Attack helicopter armament
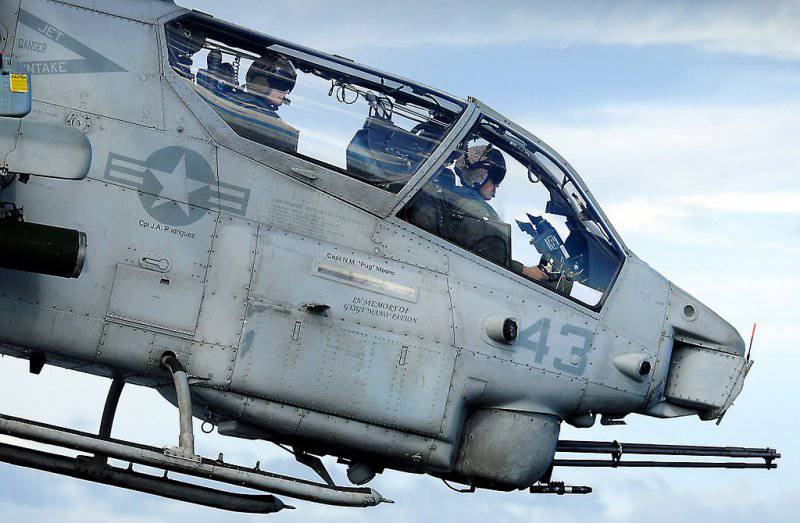

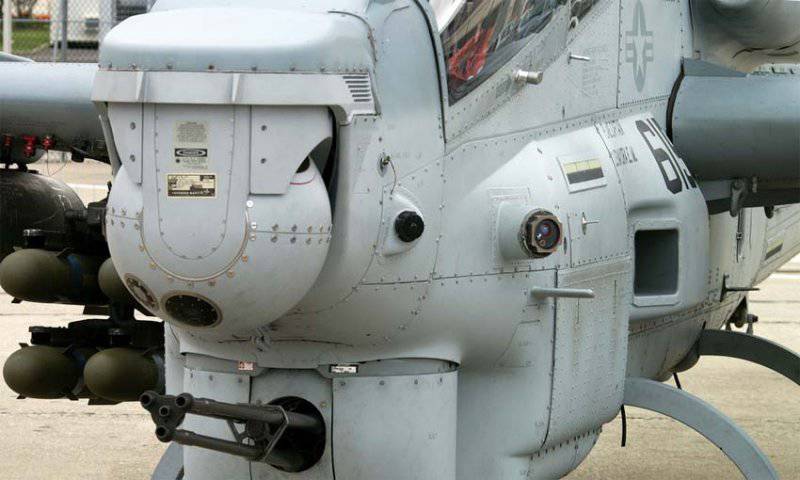
The three-barrel 20-mm M197 gun from General Dynamics Armament and Technical Products in the ventral gondola of the Bell AH-1 W SuperCobra helicopter
All helicopters are sensitive to the load, and therefore the emphasis in choosing weapons for them is invariably placed on the mass of the helicopter. However, while multipurpose helicopters need to weapon For circular self-defense, attack helicopters need forward-firing weapons that can destroy fortified targets from a safe distance, as well as a cannon in a mobile unit for firing less complex targets.
If you take the light part of the weapons spectrum, then machine guns are usually not used on attack helicopters, although the Bell AH-1G Cobra helicopter began life from the front of the Emerson Electric TAT-102A nacelle with the installed GAU-7,62B / A Minigun six-barrel machine gun from General Electric. Similarly, the Mi-2 attack helicopter was originally equipped with a four-barreled 24-mm Yakushev-Borzov machine gun (YakB-12,7) 12,7A9 in a remote-controlled installation.
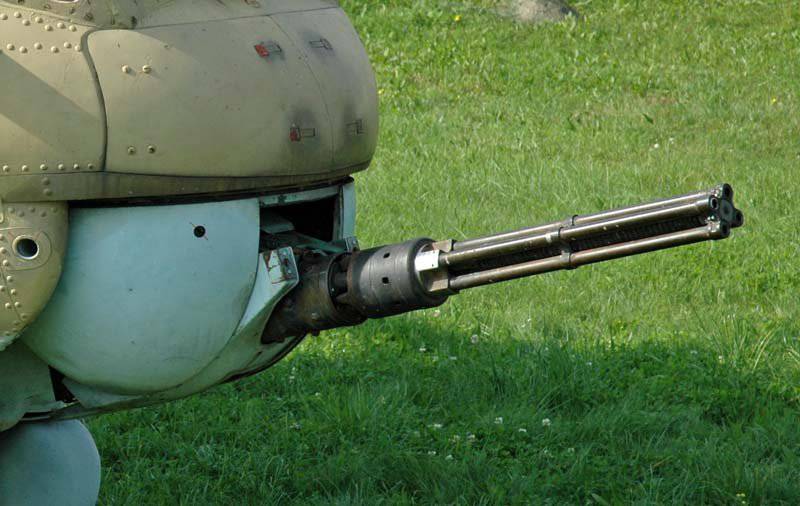

