In the US, thinking about the space drone
New space drone received the designation XS-1 is not accidental. Previously, the X-1 cipher belonged to an experimental aircraft with a rocket engine, which was created by Bell in the first half of the 40-s of the last century. It was X-1 in October that 1947 was the first in stories manned vehicles, which managed to overcome the speed of sound. During the flight, this experimental aircraft reached a speed of at 1,04 Mach or about 1150 km / h. Already in 1948, the Bell X-1 demonstrated a new record, developing speed in 1600 km / h, and in 1954, at all 2600 km / h.
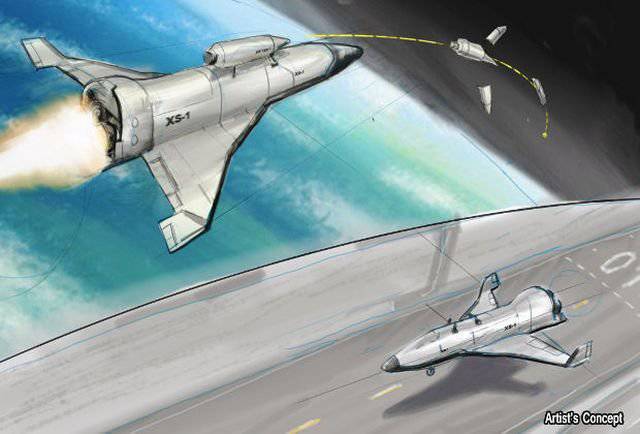
It is worth noting that for the first time information about the eXperimental Spaceplane-1 program appeared as early as September 2013. At that time, this program was considered only as an addition to the already existing ALASA (Airborne Launch Assist Space Access) program, in which it was planned to develop a new solution for launching microsatellites worth less than 1 million dollars using traditional aircraft. Now the program has changed, and XS-1 is highlighted in an independent development, which provides for the maintenance of the full cycle of work on the creation of this unit. In the description of the program it is reported that the hypersonic space drone should be not only cheap, but also expandable, suitable for simple repairs, as well as initially reusable.
According to the requirements of the US military, XS-1 will have to reach speeds around 10 Mach numbers (of the order of 11,5 thousand km / h) and carry on board a variety of payloads from 1,36 to 2,27 tons. In this case, the cost of launching such a space UAV should not exceed 5 million dollars. The device will have to withstand a whole series of 10 launches into orbit during the 10 day in a row.
XS-1 image from DARPA website
Currently, the fate of the device XS-1 is not completely resolved. There are numerous consultations with potential creators of a hypersonic space drone regarding the implementation of this project. In the event that the project will be implemented in practice, the device will be designed according to a scheme that is similar to the scheme of another space drone - X-37B. This unit was created in the interests of the US Air Force concern Boeing. In total, two X-37B drones were built, one of them spent more than 400 days in orbit.
The take-off mass of this drone, which, after returning from Earth's orbit, can land in an aircraft-based manner, is about 5 tons. The length of X-37B is 8,8 m, the wingspan is 4,5 m. The estimated duration of stay in the near-earth orbit is 270 days. According to unconfirmed information at the moment, X-37B drones in the future may be used for reconnaissance purposes, as well as for delivery of various spacecraft to orbit.
Agency for Advanced Development DARPA expects to conclude the first contracts to create a new hypersonic space drone in the near future. The test flight will have to be completed in 2017 year. It is assumed that the main part of the contracts for the design of XS-1 or eXperimental Spaceplane-1 will be issued during April-May of the current year. DARPA specialists expect that the program for creating the XS-1 device will significantly reduce the cost of delivery to orbit of cargo.
With the help of a new drone, the military is counting on delivering various cargoes into orbit from 1,36 to 2,3 with an average launch cost of a UAV below 5 million dollars. At the same time, the drone will be able to go into space almost monthly, and it is planned to carry out 10-12 starts a year. In the program description it is indicated that the majority of all developments will be directed specifically at reusable space flights, but some of the developments will be focused on the development of supersonic atmospheric vehicles of both military and civilian purposes.
