Soviet tank KBT-7
Quite an interesting prototype, created on the basis of the BT-7 tank, is the KBT-7 (commander's BT), which was the first Russian specialized command and staff vehicle. This machine was intended for "commanders of companies and above to ensure them reliable control of units, as well as observation and communication in battle under the fire of enemy machine guns." The machine was developed on the basis of the tactical and technical specifications of the Red Army headquarters of the Bulgarian State Technical University developed in 1937
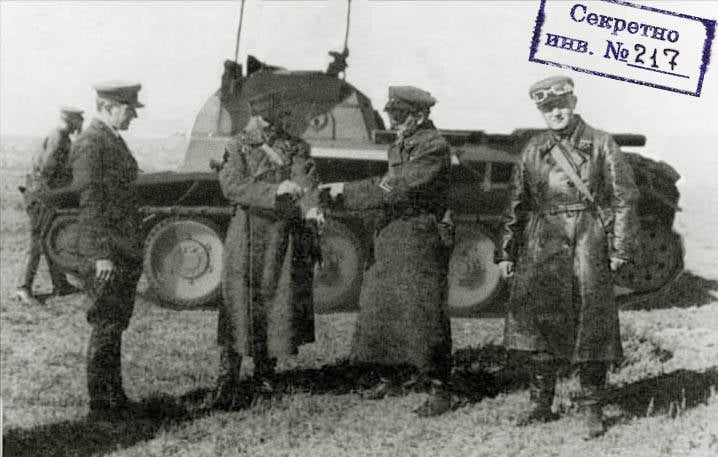

The design and construction of a command tank was carried out under the guidance of engineer N. I. Korotonoshko at NATI in 1937.
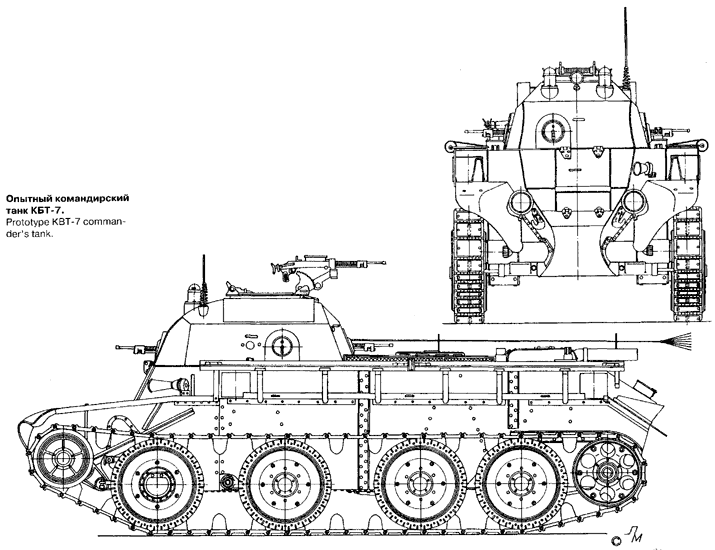
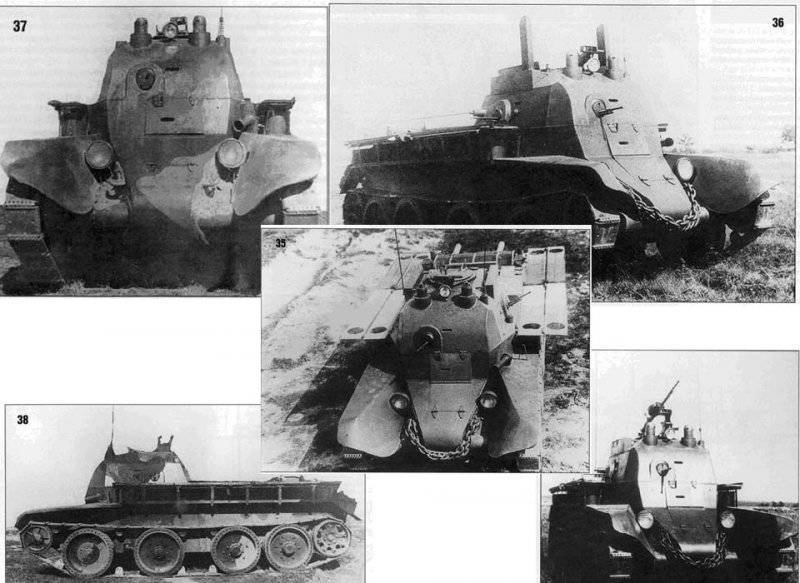
From the BT-7 serial, the KBT-7 tank was distinguished by the fact that the cannon tower was replaced with an armored superstructure-cabin with a height of 600 millimeters and a width equal to the width of the hull in which the special equipment was located.
