Space Innovations from Shvabe Holding
The Shvabe holding (earlier it was called the research and production concern Optical Systems and Technologies) was formed in 2008 in the framework of the state policy aimed at reforming the Russian defense industry. The main reason for reforming enterprises that are part of the holding was the need to increase the competitiveness of the optical-electronic industry in Russia and its products on the international market. The optical-electronic holding company got its name in honor of Fyodor Shvabe, who was the founder of one of the very first enterprises of the holding (this is the Ural Optical-Mechanical Plant).
Currently, the Russian holding includes 37 of various enterprises and organizations, which employ about 20 thousands of people. In addition to industrial enterprises, the holding includes design bureaus, research and production associations, research institutes. At the moment, the enterprises that are part of the Shvabe holding company carry out a full cycle of works on the design, production, sales and service of optical-electronic complexes and systems for the needs of the armed forces: Air Force, Navy, Air Force, and also special services. In addition, the holding enterprises produce a variety of medical equipment, thermal imaging modules and a fairly wide range of civilian products. In total, Shvabe produces about 6 thousands of optical-electronic product names, which today are supplied to more than 85 countries of the world.
According to Sergey Maksin, Director General of Shvabe Holding, the company is currently tasked with developing lightweight head mirrors for promising large-size space telescopes that are planned to be used in the remote sensing system of our planet. According to Sergey Maksin, at present, the Krasnogorsk Plant (KMZ) is the leading domestic enterprise, which is engaged in the production of space monitoring systems and equipment for optical-electronic complexes of remote sensing of the Earth. The competition won by the company opens up prospects for the development of innovative space equipment.
The Krasnogorsk plant named after S. Zverev (KMZ OJSC) is today one of the leading Russian enterprises in the field of creating optical-electronic products for various purposes. For several decades now, the specialists of this company have been providing the process of creating, testing and mass production of optical-electronic systems and optical devices. At present, KMZ OJSC successfully develops and manufactures: means of controlling space; Earth remote sensing systems from air carriers and from space; OMS armored vehicles; surveillance and sighting systems of airborne; day-to-day surveillance systems, laser range finders, target designators, sights for small arms; medical products; observation instruments; photo equipment.
Nowadays, the scientific and technical center of the KMZ is a diversified subdivision that is able to solve the whole complex of issues on the development of new, promising models of technology, including space, as well as to carry out research and development, search and development work, to provide complete the process of design support of all finished and manufactured products. At present, the Scientific and Technical Center (STC) has unique test, research and test bases for experimental and design development. At the same time, the center employs high-level specialists: candidates and doctors of technical and physical and mathematical sciences.
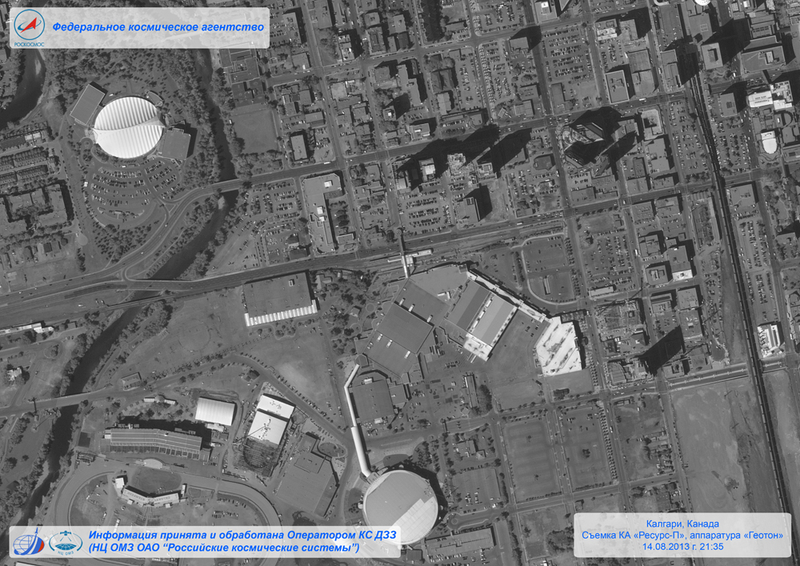