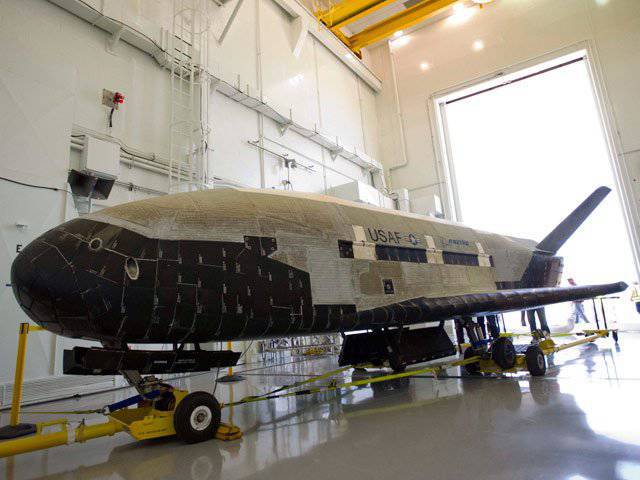

X-37B
The description of the novelty says that it will have an open architecture and will be able to work on any type of fuel. At the same time, DARPA agency experts say that they can give the contract for the production of XS-1 to one contractor or several independent firms. Independent experts are already noting the fact that the XS-1 space drone is likely to be focused on meeting the needs of government users in space, but not intelligence or military, but primarily civilian agencies: meteorology, civilian communications, rural household, etc.
The drone, which will have to reach speeds of more than 10 Mach numbers, will be able to carry in a special detachable stage payload weighing from 1,36 to 2,27 tons. Especially stipulated is the fact that within the series of launches the device should not need repair and maintenance. Preparation for each subsequent launch of the XS-1 should be limited only to refueling and a general check of the onboard systems of the device.
Of particular note is the launch cost, which should not exceed 5 million dollars. As a comparison, you can bring a four-stage rocket Minotaur IV, which the US Air Force is using today to launch small satellites into orbit. This launch vehicle is able to put into orbit up to 1,73 tons of payload, while the cost of its launch is estimated at 55 million dollars. These missiles are used from 2010 year. In total, only 5 launches were carried out during this time, which is a little more than one space launch each year.
It is assumed that the XS-1 will climb into the upper atmosphere of the Earth, where the separation of the expendable stage containing the payload will occur. This stage will take satellites and other devices into orbit. It is reported that the price of a detachable stage will be 1-2 million dollars. The mass of the stage together with the mass of the payload will be no more than 6,8 tons. The maximum take-off mass of the space drone will be no more than 101,6 tons (the launch mass of the Minotaur-IV launch vehicle is 86,2 tons).
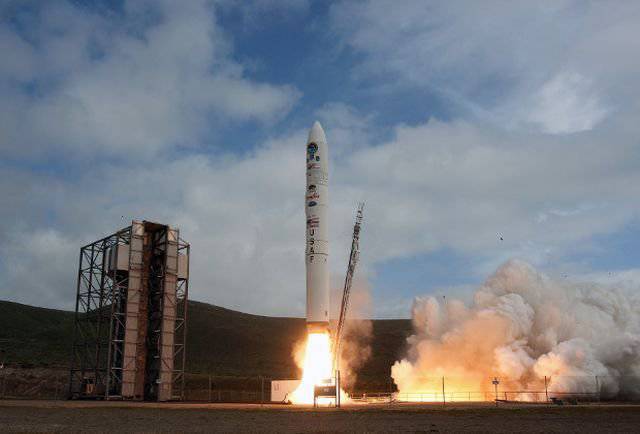

Minotaur-IV Booster
The first contracts for the development of the XS-1 drone should be concluded in the first half of 2014. It is assumed that the value of each of the contracts will be 3-4 million dollars. Already in 2015, it is planned to conclude an agreement with one of the companies on the economic appraisal of the project, the release of a prototype drone and the conduct of a series of tests worth 140 million dollars. If there is no change in the financing of this program, then the device will be able to take to the air in the 3 quarter of the 2017 year. And the first flight to near-earth orbit will be held in 2018 year.
During a series of tests, the XS-1 will have to at least once overcome the speed of Mach numbers in 10, launch a payload into orbit, make 10 flights in 10 days. In this case, the requirements for the mass of the payload and for the turnover of the device, that is, the strict observance of the rule "1 flight every 24 hours" will not be presented.
The military emphasizes the fact that the creation of a hypersonic space drone will allow them to get rid of the rigid launch schedule of spacecraft. Today, every rocket launch has to be planned in advance, with all space launches usually already scheduled for several years ahead. At the same time, programs for the creation of new spacecraft that need to be launched into space can also be significantly out of the previously scheduled timeline. And this, in turn, may threaten the disruption of the planned missile launches. At the same time, it will be possible to forget about this problem with multiple-destination drones, since in the case of one or other delays, the start of the device can be postponed as many times as necessary. At the same time, the US military is pursuing another goal. They seek to provide themselves with an additional source of attracting profits, which can be directed to the implementation of other important military projects from the point of view.
Information sources:
http://lenta.ru/articles/2014/02/12/xs1
http://vpk.name/news/105517_darpa_proektiruet_kosmicheskii_samolet_xs1.html
http://vpk-news.ru/news/19118
Information