The crew of the KBT-7 tank consisted of four people: the chief of staff, the commander of the unit, the driver-mechanic, and the radio operator-gunner. The workplace of the driver was located, as well as on the BT-7 serial tank, the commander was located to the right, to his left was the chief of staff, in front of which the folding table was mounted, the radio operator’s workplace was located at the engine compartment partition .
For the manufacture of the hull of the tank KBT-7 used armor and steel sheets. The case was a box-shaped rigid structure with double side walls, an oblong, rounded constricted bow, trapezoidal stern. Reservations - bulletproof. Most of the one-piece body connections were done by welding and some by riveting. The hull consisted of the bottom, roof, sides, bow, stern and internal partitions. To reduce the likelihood of damage to the crew, the armor plates of the superstructure were installed at an angle. Front and stern sheets, respectively, 18 and 13 mm thick, were tilted at an angle 20 °, side sheets 13 mm thick - at an angle 15 °. The upper inclined sheet had a thickness of 10 mm.
Instead of the tower, a fixed 600 millimeter cabin was installed. The width of the cabin was equal to the width of the hull. Since there was no circular fire, it was compensated for by the presence of four ball mounts for the DT machine gun in all the walls of the cabin. The superstructure on the prototype was made of ordinary structural steel grade 3.
Armament consisted of a pair of machine guns DT caliber 7,62 mm, installed in the right side and front sheets. The third, spare, machine gun at the same time served as anti-aircraft. On the roof of the wheelhouse mounted turret P-40, and in the floor of the tank - a lifting platform for firing from an anti-aircraft machine gun. Ammunition - 1953 cartridge in the 31 store.
To monitor the situation on the battlefield and subordinate units, two PTK commander devices were installed, as well as four triplexes mounted in each wall of the wheelhouse. The workplace of the commander made it possible to alternately fire one person from all machine guns, without interfering with the work of other crew members.
The structure of the special equipment of the tank included two surveillance devices, two radio stations, a tank intercom, two light-signal semaphores on the cabin roof, as well as an aircraft signal device for communicating with reconnaissance aircraft. The driver also had a KI compass for driving in difficult conditions.
For external communication over long distances, a RTU radio station was used, which has a whip antenna, and at short range - a 71-TK-1 radio station, which has a lifting whip antenna. The internal communication between the crew members was carried out with the help of a TSPU-5 tank intercom, designed for four subscribers.
For control inside the tank unit, STS light-semaphores were used, located in armored boxes on the upper inclined superstructure sheets.
Communication with the reconnaissance aircraft, night and day, was carried out by a special tank aircraft signaling device placed on both fenced shelves (4 of 1900xXNNXX mm web). The sheets were controlled by a special switchgear, which made it possible to recruit various combinations. The illumination of TASP signal panels at night was carried out by searchlights (two per board) installed in armored glasses on fences.
The power train, transmission and installation were the same as on the serial BT-7. The 12-cylinder four-stroke carburetor engine M-17 was installed in the rear of the hull. In the stern of the tank installed fuel tank capacity 650 l. With the 1550-1650 rpm, the engine power was hp 400. This allowed the KBT-7 tank to develop 52 speed per kilometer per hour on the tracks on tracks, and 72 kilometers per hour on wheels. The dry weight of the engine was 550 kg. Cooling system - forced, water, using the M17 centrifugal pump. Radiator capacity - 100 l. The cruising range of the tank on the highway reached: on a wheeled track 450 km, on a caterpillar track - 220 km.
The KBT-7 tank had a combined wheel-tracked propulsion consisting of two rear drive wheels with a diameter of 640 millimeters, two guiding front wheels with a diameter of 550 millimeters, 8 track rollers with a diameter of 815 millimeters with rubber bands, and two multi-link steel tracks with a width of 9 mm wide with gauges with a width of 2 multi-link steel tracks with a width of 263 mm with rubber bandages and two multi-section steel tracks with a width of 4 mm with rubber bandages and two multi-link steel tracks with a width of 0 x X. When the tank was in motion on a wheeled track, the tracks were removed, the components were dismantled on the XNUMX and placed in the fenders. When driving on a wheel drive, the drive was made on the rear supporting rollers. Control drives are mechanical. The turn on the track was carried out with the help of two levers, acting on the brakes and side clutches; turn on the wheel was carried out by the steering wheel. While driving on a caterpillar, the steering wheel was removed and placed at the left side of the tank in the control compartment.