It is worth noting that the KMZ developments (GSA hyperspectrometer and Geoton-L1 remote sensing equipment) were installed on the first Russian aerial photo-television spacecraft, which allows real-time recording of the Earth's surface in high resolution. Among the new developments of the domestic enterprise, one can distinguish modernized sniper sights, a gunner’s thermal imaging sight tank and commander’s tank sight with a domestic thermal imager. If we talk about space products, then by 2020 the company plans to increase its share to 20% in the total volume of products.
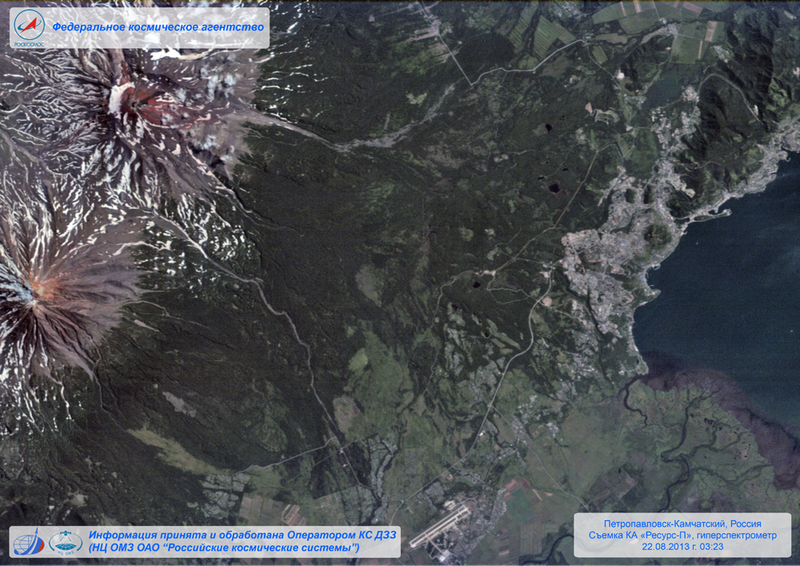
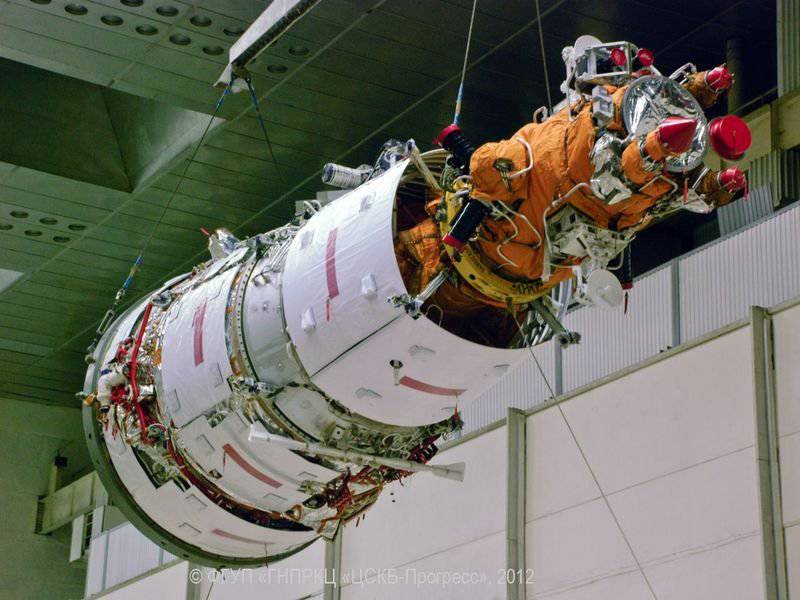
Spacecraft Resource-P
25 June 2013, the launch of the carrier rocket "Soyuz-2.1". The rocket was sent into space from the Baikonur cosmodrome, on board was the Russian spacecraft Resource-P, which uses unique techniques of CMH. Among other equipment, the GSA hyperspectrometer and the upgraded remote sensing equipment of our planet, called the Geoton-L1, were installed on board the Resource-P. The equipment manufactured by KMZ successfully passed all flight tests and since October 1 of last year it has been working as a regular part of the Resurs-P spacecraft.
Resource-P is a modern spacecraft with completely new capabilities. The new Russian spacecraft will be used on a near-circular solar-synchronous orbit, which will positively affect the conditions of observation of the Earth’s surface. Resource-P will be able to shoot from the same height and under the same lighting conditions. Compared to its predecessors, the frequency of observation of the apparatus was reduced from 6 to 3 days. In addition, the developers managed to improve the accuracy of binding of the taken pictures and their consumer properties.

The build-up of the new-generation spacecraft performance characteristics occurred due to the use of several types of equipment on it. An optical-electronic equipment was mounted on Resource-P, which is able to create highly detailed images of the Earth with a resolution of up to 1 meters from 475 kilometers in the panchromatic range. In narrow spectral ranges, the spacecraft can take pictures with a resolution no worse than 3-4 meters.
2 of shooting equipment type was immediately introduced into the Resurs-P onboard equipment: this KSHMSA is a complex of wide-range multispectral imaging equipment (developed by OPTEKS, part of OSPRS TsSKB-Progress) and GSA-hyperspectral imaging equipment (developed by "KMZ"). The KSHMS allows the spacecraft to conduct wide-ranging detailed observation of the terrain with a resolution of 12 meters in the capture band of about 100 kilometers and with a resolution of 60 meters in the capture band of 440 kilometers. At the same time, the GSA capture band is 25 kilometers, and the resolution is about 25 meters. The presence of such equipment allows to improve the quality and the list of accomplishments of the tasks solved by spacecraft in the interests of the socio-economic development of Russia and its individual regions.
Unique development "Shvabe"
Enterprises that are part of the Shvabe holding company have today mastered the production of almost 80 various unique technologies. For example, at the Lytkarinsky optical glass factory, unique large-size optics for large telescopes are currently being produced. The weight of one billet for a telescope can be 75 t. Glass of this size should only cool for a year, after which it is polished with webbing. Optical glasses of this company are world-class know-how, they are delivered to India, EU countries, as well as other foreign customers.

In addition, the holding company "Shvabe" takes part in the development of ITER - the International Experimental Thermonuclear Reactor. As part of this ambitious international project, the holding is working to create an optical diagnostics system for plasma parameters. At the enterprises of the holding today produced about 300 types of various glasses. Among them are very difficult to manufacture samples. For example, Shvabe is able to produce leucosapphires or artificial diamonds. Such optics is widely used in sighting systems, medicine, laser technology.
Of the most recent examples of successful developments of Shvabe, a laser complex developed from scratch can be noted, which is able to cut the ice cover with a thickness of 1-2 meters. The development of this complex involved the national center of laser systems and complexes "Astrophysics". It should be noted that this is the only state scientific center in our country that works in the field of creating laser-optical technologies. There is no such laser development anywhere in the world. Through the use of this installation, it is possible to significantly expand the possibilities of industrial development of sea routes and offshore fields in the polar latitudes. In 2013, at the international innovation exhibition held in Switzerland, the development of Astrophysics, the Ship Laser project, won a gold award.
Information sources:
http://rostec.ru/news/4155
http://rostec.ru/news/2159
http://www.federalspace.ru/19661
http://expert.ru/expert/2013/43/gordost-shvabe
Information