American developments in the field of military medicine
Navistar Defense has now manufactured the 250 MAXXPRO DASH Ambulance ambulances, which have arrived in the army and are working successfully there. Hendrickson and AxleTech International as part of General Dynamics supplied an independent suspension for them. Their DXM solution uses an AxleTech 5000 series independent suspension and a special Hendrickson subframe.
The US military has achieved success at all levels of military medicine, ranging from a medic or a doctor on the battlefield to a field hospital and modern care of the wounded and injured in military medical centers.
And indeed, ten years of war in Iraq and Afghanistan have revolutionized military medicine. As improvised explosive devices (IEDs) became the preferred type weapons for insurgents and various forces fighting against the ground forces of NATO and other countries, they randomly inflicted “multiple injuries” or multiple injuries on their victims. And while the lethality, efficiency, and deployment of IEDs and other weapons in these two countries increased, the medical industry community consistently provided new strategies and equipment to improve the survival rate of the wounded and injured.
Many strategies
A good example in the development of military medicine is the US Navy. For decades, the fleet has supplied paramedics and other medical specialists to its cousinly military branch - the Marine Corps - with increasingly impressive results. Community efforts fleet to improve the quality of service provided to the Marine Corps and coalition forces on the battlefield, "led to a survival rate of more than 98% for all victims who arrived at Role III Hospital," said Captain Vincent Desicco, director of clinical programs at the corps headquarters.
Hospital Role III is usually located at the division level and above. It includes special diagnostic tools, specialized surgical and medical care, and other resources.
Military medicine has combined training, methods, technologies and other processes to solve the complex problems of an asymmetric 21 battlefield.