Tank IPA-7 had a mechanical transmission consisting of: a five-speed gearboxes (4 forward gear, 1 adjustable), the main multi-plate clutch, operating on the principle of dry friction, two bead multidisk clutches with band brakes, two bead one-step reduction gears and two gearboxes drive to the supporting rear rollers - leading when wheeling.
Suspension type - classic Christie, distinguished as an individual spring suspension. Three springs, mounted vertically relative to the left and right sides of the hull, were located between the inner wall of the hull side and the outer bronelist, and one was installed in the middle part of the fighting compartment inside the hull in a horizontal position. Vertically mounted springs were connected through balancers to rear and middle support rollers, and horizontally installed springs were connected to front-controlled rollers.
A new tricolor camouflage was tested on the tank, which later found limited use in tank forces.
The tests of the tank took place from 7 to 20 in August of 1937. The conclusions were as follows:
“The test commander tank, created on the basis of the BT-7 tank, imposed on the commander tank tactical and technical requirements, does not satisfy for the following reasons:
1. The machine does not have the necessary sectors of fire and observation.
2. From the BT-7 linear tanks, the commander's tank differs sharply in its configuration and therefore can be detected by the enemy at a distance of 1 km with the naked eye and, together with the unit commander, is incapacitated.
3. The presence of the TASP device on the commander tank KBT-7 unmasks it.
4. The capacity of batteries used to power communication devices is insufficient.
Conclusion.
The Commission, on the basis of the above, believes that the commander tank KBT-7 based on BT-7 cannot be recommended for arming the armored troops of the Workers 'and Peasants' Red Army. In accordance with the materials obtained during the tests, it is necessary to refine the tank. For further testing, the commission considers it necessary to give this tank to units in the exercise. ”
The tank was not adopted for service because of the unsatisfactory conditions of firing from machine guns, cramped chopping, unmasking signs, and probably because of the reluctance to reduce the number of linear tanks.
Although this tank was adopted for service and was not, it was a very interesting machine. The concept of this tank has incorporated not only outdated archaic elements (for example, semaphores), but also many advanced ideas that were later implemented. For example, the use of a base tank base, a wheelhouse, two radio stations, a larger crew than a line tank. All this was later embodied in the German command tanks, and at the end of the war in the Soviet command and staff vehicles.
Specifications:
Crew - 4 person.
Combat weight - 13 tons.
Main dimensions:
Length - 5580 mm.
Width - 2230 mm.
Height - 2700 (ЗПУ) mm.
Ground clearance - 350 mm.
Armament - 3 machine gun DT (including 1 spare) caliber 7,62 mm.
Ammunition - 1953 ammo.
Reservations (thickness / angle):
The forehead of the body is 13 (20) mm / 60-18 degrees.
Housing side - 13 mm / 90 deg.
Body Feed - 13 mm / 90 deg.
The roof of the case - 10 mm / 180 deg.
Bottom - 6 mm / 180 deg.
Tower (chopping) - 18 mm / 20 deg.
Speed (tracks / wheels):
Maximum - 50 / 72 km / h.
The average country road is 34,6 / - km / h.
Overcoming obstacles (tracks / wheels):
Rise - 37 / 15 hail.
Descent - 37 / 15 grad.
Roll - 30 / - hail.
Moat - 2,4 / - m
Ford - 0,9 / - m.
Vertical wall - 0,8 / - m.
The average ground pressure is 0,62 kgf / cm2.
Power reserve (tracks / wheels):
By country road - 160 / - km.
On the highway - 220 / 450 km.
Tank capacity - 650 l.
Engine - M-17Т, V12 carburetor, power 500 hp, 1650 r / min.
Transmission - two-shaft, manual, the number of gears - 4 forward / 1 back.
Track width - 260 mm, 167 pitch mm.
Radio stations and intercoms - RTU, 71-TK-1, TSPU-5.
Prepared by materials
alternathistory.org.ua
www.dishmodels.ru
bronetehnika.com
militera.lib.ru
Information