America vs England. Part of 3. Great break
 The Great Depression was a great test for the peoples of North America and Western Europe. Russian historian and publicist Boris Borisov talks about the consequences of the Great Depression for the United States, comparable to the policies of forced industrialization and collectivization of agriculture in the late 1920-s in the USSR.
The Great Depression was a great test for the peoples of North America and Western Europe. Russian historian and publicist Boris Borisov talks about the consequences of the Great Depression for the United States, comparable to the policies of forced industrialization and collectivization of agriculture in the late 1920-s in the USSR.He equates the well-to-do Soviet peasants dispossessed of nowhere to the American farmers and their families deprived of land and housing. Forced labor in the gulag - to Roosevelt's public works. Hunger in Ukraine, the North Caucasus, the Volga region, the Southern Urals and northern Kazakhstan to the famine in American cities and rural areas. In this part, we will see that America had its Great turning point in the era of prosperity - prosperity, roaring 20's.
In July, 1927, a conference was held on Long Island with the participation of the Heads of the Central Banks of England and Germany, Norman and Mine, the second person in the French Bank Charles Rist and the head of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York Strong. “The result was a seemingly inconspicuous reduction in the interest rate of the Federal Reserve Bank from 4 to 3,5 percent in August 1927 of the year. The rate in New York was one point lower than in London.
However, this seemingly innocuous cheapening of money in New York, combined with an increase in the takeover of securities by the Federal Reserve Bank, became a turning point in the period between the two world wars. This is a re-inflation of the money market, complementing the more powerful and until then effective inflationary push of the end of 1924, the shameful take of Wall Street to the truly Faustian heights in September of 1929.
Thus, “the board of directors of the Federal Reserve Bank allowed speculative activity to increase, which by August 1928 had gone out of control and had become catastrophic by July 1929” (Preparata GD Hitler, Inc. How Britain and the United States created the Third Reich / / http://litrus.net/book/read/103531?p=62). According to Liaquad Ahamed, “although the reduction in rates was insignificant - only 0,5% - and short-lived - after six months everything returned to normal, the fact that the market rose in the same month, in August, 1927, when the money fell, could not be a coincidence. The Fed's move was a spark that caused a forest fire ...
After the Long Island meeting ... the Federal Reserve ... made a powerful credit issue ”(Ahamed L. Finance Lords: Bankers Turning the World / Translated from English - M: Alpina Publishers, 2010. - C. 264, 272). In other words, the Federal Reserve began pumping money into the country. Money supply was increased by 62%. Money was in abundance ”(Karasev D. Killer banks // http://lib.rus.ec/b/132387/read). Rates of leading American companies rushed up, but “out of any connection with the growth of corporate income — if the former almost doubled in price, the latter maintained steady 10% growth” (Ahamed L. Decree. Op. - C. 272).
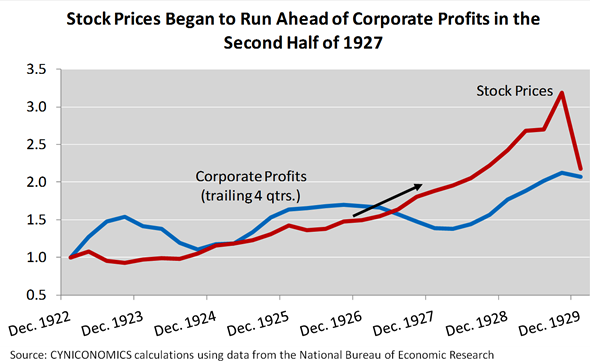
In the Soviet Union, the five-year plan has not yet been approved, and the first five-year plan has already begun “October 1 1928 (at that time the business year began in October). ... Gosplan completed its development, relying mainly on the directives of the XV Congress. ... In November 1928, the control figures of the five-year industrial development plan, developed by the Supreme Council of the USSR National Economy, were published. The Eighth Congress of Trade Unions, which was taking place at that time, heard the report of the Chairman of the Supreme Economic Council V.V. Kuybysheva noted that “the industry’s benchmarks correctly reflect the general course of the party at the rapid pace of industrialization of the USSR, the priority development of heavy industry in order to build socialism and eliminate the technical backwardness of the country” (World story. The 24 T. T. 22. Eve of World War II. - M .: AST; Minsk: Harvest, 2002. - S. 21, 32).