Four-barreled 12,7-mm machine gun Yakushev-Borzov (YakB-12,7)
Guns almost everywhere replaced machine guns as gondola weapons. One of the few exceptions is the Eurocopter Tiger UHT of the German army, currently it can carry automatic weapons only in the form of fixed containers with weapons.
In December, the TNG UHT helicopters in service with the German KHR2012 helicopter regiment in Afghanistan installed FN Herstal HMP36 containers, each with an M400P 12,7-mm machine gun and 3 cartridges. The container weighs 400 kg, and the machine gun has an 138 rate of fire per minute.
Modified by Eurocopter to the standard Asgard-F (Afghanistan Stabilization German Army Rapid Deployment - Full, rapid deployment of the German army for stabilization in Afghanistan - Full), these Tiger helicopters also have 19-charging rocket launchers for 70-mm missiles and guided missiles MBDA Hot.
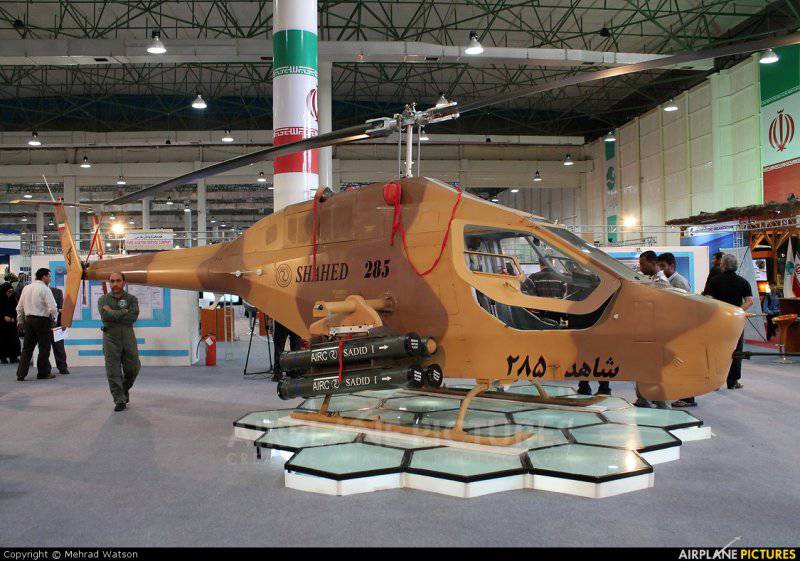
Another attack helicopter, which still holds the turret machine-gun, is the Iranian Hesa Shahed (Witness) 285. This is a very lightweight (1450 kg) single unit - a modification of the Bell 206 JetRanger. The helicopter under the designation AH-85A is armed with a single-barrel 7,62-mm PKMT machine gun in the front turret; he is reportedly in limited operation in the air force of the Iranian Revolutionary Guard.
Gun
The ousting of machine guns with cannons as helicopter armaments has a very rational explanation. America discovered in Vietnam, and later the USSR in Afghanistan, that machine guns mounted on a helicopter are easily “fired” from the ground with heavy automatic weapons.
In ground-air operations, the 7,62-mm machine gun is effective only at a distance of approximately 500 meters and only against unarmored targets, such as personnel in open space. The 12,7-mm machine gun increases the range to 1000 meters and can handle a wider range of targets. The gun (capable of shooting high-explosive ammunition) starts with a caliber 20 mm; it is quite effective at distances up to 1700 meters and can destroy light armored vehicles.
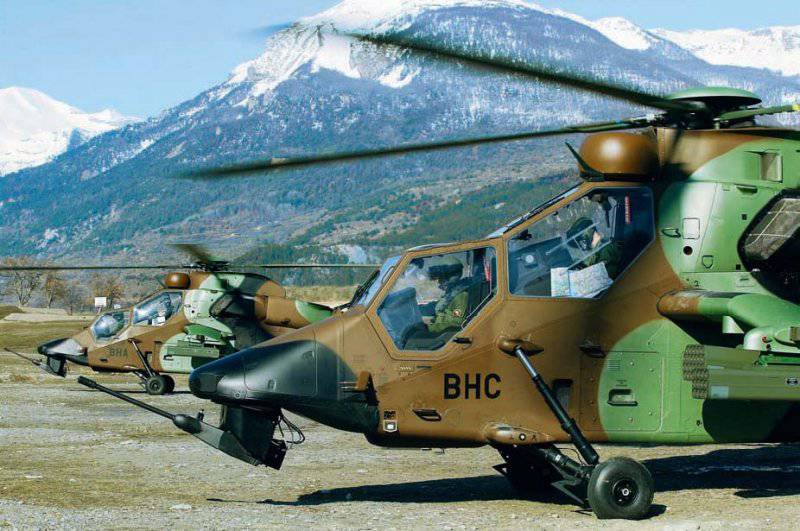

Mounted in front of the turret allows you to raise the gun above the line of the fuselage. In the case of the Eurocopter Tiger HAP helicopter of the French Army, the 30-mm gun Nexter Systems 30M781 in the turret THL30 can rotate 30 degrees up and down and 90 degrees in each direction
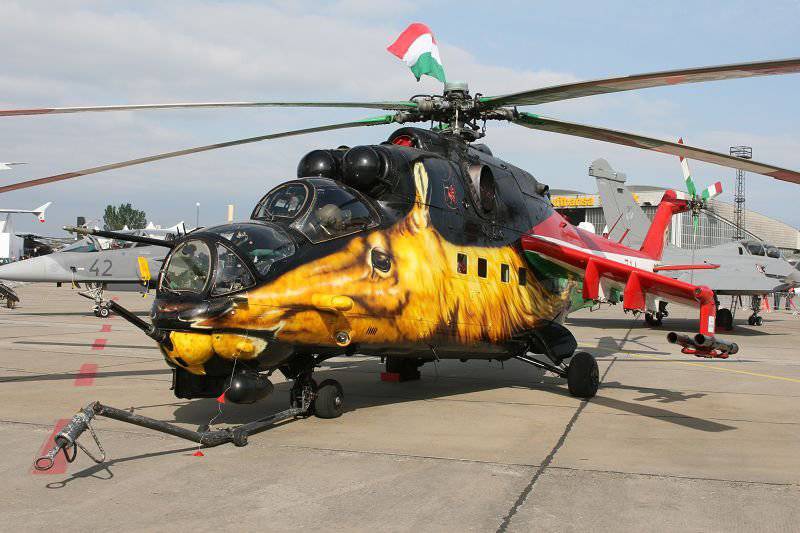

