T-80 - 35 years in service
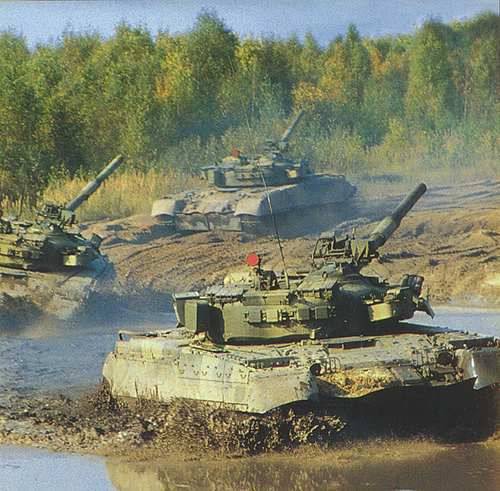

Thirty-five years ago, on July 6, 1976, the T-80 main battle tank (MBT) was adopted by the Soviet Army. Currently, in the Western Military District (ZVO) MBT T-80 is in service tank brigades, 4 motorized rifle brigades, and is also used to train personnel in the district training center, as well as cadets and officers in military universities and academies. In total, there are more than 1800 T-80 tanks and its modifications in the ZVO, the Western Military District Information Support Group said.
The combat vehicle was created in a special design office (SKB) of transport engineering at the Leningrad Kirov Plant by a group of designers under the direction of Nikolay Popov. The first series of T-80 tanks was released in 1976-1978. The main feature of the T-80 was the gas turbine engine, which was used as a power plant of the tank. On some of its modifications installed diesel engines. Tank T-80 and its modifications are characterized by high speed (up to 80 km / h with a crew of 3 people). T-80 participated in the fighting in the North Caucasus. It is in service with the land forces of Russia, Cyprus, Pakistan, the Republic of Korea and Ukraine.
Tank T-80 - designed to conduct offensive and defensive battles in different physiographic and climatic conditions. For fire destruction of the enemy, the T-80 is equipped with a 125-mm smooth-bore gun stabilized in two planes and an 7,62-mm PKT machine gun paired with it; 12,7-mm anti-aircraft machine-gun complex "Cliff" on the commander's turret. To protect against guided weapons, the Tucha grenade firing system was installed on the tank. The T-80B tanks are equipped with the Cobra ATGM complex 9K112-1 and the PTN 80K9 PTXUR Reflex system in the T-119U. The loading mechanism is similar to the T-64 tank.
The T-80B fire control system includes a laser rangefinder, a ballistic computer, a weapon stabilizer and a set of sensors for monitoring wind speed, heel and tank speed, course target angle, etc. The fire control on the T-80U is duplicated. The gun is made with stringent requirements for the barrel, which is equipped with a metal heat shield to protect against external influences and reduce the deflection during heating. Combat weight of the tank 42 t.
A smooth-bore gun with a caliber of 125-mm ensures the destruction of targets at a distance of up to 5 km. Ammunition of the tank: shots - 45 (type BPS, BCS, OFS, guided missile). Combined armor protection. A multi-fuel GTE-1000T with a power of 1000 kW is used as a power plant. Cruising on the highway - 500 km, the depth of the water barrier to be overcome - 5 m.
Main tank T-80
the USSR
When the Minister of Defense of the Syrian Arab Republic, Mustafa Glas, who led the Syrian army in Lebanon in 1981-82, Spiegel magazine asked: "I would like a former tank driver Glas to have a German Leopard 2, who is so eager to get in Saudi Arabia ? ”, the minister replied:“ .... I don’t strive to have it at any cost. The Soviet T-80 is Moscow’s answer to the 2 Leopard. ”It is not only equal to the German machine, but also significantly exceeds it. As a soldier and tank specialist "I consider the T-80 the best tank in the world." The T-80 - the world's first serial tank with a single gas-turbine power plant - began to be developed at the Leningrad SKB-2 Kirov Plant in the 1968 year. but story domestic gas turbine tank building began much earlier. GTE, which won in the 1940s an absolute victory over piston engines in combat aviation. began to attract the attention of the creators of tanks. A new type of power plant promised very substantial advantages over a diesel engine or gasoline engine: with an equal occupied volume, the gas turbine had significantly greater power, which allowed to sharply increase the speed and acceleration characteristics of combat vehicles, and improve tank control. Reliably ensured and quick engine start at low temperatures. For the first time, the idea of a gas turbine combat vehicle was born in the Main Armored Directorate of the USSR Ministry of Defense back in 1948.
The elaboration of a heavy tank project with a gas turbine engine was completed under the direction of Chief Designer A.X. Starostenko at the SKB turbine production plant of the Kirov Plant in 1949 year. However, this tank remained on paper: the authoritative commission, which analyzed the results of the design studies, came to the conclusion that the proposed machine did not satisfy several important requirements. In 1955, our country once again returned to the idea of a tank with a gas turbine engine, and again the Kirov plant undertook this work, entrusted with creating a heavy tank of a new generation - 52-55 t armed in the world, armed with 130-mm a tool with an initial velocity of the 1000 projectile, m / s, and an 1000 horsepower engine It was decided to develop two versions of the tank: with a diesel engine (277 object) and with GTE (278 object), differing only in the engine compartment. The work was headed by NM Chistyakov. In the same year, 1955, under the leadership of G. A. Ogloblin, the creation of a gas turbine engine for this machine began. The meeting on this topic, held by Deputy Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the USSR V.A. Malyshev in 1956, contributed to the increase of interest in tracked gas turbine technology. The famous “tank commissar”, in particular, expressed confidence in the fact that “in twenty years the GTE will appear on land transport vehicles”.