It should be noted that the basis of industrialization was the "system of massive transfer of financial, material and labor resources from the agricultural sector to the industrial one." “As a result of the famine caused by forced collectivization, many regions of the RSFSR (the Volga region, the Central Black Earth region, the North Caucasus, the Urals, the Crimea, part of Western Siberia), Kazakhstan, Ukraine, and Belarus suffered. From hunger and diseases associated with malnutrition in 1932-1933, about 7 million people died there.
The peoples of the USSR paid a huge price for industrialization, for the gigantic economic breakthrough that occurred in those years. Eternal monument to the heroes and victims of 30-ies became the Dnieproges, Magnitogorsk and Kuznetsk metallurgical plants, metallurgical giants of Ukraine “Zaporozhstal”, “Azovstal”, “Krivorozhstal”, large coal mines in the Donbass, Kuzbass, Karaganda, Kharkov tractor plant, Moscow and Goghard’s coal mines in the Donbass, Kuzbass, Karaganda, Kharkiv tractor plant, Moscow and Gogorodskstal, Moscow and Moscow and Coal mines in the Donbass, Kuzbass, Karaganda, Kharkov tractor plant, Moscow and Gogorodsk coal mines. automobile factories - in total more than 1500 industrial enterprises "(In memory of the victims of 30's famine in the USSR. Statement of the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the fifth convocation of 2 on April 2008 of the year // h ttp: //www.regnum.ru/news/980696.html).
"In the 1929 year, when Laborites returned to power in England, diplomatic and trade relations between the USSR and England were restored." Meanwhile, “by the end of 1920, influential circles in the UK and the USA decided to support the course of radicalization in Germany” (Engdal U.F. The Centenary of War: Anglo-American Petroleum Policy and the New World Order // http: //www.warandpeace. ru / ru / news / view / 9097 /). For the sake of bringing Hitler to power in Germany, the Fed and Morgan’s banking house decide to stop lending to Germany by instigating a banking crisis and economic depression in Central Europe ”(Rubtsov, Y. Hitler took credit for world war from America // http://svpressa.ru / war / article / 13438 /).
"Expansion of lending at the end of 1920's. was carried out by German banks against the background of a low level of own funds that posed a threat in the event of non-payment of a loan or other crisis. By the time of the collapse of the New York Stock Exchange 1929-1930, Germany was in a unique position among the major industrial countries of Europe. Its debt to foreign banks on short-term loans was about 16 billion Reichsmarks. To completely overthrow the unhealthy banking system, it was enough just a slight jolt.
The push came from the Federal Reserve Bank and the Bank of England, which in 1929 had successively raised interest rates after two years of unprecedented stock exchange speculation on lower interest rates. The quite predictable collapse of the New York Stock Exchange and the London market led to a massive withdrawal of American and British banking capital from Germany and Austria (Engdahl W.F. Ibid.). “The worst moment to strike in Germany was difficult to choose. In accordance with the Dawes Plan, the country should have finally recovered and from 1929 pay reparations without any concessions in full to 625 million dollars a year, which was about 5% of GDP. ”(Ahamed L. Decree. Coun. - C. 288).
“Having proved his intransigence, Norman made a decisive step and 7 February 1929 of the year raised the bank interest rate by a whole point, bringing it to 5,5 percent, expecting an immediate response from New York. But New York was slow. Failure occurred within the American banking grid; Harrison [the new head of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York - SL] and the Anglophiles in New York wanted to play along and raise the interest rate to 6 percent, but the seven members of the Federal Council, the resident supervisor in Washington, seem to have stopped understanding at all. what and with what intentions they are doing in New York ”(Preparata GD ibid.).