One of the officers of the medical corps in Arlington focused on preliminary training in such courses as, for example, Fleet courses in traumatology, which significantly increased the readiness of medical fleet services before they were sent to theaters. “Such courses in evacuating the wounded, nursing, and pre-hospital medical care also increased the effectiveness of naval medicine in battle,” he said, “a course of trauma treatment is now required at all levels of medical personnel. The course curricula are constantly being improved and are being finalized on the basis of practical experience and operational analysis of military clashes. ”
From the point of view of the logistics perspective, the medical community of the fleet reviews every four years the list of authorized medical equipment, the list of approved dental equipment and the assembly of individual first-aid kits. Outdated and inefficient medical equipment is being replaced, and stocks are replenished or destroyed in order to ensure that the right amount of the right equipment and consumables is available on the battlefield.
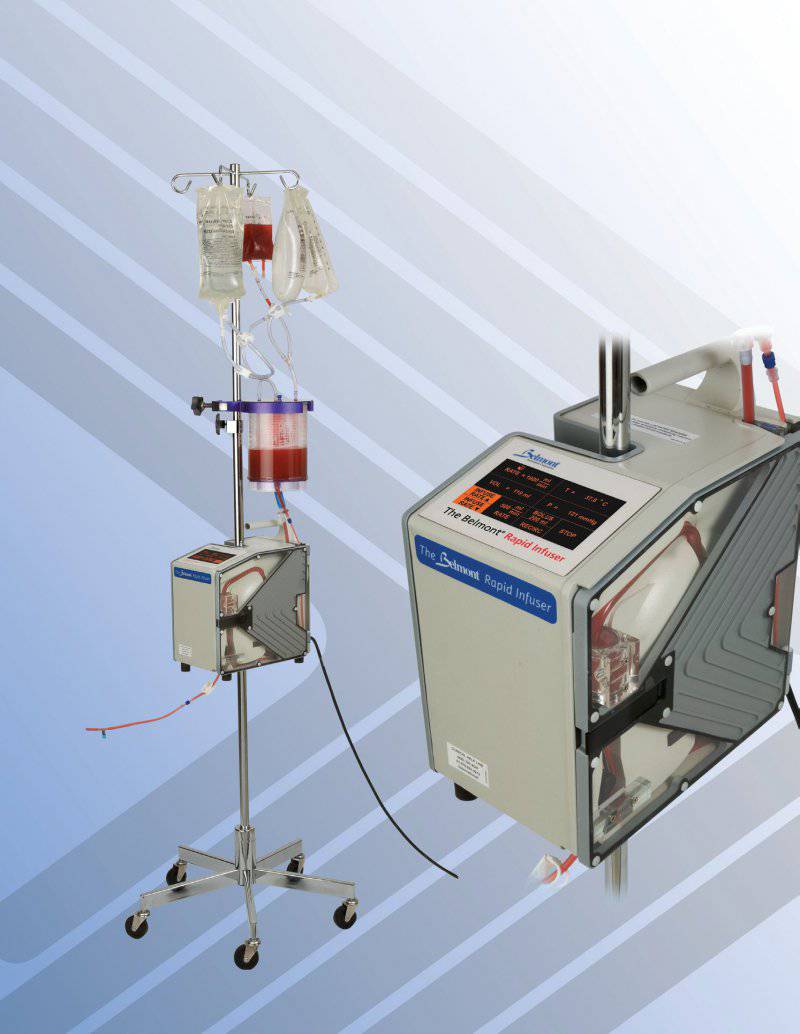
The guidelines of the clinical practice of childbirth also helped to identify and more effectively treat the wounded with suspected traumatic brain damage - one of the common polytrauma as a result of explosions on the SVU. Desicco also noted that the methods of wrapping and bandaging patients reduced the effects of hypothermia during the evacuation of the wounded to higher level medical facilities. “Physical solutions heaters and infusion pumps recently introduced into the lists of approved medical equipment for advanced resuscitation surgery teams and trauma relief platoons improve the standards of medical care available to the fighter, allowing for quick resuscitation actions closer to the site of injury, which increases the survival rate of the wounded,” he added.
Example of Belmont Infusion Pump
Other technological improvements
Medics and doctors on the battlefield and their colleagues in military medical institutions continue to receive for the treatment of the wounded and injured a combination of improved technologies, both simple and advanced.