In 1956-57 For the first time, two experimental tank gas turbine engines GTD-1 with a maximum power 1000 hp were manufactured by Leningraders. The GTE was supposed to provide the tank with a mass of 53,5 and an opportunity to develop a very solid speed - 57,3 km / h. However, the gas turbine tank was never born, largely due to subjective reasons, known in the history as "voluntarism": two 277 diesel objects, released a little earlier than their gas turbine counterpart, in the 1957 year, successfully passed factory tests, and soon one of They were shown NS Khrushchev. The show had very negative consequences: Khrushchev, who had embarked on a rejection of traditional weapons systems, was very skeptical of the new combat vehicle. As a result, in 1960, all the work on heavy tanks was abandoned, and the 278 prototype was never completed. However, there were objective reasons that prevented the introduction of the CCD at that time. Unlike a diesel engine, the tank gas turbine was still far from perfect, and it took years of hard work and a lot of experimental "objects", during two and a half decades of ironing landfills and tracks, before the GTE could finally "register" on a production tank.
In 1963, in Kharkov, under the leadership of A.A. Morozov, simultaneously with the medium tank T-64, its gas turbine modification was created - an experienced T-64T, which differs from its diesel counterpart by the installation of the GTD-ZTL helicopter with a power 700 hp. In 1964, an experimental 167T object with a GTD-3T (800 hp) developed by the direction of L.N. Kartsev came out of the Uralvagonzavod gate in Nizhny Tagil. The designers of the first gas turbine tanks faced a number of intractable problems that prevented the creation of an efficient tank with a gas turbine engine in the 1960s. Among the most difficult tasks. demanding the search for new solutions, issues of air purification at the turbine inlet were highlighted: unlike a helicopter whose engines suck up dust, and even in relatively small quantities, only in takeoff and landing modes, a tank (for example, making a march in a column) can constantly move in a dust cloud, passing an 5-6 m3 of air per second through the air intake. The gas turbine attracted the attention of the creators of a fundamentally new class of combat vehicles - rocket tanks, which were actively developed in the USSR from the end of the 1950's.
This is not surprising: after all, according to the designers, one of the main advantages of such machines was increased mobility and reduced size. In 1966, an 288 test object, created in Leningrad and equipped with two GTE-350 with a total power of 700 hp, was released. The power plant of this machine was created in another Leningrad team - aircraft manufacturing NPO them. V.Ya.Klimova, who by that time had a lot of experience in creating turboprop and turboshaft engines for airplanes and helicopters. However, during the tests, it turned out that the “Spark” of two GTEs has no advantages over a simpler monoblock power plant, which, in accordance with the government’s decision, the “Klimovtsy”, in conjunction with KB-3 of the Kirov Plant and VNIITransmash, started 1968 year. By the end of the 1960-ies, the Soviet army had the most advanced for its time armored vehicles.

The medium tank T-64, which was put into service in the 1967 year, was significantly superior to its main combat indicators by its foreign counterparts - the M-60А1, Leopard and Chiefen. However, in the United States and Germany, with 1965, joint work was launched on the creation of the main battle tank of the new generation - MVT-70, which is characterized by increased mobility, reinforced armament (Xilum ATGM launcher and launch armor). From the Soviet tank industry required an adequate response to the NATO challenge. 155 April 16 was issued by a joint resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the USSR Council of Ministers, according to which the SKB-1968 at the Kirov plant was tasked with developing a variant of the T-2 medium tank with a gas turbine power plant, characterized by enhanced combat performance. The first "Kirov" gas turbine tank of a new generation, the 64sp 219 object, manufactured in 1 year, was outwardly similar to the experienced Kharkov T-1969T gas turbine.
The machine was installed engine GTD-1000T power 1000 l. s., developed by the NGO them. V.Ya.Klimova. The next object, 219sp2, was already significantly different from the original T-64: tests of the first prototype showed that the installation of a new, more powerful engine, the increased mass and the changed dynamic characteristics of the tank require significant changes to the undercarriage. The development of new driving and guide wheels, support and support rollers, tracks with rubberized treadmills, hydraulic shock absorbers and torsion shafts with improved characteristics was required. The shape of the tower was also changed. From T-64A preserved gun, ammunition, automatic loader, individual components and systems, as well as elements of body armor. After the construction and testing of several experimental machines, which took about seven years, on July 6, the new tank was officially adopted under the designation T-1976. In 80-1976, the Kirovsky Zavod production association produced a series of "eighty-ten" admitted to the troops.