In March 1929, the inauguration of US President G. Hoover elected in 1928 took place. Meanwhile, in the Soviet Union in April 1929 of the year, the XVI party conference was approved, and in May, the V 5th Congress of the Soviets of the USSR adopted the first five-year plan for the development of the national economy of the USSR at 1928-1932. In anticipation of the economic crisis from overseas, the Nazis were provided with effective economic assistance. “The leading financial and industrial groups of the USA - Rockefeller, Morgan, Lamont, Kun Loeb and others - are actively involved in financing the Nazis and pushing them to power. Especially close ties with the Hitlerites existed with the banks, through which the American monopolists provided loans to Germany -“ J. Henry Schroeder Banking Corporation, whose director for many years was Allen Dulles, Dillon Read & Co., Coon Loeb & Co..
In July 1929, a representative of the Morgan group, Carter, convened a meeting in New York, in which Rockefeller’s son-in-law Aldrich, five other bankers, and a representative of the Royal Dutch Shell Klin participated. The meeting participants discussed the situation in Germany and recognized that it was necessary to provide effective support to the Nazi party so that it could play a large role in the political life of the country. In order to find out what help the Hitlerites need, one of the participants in the meeting, the banker Warburg, who was fluent in German, was sent to Germany. There, with the assistance of the Mayor of Munich, he met with Hitler and his financial expert director of the Tissen bank, Heidt. After the conversation, Heidt traveled with Warburg to Amsterdam, where he received 10 million dollars for the Nazis at Mendelssohn’s bank ”(Rozanov GL Germany under fascist rule (1933-1939)) - M .: IMO, 1961 - S. 24-25 //
http://library.nulau.edu.ua/POLN_TEXT/KNIGI/ROZANOV_GERMAN_1961.htm#Г_1).
“Ten times in a row, from February to August 1929, fearing that this would adversely affect business activity, the Council rejected New York’s proposal to raise the rate to 6 percent. Finally, 9 August 1929 of the year ... The Federal Reserve Board finally set the rate at 6 percent ”(Preparata GD Ibid.). Thus, the Federal Reserve began to reduce the amount of money in circulation. Therefore, it is not a coincidence that the biographies of all Wall Street bosses of that time are John Rockefeller, JP Morgan, Joseph Kennedy [the future representative of the United States of America in England and the father of US President John Kennedy - S.L.], Bernard Baruch and their ilk [Owen Jung, for example - S.L.], contain a reference to the fact that they managed to close their positions in securities transactions before the market collapse and invested all assets and cash in gold. ...
October 24 1929 major New York bankers began to issue loans to brokers only on demand with a repayment term of 24 hours. This meant that both stock brokers and their clients had to “merge” their shares on the market at any price in order to repay loans. As a result, the market collapsed ”(Karasev D. ibid.). “On that day, dubbed“ Black Thursday, ”12,8 million shares were sold on Wall Street, 1,5 times more than ever before. A few days later, October 29, on Black Monday, reached the peak of speculative excitement when 16,4 million shares passed from hand to hand (Economic history of foreign countries: Textbook: 3 ed., Ext. And pererabot - Minsk: Interpressservice: Eco Perspective, 2002. - C. 284).
“It was this day that Churchill chose to make an introductory visit to the stock exchange. He was invited inside so that he personally saw the scene where the main events unfold ”(Ahamed L. Decree. Op. - S. 322). Few people at that moment could have foreseen what the autumn events in the American stock market would turn into. Among the few chosen ones were Hitler and his entourage.
As you know, after the beer coup “to reduce the threat of deportation, Hitler on April 7, 1925, officially renounced his Austrian citizenship. The Austrian authorities were quick to agree. But as a result, Hitler turned into a man without a homeland. Having renounced Austrian citizenship, he did not acquire German "(Shearer WL The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich // http://www.litmir.net/br/?b=139380&p=55). However, now, on the eve of the destabilization of the American, and after it the German, economies and on the eve of the struggle for power, Hitler needed to legalize himself in Germany. And it was in the fall of 1929 that Wilhelm Frick (head of the criminal investigation department of the Munich police and head of the NSDAP faction in the Reichstag) unsuccessfully tried to settle the issue of Hitler's citizenship in Munich (Fest I. Hitler. Biography. Way up / Translated from German - M. : Veche, 2006. - S. 520).
