetsov design bureau engines. The same ones were put on the IL-62, if I'm not mistaken, however, here is their marine version, plus rotary nozzles. Engine type 8 TRD NK-87. Thrust, kgf 8 x 13000.
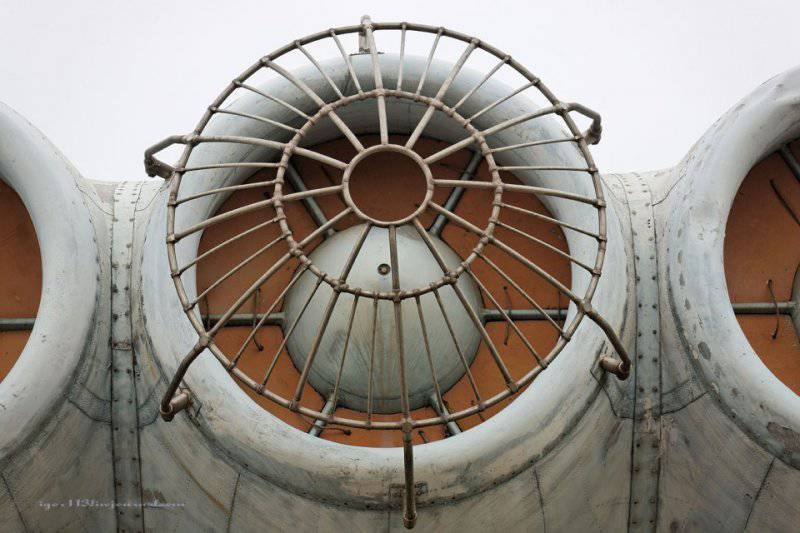
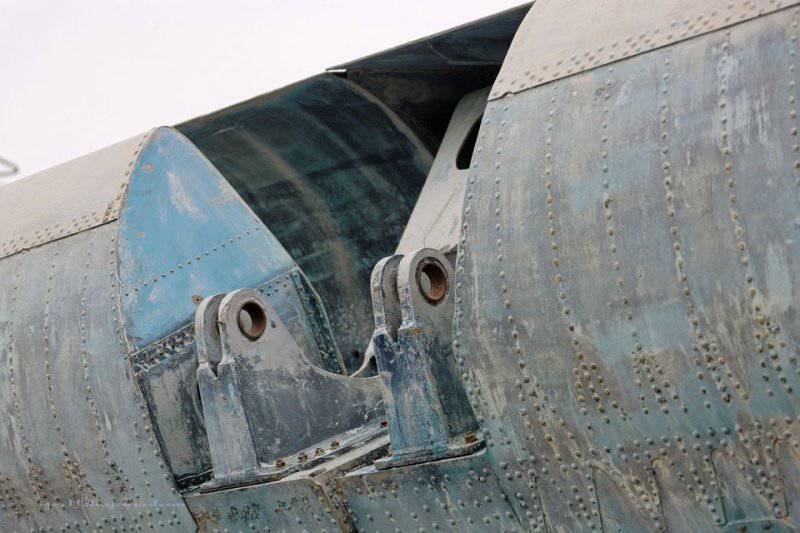
8. It remains a mystery to me: why is only one engine covered with such a grille?
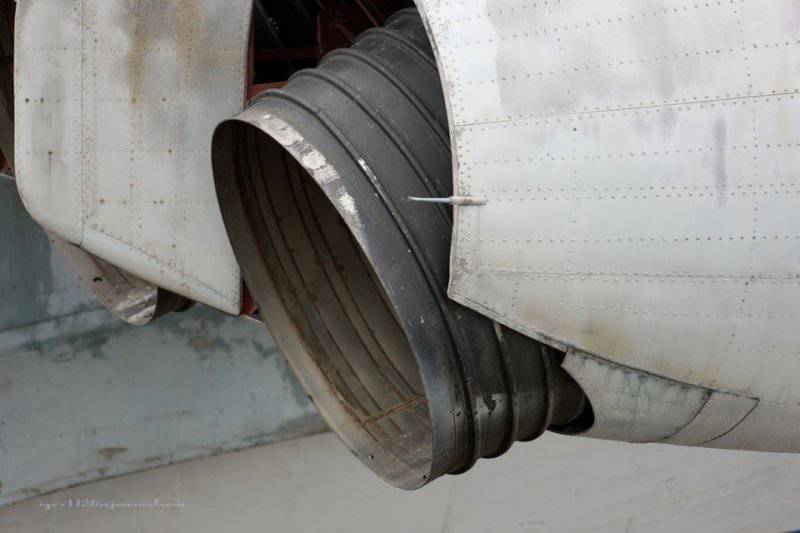
9. View of the nozzles.
10.
11.
12.
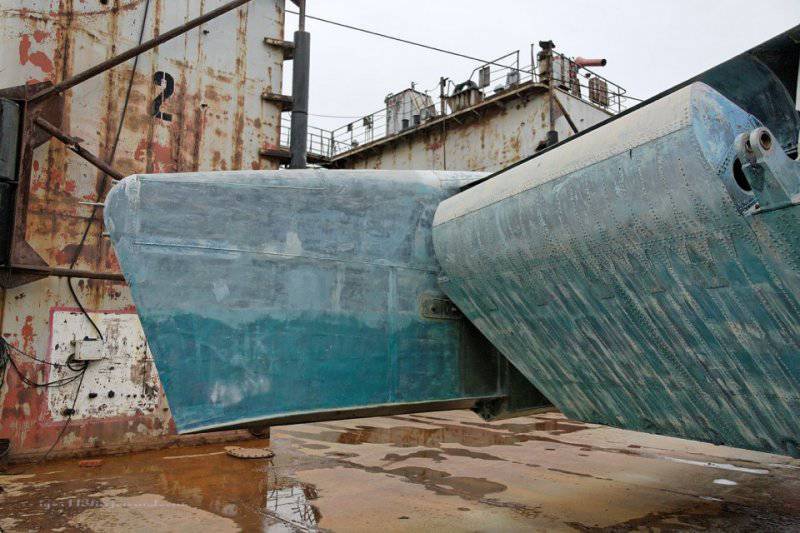
13. View from the side of the wing.
14. From the ground.
15. If the Lun will be restored, then it is planned to replace the engine with those that are on the unfinished "Rescuer".
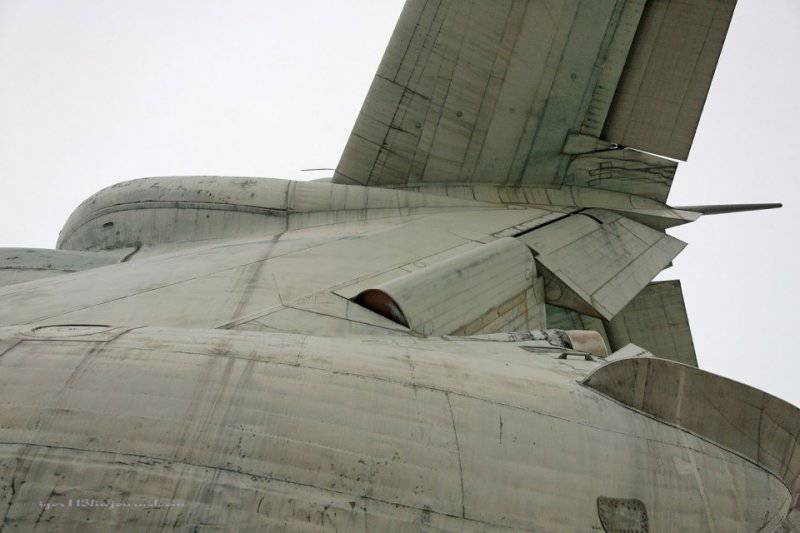
16. The body of the ekranoplan is functionally divided along the length into four parts (regions): the bow, middle, stern and the keel and stabilizer area. In the bow (rooms with equipment and structures that ensure the movement of the PSE) there is a wheelhouse for the crew, a pylon on which the main engines are located, and rooms in the pylon area with auxiliary engines and power plant systems; in the middle (premises from the bow to the middle of the hull) - equipment for testing and combat, as well as a galley, toilet, crew cabin, in the "stern (from the middle of the hull to the stern) - so far also filled with test equipment; in the keel area - an electric power plant to provide the ekranoplan with electricity in the parking lot, a complex of radio-electronic equipment to provide navigation and communications. In the crosshairs of the keel and stabilizer, at a height of 12 m from the waterline, there is a shooter's room. The crew of the ekranoplan consisted of 7 officers and 4 contractors (midshipmen). Its autonomy is 5 days.