Like other Russian tanks 1960-70-s. - T-64 and T-72, T-80 has a classic layout and a crew of three. Instead of one viewing device, the driver has three, which allowed a significantly improved view. Designers have provided and heating the workplace of the driver with air taken from the GTE compressor. The body of the car is welded, its frontal part has an angle of inclination 68 °, the tower is cast. The frontal parts of the hull and the tower are equipped with multi-layer combined armor, combining steel and ceramics. The remaining parts of the body are made of monolithic steel armor with a large differentiation of thickness and angle of inclination. There is a protection against weapons mass destruction (slaughter, whipping, sealing system and air purification). The layout of the combat compartment of the T-80 is generally similar to the layout adopted on the T-64B. The motoblock in the aft hull of the tank hull is located longitudinally, which required a slight increase in the length of the machine compared to the T-64. The engine is made in a single unit with a total weight of 1050 kg with a built-in reduction bevel-helical gearbox and is kinematically connected with two onboard planetary gearboxes. The engine compartment has four fuel tanks with a capacity of 385 liters (the total reserve of fuel in the booked volume was 1140 liters). GTD-1000T is made on a three-shaft scheme, with two independent turbochargers and a free turbine. The adjustable nozzle apparatus (PCA) of the turbine limits the frequency of its rotation and prevents "spacing" when changing gears. The absence of a mechanical connection between the power turbine and turbochargers increased the tank's permeability on soils with low bearing capacity, in severe driving conditions, and also eliminated the possibility of engine stalling when the vehicle suddenly stopped with the gear engaged.
An important advantage of the gas turbine power plant was its multi-fuel. The engine was powered by jet fuel TC-1 and TC-2, diesel fuel and automotive low-octane gasoline. The process of starting the CCD is automated, the promotion of compressor rotors is carried out using two electric motors. Due to the exhaust back, as well as the turbine's own low noise compared to a diesel engine, it was possible to slightly reduce the acoustic visibility of the tank. The special features of T-80 include the first implemented combined braking system with simultaneous use of GTE and mechanical hydraulic brakes. An adjustable nozzle apparatus of the turbine allows you to change the direction of the flow of gases, forcing the blades to rotate in the opposite direction (of course, this greatly loads the power turbine, which required the adoption of special measures to protect it). The process of braking the tank is as follows: when the driver depresses the brake pedal, braking begins through the turbine.

With further pedal depressing, mechanical braking devices are also activated. The GT-X of the T-80 used an automatic engine control system (SAUR), including temperature sensors located in front and behind the power turbine, a temperature controller (RT), and limit switches installed under the brake and PCA pedals associated with the PT and fuel supply system. Application of SAUR allowed to increase the resource of turbine blades by more than 10 times, and with frequent use of the brake and the PCA pedal for shifting gears (which occurs while the tank is moving on rough terrain), fuel consumption is reduced by 5-7%. To protect the turbine from dust, an inertial (so-called "cyclonic") method of air purification was applied, providing 97-percent purification. However, unfiltered dust particles still accumulate on the turbine blades. To remove them when the tank is moving under particularly difficult conditions, a procedure is provided for the vibration cleaning of the blades. In addition, before starting the engine and after it stops, purging is performed. Transmission T-80 - mechanical planetary. It consists of two units, each of which includes an onboard transmission, an onboard reducer and hydro-drives of the motion control system. Three planetary rows and five friction control units in each side box provide four gears forward and one back. Track rollers have rubber bands and aluminum alloy wheels. Tracks - with rubber treadmills and rubber mounts.
Tension mechanisms - worm type. The tank suspension is an individual torsion bar with a non-axial arrangement of the torsion shafts and hydraulic telescopic shock absorbers on the first, second and sixth rollers. There is equipment for underwater driving, which provides, after special training, the overcoming of a water barrier to a depth of five meters. The main armament of the T-80 includes the 125-mm smoothbore 2A46M-1 cannon, unified with the T-64 and T-72 tanks, as well as the Sprut self-propelled anti-tank weapon. The gun is stabilized in two planes and has a direct shot range (substage caliber with an initial speed of 1715 m / s) 2100 m. Ammunition also includes cumulative and high-explosive fragmentation projectiles. Shots - separate-cartridge loading. 28 of them (two less than that of T-64А) are placed in the "roundabout" of the mechanized combat pack, three shots are stored in the fighting compartment, and seven more shells and charges are in the control compartment. In addition to the cannon, an experimental machine was installed an 7,62-mm PKT machine gun paired with a gun, and an anti-aircraft 12,7-mm machine gun NSVT "Utes" was also installed on the serial tank on the basis of the commander's hatch.
Shooting from it is the commander, being at this time outside the reserved volume. The firing range of the Cliff air targets can reach 1500 m, and the ground 2000 m. Mechanized ammunition is located along the perimeter of the crew compartment, the habitable part of which is made in the form of a cabin separating it from the ammunition conveyor. Shells are placed in the tray horizontally, "heads" to the axis of rotation. Partial-burning propellant charges are mounted vertically, up pallets (this distinguishes the mechanized ammunition of the T-64 and T-80 tanks from the T-72 and T-90 ammunition, where the shells and charges are placed horizontally in the cassettes). At the gunner’s command, the “drum” begins to rotate, leading the cassette with the selected type of ammunition to the loading plane. Then the cassette rises up along the dismounting line by means of an electromechanical lift, after which the charge and projectile are pushed into the charging chamber fixed at the loading angle of the gun with one stroke of the rammer. After the shot, the pallet is caught by a special mechanism and transferred to the empty tray. The rate of fire is six to eight shots per minute, very high for a gun of this caliber and independent of the physical condition of the loader (which significantly affects the rate of fire of foreign tanks). In the event of a failure of the machine, you can also manually load, but with this, the rate of fire naturally decreases sharply. An optical stereoscopic rangefinder TPD-2-49 with independent stabilization of the field of view in the vertical plane provides the ability to accurately determine the distance to the target within 1000-4000 m.