“It was done: Norman put an end to the long season of American profits, which lasted 15 years, from 1914 to 1929 year, a time of greedy dreams and unprecedented abundance, prepared by Britain and inspired by the devastation of Europe. After that, the interest rates of London and New York, intertwining like two mad snakes, rolled: the world economy was disfigured by debt obligations concluded during the boom at unthinkably high interest rates, and the collapse of central banks caused such a decline in prices that the money instantly went into the ground ; they were locked in basements - rates dropped, banks stopped lending, the grille closed. The crisis began, the equal of which were nowhere and never. ...
The ratio of gold to total credit in America in April 1929 of the year fell below 7 percent, this is the lowest level in the entire history of its history; when the collapse struck the United States, the paralysis was universal: by ruining the banks, the American elite burned a third of their banking grid while playing British games. It took ten years for the United States to get out of depression. The Dawes plan was finished, and with it the loans that ensured the breakthrough of the German economy in a coma: the Americans demanded their money back. In America, German securities suddenly and completely stopped buying ”(Preparata GD ibid.).
“Within a matter of weeks, the market lost 3 billion dollars. Over the year, the market has shrunk by 40 billion. ... It is curious that at this time the Federal Reserve undertook - instead of saving the economy, quickly lowering the discount rate, he continued to stubbornly reduce the money supply, further aggravating the depression. As a result, between 1929 and 1933, the amount of money in circulation decreased by 33%. Although most Americans have never heard that the Fed has caused the Great Depression, this is well known among major economists. For example, Elifron Friedman, a Nobel Prize winner at Stanford University, said in an interview with National Public Radio in January 1996, the following: “The Federal Reserve definitely caused the Great Depression, reducing the amount of money in circulation from 1929 to 1933 in 1 / 3 "(Karasev D. ibid.).
At the London Maritime Conference in 1930, the United States “achieved equality fleet with the English fleet in all categories of vessels ”(World History. Vol. 22. Decree. Op. cit. - P. 189). Meanwhile, it did not bring peace to the Anglo-Saxons. “When in 1928 there were suggestions that Chaco might have oil reserves, two corporations entered the struggle for this region: American Standard Oil supported Bolivia, and Shell Oil supported Paraguay. Since the end of 1931, both countries began to intensively rearm their armies. ... June 15, 1932, after an attack by the Bolivian troops of the garrison of the Paraguayan city of Pitiantut, an open war began (officially it was declared only on May 10, 1933). ...
Interestingly, among the command of the Bolivian army were 120 German emigre officers (among them the commander of the Bolivian army, Hans Kundt [in 1925-1931. Ernst Rom was a military instructor in Bolivia - SL]), while in the Paraguayan army served as 80 former White Guard officers who emigrated from Russia (including two white generals - the chief of the General Staff of Paraguay, IT Belyaev and NF Ern); both of them participated in the First World War at one time and actively used its experience during the battle ”(Chak war) // http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A7%D0%B0%D0% BA% D1% 81% D0% BA% D0% B0% D1% 8F_% D0% B2% D0% BE% D0% B9% D0% BD% D0% B0).
“In March 1930 of the year, a few months before the British-American bankers introduced restrictions on lending to Germany, the president of Reichsbank, Yalmar Schacht, unexpectedly asked the government for resignation. The reason for the resignation was an emergency stabilization loan for 500 of millions of Reichsmarks offered by the Swedish industrialist and financier Ivar Kruger, the famous Swedish “match king”. Kruger and his American bankers, Lee Higginson and Co., were major lenders in Germany and other countries that were denied lending to banks in London and New York. However, the loan offered by Kruger at the start of the 1930s contained explosive and unacceptable political implications for the long-term strategy of Montague Norman's friends. German Finance Minister Rudolf Hilferding persuaded Mine, who, under the terms of the Dawes reparation plan, had to approve every foreign loan, accept the Kruger offer. Schacht refused and on March 6 handed his resignation to the Reich President von Hindenburg. He had other things to do.
