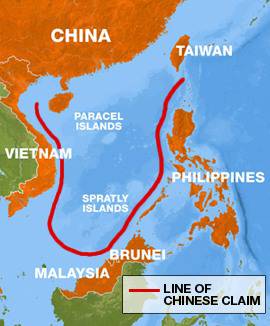
Spratly Islands - a zone of possible military conflict in Southeast Asia
 The Spratlys archipelago in the South China Sea could become a new zone of the Great War. The Philippines declares its desire to strengthen its position in this disputed region. To strengthen the capabilities of the Navy and the Air Force in this region, Manila allocates additional 184 million dollars.
The Spratlys archipelago in the South China Sea could become a new zone of the Great War. The Philippines declares its desire to strengthen its position in this disputed region. To strengthen the capabilities of the Navy and the Air Force in this region, Manila allocates additional 184 million dollars.Manila does not want to give up positions in this region to its neighbors, and first of all to China. The statement of the Philippine authorities, apparently, is due to the fact that in early March the ship of the Chinese Navy ousted the Philippine vessel, which was conducting oil exploration, from the disputed area. Manila expressed a formal protest to Beijing, but the Chinese authorities did not respond. In Beijing, they consider almost the entire region to be theirs and have repeatedly proved their readiness to defend their claims by force.
The Philippines intends to control at least 25% of the archipelago, that part of it, which is located near the Philippine island of Palawan. Manila has also repeatedly expressed its readiness to fight for the islands, if necessary. So, in 2008, there was a promise to "fight to the last sailor and marine." According to General Eduardo Oban, part of the money allocated will be spent on the modernization of the airfield on the island of Pagasa.
Help: Spratly Islands (Nanshaquando) - This is an archipelago in the southwestern part of the South China Sea. It consists of more than 100 islands, reefs, atolls, their total area of less than 5 square meters. km The area of the region is more than 400 thousand square meters. km The center of the archipelago is located 400 km from the islands of Palawan and Kalimantan, 500 km from the coast of Vietnam and 1000 km from the Chinese island of Hainan. The value of the archipelago is not in the land, but in a strategic position - the one who controls it holds the most important sea and air routes from the Pacific to the Indian Ocean “by the throat”. In addition, the territory can be used for basing underwater fleet, other naval forces, temporary bases for the preparation of the landing on neighboring territories. So the Japanese did in World War II: they occupied them and created a base for submarines here. The islands are important in relation to bioresources - they are used as a fishing region, which is an important factor for overpopulated (with a constant significant population growth) countries of Southeast Asia. Also, hydrocarbon reserves were found on the shelf. Currently, the islands dispute each other six countries: Vietnam, China, Taiwan, Malaysia, the Philippines and Brunei.
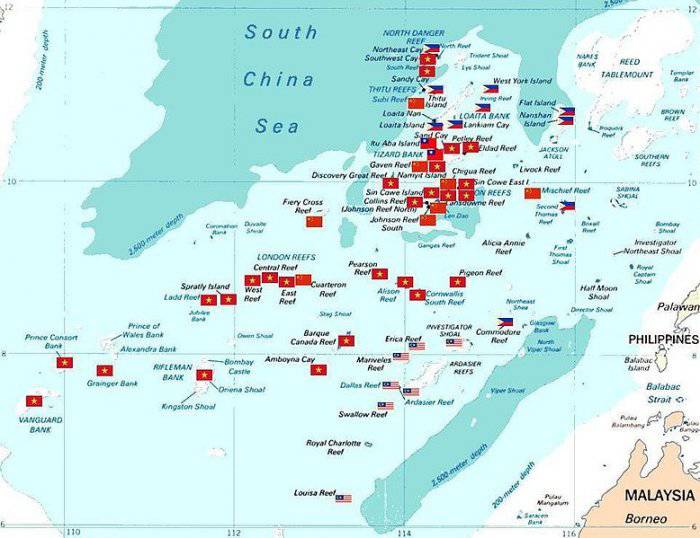
Approximately 45 islets and reefs are occupied by small military contingents from Vietnam, China, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Taiwan. It is difficult to call them full-fledged military bases; rather, these are military posts in the form of small boxes on piles.


