Space intelligence.Soviet and Russian spy satellites
16 March 1955, the US Air Force officially ordered the development of an advanced reconnaissance satellite to provide continuous monitoring of the 'pre-selected areas of the Earth' to determine the readiness for war of a potential enemy.
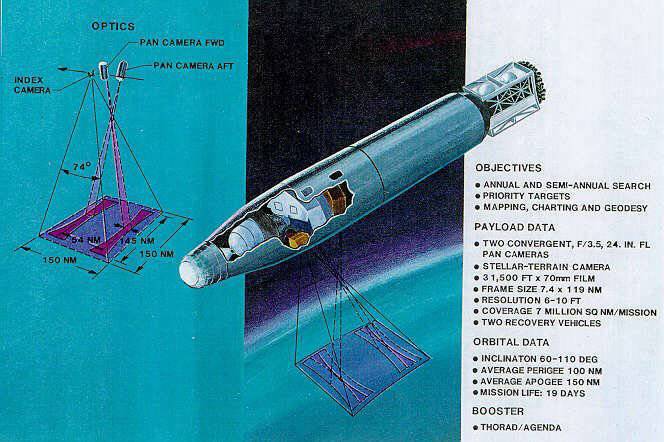
28 February The first photo-reconnaissance satellite created using the CORONA program (the open name Discoverer) was launched in the USA. He was supposed to conduct reconnaissance above all over the USSR and China. Photos taken by his equipment, developed by Itek, were returned to Earth in a descent capsule.
The reconnaissance equipment was first sent into space in the summer of 1959 of the year by the fourth unit of the series, and the first successful return of the capsule with the captured film was made from the Discoverer 14 satellite in August of 1960.
22 on May 1959 of the year was issued Resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the USSR Council of Ministers No. 569-264 on the creation of the first Soviet reconnaissance satellite 2К (Zenit) and, based on it, the Vostok manned vehicle (1К). In 1960, the Krasnogorsk Mechanical Plant began designing the “Fluorine-2” equipment for survey-cartographic and detailed photography. Serial production of this photographic began in the year 1962. At the beginning of 1964, by order of the USSR Minister of Defense No. 0045, the Zenit-2 survey photointelligence complex was put into service. All spy satellites launched under the ordinal names "Cosmos". Over the 33-year period, more than five hundred Zenits were launched, making it the most numerous type of satellite of this class in stories space flight.
Satellite - spy "Zenith". In 1956, the Soviet government issued a secret decree on the development of the “Object D” program, which led to the launch of the Satellite-3 and Satellite-1 (PS-1) programs and is a greatly simplified secondary version of the Object D. The text of the decree is still a state secret, but apparently it was this decree that led to the creation of another satellite - “Object OD-1”, which was to be used for photographing from space.
By 1958, OKB-1 simultaneously worked on the construction of the OD-1 and OD-2 objects, which led to the creation of the first manned spacecraft Vostok. By April 1960, the conceptual design of the Vostok-1 spacecraft, developed as an experimental device, was developed to test the design and create on its basis the Vostok-2 reconnaissance satellite and the Vostok-3 manned spacecraft. The order of creation and launch dates of satellite ships was determined by a resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU No. 587 — 238 “On the space exploration plan” of 4 June 1960. All ships of this type had the name "Vostok", but after it became known in 1961 year as the name of the spacecraft Yuri Gagarin, the reconnaissance satellite "Vostok-2" was renamed "Zenit-2", and the series of spacecraft of this type called "Zenith".

The first launch of “Zenith” took place on December 11 1961, but due to an error in the third stage of the rocket, the ship was destroyed by exploding. The second attempt of 26 on April 1962 was successful and the device received the designation Cosmos-4. However, a failure in the orientation system did not give the first results from the satellite. The third Zenith (Cosmos-7) was launched on July 28 1962 of the year and successfully returned with photos eleven days later. The 13 launches of the Zenit-2 spacecraft were conducted, of which 3 ended up with a launch vehicle crash. In total, the launch of the Zenit-2 spacecraft was carried out 81 times as part of its normal operation (7 launches ended in a launch vehicle crash on the active site). In 1964, the Order of the USSR Ministry of Defense was adopted by the Soviet Army. Serial production was organized at TsSKB-Progress in Kuibyshev. Since 1968, a gradual transition to the upgraded Zenit-2М satellite began, and the number of launches of the Zenith-2 began to decline.