A few months later, at the beginning of 1932 of the year [March 12 - SL], Kruger was found dead in a hotel room in Paris. The official autopsy report states that the death was caused by suicide, but a thorough investigation conducted by Swedish specialists several decades later convincingly showed that Kruger was killed. The individuals who profited the most from Kruger’s death were in London and New York, but the details of this case appear to have been buried with Kruger. With the death of Kruger, Germany lost hope of salvation. She was completely cut off from international loans.
In turn, after the resignation of the president of Reichsbank, Schacht was not idle. He devoted all his energy to organizing financial support for a man whom he and his close friend Norman considered the right person for Germany in crisis. Schacht secretly supported Adolf Hitler’s radical NSDAP batch since 1926. After leaving Reichsbank, Schacht became the main link between powerful but skeptical major German industrialists, industrial tycoons of the Ruhr, and major foreign financiers, especially Lord Montague Norman. ”
It is not surprising that in September 1930, a financial miracle occurred with the NSDAP: “as a result of large donations from Thyssen,“ IG Farbenindustry ”and Kirdorf’s party receives 6,4 million votes, takes second place in the Reichstag, after which generous injections from abroad are activated” (Engdal U.F. Ibid.). In the meantime, in the 1930, Thuringia’s Ministry of the Interior, V. Frick, “wanted to arrange German citizenship for Hitler by making him a civil servant of this land” and offered him “free space for the commissioner for gendarmerie in Hildburghausen, but Hitler refused all this ridiculous fuss” (Fest Y Decree op. - C. 520).
“In August 1929 and January 1930, reparation conferences were held, at which it was decided to grant Germany privileges, and a new reparation payment plan was adopted, called Jung's plan, after the American banker, the chairman of the committee of experts [and one of the bankers from the clan Morganov - SL]. Jung's plan provided for the early termination of the occupation of the Rhineland in 1930. The total amount of reparations was reduced from 132 to 113,9 billion marks, the repayment term was provided for in 59 years, the annual payments decreased. In 1931 - 1934 the amount of payments was to increase, starting with 1 billion. 650 million marks.
In the next 30 years, reparations were to be paid at 2 billion marks. In the remaining 22 of the year, the amount of annual contributions decreased. It was decided to abolish control over the German economy. Reduced natural supply. Some of the reparations were unconditional, and they were intended to pay off all-union debts. Pa coming years 10 unconditional reparations were defined in 700 million marks.
To implement the decisions taken, the Bank for International Settlements was established, which was located in Basel. However, the deepening crisis continued, the economic and social situation in Germany was exacerbated, so the implementation of the Jung plan was recognized as dangerous. As early as June 1931, US President Hoover demanded a suspension of payments on reparations [and the military debts of England, France and other states - SL] for one year. In June, the 1932 conference in Lausanne reduced all payments to 3 billion marks and determined the term of their payment in 15 years ”(Economic History of Foreign Countries. Decree. Op. - C. 313).
“Established in accordance with the so-called“ Young Plan ”(a plan for collecting reparation payments in Germany, developed in 1929-1930 instead of the“ Dawes Plan ”; according to a unilateral decision of the German government, it almost ceased from 15 in July 1931) Owen Jung, one of the Morgan clan bankers, the BIS was conceived as a financial institution designed to ensure the collection of reparation payments imposed on Germany after the First World War. However, less than a year after the establishment, the bank began to perform opposite functions, turning into a channel through which American and British money was freely transferred to Nazi tanks. By the beginning of the Second World War, the BIS completely came under the control of Hitler ”(Hayem C. Trade with the enemy // http://www.x-libri.ru/elib/highm000/00000007.htm).