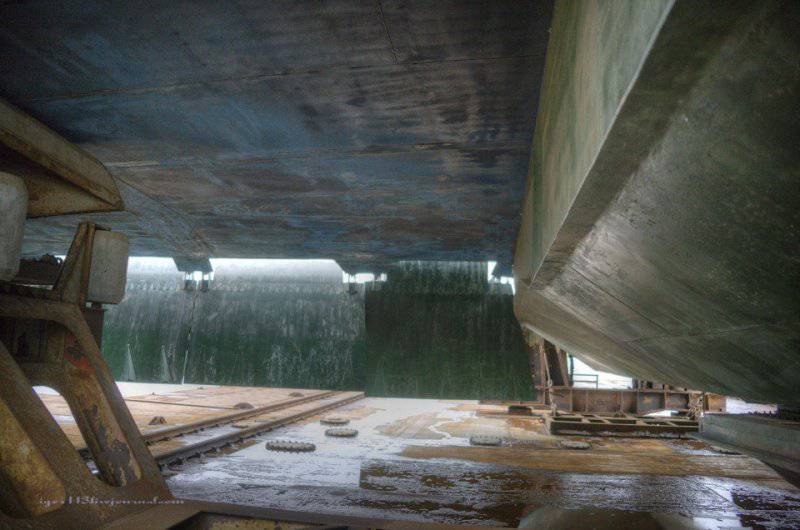
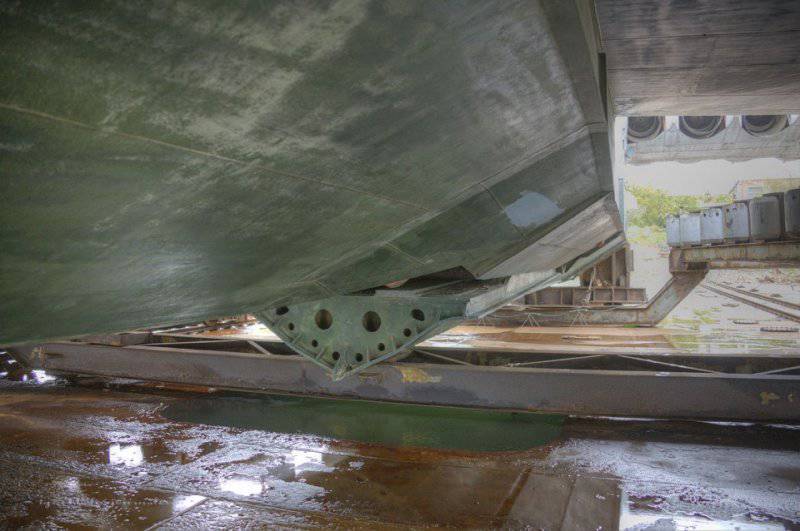
17. This is a bottom view of the engine pylon.
18. In fact, the screen effect is the same air cushion, only formed by air injection not by special devices, but by the oncoming flow. That is, the “wing” of such devices creates lift not only due to rarefied pressure above the upper plane (as in “normal” aircraft), but additionally due to increased pressure under the lower plane, which can only be created at very low altitudes (from a few centimeters up to several meters). This height is commensurate with the length of the mean aerodynamic chord (MAC) of the wing. Therefore, they try to make the wing of the ekranoplan with a slight elongation.