To determine shorter distances, as well as firing at targets that do not have a vertical projection (for example, trenches), in the field of view of the sight, there is a rangefinder scale. Data on the distance to the target are automatically entered into the sight. Also automatically introduced an amendment to the speed of movement of the tank and data on the type of the selected projectile. In one unit with an eye, a remote control is performed to guide the weapon with the buttons for determining the range and shooting. Night sights of the commander and gunner T-80 are similar to those used on the T-64A. The tank has a welded hull, the frontal part of which is inclined at an angle 68 °. The tower is cast. The sides of the hull are protected by rubber-fabric screens that protect against damage by cumulative projectiles. The front part of the hull has a multi-layer combined booking, the remaining parts of the tank are protected by monolithic steel armor with differentiated thicknesses and angles of inclination. In 1978, the modification of T-80B was adopted. Its principal difference from the T-80 was the use of a new cannon and a complex of guided missile weapons 9K112-1 "Cobra" with a radio-controlled rocket 9М112. The complex included a guidance station, installed in the fighting compartment of the vehicle, behind the gunner’s back. "Cobra" provided missile firing at a distance of up to 4 km from a place and on the move, while the probability of hitting an armored target was 0,8.
The rocket had dimensions corresponding to the dimensions of the 125-mm projectile and could be placed in any tray of the mechanized combat pack. At the head of the ATGM there was a cumulative warhead and a solid-fuel engine, in the tail part there was a hardware compartment and a throwing device. The interfacing of parts of the ATGM was carried out in a loading mechanism tray when filing into the gun barrel. Rocket guidance is semi-automatic: the gunner only needed to hold the aiming mark on the target. The coordinates of the ATGM relative to the line of sight were determined by the optical system using the source of modulated light mounted on the rocket, and the control commands were transmitted over a narrow beam. Depending on the combat situation, it was possible to select three rocket flight modes. When firing from dusty soils, when the dust raised by muzzle gases can close the target, a small angle of elevation above the aiming line is attached to the gun. After the release of the rocket from the barrel, it makes a "slide" and returns to the line of sight. If there is a threat of a dusty plume behind the rocket unmasking its flight, the ATGM, after ascent, continues to fly with some excess above the line of sight and, only immediately before the target, sinks to a low altitude. When firing a rocket at a short range (up to 1000 km), when the target suddenly appears in front of the tank, the gun of which is already loaded with a rocket, the gun barrel is automatically given a small angle of elevation, and the ATGM is lowered onto the sighting line through the 80-100 from the tank.
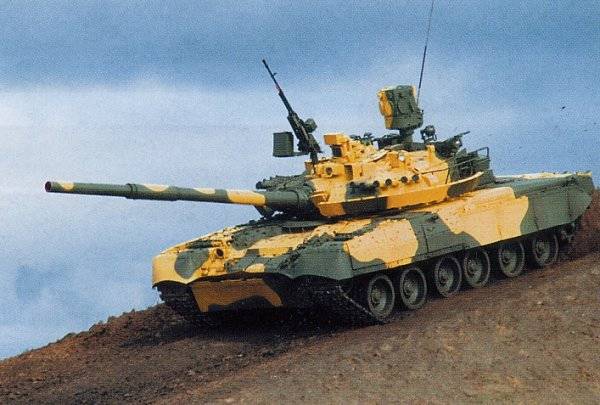

In addition to advanced weapons, the T-80B also had more powerful armor protection. In 1980, T-80B received a new engine, the CCD-1000TF, whose power increased to 1100. with. In 1985, the modification of the T-80B with a complex of hinged dynamic protection is adopted. The car received the designation T-80BV. Somewhat later, in the process of planned repair, the installation of dynamic protection began on the previously built T-80B. The growth of the combat capabilities of foreign tanks, as well as anti-tank weapons, constantly demanded further improvement of the "eighty". Work on the development of this machine were carried out both in Leningrad and in Kharkov. Back in 1976, the design and design of the 80 object, which had significantly increased combat and technical characteristics, was made at KKBM on the basis of T-478. The tank was supposed to be equipped with a diesel engine, traditional for Kharkiv citizens - 6ТДN of 1000 l capacity. with. (A variant with a more powerful 1250-strong diesel engine was also worked out). At the 478 facility, it was supposed to install an improved turret, guided missile weapons, a new sight, etc. Work on this machine served as the basis for the creation in the second half of the 1980-ies of the serial diesel tank T-80UD. A more radical modernization of the "eighties" was to be the Kharkov object 478М, the design studies for which were also carried out in the 1976 year. The design of this machine was planned to use a number of technical solutions and systems that have not been implemented to date. The tank was supposed to be equipped with 124Ч diesel in 1500 l. p., which increased the specific power of the machine to a record value - 34,5 l. s./t and allowed to reach speeds up to 75-80 km / h. The security of the tank should have increased dramatically due to the installation of a promising active protection complex "Tent" - a prototype of the later "Arena", as well as an anti-aircraft 23-mm machine with remote control.