Simple technology solutions include improved harnesses that have helped emergency services reduce mortality due to heavy bleeding. Desiccot also noted that hemostatic gauze in a similar way contributed to an increase in survival in hemorrhagic wounds, especially those that are not amenable to hemostasis, such as wounds of the body and head. The insatiable need for an improved gauze was partially met in April 2013, when Combat Medical Systems (CMS) received a five-year Pentagon contract for the supply of military medical equipment and equipment.
This contract included the QUIKCLOT Combat Gauze gauze - the standard of the Ministry of Defense for assisting at the front line in life-threatening bleeding. CMS is the exclusive defense supplier of Z-Medica hemostatic products for all military branches; they are approved for each individual first-aid kit, rescue warrior bags, and medical and paramedical kits.
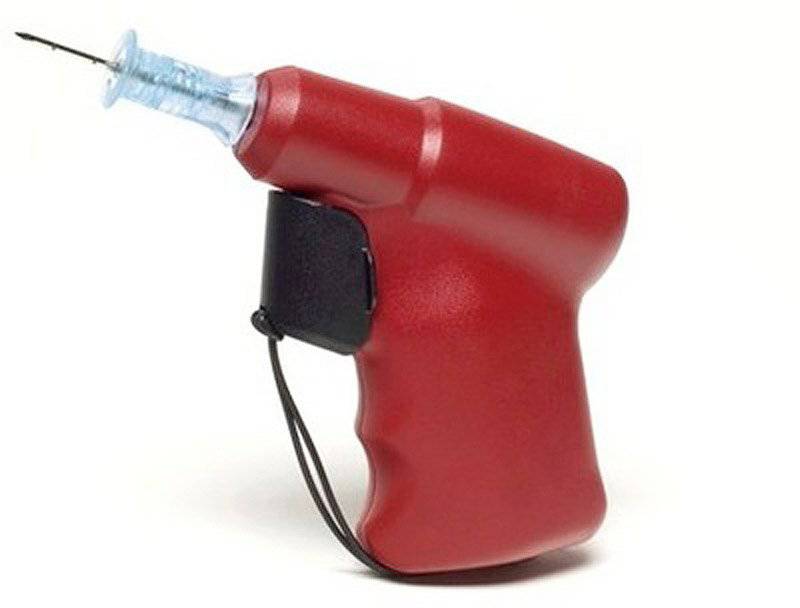
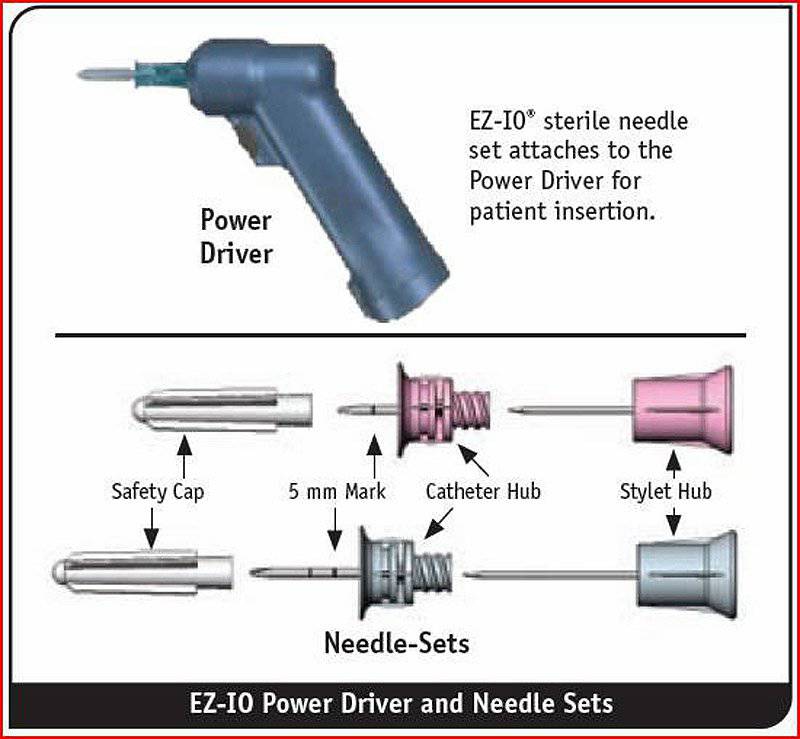
The EZ-IO system combines a battery-powered device like a drill and special needles for fast and safe penetration into the bone in six places. With this system, you can deliver necessary liquids and medications to the right place within 90 seconds.
Moving towards the complication of technology, let us pay attention to the company Vidacare, which has supplied its intraosseous vascular access system EZ-IO for military health care in the United States and other countries. This product can be found in Afghanistan. This device corresponds to the long-standing need of the medical service on the front line in fast vascular access for wounded soldiers through the use of the largest stiff vein - intraosseous space. A company spokeswoman, Lisa Owens, reported that EZ-IO combines a battery-powered drill-type tool and specially crafted needles for quick and safe penetration into the bone at six insertion sites. With this tool, it takes only 90 seconds to deliver vital fluids and medications.
"Studies have confirmed that the absorption of drugs and fluids through the intraosseous space is actually equivalent to the intravenous method, contributed to the rapid development of the possibilities of using this stiff" vein ". The EZ-IO system became the ancestor of medical standards for intraosseous access, providing instant, reliable and controlled intraosseous access, safely passing the bone marrow in a few seconds, ”explained Owen.