The effect of the screen is connected with the fact that disturbances (pressure increase) from the wing reach the ground (water), are reflected and have time to reach the wing. Thus, the pressure rise under the wing is large. The propagation speed of the pressure wave is, of course, equal to the speed of sound. Accordingly, the manifestation of the ground effect begins with h <(lxV) / 2v, where l is the wing width (wing chord), V is the speed of sound, h is the flight height, v is the flight speed. The higher the wing's MAR, the lower the flight speed and altitude, the higher the ground effect.
For example, the maximum flight range of the Oriole ecologolet at the height of 0,8 m is 1150 km, and at the height of 0,3 the meter with the same load is already 1480 km. Traditionally, at flight speeds near the ground, it is considered to be the height of the screen half the wing chord. This gives a height of the order of a meter. But with sufficiently large WIG, the height of the flight “on the screen” can reach 10 and more than meters. The center of pressure (the common point of application of force) of the screen effect is closer to the rear edge, the center of pressure of the “normal” lifting force is closer to the leading edge, therefore, the greater the contribution of the screen to the total lifting force, the more the center of pressure shifts back. This leads to balancing problems. A change in height changes the balancing, a change in speed, too. The roll causes a diagonal displacement of the center of pressure. Therefore, the management of WIG requires specific skills.
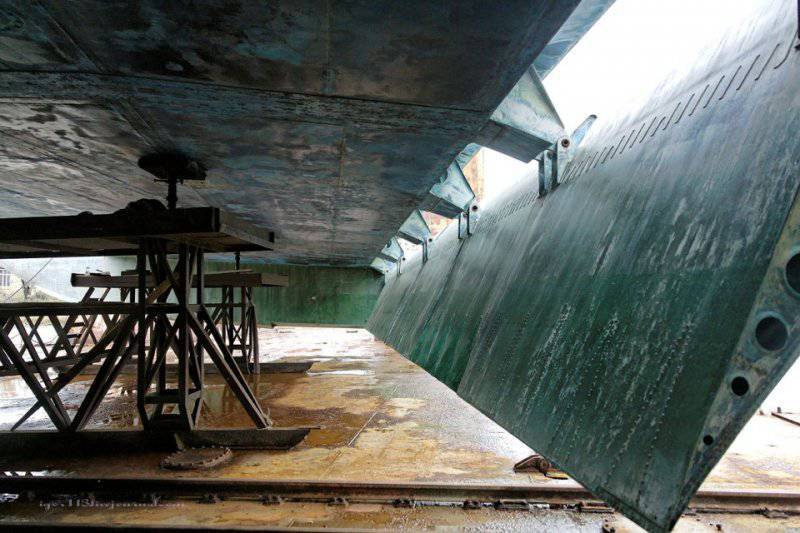
This is the view from under the wing on the flaps (or how to call them correctly?). After they are lowered: this is exactly the position they occupy, after which the engines force air under the wing, the WIG rises from the water and starts moving.