In parallel with the 478 facility in Leningrad, the development of a promising modification of the T-80А (219А facility), with improved protection, new missile armament (“Reflex” ATGM), as well as a number of other improvements, in particular, the built-in dozer equipment for self-encroaching, was conducted. An experienced tank of this type was built in the 1982 year, later several more cars were produced, which had minor differences. In 1984, they were tested on a set of mounted dynamic protection. To test the “Reflex” guided missile system with laser-guided missiles, as well as the Irtysh weapon control system, design bureau LKZ in 1983, based on the T-80B serial tank, created another experimental machine - the 219В object. Both experimental tanks gave impetus to the next important step in the evolution of "eighty dozen" made by Leningrad designers. Under the leadership of Nikolay Popov, by the 1985, the T-80 tank was created - the last and most powerful modification of the "eighty", recognized by many domestic and foreign experts as the strongest tank in the world. The machine, retaining the basic layout and design features of its predecessors, has received a number of fundamentally new units.
At the same time, the mass of the tank compared to the T-80BV increased only by 1,5 t. The tank’s fire control system includes an information-computational daytime sighting system of the gunner, a sighting and observation complex of the commander and a nighttime sighting system of the gunner. The firepower of the T-80U has significantly increased due to the use of a new complex of guided missile weapons "Reflex" with a noise-proof fire control system, which increases the range and accuracy of shooting while reducing the time for preparing the first shot. The new complex provided the opportunity to fight not only with armored targets, but also with low-flying helicopters. The 9М119 rocket, controlled by a laser beam, provides a target range of a tank type when fired from a place at 100-5000 m ranges with a probability of 0,8. The 2А46М-1 cannon ammunition, including 45 ammunition, also consists of armor-piercing-cumulative and high-explosive fragmentation rounds. An armor-piercing projectile has an initial speed of 1715 m / s (which exceeds the initial speed of the projectile of any other foreign tank) and is capable of striking highly armored targets at a direct shot range of 2200 m.
With the help of a modern fire control system, the commander and the gunner can carry out a separate search for targets, tracking them, as well as aimed fire, day and night, both from the spot and on the move, to use guided missile weapons. The Irtysh daytime optical sight with an integrated laser range finder allows the gunner to detect small targets at a distance of 5000 m and determine the range to them with high accuracy. Regardless of the gun, the sight is stabilized in two planes. His pancreatic system changes the magnification of the optical channel within 3,6-12,0. At night, the gunner searches and targets with the help of the combined active-passive sight "Buran-PA", which also has a stabilized field of view. The tank commander conducts observation and gives target indications to the gunner by means of the sighting and observation day / night complex PNK-4С, stabilized in the vertical plane. The digital ballistic computer takes into account corrections for the range, target’s flank speed, the speed of its tank, the angle of the gun trunnions, barrel bore wear, air temperature, atmospheric pressure, and cross-wind. The gun received a built-in control device for adjusting the sight of the gunner and a quick-disconnecting connection between the barrel pipe and the breech, which allows it to be replaced in the field without removing the entire gun from the turret.
When creating the T-80 tank, considerable attention was paid to enhancing its security. Works were carried out in several directions. Due to the use of a new camouflaging coloration, which distorts the appearance of the tank, it was possible to reduce the probability of detecting T-80U in the visible and IR ranges. Improved survival is facilitated by the use of a tank and a self-digging system with a 2140 mm dozer blade, as well as a smoke screening system using the Cloud system, including eight 902B mortar-propelled grenade launchers. The tank can also be equipped with a KMT-6 outboard trawl, which eliminates the erosion of mines under the bottom and tracks. The armor protection of the T-80U was significantly enhanced, the design of the armor barriers was changed, the relative share of armor in the tank mass was increased. For the first time in the world, elements of built-in dynamic protection (ECD) are implemented, which are able to withstand not only cumulative, but also kinetic projectiles. VDZ covers more than 50% of the surface, nose, sides and roof of the tank. The combination of advanced multi-layer combined armor and a VDZ "removes" almost all types of the most massive cumulative anti-tank weapons and reduces the likelihood of being damaged by "blanks."
In terms of the power of armor protection, which has an equivalent thickness of 1100 mm against sub-caliber kinetic projectile and 900 mm - under the action of cumulative ammunition, T-80U surpasses most foreign tanks of the fourth generation. In this regard, it should be noted the assessment of armor protection of Russian tanks, which gave a prominent German specialist in the field of armored vehicles Manfred Held (Manfred Held). Speaking at a symposium on the development of armored vehicles, which was held at the Royal Military College (United Kingdom) in June 1996, M.Held said that in Germany tests of the T-72М1 tank, inherited by the Bundeswehr from the GDR army and equipped with active armor, were conducted . During the shooting, it was found that the frontal part of the tank hull has a protection equivalent to rolled homogeneous armor with a thickness of more than 2000 mm. According to M. Held, the T-80U tank has an even higher level of protection and is able to withstand shelling by sabot shells fired from 140-mm advanced tank guns, only being developed in the United States and some Western European countries. “Thus,” concludes the German specialist, “the newest Russian tanks (first of all T-80U) are practically invulnerable in frontal projection from all types of kinetic and cumulative anti-tank ammunition in service with the NATO countries and have more effective protection than their Western counterparts (Jane's International Defense Review, 1996, # 7) ".