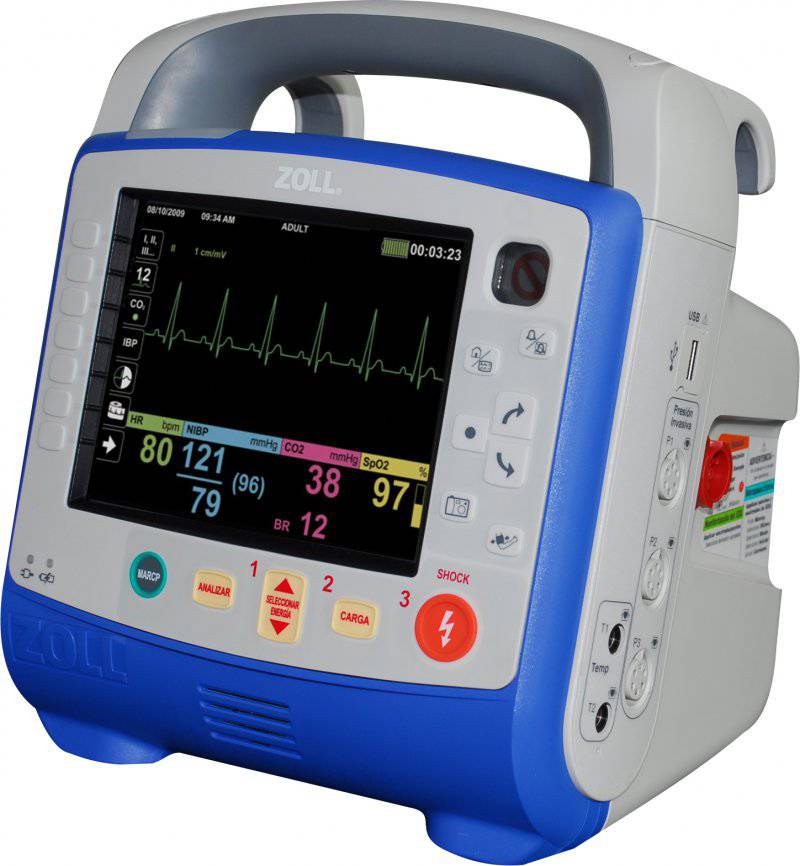
Among the new equipment used by the military medical community, we can distinguish the vital signs monitor PROPAQ M
Zoll's portfolio has been replenished with high-tech developments: a new PROPAQ MD monitor / defibrillator and a PROPAQ M. core monitor, a company spokesman. Diane Egan, a company representative, said that both devices were updated in 2013. Improved clinical parameters and expanded communication capabilities, all in one single lightweight device. “PROPAQ MD is 60% less and 40% lighter than other similar monitors / defibrillators. The PROPAQ M in full configuration is lighter on 5 pounds than the PROPAQ 206 Encore model. Both PROPAQ configurations include the latest MASIMO RAINBOW SET CO-Oximetry technology, which measures the patient's hemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin and methemoglobin oxygenation. The new PROPAQ devices also provide 12 electrocardiogram derivations with decryption, life-threatening arrhythmia signaling, Oridion ЕtCO2, non-invasive blood pressure measurement Welch Allyn, three invasive blood pressure and two constant temperatures. Taken together, the combination provides the most powerful monitor and monitor / defibrillator on the market today, ”she added.
Egan noted that although Zoll products serve in Afghanistan and elsewhere at all levels of medical care, she cannot give more details about them.
In the harnesses controlling the bleeding due to twisting, a metal rod or a piece of plastic is used as a lever called a gate. This gate creates an incredible tightening force around the limb 1-2 inches in inch. All modern vorotkovy bundles have a mechanism for fixing the rod to achieve the appropriate effort, which can stop the bleeding. Some wiring harnesses use hard plastic curvilinear ends to keep the gate from unwinding; others are fixed in place with Velcro fasteners. Modern harnesses have been improved so much lately that it is difficult to choose the best one.
Although the ATK BlackHawk High Performance Fighting Uniform Version HPFU (High Performance Fighting Uniform Version) looks like your standard unloading vest, it includes the ATK BlackHawk Integrated Tourniquet System (ITS). A single tourniquet is pre-installed in the armpit zone of each arm and in the upper thigh of each leg and is immediately activated independently or with the help of a friend to reduce blood loss in an emergency.
In the fighting in Iraq and Afghanistan, the problems of successfully transporting the wounded and injured in the city and overcoming difficult terrain, as well as moving along uneven roads in order to get to a disabled soldier, were also very acute.