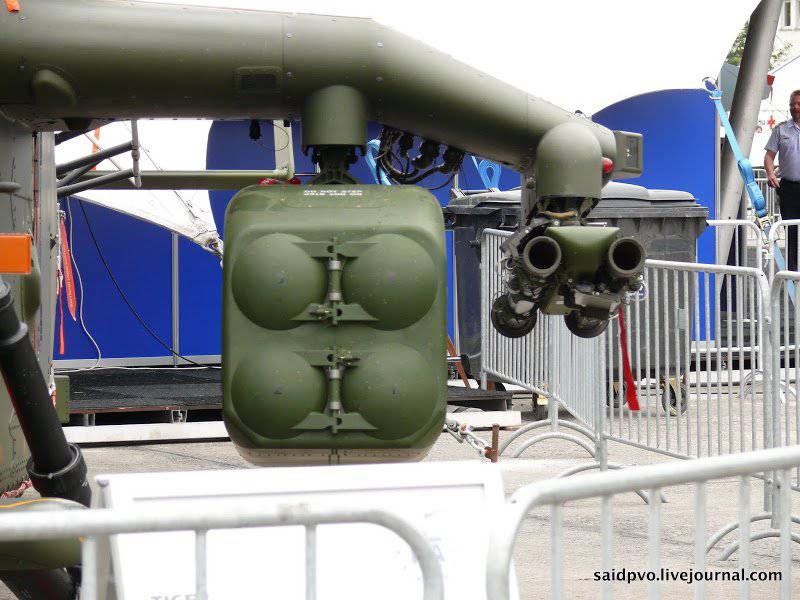
The Mi-24 helicopter painted under the moose of the Hungarian army demonstrates the original front gondola with a four-barreled 12,7-mm machine gun 9A624 (YakB-12,7)
One example of 20-mm armament for a strike helicopter is the Nexter Systems THL20 gondola with a single-barrel 20M621 gun. It is installed on the Romanian cars IAR-330L Puma, was also selected for the Indian helicopter HAL Light Combat Helicopter (LCH). Another front-body venture GI-2 from the South African company Denel Land Systems is designed to upgrade the Mi-24 helicopters of the Algerian Air Force. GI-2 is also installed on the Denel Rooivalk (Kestrel). Such guns usually have an 700 - 750 firing rate per minute.
If you need a high rate of fire (which, in general, is not needed when firing ground targets, but may be preferable when firing at aircraft and speedboats), then in this case it is advisable to gun with multiple barrels.
A typical example is the triple-barreled 20-mm Gatling M197 gun from General Dynamics Armament and Technical Products, which can fire with a rate of fire of up to 1500 shots / min and is installed in the gondola on the Bell AH-1J / W helicopter, as well on AgustaWestland A1. One of the reasons for choosing the A129 helicopter as the basis of the Turkish Atak program was the excellent accuracy of its M129 cannon mounted on the Oto Melara TM197B turret.
When developing the Mi-24 in 80-ies in order to meet operational requirements in Afghanistan, the Mil Design Bureau first replaced the original four-barreled YakB-12,7 machine gun with a double-barreled 23-mm GSH-23L gun with a mobile turret. The entire 25 Mi-24VP was manufactured, but the scope of use of the GSH-23L gun was not limited to this helicopter; it is installed in a cannon container with 250 cartridges (UPK-23-250) under the wings of various Russian helicopters.
In the production of the Mi-24P, the front turret was abandoned in favor of the double-barreled 30-mm GSH-30 gun mounted on the right side of the fuselage. However, the ventral gondola GSH-23 (NPPU-23) returned in the export version of the Mi-35М, which is in service with Brazil and Venezuela.
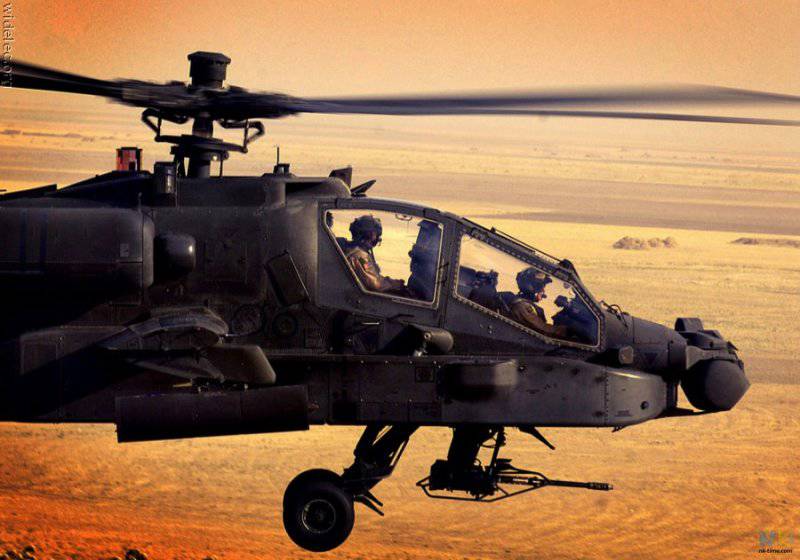
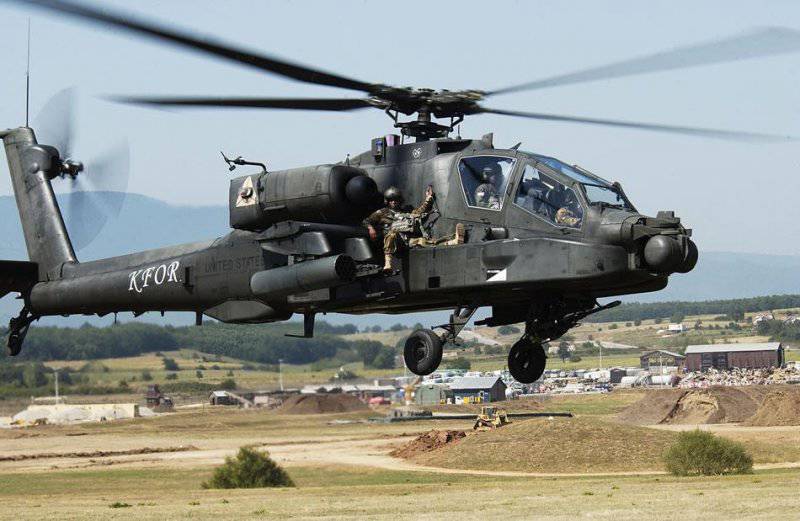


The 30-mm Chain Gun Chain Gun with a 625 gunfire per minute fire rate is an integral visual element of the silhouette of an Apache attack helicopter. Since then, the gun has been adapted for other applications, including the ship’s remote-controlled installation
With a few notable exceptions (AH-1 and A129 series), the 30-mm gun is installed on most of the attack helicopters. The leader was the Boeing AH-64 Apache helicopter with a chain-driven cannon Alliant Techsystems (ATK) M230 Chain Gun in a gondola under the front cockpit.
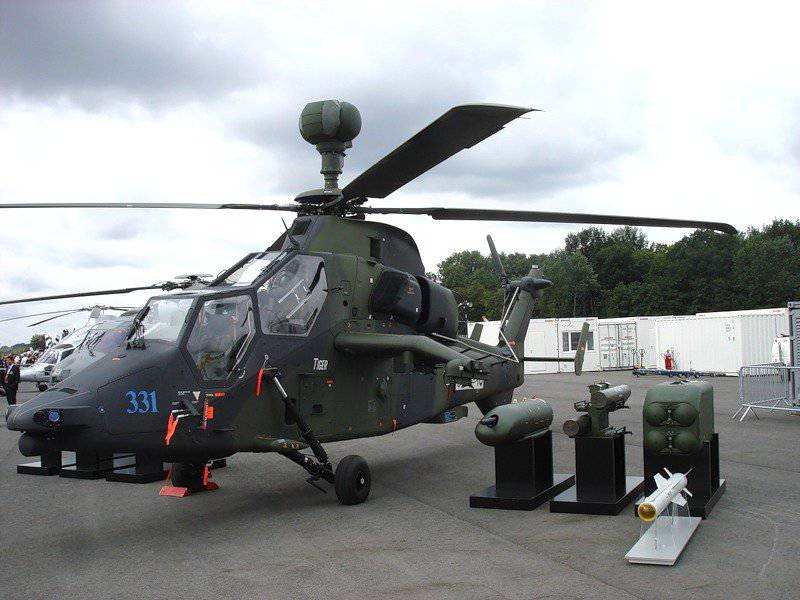
Another example is the Eurocopter Tiger ARH / HAD / HAP with the Nexter Systems 30M781 gun in the ventral turret installation THL30. As mentioned earlier, the German army’s Tiger UHT helicopter does not have a turret, but it is considering installing a RHeimetall / Mauser RMK30 unrestricted revolver cannon (Rueckstossfreie Maschinenkanone 30) in a flexible suspension, firing with non-shells, and you can use your own set-up figure.
With further refinement of the Soviet Mi-24 helicopter with the BMP-2, the proven single-barreled 30-mm dual-feed 2A42 gun was borrowed. The gun's rate of fire is chosen between 200 and 550 shots per minute.
In the case of the Mi-28H, the 2A42 cannon is installed in the gondola MUPP-28H under the front cockpit, but on the Ka-50 / 52 helicopter, this cannon is mounted in the trunnions on the right side of the fuselage and can be rotated vertically by 40,5 degrees.
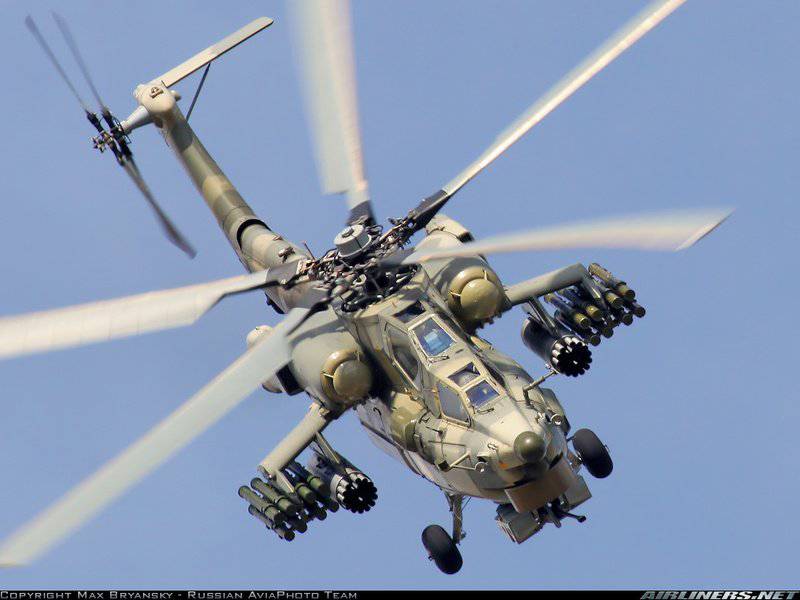
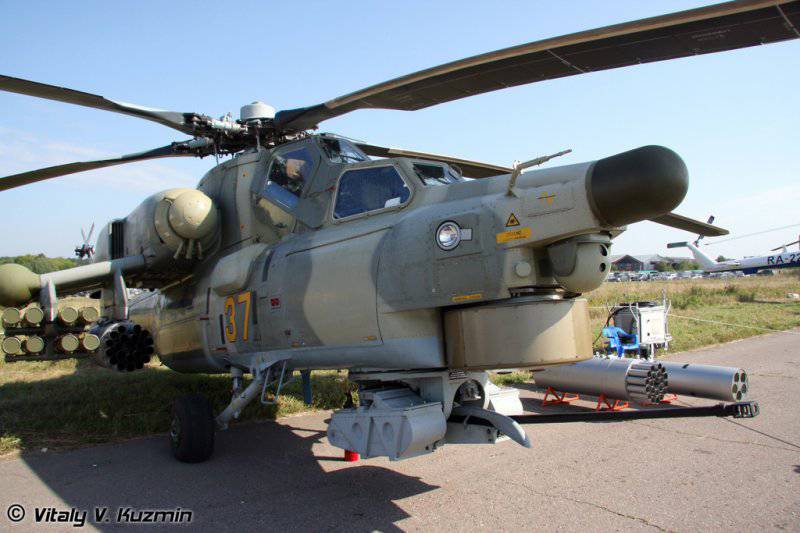