History conflict
- Under the Saragossa Treaty of 1529, Spain and Portugal have acquired these territories under their jurisdiction.
- After the US-Spanish war in 1898, the United States received them, they betrayed them to the Philippines.
- In the 1927-1930 years, the French carried out research on the islands and declared them French territory, joining their Indochinese possessions.
- In 1932, China expressed frustration to France, proclaiming the archipelago Chinese territory.
- In 1933, the French ships took control of the 9 of the largest islands. Japan made a claim, saying that one of the islands was a Japanese phosphate mine.
- In 1939, Tokyo announced a desire to take the territory of the islands under its control. Paris and London protested and secured French jurisdiction over the islands.
- In 1941, the Japanese Navy seized the islands and controlled them until the end of World War II, a submarine base was built there (on the island of Itu Aba).
- After the war, China and France put forward their rights to the islands. China began to build up its military presence in the area of the islands, in Paris, 1947 demanded that Chinese forces be withdrawn.
- At a conference in San Francisco in 1951, the representatives of Vietnam (under the control of France) presented their claims to the Spratly and Paracel Islands. At the same conference, Tokyo formally renounced all rights to the islands. But since the world community did not take decisions on the ownership of the islands, Japan has the opportunity to “remember” its rights.
- In the 1956 year, claims to the islands were declared by the Philippines, all interested parties protested, Vietnam and China occupied several islands.
- In the 1958 year, China defined its territorial waters, the Spratlys archipelago they attributed to its territory.
- In the 1961-1963 years, South Vietnam has established its ownership marks on several islands.
- In 1968, the Philippines landed troops on three islands and announced the addition of the Kalajaan island group. In 1972, the Kalajaan Islands were combined with the province of Palawan. In 1978, Manila put forward a claim card. At the start of the 80, the Philippine forces captured several more islands and built military posts.
- In 1971, Malaysia made claims on part of the islands. In 1979, Malaysia published a claim map - it includes 12 islands.
- In 1975, the united Vietnam formally put forward claims for the archipelago. In 1982, Vietnam captured several more islands and established military posts.
- In 1983, Malaysia captures the island of Layang-Layang, builds a military base and resort on it.
- In 1984, Brunei singled out the Louisiana reef in the south of the Spratly Islands to its fisheries.
- Since 1987, China has begun a constant military patrol of the islands and has built a permanent base.
 - In 1988, there was a clash between the Chinese and Vietnamese Navy, three Vietnamese and one Chinese patrol were drowned at the Johnson Reef (Xin Kou). As a result, China captured seven reefs and atolls, creating a springboard for further expansion of its sphere of influence.
- In 1988, there was a clash between the Chinese and Vietnamese Navy, three Vietnamese and one Chinese patrol were drowned at the Johnson Reef (Xin Kou). As a result, China captured seven reefs and atolls, creating a springboard for further expansion of its sphere of influence.In the future, the intensity of the Sino-Vietnamese contradictions subsided somewhat, Philippine claims (which were backed by the United States) came to the fore. In 1994-1995 The Philippine Navy repeatedly detained Chinese fishermen and destroyed Chinese border signs. In 1995, the PRC and Vietnam agreed to agree on plans for the development of island resources.
- In 2004, the Philippine patrol aircraft were fired upon (and according to the Philippine military were damaged) by the Vietnamese. Vietnam expanded tourist construction and built an airfield.
At present, China maintains a military presence on the 8-9 islands, Vietnam on the 21, the Philippines on the 8, and Malaysia on the 3. The most advantageous position in Taiwan, which controls one, but the largest island - Itu-Aba, where he built an airfield.
The probability of a big conflict, though not great, is there. Currently, almost all the clashes were small and consisted in the destruction of state symbols (which countries “mark” their “islets and reefs), the detention of fishermen, the verbal exchanges through the media. But in the end, this region of great strategic importance may become a zone of fierce conflict.
Spratly Islands with flags of the states occupying them.

Information