A total of 8 modifications were developed for vehicles of this type and reconnaissance flights continued until the 1994 year.
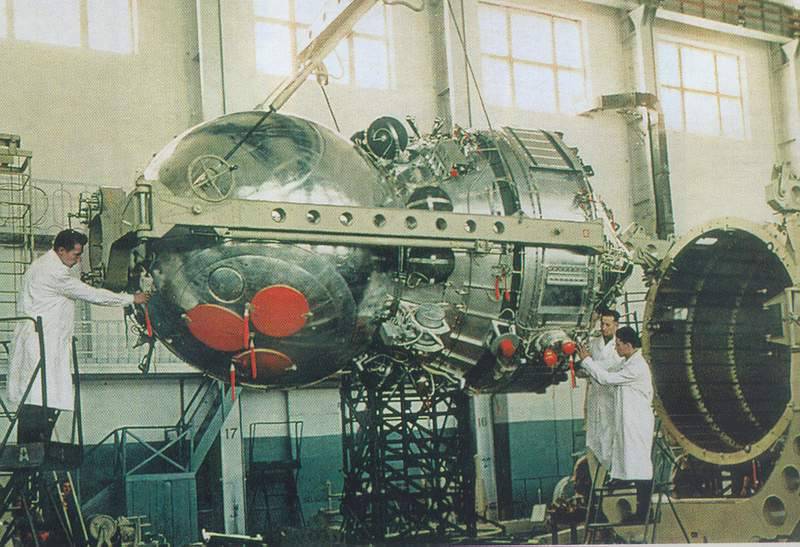
In 1964, the OKB-1, S. P. Korolev, was assigned to improve the performance of Zenit-2 reconnaissance satellites. The studies were carried out in three directions: the modernization of the Zenit satellites, the development of the manned reconnaissance ship Soyuz-R and the creation of a new reconnaissance automatic spacecraft based on the design of the Soyuz-R. The third direction received the designation "Amber".
"Amber" - a family of Russian (formerly - Soviet) specialized species reconnaissance satellites, developed in addition to, and then replacing the reconnaissance vehicles of the Zenit series.
The artificial satellite Cosmos-2175 of the Yantar-4K2 type, or Cobalt, became the first spacecraft launched by Russia after the collapse of the Soviet Union. The precision optics installed on the satellite allows you to capture details of the earth surface up to 30 in the satellite. See the images taken to Earth in special capsules, which after landing will be delivered for processing to the Center for Space Intelligence. It takes about a month between the photography and the descent of the capsule, which significantly reduces the value of the images, in contrast to the Persona spacecraft, which transmits information via a radio channel.
Yantar-Terylene (launched from 28.12.1982goda) became the first Russian digital intelligence platform transmitting the collected data via streaming satellites to the ground station in near real-time mode. In addition, the Yantar series devices became the base for the development of later Orlets and Persona reconnaissance satellites and Resurs-DK, a civilian remote sensing satellite.
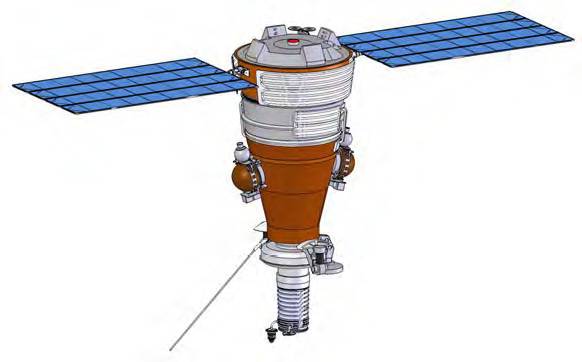
In total, the 174 satellite of the “amber” series was launched, nine of them were lost in emergency launches. The most recent spacecraft of the series was the Yantar-2480K4М or Cobalt-M type photo-reconnaissance satellite, launched into the 2 orbit on May 17. All vehicles of the series were launched using the Soyuz-U launch vehicle, and the launch of Kosmos-2012 was announced as the last launch of this type of launch vehicle. In the future, it is planned to use the Soyuz-2480 launch vehicle to put satellites of the Yantar family into orbit.