Of course, this assessment may be opportunistic in nature (you need to "lobby" the creation of new types of ammunition and guns), but you should listen to it. When penetrating armor, the survivability of the tank is ensured through the use of high-speed automatic fire system "Frost", which prevents the fire and explosion of the fuel-air mixture. To protect against the explosion of mines, the driver’s seat is suspended from the sheet sheet, and the rigidity in the area of the control compartment is enhanced by the use of a special pillers behind the driver’s seat. An important advantage of the T-80U was its perfect system of protection against weapons of mass destruction, surpassing the similar protection of the best foreign cars. On the tank, podboy and nadboy are used from hydrogen-containing polymers with lead, lithium and boron additives, local protection screens made of heavy materials, automatic sealing systems for habitable compartments and air purification. A significant innovation was the use of the auxiliary power unit GTA-18A with a capacity of 30 l on the tank. with., allowing to save fuel during the parking of the tank, while conducting a defensive battle, as well as in ambush. Saves and resource of the main engine.
The auxiliary power unit, located in the stern of the machine, in the bunker on the left fender, is “integrated” into the general system of GTE operation and does not require any additional devices for its operation. At the end of 1983, an experimental series of two dozen T-80Us were made, eight of which were handed over to military trials. In 1985, the tank was completed and its large-scale mass production began in Omsk and Kharkov. However, despite the excellence of the CCD, in a number of parameters, first of all - in terms of efficiency - it was inferior to the traditional tank diesel engine. Besides. the cost of the diesel engine was significantly lower (for example, the B-46 engine in the 1980-s was costing the state in 9600 rubles, while the GTD-1000 - in 104 000 rubles). The gas turbine had a considerably smaller resource, its repair was more complicated.
The unequivocal answer: what is better - a tank gas turbine or an internal combustion engine could not be obtained. In this regard, interest in installing on the most powerful domestic diesel tank was constantly maintained. In particular, there was an opinion about the preference of differential use of turbine and diesel tanks in various theaters of military operations. Although the idea of creating the T-80 variant with a unified engine-transmission compartment, which allowed the use of interchangeable diesel and gas turbine engines, was in the air, it was not possible to implement, but the creation of the eighty-diesel version began in the middle of the 1970-s. In Leningrad and Omsk, experimental vehicles "219РД object" and "644 object" were created, equipped, respectively, with А-53-2 and В-46-6 diesel engines. However, the greatest success was achieved by Kharkiv, who created a powerful (1000 hp) and economical six-cylinder diesel 6TD - the further development of 5TD. The design of this engine began in the 1966 year, and from the 1975 year, it was tested on the chassis of the “476 object”. In 1976, in Kharkov, a variant of the T-80 tank with 6TD ("478 object") was proposed. In 1985, the “478B object” (“Birch”) was created at its base under the leadership of the General Designer IL Protopopov.
Compared with the "reactive" T-80U diesel tank had a slightly worse dynamic characteristics, but had an increased power reserve. The installation of a diesel engine required a number of changes in the transmission and control drives. In addition, the machine received a remote control anti-aircraft machine gun "Rock". The first five serial "Birches" were assembled by the end of 1985, in 1986, the car was launched in a large series, and in 1987, it was put into service under the designation T-80UD. In 1988, the T-80UD was upgraded: the reliability of the power plant and a number of units was increased, the mounted “Contact” dynamic protection was replaced with the built-in dynamic protection, and the weapons were modified. Until the end of 1991, in Kharkov, they released about 500 T-80UD (of which only 60 was transferred to units deployed in Ukraine). In total by this time in the European part of the USSR there were 4839 T-80 tanks of all modifications. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, the output of cars dropped sharply: Independent Ukraine was not able to order military equipment for its own armed forces (however, the position of "independent Russia" was not much better).
The output was found in the offer of a diesel version of the T-80 for export. In 1996, contact was made for the supply of 320 vehicles that received the Ukrainian designation T-84, to Pakistan (this number probably included tanks that are part of the Ukrainian armed forces). The export value of one T-84 was 1.8 million dollars. Work is underway in Kharkov to create a more powerful (1200 hp) diesel 6ТD-2, intended for installation on modernized T-64 samples. However, in the light of the economic situation in Ukraine, as well as the break in cooperation with the Russian military-industrial complex, the prospects for tank construction in Kharkov look very uncertain. In Russia, the gas turbine T-80U continued to be improved, the production of which completely shifted to the Omsk plant. In 1990, the production of a tank with a more powerful GTE-1250 engine (1250 hp) began, which made it possible to slightly improve the dynamic characteristics of the vehicle. Overheat protection devices were introduced. The tank received an advanced missile system 9K119M. To reduce the radar signature of the T-80U tank, a special radio absorbing coating was developed and applied (Stealth technology - as such things are called in the West). The reduction of the effective dispersion surface (EPR) of ground combat vehicles acquired special importance after the advent of real-time radar reconnaissance aviation systems using high-resolution side-looking radar with synthetic aperture. At a distance of several tens of kilometers, it became possible to detect and track the movement of not only tank columns, but also individual units of armored vehicles.