19. View of the flaps (or how to call them correctly?) from the tail of the ekranoplan.
20. View from the body towards the wing tip.
21. View of the left wing.
22. These things are so massive and made like a ship that you are amazed.
23. Device for turning and locking flaps.
24. Left wing and floats at its end.
25. Float surface.
26. He is from the side of the body.
27. Advantages of ekranoplanes and ekranoplanes proper (ekranoplane differs from ekranoplan in that it can break away from the screen and rise to great heights):
• high survivability;
• sufficiently high speed;
• ekranoplanes have high efficiency and higher carrying capacity compared to airplanes, since the lifting force is added to the force generated from the ground effect;
• ekranoplanes surpass hovercraft and hydrofoils in terms of speed, combat and lifting characteristics;
• for the military, the low visibility of the ekranoplan on radar due to flight at a height of several meters, high speed, immunity to anti-ship mines are important;
• Ekranoplanes do not care about the type of surface that creates the effect of the screen - they can move over the frozen water surface, snowy plains, over impassable roads, etc.; as a result, they can move along “direct” routes, they do not need ground infrastructure: bridges, roads, etc.;
• modern ekranolet is much safer than conventional aircraft: in case of detection of a malfunction in flight, the amphibian can land on the water even in heavy seas. Moreover, this does not require any pre-landing maneuvers and can be done simply by releasing gas (for example, in the event of engine failure). Also, the engine failure itself is often not so dangerous for large ekranoplans due to the fact that they have several engines divided into launch and march groups, and the failure of the march group engine can be compensated by starting one of the engines of the launch group;
• ekranolet belong to non-aerodrome aviation - for take-off and landing, they do not need a specially prepared take-off runway, but only a sufficiently large water area or a flat land area;
28. Disadvantages:
• one of the serious obstacles to the regular operation of ekranoplans is that the place of their intended flights (along the rivers) very exactly coincides with the zones of maximum concentration of birds;
• Ekranoplan control differs from aircraft control and requires specific skills;
• the ekranoplan is "tied" to the surface and cannot fly over uneven surfaces. This shortcoming is deprived of the ekranolet;
• although the flight "on the screen" is associated with lower energy costs than that of an aircraft, however, the launch procedure requires a greater thrust-to-weight ratio comparable to that of a transport aircraft, and, accordingly, the use of additional starting engines that are not used in the cruising mode (for large ekranoplans), or special starting modes for the main engines, which leads to additional fuel consumption;
29. Lately story with ekranoplans received a completely unexpected turn. After analyzing the prospects of this type of technology and having come to the conclusion that, to put it mildly, there is a significant backlog of work (due to the actual absence of such) in the field of ekranoplanostroeniya, the US Congress created a special commission to develop an action plan to eliminate the “Russian breakthrough”. Members of the commission offered to ask for help ... to the Russians themselves and went directly to the Central Clinical Hospital for SEC. The leadership of the latter informed Moscow and received permission from the State Committee for Defense Industry and the Ministry of Defense to hold talks with the Americans under the auspices of the Commission for the Export Control of Arms, Military Equipment and Technologies of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation. And in order not to draw too much attention to the subject of negotiations, inquisitive Yankees offered to use the services of an American company under the neutral name “Russian-American Science” (RAS), and with her mediation, a delegation of overseas specialists had the opportunity to visit the Central Design Bureau for SEC, to meet with EKN designers, find out, if possible, the details of interest. Then the Russian side kindly agreed to arrange a visit by American researchers to the base in Kaspiysk, where they were able to capture, without any limitations, a “Eaglet” specially prepared for the flight on a photo and videotape.
Who was part of the American "landing"? The head of the delegation is Colonel of the US Air Force Francis, who heads the program for creating a promising tactical fighter. Under his leadership were prominent experts from research centers, including from NASA, as well as representatives of American aircraft manufacturing companies. Among them, the most famous person was Bert Rutan, who designed the aircraft of the non-traditional aerodynamic scheme "Voyazher", in which several years ago his brother made a nonstop round-the-world flight. In addition, according to representatives of the Russian authorities present at the show, the delegation included persons who, over the years, collected information in all possible ways about Soviet ekranoplans and for the first time suddenly had the opportunity to see with their own eyes - and even touch - the object of their close attention.
As a result of these visits, which cost American taxpayers only 200 thousands of dollars, our new friends will be able to save several billion dollars and significantly, by 5 - 6 years, shorten the development time of their own ekranoplan projects. US representatives have raised the issue of organizing joint activities to eliminate their backlog in this area. The ultimate goal is to create an ekranoplan transport-assault landing vehicle with a take-off weight of up to 5000 tons for the American rapid reaction force. The entire program may require 15 billion. How much of this amount can be invested in Russian science and industry - and whether it will be invested at all - is still unclear With such an organization of negotiations, when the 200 thousand dollars received do not cover the costs of the Central Design Bureau and the pilot plant in the amount of 300 million rubles for bringing to flight condition " Eaglet ", rely on the mutual benefit of cooperation is not necessary.