In particular, during World War II, the BIS, the Bank for International Settlements, passed 378 million dollars in gold. Gold "was partially looted from the national banks of Austria, Holland, Belgium and Czechoslovakia, and partially melted from gold crowns, eyeglass frames, cigarette cases, lighters and wedding rings of Jews killed in concentration camps." Moreover, gold did not have to leave, for example, London, “so that it could be used in Berlin. According to the agreement between the BIS and member banks, transactions are usually made by simply matching the gold deposit accounts. The sophisticated financiers believed that direct transfer of money was difficult and dangerous, since the sums should have been included in customs declarations ”(Hayem C. Ibid.).
The essential moment of transferring funds during the war through bank details should be their safety. As it is known, during the Great Patriotic War, the British merchant ship Port Nicholson with 71 tons of platinum, the cruiser Edinburgh with 5,5 tons of gold and the Soviet destroyer “Zealous” with 3 tons were killed during the transportation of gold against military supplies from the Soviet Union to England and the USA. gold The secrecy of the transfer of funds through the Bank for International Settlements allowed Britain and the United States to maintain trade and economic ties with Germany even after the start of the war with her.
“The Dawes Plan provided for the priority of private creditors over recipients of reparations in the event of a crisis of payments. In fact, this meant that government lenders — the governments of France, Belgium, and the United Kingdom — had to stand in line, waiting for Germany to pay off private creditors. Jung's plan ... canceled the article on the protection of transfers ... and therefore private creditors, having lost guarantees, could no longer count on privileges in the event of a crisis, and found themselves in a common lineup with major government creditors. It is not surprising that lending to Germany by private capital has come to naught ”(Ahamed L. Decree. Op. - C. 363-365).
"In Germany ... the Dawes' car crash caused by the cessation of the" flow "caused such strong political despair that in March 1931, Germany and Austria, the two countries that experienced Norman’s help, announced their intention to create a customs union (Zollverein), a means of overcoming commercial stagnation in Central Europe ”(Preparata GD ibid.). However, France frustrated the German-Austrian negotiations on a customs union as violating the Versailles Treaty. 8 May 1931, the leading Austrian bank went bankrupt. “The news of the serious difficulties of the leading bank in Austria immediately gave rise to fears that the“ contagion ”would spread to the main bank in Germany. … Money flowed from Germany like a river ”(Ahamed L. Decree. Op. - C. 368).
In July, banks were closed throughout Germany for two weeks. “For the second time in the last eight years, Germany faced a real threat of economic catastrophe. ... The collapse of the German banking system in the summer of 1931 hit the back of an already lame economy, and it rolled down again. ... Meanwhile, following the closure of German banks, a wave of crisis swept through the rest of the global financial system, destroying everything in its path. ” Financial institutions of Hungary, Romania, Latvia and Poland suffered a blow. In Latin America, the crisis hit Bolivia, Peru, Chile and Mexico (Ahamed L. Decree. Op. - C. 380-381).
“During the period of economic crisis ... the government of H. Brüning ... set a course for curtailing relations with the USSR" (S. Gorlov, Top Secret: Alliance Moscow - Berlin, 1920-1933. - M .: OLMA-PRESS, 2001 // http : //militera.lib.ru/research/gorlov1/05.html). By signing 24 on June 1931 in Moscow, a protocol extending the Berlin Treaty, the government of Brüning did not ratify it. “Bruening, in his memoirs on this subject, wrote:“ Since the spring of 1931, the French have continually tried in vain to break away Russia from us. ” The following words of Brüning are symptomatic in this connection: "We will let go of the little finger of Russia, which we hold now, only when we firmly hold the hand of France in our hands." But this “hand of France” just was not.
It is no accident that Brüning, regretting subsequently the Soviet-German relations that had begun to deteriorate at that time, noted: "The basis for a complete withdrawal from Russia was laid without any benefit for us in return." "In the conditions of the economic crisis 1929 - 1933. (“Great Depression”) the value of the USSR as a market for German industrial, including military-industrial products, increased dramatically. So, if Germany's exports to countries such as France, Holland, and the United Kingdom in 1932 compared to 1929 decreased by 48,6%, 53,2% and 65,7%, respectively, its exports to the USSR, on the contrary, increased by 176%. ...