The first two aircraft with similar equipment - Northrop-Martin / Boeing E-8 JSTARS - were successfully used by the Americans during Operation Desert Storm, as well as in the Balkans. Since 1992, on the part of T-80, the Agava-2 thermal imaging and aiming device began to be installed (the industry delayed the delivery of thermal imagers, so far from all machines received them). The video image (for the first time in a domestic tank) is displayed on a television screen. For the development of this device by its creators was awarded the Kotin Prize. The T-80U serial tank with the above-listed enhancements is known by the designation T-80UM. Another major innovation. significantly increased the combat survivability of the T-80U. was the use of complex opto-electronic suppression TSHU-2 "Curtain". The purpose of the complex is to prevent an aiming hit of anti-tank guided missiles into the tank with a semi-automatic guidance system. as well as interference with enemy target weapon control systems and laser rangefinders.
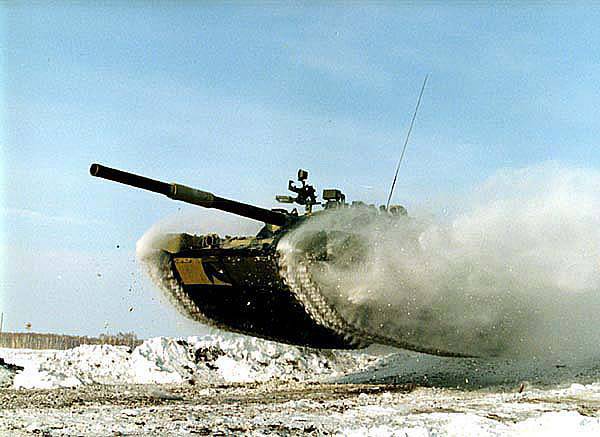

The complex included the station of opto-electronic suppression (SOEP) TSHU-1 and the system for setting the aerosol curtain (SDR). SOEP is a source of modulated infrared radiation with parameters close to the parameters of ATGM tracers such as "Dragon", TOW, NOT, "Milan", etc. By acting on the infrared receiver of the semi-automatic guidance system for ATGM, it disrupts missile guidance. SOEP provides interference in the form of modulated infrared radiation in the sector +/- 20 ° from the axis of the bore channel horizontally and 4,5 "vertically. In addition, TSHU-1, two modules of which are located in front of the tower of the tank, provide IR - Illumination at night, aiming firing with night vision devices, and also used to blind any (including small-sized) objects. SDR, designed to disrupt the attack of such missiles as Maverik, Helfire and artillery Adjustable 155- mm of the Copperhead projectile, responds to laser radiation within 360 "in azimuth and -5 / + 25" in the vertical plane. The received signal is processed at high speed by the control unit, and the direction to the quantum radiation source is determined.
The system automatically determines the optimal launcher, generates an electrical signal proportional to the angle to which the tank tower with grenade launchers should be turned and issues a command to fire a grenade forming an aerosol curtain at 55 distance m three seconds after the grenades are shot. SOEP operates only in automatic mode, and SDR - in automatic, semi-automatic and manual. The ground tests of the Curtains-1 confirmed the high efficiency of the complex: the likelihood of missiles entering the tank with semi-automatic command guidance decreases 3 times, missiles with laser semi-active self-guidance - 4 times, and corrected artillery shells - 1,5 times. The complex is able to provide resistance at the same time against several missiles attacking a tank from various directions. The “Blind-1” system was tested on an experienced T-80B (“219 object”) and for the first time began to be installed on the T-80-K series commander tank — a variant of the T-80U machine designed to provide control of tank units. In addition, the command tank received a system of remote blasting of fragmentation-firing shells with non-contact electronic fuses. Communication facilities T-80UK work in the VHF and KB bands. The P-163-U ultrashort-wave radio station with frequency modulation operating in the 30 MHz operating frequency range has 10 pre-tuned frequencies. With a four-meter whip antenna in mid-terrain conditions, it provides a range of work up to 20 km.
With a special combined antenna type "symmetrical vibrator" installed on the 11-meter telescopic mast mounted on the body of the machine, the communication range increases to 40 km (with this antenna, the tank can work only in the parking lot). Shortwave radio station P-163-K, operating in the frequency range 2 MHz in telephone and telegraph mode with frequency modulation. designed to provide long-range communications. It has 16 pre-prepared frequencies. With the whip HF antenna length 4, which provides work while the tank is moving, the communication range was initially 20-50 km, but due to the introduction of the possibility of changing the antenna pattern, it was possible to increase it to 250 km. With a pin 11-meter telescopic antenna, the range of operation of the P-163-K reaches 350 km. The commander tank is also equipped with a THA-4 navigation system and a petrol power generator of autonomous power supply AB-1-П28 with 1,0 kW power, an additional function of which is to recharge the batteries while stationary while the engine is not running. The creators of the machine successfully solved the issue of electromagnetic compatibility of numerous radio-electronic means.
For this in particular. applied special conductive track. Armament, power plant, transmission, chassis, surveillance devices and other equipment T-80UK corresponds to the tank T-80UM. however, the gun ammunition reduced to 30 shells, and PKT machine gun - to 750 ammunition. Development of the tank T-80 was a major achievement of the domestic industry. The designers A.S.Ermolaev, V.A.Marishkin, V.I.Mironov, B.M.Kupriyanov, PD.Gavra, V.I. Geigerov, B.A. Dobryakov and many others made a great contribution to the creation of the tank. other specialists. The amount of work done says more than 150 copyright certificates for inventions proposed in the process of creating this machine. A number of tank designers won high government awards. The orders of Lenin were awarded to A.N. Popov and A.M. Konstantinov, the orders of the October Revolution - to A.A. Druzhinin and P.A. Stepanchenko .....