This night hunter, the Mi-28H, illustrates three types of armament: 30-mm 2-gunner with double feed in the ventral gondola, NPPU-42H, 28-mm C-80 rocket in the 80-shell B20В8 rocket launchers B20ВX-offrographs BXNUMXВX-offrograms BXNUMXВ-rocket systems BXNUMXВ-rocket C-XNUMX rocket in XNUMX-projectile BXNUMXВXNUMX rocket launchers of BXNUMXВX-offrodes BXNUMX rocket launcher systems BXNUMXВX-offrodes BXNUMX rocket rifle systems in XNUMX-projectile rifles BXNUMXВX-offro, BXNUMX rocket systems.
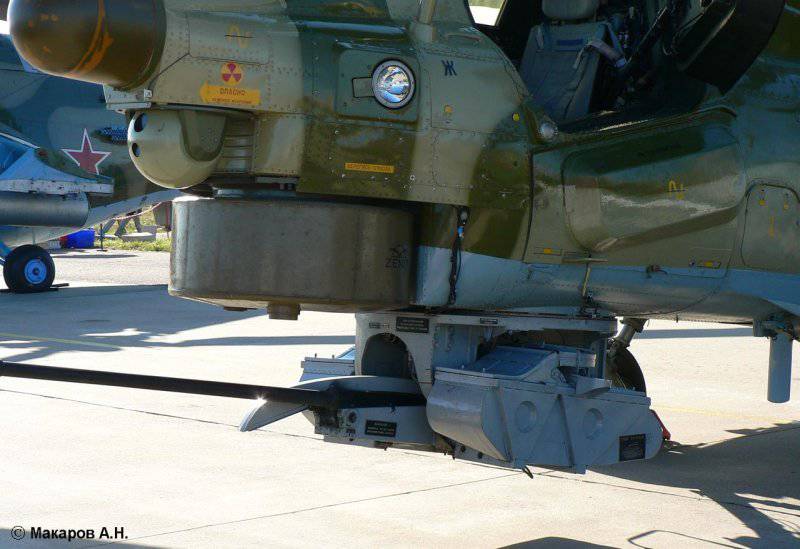