The reaction of the responsible official of the Commission for Export Control of Armaments, Military Equipment and Technologies of the Russian Defense Ministry Andrei Logvinenko to the appearance of press representatives in Kaspiysk (simultaneously with the Americans) leads to doubts about the benefits of such contacts for the state interests of Russia. Officially referring to considerations of secrecy, he tried to ban journalists from entering the base, and in the private conversation that followed, he explained that his task was to prevent information leaks to the press about Russian-American contacts about ekranoplans, and added that after the Americans left, we could shoot and write anything, but without a word mentioning the American visit to the former secret object.
Based on this, we can assume that there are no longer any things unknown to our probable adversary in this paradoxical technique.
Let's look at these beautiful contours, like a speedboat.
30.
31.
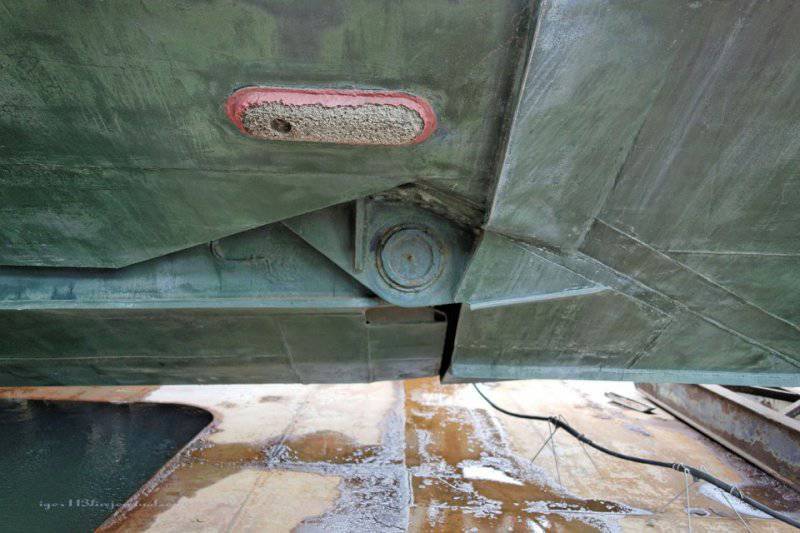