8 June 1993 by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation N.S. Popov, group of specialists and general designer of the T-80 tank, was awarded the State Prize of the Russian Federation in the field of science and technology for developing new technical solutions and introducing the machine into mass production. However, T-80 is far from exhausted the possibilities of further modernization. Continuing improvement and active protection of tanks. In particular, on the experienced T-80B, the Arena active protection complex (KAZT), developed by Kolomna KBM and designed to protect the tank against ATGMs and anti-tank grenades attacking it, was tested. Moreover, it provides a reflection of ammunition, not only flying directly to the tank, but also intended to defeat it when flying from above. To detect targets in the complex, a multifunctional radar with an "instant" overview of the space in the entire protected sector and high noise immunity is used. For targeted destruction of the enemy’s missiles and grenades, narrowly targeted protective munitions are used, which have very high speed and are located around the perimeter of the tank turret in special installation shafts (the tank carries 26 of such ammunition). Automatic control of the complex is carried out by a specialized computer, which provides. also, monitoring its performance.
The sequence of operation of the complex is as follows: after it is turned on from the remote control of the tank commander, all further operations are performed automatically. Radar provides search targets flying up to the tank. Then the station is transferred to the auto tracking mode, generating the target movement parameters and transmitting them to the computer, which selects the number of the protective ammunition and the response time. The protective ammunition forms a bundle of destructive elements that destroy the target on the approach to the tank. The time from detecting a target to hitting a record is short — no more than 0,07 seconds. After 0,2-0,4 seconds after the defensive shot, the complex is again ready to “shoot” another target. Each protective ammunition fires its sector, and the sectors of closely located ammunition overlap, which ensures the interception of several targets approaching from one direction. The complex is all-weather and "all-day", it is able to work when the tank is moving, when the tower is turning. An important problem that was successfully resolved by the developers of the complex was to ensure the electromagnetic compatibility of several tanks equipped with the Arena and operating in a single group.
The complex practically does not impose restrictions on the formation of subunits of tanks under the terms of electromagnetic compatibility. The Arena does not respond to targets that are more than 50 m away from the tank, to small targets (bullets, fragments, small-caliber projectiles) that do not pose a direct threat to the tank, to targets that depart from the tank (including its own projectiles), on low-speed items (birds, clods of land, and n.). Measures have been taken to ensure the safety of the escorting tank infantry: the danger zone of the complex, 20 m, is relatively small, and there are no side slaughter fragments when the shells are fired. There is an external light alarm warning the infantrymen, who are behind the tank, to turn on the complex. Equipping the T-80 "Arena" allows you to raise the survival rate of the tank during offensive operations approximately twice. At the same time, the cost of losing tanks equipped with KAZT is reduced by 1.5-1.7 times. Currently, the complex "Arena" has no world analogues. Its use is especially effective in local conflicts. when the opposing side is armed only with light anti-tank weapons. The T-80UM-1 tank with KAZT Arena was for the first time publicly demonstrated in Omsk in the autumn of 1997. A version of this tank with another complex of active protection, the Thrush, was also shown there. In order to increase capabilities to combat air targets (first of all, attack helicopters), as well as enemy tank-dangerous manpower, the Tochmash Central Research Institute created and tested a set of additional weapons for the T-80 30-mm automatic gun 2-X42 (similar to the BMP -3. BMD-3 and BTR-80А). The gun, which has a remote control, is installed in the upper rear part of the turret (the 12,7-mm “Cliff” machine gun is being dismantled). The guidance angle relative to the tower is 120 "but the horizon and -5 / -65" are vertical. Ammunition installation -450 shells.
Characteristics of KAZT "Arena"
Speed range of targeted targets: 70-700м / sec
Azimuth Protection Sector: 110 °
Detection of flying targets: 50 m
Complex reaction time: 0,07 seconds
Power Consumption: 1 kW
Power supply: 27B
Mass of complex: 1100 kg
The volume of equipment inside the tower: 30dm sq.
Further development of the T-80 was the tank "Black Eagle", work on the creation of which was carried out in Omsk. The car that retained the T-80 chassis is equipped with a new turret with horizontal placement of the automatic loader, as well as an 1 TD with 1500 power. with. At the same time, the mass of the machine has increased to 50 t. As the main armament on the Black Eagle, promising guns with a caliber of up to 150 mm can be used. Currently, the T-80 is one of the most popular mainstream tanks of the fourth generation, second only to the T-72 and the American M1 Abrams. As of the beginning of 1996, the Russian army had approximately 5000 T-80, 9000 T-72 and 4000 T-64. For comparison, in the US armed forces there are 79 IS Mi tanks. Ml A and M1А2, in the Bundeswehr - 1700 "Leopards", and the French army plans to purchase, in total, only 650 tanks "Leclerc". Besides Russia, T-80 also has Belarus, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, and Syria. The press reported about the interest in acquiring "eighty" of India, China and other countries.


Information