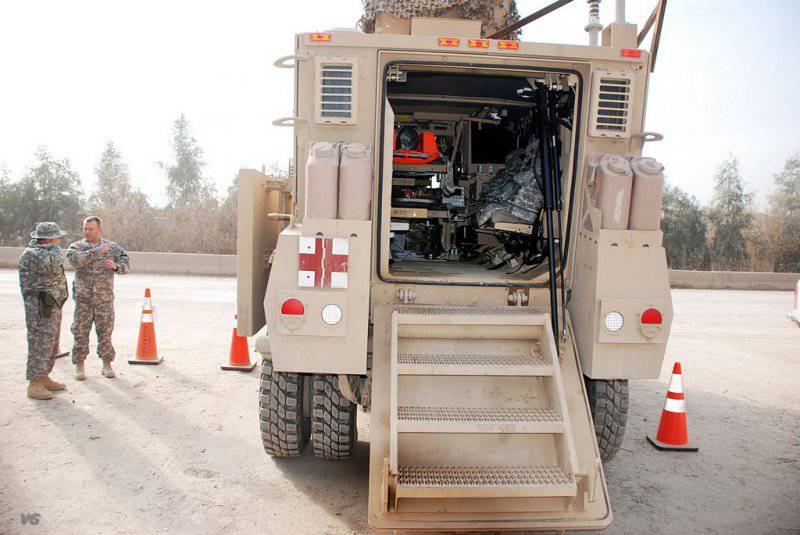
Oshkosh Defense developed the M-ATV Tactical Ambulance Ambulance in response to these needs. Serge Buchakjyan, vice president of international programs at Oshkosh Defense, noted that M-ATV Tactical Ambulance has excellent off-road maneuverability and level protection of MRAP vehicles in order to help military medics get to places that cannot be reached by other means. “The machine is part of our M-ATV family of machines, which supports coalition forces in Afghanistan. This family has become the standard for secure off-road vehicles since its very first deployment in 2009. To date, we have received orders for more than 9500 M-ATV machines from many countries, ”Buchakjyan said in the late spring of 2013.
In service with the American army in the country are several models of ambulances in the configuration of the MRAP, among them are BAE RG33L and Navistar MAXXPRO Plus.
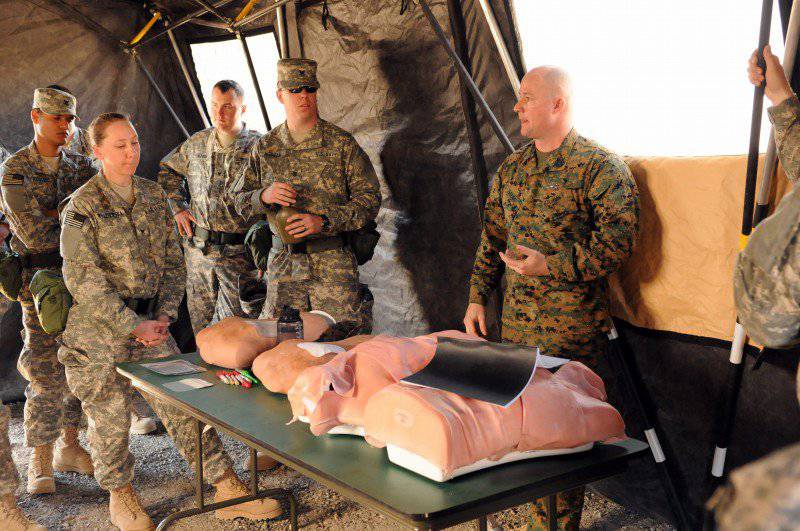
Students at the Camp Pendlton Medical School complete an intensive training program before being sent to Afghanistan. Expanded medical training has increased the survival rate of all victims arriving at the Role 3 medical center in Kandahar, up to 98%
On the horizon
While the United States is winding up its military mission in Afghanistan, the medical community of all the military branches continues to promote modern developments in the field of military medicine. Desicco identified several developments that medical fleet units will see in the next 6 – 12 months.
One example is the use of plasma-substituting agents in pre-hospital care, which will be used by fleet medical personnel in certain combat situations. Applications in the form of smartphones for the early diagnosis of traumatic brain damage will also become available throughout the year.