32. And this is a special protection (electro-chemical) against corrosion of the body. Extremely often used in shipbuilding.
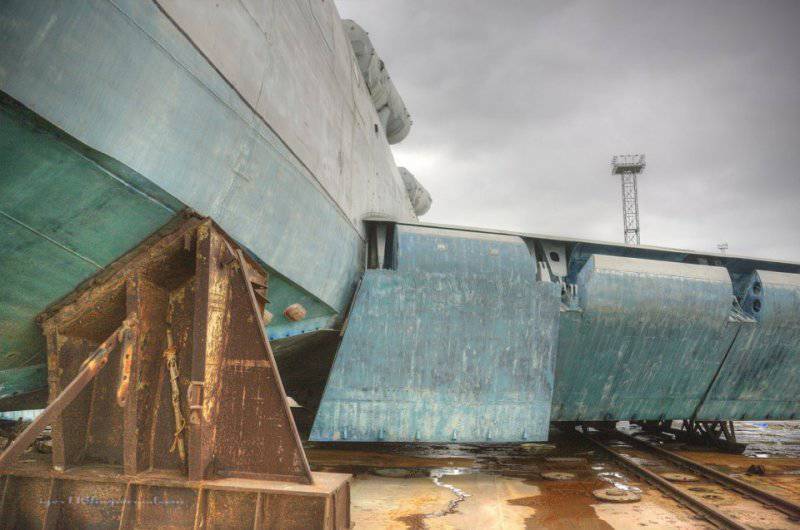
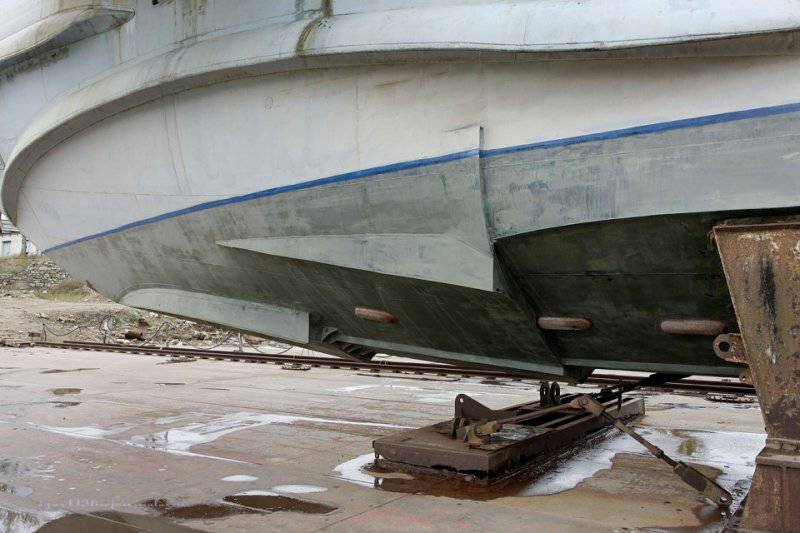
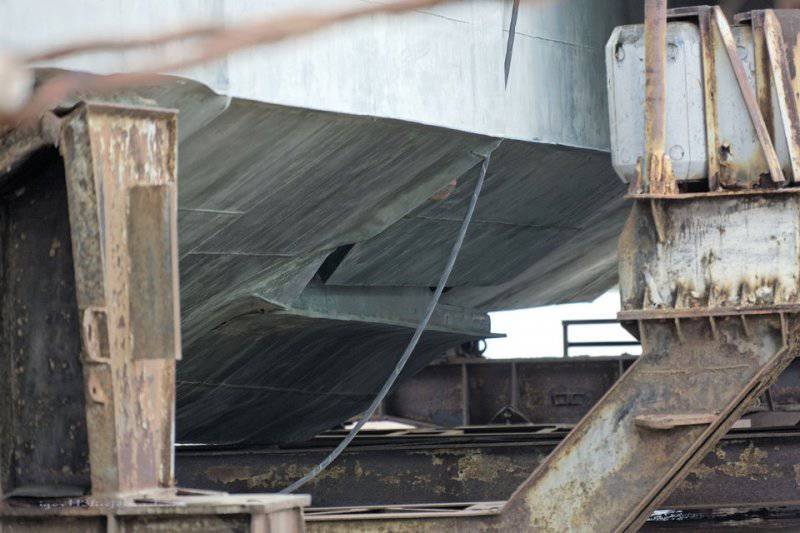
33. A hydro-ski is used to soften the landing. Thanks to this, the ekranoplan can take off and land in waves up to 5 meters.
34. View of the hydro-ski from the tail.
35. Hinged hydro-ski.
36. Another view of the hydro-ski.
37. In the designs of ekranoplanes, two schools can be distinguished: the Soviet (Rostislav Alekseev) with a straight wing and the western (Alexander Lippisha) with a delta wing (back angle, that is, with reverse sweep) with a pronounced reverse transverse V.
Scheme P.E. Alekseeva requires more work to stabilize, but allows you to move at high speeds and in airplane mode.
The Lippish scheme includes a means of reducing excessive stability (wing with reverse sweep and reverse transverse V), which reduces the disadvantages of balancing WIG in conditions of small size and speed.
View of the tail.



































Information