Close-up ventral gondola НППУ-28Н
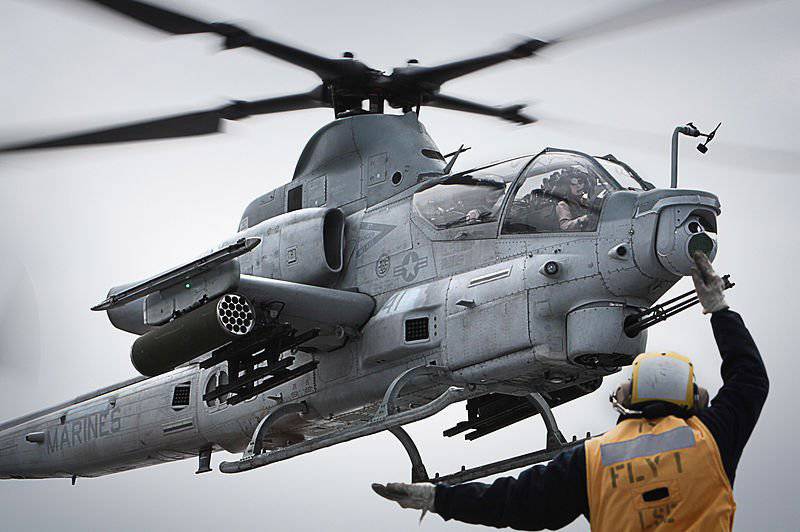

Different from the AH-1W with its four-blade propeller, this Bell AH-1Z Cobra Zulu from the 367 'Scarface' Marine Corps Light Helicopter Division is armed with the 20-mm Gatling M197 cannon and the 19-Tube Launchers of the Hydra-70 rocket launchers. It also features a pair of AGM-114 Hellfire four-pipe rocket launchers and two Raytheon AIM-9 Sidewinder missile launch guides.
Unguided rockets
The above guns are economical means of dealing with a wide range of targets, determined at large angles of deviation from the axis of the aircraft. However, helicopter guns are easily "beaten up" by modern air defense systems. For example, the widely used four-barreled 23-mm self-propelled anti-aircraft gun ZSU-23, firing at speeds up to 4000 shots / min, has a valid slant range 2000 meters. While MANPADS have a maximum range of 4000 - 6500 meters.
Unmanaged air-launch missiles can in turn outnumber ground automatic weapons. The most common Western unguided rockets are Thales / TDA Armements 68-mm SNEB and General Dynamics Armament and Technical Products 2,75-mm Hydra-70 70-mm Hydra-90 7 and Magellan Aerospace CRVXNUMX rocket.
The Hydra-70 rocket is a modification of the FFAR (Folding-Fin Aircraft Rocket - a rocket with folding stabilizers) that was developed at the end of 40's as an unguided air-to-air missile, mainly to quickly and reliably hit a Soviet bomber carrying atomic bomb. It served as a temporary tool until such advanced missiles as AIM-7 came into service.
Modern Hydra-70 is produced with nine different warheads, including M151 (4,5 kg high explosive), M229 (7,7 kg high explosive) and M255A1 (with striking elements), plus smoke screen options, illuminating and practical. Over four million Hydra-70 missiles have been manufactured by GDATP since 1994. It charges in 7 and 19 pipe installations.
The Canadian CRV7 rocket is said to have excellent performance with a valid range of up to 8000 meters. Over 800000 of these missiles were manufactured for 13 countries.
 The Russian 57-mm C-5 rocket is currently being supplanted by the 80-mm C-8 rocket, which weighs 11,1 - 15,2 kg and is installed on helicopters in the B20B8-A X-gun. It has a maximum peak speed of Mach 20 and has a maximum range of 1,8 meters. The C-4500KOM has an armor-piercing cumulative warhead, and the C-8BM is designed to destroy personnel in fortifications.
The Russian 57-mm C-5 rocket is currently being supplanted by the 80-mm C-8 rocket, which weighs 11,1 - 15,2 kg and is installed on helicopters in the B20B8-A X-gun. It has a maximum peak speed of Mach 20 and has a maximum range of 1,8 meters. The C-4500KOM has an armor-piercing cumulative warhead, and the C-8BM is designed to destroy personnel in fortifications.The Mi-28 helicopter can also carry two B-13L1 launch blocks, each with five X-NUMX-mm C-122 missiles, which are practically the most powerful missiles fired from helicopters. C-13T weighing 13 kg has a tandem warhead capable of penetrating one meter of reinforced concrete or six meters of soil. 75-kg C-68OF has a high-explosive fragmentation warhead, which creates a cloud of 13 diamond-shaped elements along 450 - 25 grams.
The Mi-28H is capable of carrying two 240 mm C-24B missiles weighing 232 kg. It can be noted that Russian attack helicopters use bombs weighing from 50 to 500 kg and a universal container of small cargoes KMGU-2 for dropping submunitions.
It should be noted that due to its special nature laser-guided missiles will be considered in the following reviews. They are developed relatively recently and are intended in particular to provide the new efficient armament of light universal helicopters, which are much cheaper to operate compared to specialized attack helicopters.
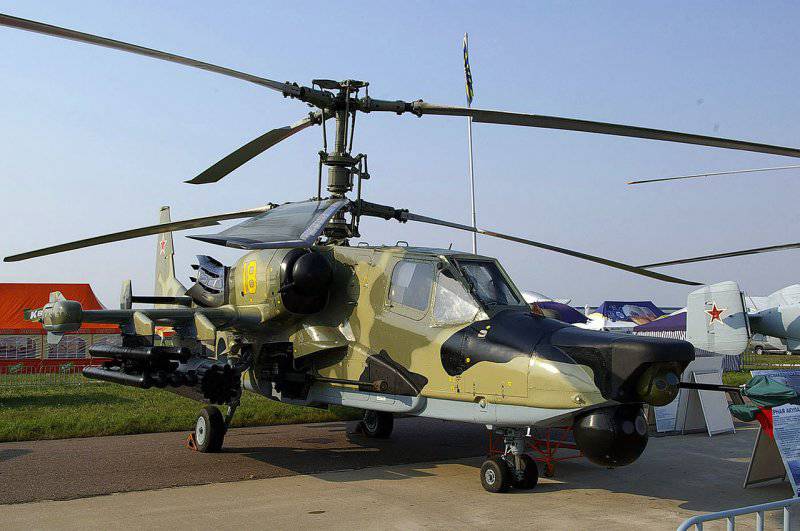

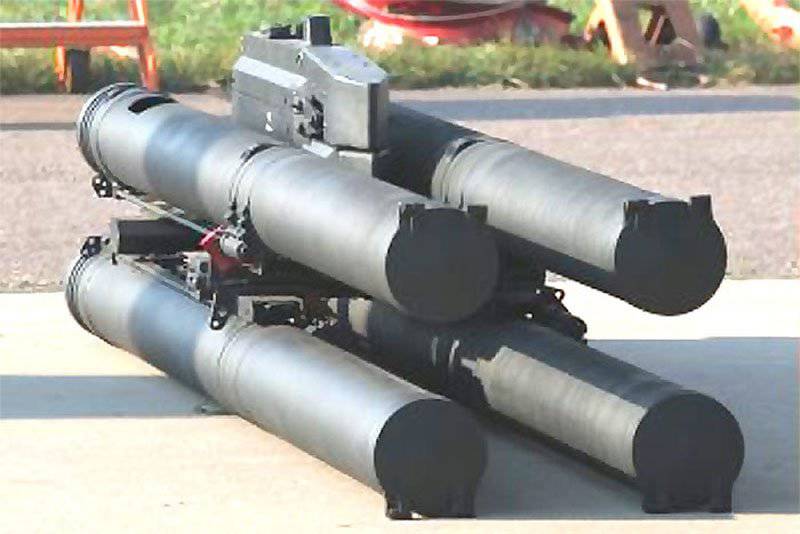
The Ka-50 30-mm Shipunov cannon, mounted in the trunnions on the right side of the fuselage, has elevation angles (vertical) from + 3,5 degrees to -37 degrees. The photo of the Ka-50 is shown with 20-pipe blocks БХNUMXВ8-A for 20-mm С-80 missiles and six-tube UPP-8 for 800M9 armor-piercing missiles Vortex
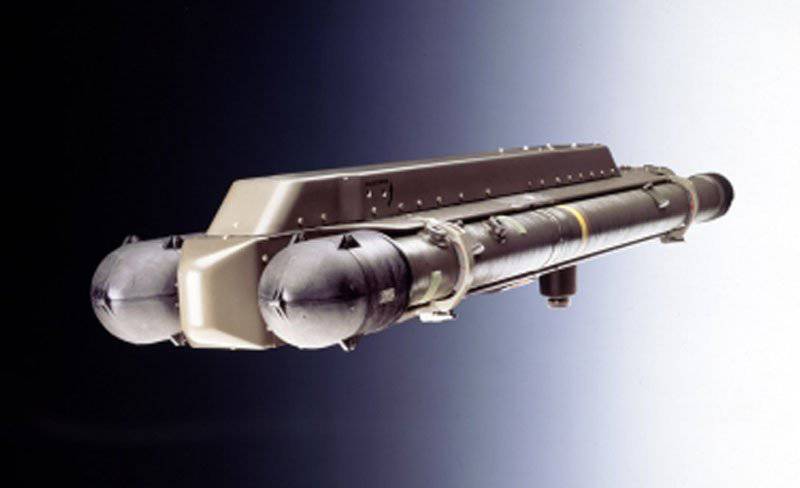
The MBDA Mistral 2 rocket with IR-guided mass of 18,7 kg has a slightly greater firepower compared to missiles launched from MANPADS. On a Eurocopter Tiger helicopter, the missiles are installed in dual Atam launcher (Air-To-Air Mistral)
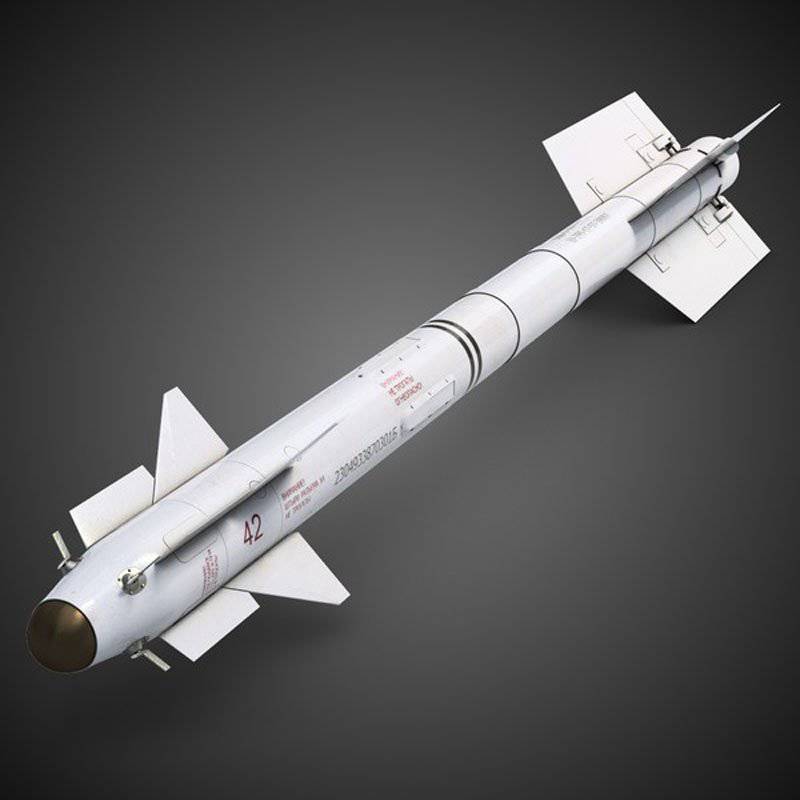