In parallel, the French stepped up diplomatic pressure on Moscow, inviting 20 on April 1931 to conclude a non-aggression pact. But when 10 August 1931 Mr. Briand and Soviet Envoy VS. Dovgalevsky initialed the text of the pact, the French put forward the condition of the signing of the pact, the conclusion of the USSR of a similar pact with Poland. Two months later, on October 14, 1931. Mr. Litvinov proposed that the Polish attorney in Moscow sign the Soviet-Polish non-aggression pact. ...
18 August 1931 Mr. Brüning explained to the business community of the German steel industry that, rejecting "Russian orders", which industrialists insisted on retaining, he was guided by the fact that they were used throughout the world for military purposes. It was at that time that rumors appeared in Germany, from which it followed that the German government had agreed with French Foreign Minister Briand that, if German interests were taken into account, at the Geneva Conference on Disarmament Germany would stop cooperating with the Red Army. Their distribution was directly connected with the plans of Papen and Rechberg to conclude an alliance with France at the expense of the USSR ”(S. Gorlov, Ibid.).
In September, 1931, seeing that the Labor government did not have enough influence to bring the country out of the economic crisis, MacDonald resigned as prime minister. “However, the Conservative Party was not ready to assume full responsibility for bringing the country out of the crisis.” Its leadership was weakened by the struggle of the factions N. Chamberlain and Winston Churchill. In this situation, the idea of creating a "national government" of Laborites, conservatives and liberals.
“It was proposed to lead him to MacDonald. Consent cost him a place in the Labor Party. Most of its members ... declared supporters of MacDonald ("National Labor") renegades and expelled from the party. ... However, a Conservative, National Labor and National Liberal government was created, and the coalition of these parties won the elections in October 1931 of the year. ” Despite the coalitional nature of the national government, the conservatives took decisive positions in it. “Neville Chamberlain, who headed not only the Ministry of Finance, but also the secret office, had a special influence” (Newest history of European and American countries. The 20th century: studies for university students: In 3, including 1. 1900-1945. - S. 197).
“On Monday, 21 September, in front of the world dumbfounded by amazement, Britain canceled payments in gold. Within four weeks, eighteen countries followed suit, also abandoning the gold standard. ... Thus, she deliberately destroyed the international payment system, completely blocking the financial oxygen for the Weimar Republic. ... September 1931 of the year was the "turning point of the period between the two wars." British treason signaled “the end of the international financial system, established in the twenties and undermining the foundations of the international economy.
Setting the gold standard and bearing in mind its future unavoidable cancellation, Norman gathered together the divisions of the banking system of the British Empire: South Africa, Canada, India, New Zealand and Australia were financially rebuilt; central banks were organized or modernized there. Thus, September 1931 of the year found the empire financially compact and self-sufficient, possessing a huge closed market, protected by imperial preferences, supplemented by the 1932-percent tariff in October 20 of the year (Preparata GD).
Summarize. In 1927, the US Federal Reserve Bank began inflating the money market, and in 1929, sharply reducing the amount of money in circulation caused cessation of lending, lower prices (deflation) and overproduction crisis, thereby paralyzing the entire American economy. From America, adversity immediately spread to Germany. American and British banking capital was withdrawn from Germany as soon as possible. The receipt of new loans was stopped by the mine.
The Dawes Plan with its German benefits was suspended. The German-Austrian negotiations on the customs union were nipped in the bud. The bankruptcy of the largest Austrian bank undermined confidence in the German banking system, which was subsequently blocked for two weeks. In addition, Germany itself began to curtail trade relations with the Soviet Union. While trade with England and France, in view of the intensification of the crisis, began to decline rapidly. Britain’s abolition of the gold standard destroyed the international payment system and finally cut off “financial oxygen for the Weimar Republic”, which in its rapid decline approached the very bottom of the economic and social crisis.
Information