"A person" - the third-generation Russian military optical reconnaissance satellite, designed to receive high-resolution images and promptly transmit them to Earth via radio. A new type of satellites was developed and manufactured at the Samara Rocket and Space Center TsSKB-Progress, while the optical system is manufactured at the St. Petersburg optical-mechanical association LOMO. The satellite was ordered by the Main Intelligence Directorate of the General Staff (GRU GS) of the Russian Armed Forces. The spacecraft replaced the previous generation of Neman satellites (Yantar 4X1m).
The competition for the creation of a new satellite of optical-electronic intelligence "Person" of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation was held in 2000 year. The projects of TsSKB-Progress and the NGO named after S. A. Lavochkin were reviewed. The TsSKB-Progress project was a modification of the previous generation Neman satellite. In addition, he inherited a lot from the civilian Resurs-DK satellite. The competing project of the S. A. Lavochkin NPO was also an advanced satellite of the previous generation “Araks”. After winning the Persona project competition, the launch of the first spacecraft was planned for the 2005 year, but due to the delay in ground tests, it was launched only in the 2008 year. The cost of creating the first satellite is estimated at 5 billion rubles. The launch of the second Persona unit is scheduled for March 2013.
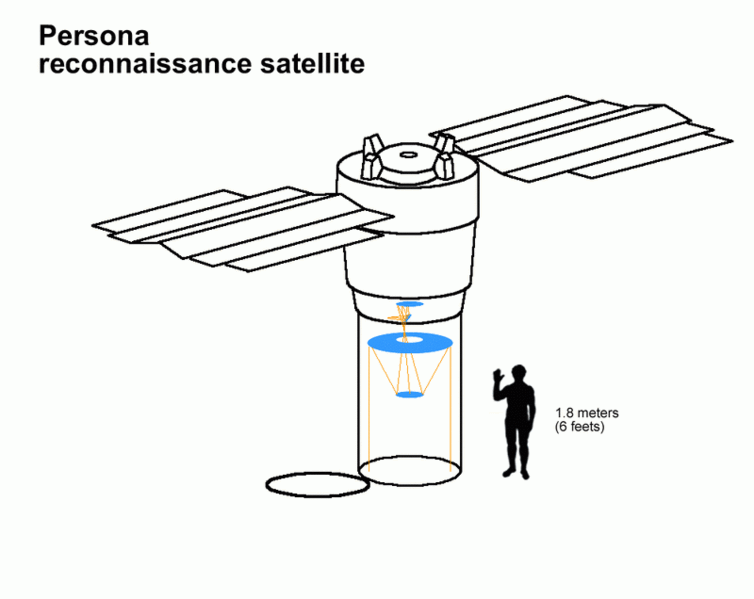
The idea of the overall dimensions of the Persona spacecraft.
Don (Orlets-1) - code name of a series of Russian satellites of broadband detailed and survey photointelligence. The resolution of the obtained images - 0.95 m per point.
The development of the device began in April at 1979 at the TsSKB-Progress State Rocket and Space Center. The first satellite launch took place on 18 on July 1989, and it was put into operation on 25 on August 1992.
For prompt delivery of the captured film to the ground on the machine, there is a drum with eight returned capsules. After the photo is taken, the film is loaded into the capsule, it is separated from the apparatus and makes a descent and landing in a given area.
During the period of 1989 — 1993, regular annual launches of “Don” were held, the average operating time was about 60 days. In the interval 1993 — 2003 only one device was launched — on 1997 — and it worked in orbit twice as long as the previous devices — 126 days. The next launch took place in August 2003. After launching the satellite, it received the designation "Cosmos-2399". The latest launch of the Don satellite was 14 September 2006 of the year under the designation Cosmos-2423.
Manned space stations of the Ministry of Defense of the USSR.
"Almaz" (OPS) - a series of orbital stations developed by TsKBM for the tasks of the Ministry of Defense of the USSR. The stations were injected into orbit using a Proton launch vehicle. Transport service of the station was assumed both by the spacecraft TKS, developed by the same program "Almaz", and previously developed by "Soyuz". Stations for manned operation received the name "Salute", adjacent to civilian stations DOS. All in all, the 5 stations Almaz —OPS - manned Salyut-2, Salyut-3, Salyut-5, as well as automatic modifications of Cosmos-1870 and Almaz-1 were launched.