Rocket Pennant P-73 mounted on helicopters Mi-28 and Ka-50 / 52
Air-to-air missiles
The heaviest air-to-air guided weapons are the 105-kg missile Vympel P-73 or NATO classification AA-11 (on the Mi-28 and Ka-50 / 52) and 87-kg Raytheon AIM-9 Sidewinder (on AH -1W / Z). Both have an excellent range according to the standards for short-range missiles; the stated figure for the base rocket P-73 (when launched from jet planes in a frontal battle) is 30 km. The choice of the AIM-9 rocket by the US Marine Corps for Cobra series helicopters was apparently determined by the need to minimize the number of different types of missiles on the same aircraft.
It has been suggested that Brazilian Mi-35M helicopters could be equipped with air-to-air missiles MAA-1B Piranha II Mectron or Darter-A Denel / Mectron.
The desire to maximize the weight of airborne weapons contributes to the adaptation of man-portable air defense systems (MANPADS) as a helicopter weapon of self-defense "air-to-air". The leaders here are 18,7-kg MBDA Atam (Air-To-Air Mistral, installed on Tiger), and even lighter 10,6-kg 9K38 Rocket Needle or CA-18 (on Mi-28 and Ka-50 / 52) and 10,4- kg Raytheon AIM-92 Stinger (by AH-64 helicopter). The Atam complex is based on the Mistral 2 rocket and is a dual launcher. It has shock and remote fuses and a maximum range of 6500 meters.
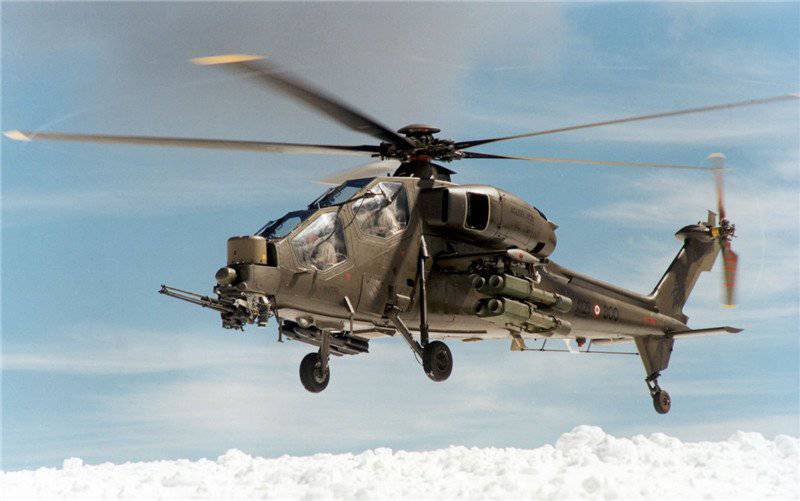

For a relatively light attack helicopter, the AgustaWestland A129 has a very effective weapon system. In addition to the Gatling GD M20 197 guns, he carries four MBDA Hot and four AGM-114 Hellfire armor-piercing missiles from Lockheed Martin.
Air-to-surface missiles
Attack helicopters were developed mainly for the destruction of armored combat vehicles, and therefore the most important type of weapons for them has traditionally been anti-tank guided weapons. At the beginning of the 40s, Germany was a pioneer in the field of missile guidance through wires. In the early post-war period, the UK conducted several tests and concluded that this concept is too prone to breakage and damage. And as a result, Britain subsequently missed an entire generation of anti-tank missiles.
In the very first rockets used manual command guidance, which gave poor accuracy. In general, it was decided instead to accept the so-called Saclos guidance (semiautomatic command to line-of-sight - semi-automatic control signals along the line of sight). Here, the operator keeps his aim at the target, and the system automatically tracks the exhaust jet of the rocket and produces corrective signals to return it to the line of sight.
The world's first air-to-ground missile mounted on a helicopter was the French Nord AS.11 (adapted SS.11 ground-launched missile), which had manual control over the wires and was adopted by the US Army under the designation AGM-22. It was installed on two UH-1B helicopters and was first used by the army in real conditions in October 1965. The AGM-22 was later supplanted (Hughes) by the BGM-71 Tow, which was also controlled by wire, but used Saclos optical tracking. It was first used in combat in May 1972, where it destroyed Tanks T-54 and PT-76. The most widely used wire-guided missiles are 12,5 kg 9M14M Baby-2 or AT-3, 22,5 kg Raytheon BGM-71 Tow and 24,5 kg Euromissile Hot. Guidance over the wires is limited to a range of about 4000 meters, but this fits well with the concept of the Warsaw Pact of the last century of an armored strike on the northern German plain. Then it was believed that a review of targets at long ranges was unlikely due, as a rule, to poor visibility and smoke of the battlefield.
Radio guidance eliminates this range limitation, but may be vulnerable to jamming. As for the guidance through the wires, here the line of sight at the target must be maintained throughout the flight of the rocket.
One of the first samples of a radio-controlled anti-tank missile was the widespread 31,4-kg 9M114 Cocoon or AT-6, this missile was used as part of the Sturm 9K114 complex. The base weapons that entered service in the 1976 year had a range of 5000 meters.
In 90's, 9K114 began replacing 49,5-kg with the 9K120 Attack-B or AT-9 complex. The launching guides and the 9K114 sighting system were saved in the complex, but at the same time it received a supersonic (1,6 Mach) 9M120 rocket, which in the base version has an 5800 meter range. The Mi-28H can carry the 16 of these missiles in two eight-block units.
The 9M120 has a tandem warhead to combat armored targets, while the 9M120F has a thermobaric warhead to destroy lightly armored targets, buildings, caves and bunkers. The 9A2200 variant has a warhead with an enlarged core to combat aircraft.