The most notable systems include a single integrated device for oxygen ventilation and external suction MOVES (Monitoring Oxygen Ventilator and External Suction), which will be used in the Navy Care System during transportation - En Route Care System. “MOVES replaces five separate devices, which together weigh around 200 pounds. MOVES weighs roughly 55 pounds and is installed on a stretcher to provide better patient access. MOVES runs on battery, its operating time is 4-5 hours. One important improvement is that the system includes the function of oxygen saturation, which eliminates the need to hold oxygen cylinders under pressure on board the aircraft, ”Desicco stressed.
MOVES is delivered to the department of the CPA in accordance with a contract issued to the Toronto Research Center in October 2012.
The field anesthesia system FAS (Field Anesthesia System) produces and delivers isoflurane and sevoflurane in vapor form. The system will replace the hood over the anesthetic vaporizers. “FAS is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. Her work is very similar to the work of anesthesia systems used in continental clinics, that is, it is a device that is more familiar to anaesthesiologists and anesthesiologists' assistants. Users will be able to learn how to use the device before deploying, said Desicco. - The device will weigh less than 10 pounds and have a small footprint; It can be mounted on a tripod for droppers. The system can be configured for closed loop or flow through; it is designed to work with already used lung ventilators, including MOVES. ”
There are other breakthrough projects that will increase the level of medical care for wounded soldiers in the near future. These include the development of new resuscitation fluids for use on the battlefield. Dr. Douglas Tadaki, Deputy Department of Restorative Medicine at the Naval Medical Center, noted that the current procedure for stopping bleeding, used by thousands of paramedics and emergency services, includes the introduction of saline to replace lost blood. “This resuscitation fluid was created in the 1850s and has changed little since then. The Ministry of Defense has become a pioneer in the use of new methods, not only in replacing the volume of lost blood, but also in stabilizing the patient, ensuring blood clotting during bleeding, and delivering oxygen to the tissues. ”
Among the mass-produced systems, the Zoll PROPAQ platform maintains the technology on which it is based. Egan noted that in response to a request from the military to measure advanced clinical parameters, her company would offer the MASIMO E1 sensor, designed to quickly detect changes in oxygen saturation, especially in conditions of weak blood flow. “Zoll will also include several additional MASIMO RAINBOW SET parameters (for example, total hemoglobin), which the military identified as critical for its next-generation monitor,” she added.
Need your help
In addition to rapidly developing technology initiatives and other works that go beyond the scope of this article, the main requirement remains a further increase in the effectiveness of emergency medical care on the battlefield and that the most important improvement is the survival rate of wounded soldiers.
At the top of the DeCicco "most important areas of work" list for industry and academia are improved monitoring methodologies that could provide nurses with quick, reliable, and practical information about the condition of the victim and this could be of great importance. It would be especially good if the information could be displayed on the display and unloaded on any carrier (preferably) or output to the printer in order to include the obtained data in the patient's pre-hospital documentation. “Monitors that can reliably determine the saturation of tissues with oxygen or other physiological parameters (which can be very useful for predicting cardiovascular insufficiency and determining resuscitation efforts) could also be a huge advantage on the battlefield,” he noted.
Similarly, the development of lighter, smaller, and energy-saving medical equipment that complies with the law on transferability and accountability of health insurance would also be very effective for naval medicine. “Devices must ensure the security of personal information and protected health information and provide greater security against cyber attacks. These are secure wireless communications that could be used on board an aircraft, plus they must be portable and durable to survive on the battlefield. Such devices should be able to communicate with the Pass-through Medical Information System of the US Armed Forces and keep electronic records of the patient from the site of injury through all levels of medical care. ”
In addition, it would be useful to conduct research on methods and technologies to improve and expand the treatment options for trauma to the respiratory tract for orderlies working in difficult combat conditions. Desicco expressed the opinion that “new technological solutions should be developed, which should be evaluated for victims with airway injuries. These devices should be small, lightweight, durable, simple and easy to use, so that they can be used by personnel with basic first aid skills with minimal training time. ”
In addition, the medical community of the fleet is interested in research on hemostatic agents that could help with multiple hemorrhages, as well as in the development of substitutes for fresh frozen plasma that do not require freezing.
Materials used:
www.monch.com
www.navistardefense.com
www.belmontinstrument.com
www.zoll.com


Information