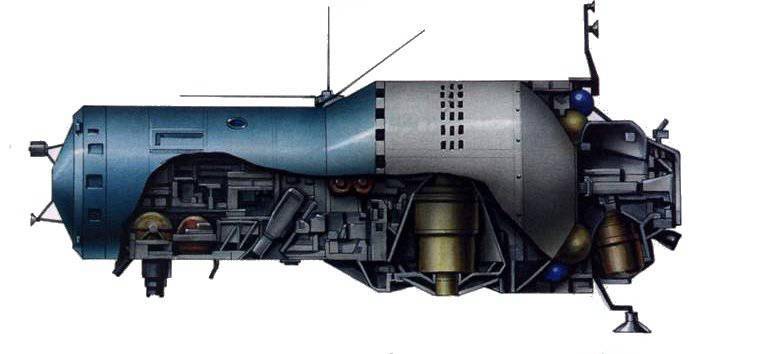
Work on the creation of the station began in the middle of the 60-ies, during the years of tough confrontation with the United States. The Almaz station was developed at OKB-52 under the direction of V.N. Chelomey for solving the same tasks as the American station MOL (Manned Orbiting Laboratory) developed at that time - conducting photographic and radio reconnaissance and control from orbit by ground military means, for which the station was equipped with a telescope-camera "Agat-1", as well as a whole complex of long-focus cameras for shooting the Earth with a total number of 14 units.
For protection from satellite inspectors and interceptors of a potential enemy, as well as in view of the possible use of space shuttles to abduct Soviet DOS (long-lived manned stations) Salyut and OPS (orbital manned stations) Almaz, from the Earth orbit, as the first stage It was equipped with a modified HP-23 automatic cannon designed by Nudelman - Richter (Shield-1 system), which later, at the first station of Almaz of the second generation, was to replace the Shield-2 system consisting s two space rockets. (According to some sources, the Shield-5 system was installed at Salyut-2, with two space-to-space rockets). The assumption of “abductions” was based solely on the cargo compartment openly declared by the American developers of the shuttles and the mass of the returned payload of the shuttles, which are close to those of the “Diamonds”.
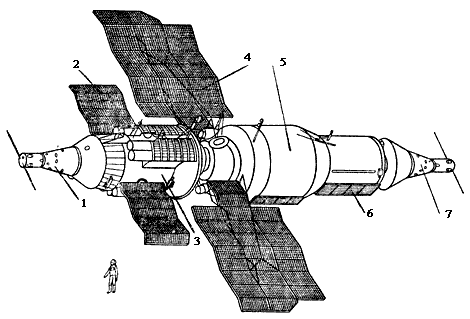
It was supposed to move to the Almaz station of the second generation in the variants with the second docking station or the return vehicle from the TKS. However, work on the manned stations "Almaz" were discontinued in 1978 year. TsKBM continued to develop an OPS station in an unmanned version for the Almaz-T spaceborne radar remote sensing system.
The automatic station OPS-1981, prepared for launch in 4, lay in one of the workshops of the assembly and test building of the Baikonur cosmodrome for several years due to delays not related to the work of the OPS. October 19 1986 of the year an attempt was made to launch this station, called Almaz-T, which was unsuccessful due to the failure of the Proton control system.
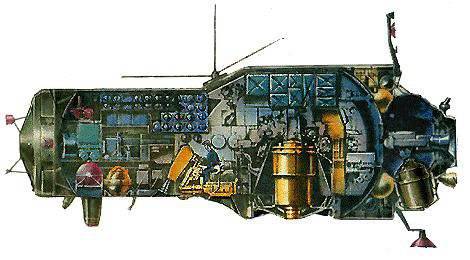

18 July 1987, the successful launch of the automatic version of the OPS "Almaz", which received the designation "Cosmos-1870". High-quality radar images of the Earth’s surface from a satellite were used in the interests of the defense and economy of the USSR.
31 March 1991, a modified automatic version of the OPS with significantly improved on-board equipment was put into orbit called "Almaz-1".
The automatic Almaz-2 OPS with further modification of the onboard equipment into orbit was not withdrawn due to the difficult state of the economy after the collapse of the USSR and the work stopping.
Information