The laser-guided Lahat 13-kg can be fired from a launcher from an aircraft or from an 105 / 120 mm tank gun. Fully equipped four-tube launcher for a helicopter has a mass less than 89 kg. Lahat has a range of over 8000 meters

A launch container for four MBDA Pars-3 LR missiles mounted on a Eurocopter Tiger helicopter. Pars3-LR has an infrared guidance with automatic recognition that allows you to capture the target after starting
Guidance on the laser beam ensures accuracy regardless of the target range. The coded laser beam allows you to designate a target using another source, aerial or ground. This facilitates the capture of the target from the shelter or outside the visual range of the operator’s direct visibility and minimizes the exposure time of the helicopter from which the rocket is launched.
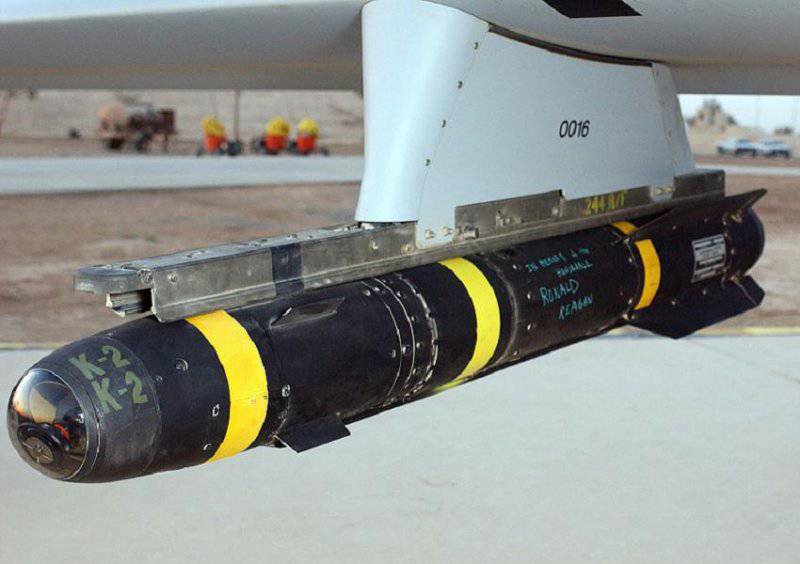
A striking example of a laser-guided missile is the Lockheed Martin’s 43-kg AGM-114 Hellfire, which has an 7000 meter range in direct viewing mode and an 8000 meter during indirect fire. The rocket is supersonic, which reduces its exposure time for enemy interceptor means in the start-up mode with a backlit target. Helicopters AH-1Z and AH-64 can carry 16 Hellfire missiles. The lighter A129 and Tiger can carry eight such missiles.
Hellfire was first used in real conditions in Operation Just Cause in Panama in 1989. It has traditionally been used with three types of warheads: AGM-114K with tandem warheads for armored targets, AGM-114M high-explosive fragmentation warheads for unarmored targets and AGM-114N with metal charges for the destruction of urban buildings, bunkers, radars, communications centers and bridges.
Starting in 2012, the Hellfire rocket became available with the AGM-114R multi-purpose warhead, which allows you to choose its effect on the target (high-explosive or armor-piercing) right before launch. Depending on the type of target, the AGM-114R also allows you to choose the angle of the meeting, from almost horizontal to almost vertical.
Other examples of laser-guided armor-piercing missiles are Lahat 13-kg from Israel Aerospace Industries and Mokopa 49,8-kg from Denel Dynamics, which have a maximum range of 8000 and 10000 meters, respectively.
The AGM-114L Longbow Hellfire, mounted on an AH-64D / E Longbow Apache helicopter, has a radar guidance system; The millimeter radar provides “shot-and-forget” opportunities day and night and in any weather.
In the Soviet Union, in turn, they decided that laser guidance was too susceptible to traps and instead developed a flight using a laser beam, although in this case the distance of the miss with the range increases. The main example of such a system is the 45-kg 9K121 rocket Vortex or AT-16, which has a peak speed above Mach 1,75 and a range of 8000 meters when launched from a helicopter. The vortex is located in two UPP-800 six-pipe installations on a Ka-50 / 52 helicopter. The rocket has a remote fuse for firing air targets.

The next Russian rocket in this category is the Hermes-A (photo above) from the KBP, a two-stage rocket flying at Mach 3 speed to the maximum range of 20 km.
Infrared guidance
Guidance on the laser beam allows you to hit specific targets, but in some circumstances (for example, in urban combat) target designation may become impossible, despite the known general location of the target. In such situations, an accurate attack is still possible due to a combination of inertial and infrared guidance. When combined with sophisticated target recognition algorithms, infrared guidance provides “shot and forget” capabilities and allows you to perform salvo launches against multiple targets.
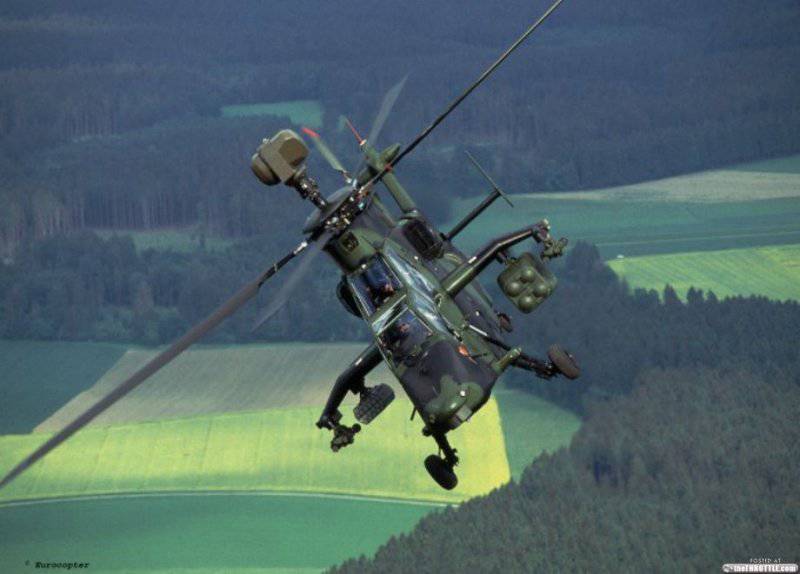


German helicopter Tiger UHT and its weapons. In the top shot is a white rocket in the foreground - Pars-3 LR
The leader in the infrared targeting category is the 49-kg MBDA Pars-3 LR rocket, which has a high subsonic speed (0,85 max) and a maximum range of 7000 meters. The rocket is mounted on a German Tiger UHT helicopter in four-tube launchers in ready-to-launch mode; during flight its sensor is constantly cooled. Four fully autonomous missiles can fire back in less than 10 seconds. It usually uses target lock before launch, but also has a proactive mode for temporarily hidden targets.
Pars-3 LR can be launched in direct attack mode, for example, through bunkers, but it is usually used in dive mode against armored vehicles. Its warhead can penetrate an 1000 mm rolled homogeneous armor protected by dynamic protection units.
The full-scale production of Pars-3 LR was launched at the end of 2012 by Parsys, a joint venture of MBDA Germany and Diehl BGT Defense, under a contract with a German defense procurement agency that will supply 680 missiles for the German army.
Another relatively new development is Spike-ER produced by Israeli company Rafael. The first armor-piercing missile with a Spike-ER fiber optic cable has an 8000 meter range and allows you to capture a target before or after launch. Together with the transport and launch container, it weighs 33 kg and has a dual-mode optoelectronic / infrared sensor that allows for day / night operations.
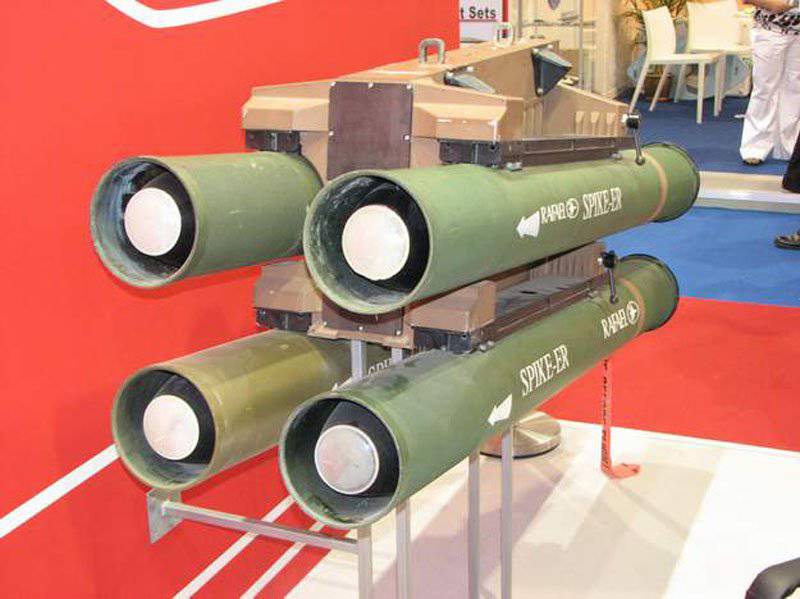
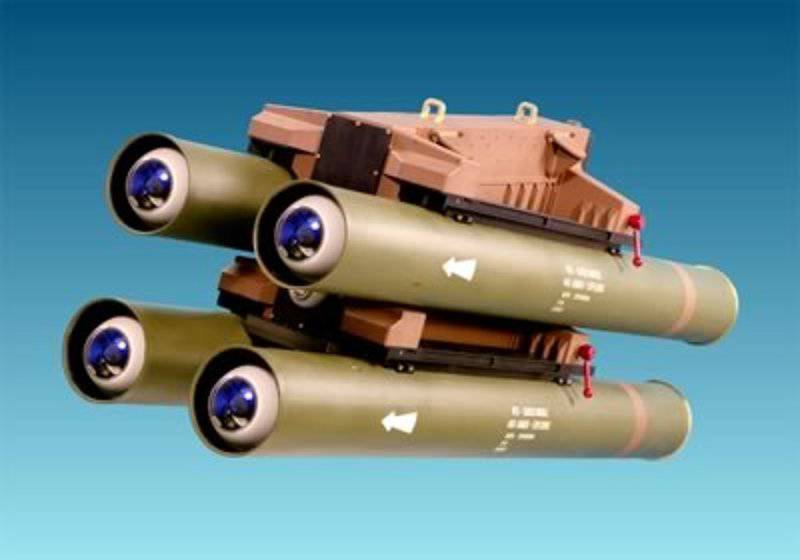


The Rafael Spike family of missiles includes the Spike-ER, which has a range of 8000 meters. It is guided over a fiber optic cable; was chosen by Israel, Italy, Romania and Spain for installation on their helicopters
It is assumed that Spike-ER is in service with Israeli AH-1 helicopters and Romanian IAR-330, it is also selected for Italian AH-109 helicopters and Spanish Tiger Had. It is part of the Spike family of rockets and has a high level of uniformity with ground launch options. Spike is also produced by the German company EuroSpike, a joint venture of Diehl BGT Defense and Rheinmetall Defense Electronics.
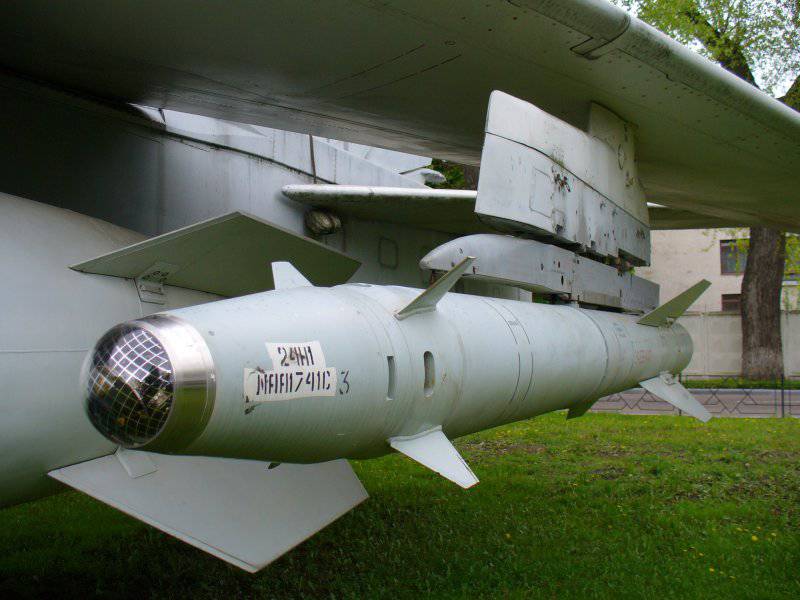
The general public has access to Ka-52 helicopters with X-300 tactical missiles or AU-25 tactical missiles installed on board 10-kg (which do not fit into the usual set of rocket armament for helicopters) in two versions: laser-guided X-25ML and anti-radar X -25MP
Materials used:
Armada International 3 / 2013








Information